Dubbo系列之 (二)Registry注册中心-注册(1)
辅助链接
Dubbo系列之 (一)SPI扩展
Dubbo系列之 (二)Registry注册中心-注册(1)
Dubbo系列之 (二)Registry注册中心-注册(2)
引导
dubbo的服务的注册与发现,需要通过第三方注册中心来协助完成,目前dubbo支持的注册中心包括 zookeeper,consul,etcd3,eureka,nacas,redis,sofa。这些注册中心的不同支持在之后的篇章进行分享。
基础铺垫
在铺垫一些基础内容之前,根据如果下几个问题来进行回答,或许能更好的阐明dubbo的实现服务的注册和发现的实现过程。
1、dubbo是在什么时机与注册中心建立连接。
2、dubbo服务注册和导出的时机在什么时候。
3、dubbo服务的订阅时机是在什么时候。
4、dubbo服务的上下线是如何通知订阅者的。
5、dubbo是如何把这些各种第三方注册中心进行整合的。
为了回答上面的五个问题,我们一起去从dubbo的源码探寻答案,这些问题和服务的注册有关,那么首先我们需要的就是去dubbo-registry这个源码模块去查询。
基础数据结构
1、dubbo 还是通过SPI技术,根据参数URL来动态选择不同的注册中心。
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface RegistryFactory {
@Adaptive({"protocol"})
Registry getRegistry(URL url);
}
RegistryFactory 就是产生一个注册中心的工程,它有个自适应的方法getRegistry,那么我们知道dubbo会通过javassist动态产生一个RegistryFactory$Adaptive类,并且getRegistry方法的内部实现大致是如下:
public class RegistryFactory$Adaptive implements RegistryFactory {
@Override
public Registry getRegistry(URL url) {
if (url == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryFactory) " +
"name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
RegistryFactory extension = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getRegistry(url);
}
}
它通过传入的URL的protocol协议字段排判断是什么类型注册中心。例如,url的protocol的协议是zookeeper,那么就会根据SPI的ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getExtension("zookeeper")得到一个产生ZooKeeper注册中心的工厂,也就是ZookeeperRegistryFactory,而ZookeeperRegistryFactory这个类的getRegistry就是返回一个Zookeeper注册中心。
2、Registry 接口是所有注册中心的抽象。它的类关系图如下:
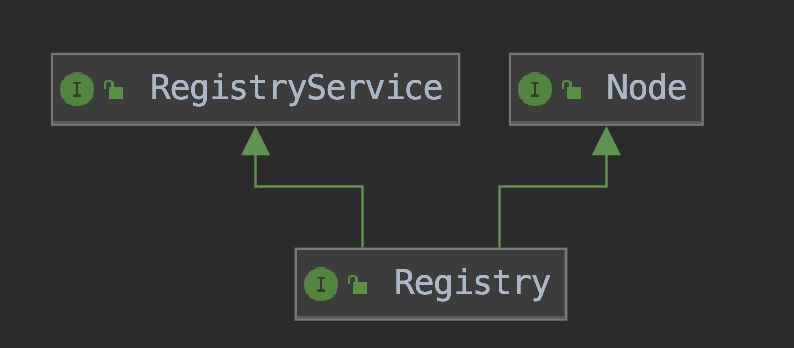
可以看出其语义,一个注册中心Registry是一个节点(extends Node),并且它具有注册服务(extends RegistryService)的功能。
dubbo支持如下这些注册中心zookeeper,consul,etcd3,eureka,nacas,redis,sofa,那么就会产生相应如下的Registry:
