[LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫 II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
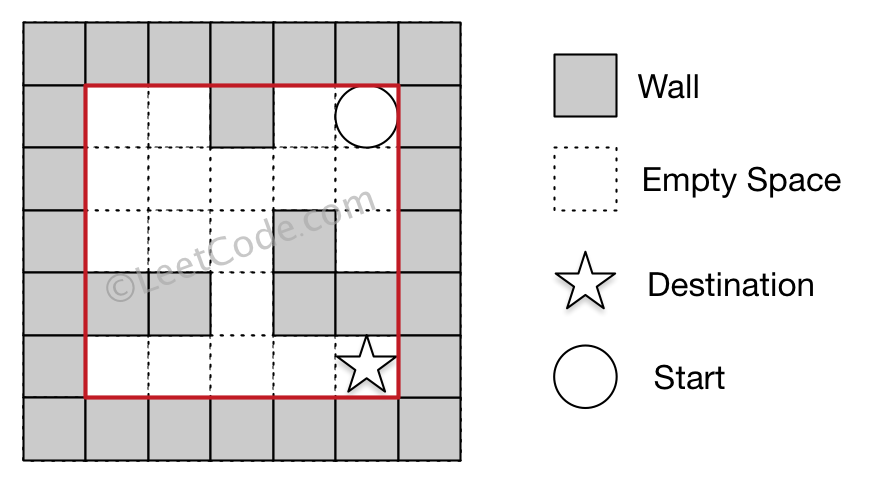
Example 1
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
Output: 12
Explanation: One shortest way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
The total distance is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
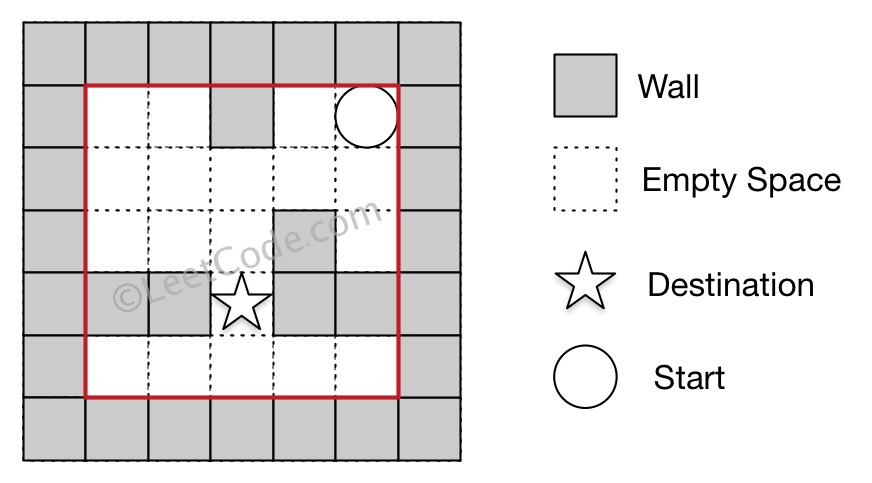
Example 2
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4) Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2) Output: -1 Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
490. The Maze 的拓展,490题只判断能否到达终点,而这道题让求出到达终点的最少步数。
要求最短的路径,普通的遍历dfs和bfs都是可以做的,但是求最短路径的话还是用Dijksra。这里相当于每个点有至多4条edge相连,每条edge的weight就是到墙之前的长度。
Java:
public class Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
// base case
if(Arrays.equals(start, destination)) return 0;
m = maze.length; n = maze[0].length;
return shortestPath(maze, start, destination);
}
int m, n;
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
private int shortestPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
// get the vertice has the minimum distance to start
PriorityQueue<Node> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.distance - b.distance);
minHeap.offer(new Node(start[0], start[1], 0));
// map that contains information of node: distance to start point
int[][] visited = new int[m][n];
for(int[] arr : visited) Arrays.fill(arr, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
while(!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = minHeap.poll();
// find the shortest path
if(cur.x == destination[0] && cur.y == destination[1]) return cur.distance;
for(int[] dir : dirs) {
int nx = cur.x, ny = cur.y;
while(isInMaze(nx + dir[0], ny + dir[1]) && maze[nx + dir[0]][ny + dir[1]] != 1) {
nx += dir[0]; ny += dir[1];
}
int distance = cur.distance + Math.abs(nx - cur.x) + Math.abs(ny - cur.y);
if(visited[nx][ny] > distance) {
minHeap.offer(new Node(nx, ny, distance));
visited[nx][ny] = distance;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private boolean isInMaze(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
class Node {
int x;
int y;
// distance to start point
int distance;
Node(int x, int y, int distance) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
}
Python:
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '')}
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
queue = collections.deque([(ball, 0, '')])
while queue:
front, dist, path = queue.popleft()
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[front]: continue
np = dmap[front][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(front, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in bmap or (ndist, npath) < bmap[np]:
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath)
queue.append((np, ndist, npath))
return bmap[hole][1] if hole in bmap else 'impossible'
Python: Dijkstra算法
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '', ball)}
vset = set()
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
while bmap:
dist, path, p = min(bmap.values())
if p == hole: return path
del bmap[p]
vset.add(p)
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[p]: continue
np = dmap[p][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(p, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in vset and (np not in bmap or (ndist, npath, np) < bmap[np]):
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath, np)
return 'impossible'
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({start[0], start[1]});
dists[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto d : dirs) {
int x = t.first, y = t.second, dist = dists[t.first][t.second];
while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += d[0];
y += d[1];
++dist;
}
x -= d[0];
y -= d[1];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
if (x != destination[0] || y != destination[1]) q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
int res = dists[destination[0]][destination[1]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? -1 : res;
}
};
C++: DFS
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
dists[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
helper(maze, start[0], start[1], destination, dists);
int res = dists[destination[0]][destination[1]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? -1 : res;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>>& maze, int i, int j, vector<int>& destination, vector<vector<int>>& dists) {
if (i == destination[0] && j == destination[1]) return;
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
for (auto d : dirs) {
int x = i, y = j, dist = dists[x][y];
while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += d[0];
y += d[1];
++dist;
}
x -= d[0];
y -= d[1];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
helper(maze, x, y, destination, dists);
}
}
}
};
类似题目:
[LeetCode] 499. The Maze III 迷宫 III



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号