新“愚公移山”-- 动态规划
新“愚公移山”
http://go.helloworldroom.com:50080/problem/2721
题目描述
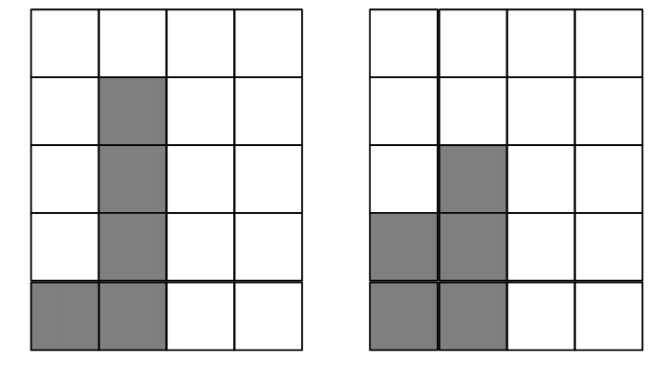
为了吸引中小学生,参观博物院不再停留在看和听,核心理念转变成了互动。新“愚公 移山”项目,屏幕上出现 n 个石块,屏幕下方的底盘是二维方格,每个方格恰好能放置一个 石块。石块放置的规则是:底盘每一竖行方格组成一列,必须从最左边的一列开始摆放,每 列从最下面的方格开始连续摆放积木,底盘至少要放两列,后一列放的积木数至少比前一列 多一个。n 个石块共有多少种摆放方案呢? 下图为 5 个积木所能摆放的 2 种方案。
输入格式
一行,包含一个正整数 n,表示生成的石块个数。
输出格式
一行,包含一个数,表示按规则摆放石头的方案总数。
样例数据
input
5output
2对于 40%的数据满足 n≤10; 对于 80%的数据满足 n≤100; 对于 100%的数据满足 n≤200;
思路

解法
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <set> using namespace std; int N; int f[202][202] = {{0}}; int main() { cin >> N; // n rocks are in one column for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++) { f[n][1] = 1; } // 1 rock is with any number of columns for (int m = 2; m <= N; m++) { f[1][m] = 0; } // column is increasing for (int m = 2; m <= N; m++) { for (int n = 2; n <= N; n++) { f[n][m] = 0; int a1_max = n / m; for (int k = 1; k <= a1_max; k++) { int left_n = n - m * k; f[n][m] += f[left_n][m - 1]; } } } // cout << endl; // cout << "----------------------------"; // for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++) { // for (int m = 1; m <= N; m++) { // cout << f[n][m] << " "; // } // cout << endl; // } // cout << endl; int count = 0; for (int m = 2; m <= N; m++) { // cout << "m == " << m << " " << f[N][m] << endl; count += f[N][m]; } cout << count << endl; }
求总方案数的入门题 -- 容易理解
Count number of ways to reach destination in a Maze
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/count-number-ways-reach-destination-maze/
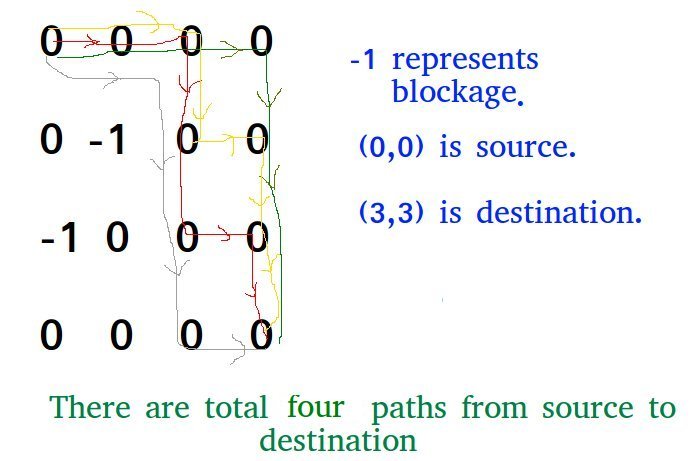
Given a maze with obstacles, count the number of paths to reach the rightmost-bottommost cell from the topmost-leftmost cell. A cell in the given maze has a value of -1 if it is a blockage or dead-end, else 0.
From a given cell, we are allowed to move to cells (i+1, j) and (i, j+1) only.Examples:
Input: maze[R][C] = {{0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, -1, 0, 0}, {-1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0}}; Output: 4 There are four possible paths as shown in below diagram.
// C++ program to count number of paths in a maze // with obstacles. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define R 4 #define C 4 // Returns count of possible paths in a maze[R][C] // from (0,0) to (R-1,C-1) int countPaths(int maze[][C]) { // If the initial cell is blocked, there is no // way of moving anywhere if (maze[0][0]==-1) return 0; // Initializing the leftmost column for (int i=0; i<R; i++) { if (maze[i][0] == 0) maze[i][0] = 1; // If we encounter a blocked cell in leftmost // row, there is no way of visiting any cell // directly below it. else break; } // Similarly initialize the topmost row for (int i=1; i<C; i++) { if (maze[0][i] == 0) maze[0][i] = 1; // If we encounter a blocked cell in bottommost // row, there is no way of visiting any cell // directly below it. else break; } // The only difference is that if a cell is -1, // simply ignore it else recursively compute // count value maze[i][j] for (int i=1; i<R; i++) { for (int j=1; j<C; j++) { // If blockage is found, ignore this cell if (maze[i][j] == -1) continue; // If we can reach maze[i][j] from maze[i-1][j] // then increment count. if (maze[i-1][j] > 0) maze[i][j] = (maze[i][j] + maze[i-1][j]); // If we can reach maze[i][j] from maze[i][j-1] // then increment count. if (maze[i][j-1] > 0) maze[i][j] = (maze[i][j] + maze[i][j-1]); } } // If the final cell is blocked, output 0, otherwise // the answer return (maze[R-1][C-1] > 0)? maze[R-1][C-1] : 0; } // Driver code int main() { int maze[R][C] = {{0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, -1, 0, 0}, {-1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0}}; cout << countPaths(maze); return 0; }
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lightsong/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号