Amr loves Chemistry, and specially doing experiments. He is preparing for a new interesting experiment.
Amr has n different types of chemicals. Each chemical i has an initial volume of ai liters. For this experiment, Amr has to mix all the chemicals together, but all the chemicals volumes must be equal first. So his task is to make all the chemicals volumes equal.
To do this, Amr can do two different kind of operations.
- Choose some chemical i and double its current volume so the new volume will be 2ai
-
Choose some chemical i and divide its volume by two (integer division) so the new volume will be
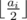
Suppose that each chemical is contained in a vessel of infinite volume. Now Amr wonders what is the minimum number of operations required to make all the chemicals volumes equal?
The first line contains one number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of chemicals.
The second line contains n space separated integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105), representing the initial volume of the i-th chemical in liters.
Output one integer the minimum number of operations required to make all the chemicals volumes equal.
3 4 8 2
2
3 3 5 6
5
In the first sample test, the optimal solution is to divide the second chemical volume by two, and multiply the third chemical volume by two to make all the volumes equal 4.
In the second sample test, the optimal solution is to divide the first chemical volume by two, and divide the second and the third chemical volumes by two twice to make all the volumes equal 1.
问要将全部数变成一样须要的最少操作数
因为数范围比較小
就能够直接暴力每一个数进行操作后能到达的数和到达这个数须要的操作量
然后对于cnt[i]==n的数中的操作数找出最小
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAXN 222222
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
int cnt[MAXN],step[MAXN];
int a[MAXN];
void solve(int num){
int xx=num;
int res=0;
cnt[num]++;
while(xx<=100000){
xx*=2;
cnt[xx]++;
res++;
step[xx]+=res;
}
xx=num,res=0;
while(xx>1){
if(xx&1){
int xres=res+1;
int xxx=xx/2;
while(xxx<=100000){
xxx*=2;
xres++;
step[xxx]+=xres;
cnt[xxx]++;
}
}
xx/=2;
res++;
cnt[xx]++;
step[xx]+=res;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
memset(step,0,sizeof(step));
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
solve(a[i]);
int ans=INF;
for(int i=1;i<MAXN;i++){
if(cnt[i]==n){
ans=min(ans,step[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}