ZookeeperRegistry,ConsulRegistry,EtcdRegistry,NacosRegistry,RedisRegistry,SofaRegistry。类图如下:
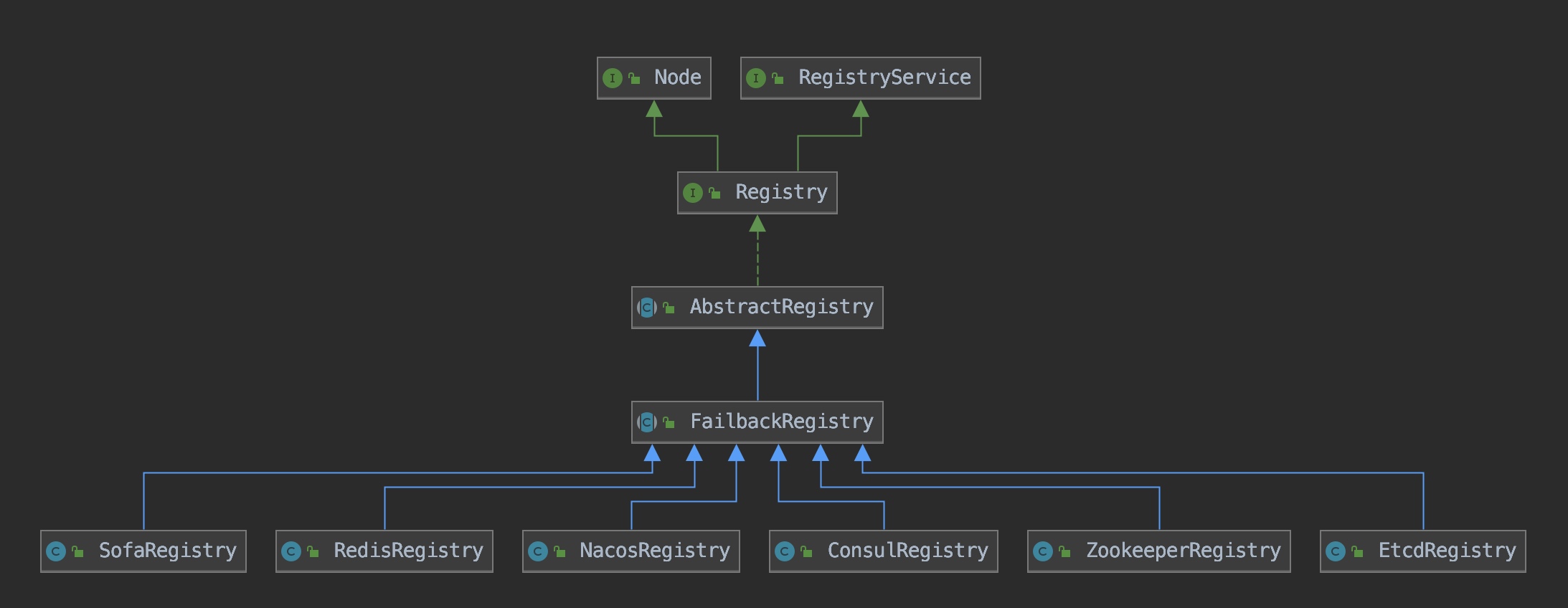
所以我们知道,这些注册中心都是继承FailbackRegistry,这个FailbackRegistry其意思就是说,如果一个服务注册到当前某个注册中心注册失败后,可会在后台产生一个daemon线程,定时的把注册失败服务重新注册,并且有一定的重试限制。
在上面的类图中我们并没有发现有个名为EurekaRegistry这样的类,因为实现了另一个接口ServiceDiscovery方式,类名为EurekaServiceDiscovery来进行服务发现。这些不同的注册中心的实现方式,会在下一个章节去讨论它。
3、RegistryProtocol
dubbo的协议是通过名为org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol来进行抽象的,那么注册协议也是一样的,是通过org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol来表达的,继承org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol。RegistryPrtocol是扩展点Protocol的具体实现,在Dubbo系列之 (一)SPI扩展文章中提到,会一次调用其setter方法来注入其需要的属性,RegistryPrtocol其中有个属性就是RegistryFactory,那么就要为它注入一个具体的RegistryFactory,那么这个具体的RegistryFactory工厂是什么类型,答案就是上面的RegistryFactory$Adaptive。为什么?因为在Dubbo系列之 (一)SPI扩展中提到了注入的属性对象会从SpringExtensionFactory和SpiExtensionFactory工厂中查询,刚好RegistryFactory也是一个扩展点,所以会在SpiExtensionFactory找出,并且SpiExtensionFactory工厂的实现如下:
public class SpiExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
if (type.isInterface() && type.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(type);
if (!loader.getSupportedExtensions().isEmpty()) {
return loader.getAdaptiveExtension();
}
}
return null;
}
}
所以知道是返回一个自适应的扩展点,即RegistryFactory$Adaptive。
Protocol协议具有导出服务export()功能,和引用服务refer()功能。在RegistryProtocol中,在这个2个方法内就有对服务注册到注册中心的操作。
4、服务导出
在服务导出中,首先要有一个认知,这个认知会在后续章节中进行详细的介绍,先开始知道有这么一件事情即可,我们做dubbo服务暴露的时候,我们有2中方式,一种是通过注解的方式:
@DubboService,@Service(非spring的)。或者通过xml的方式<dubbo:service />。
不管采用哪一种方式,最终需要暴露的服务首先会包装成一个ServiceBean的对象。这个ServiceBean 持有具体需要服务注册的对象ref。ServiceBean的类图如下:
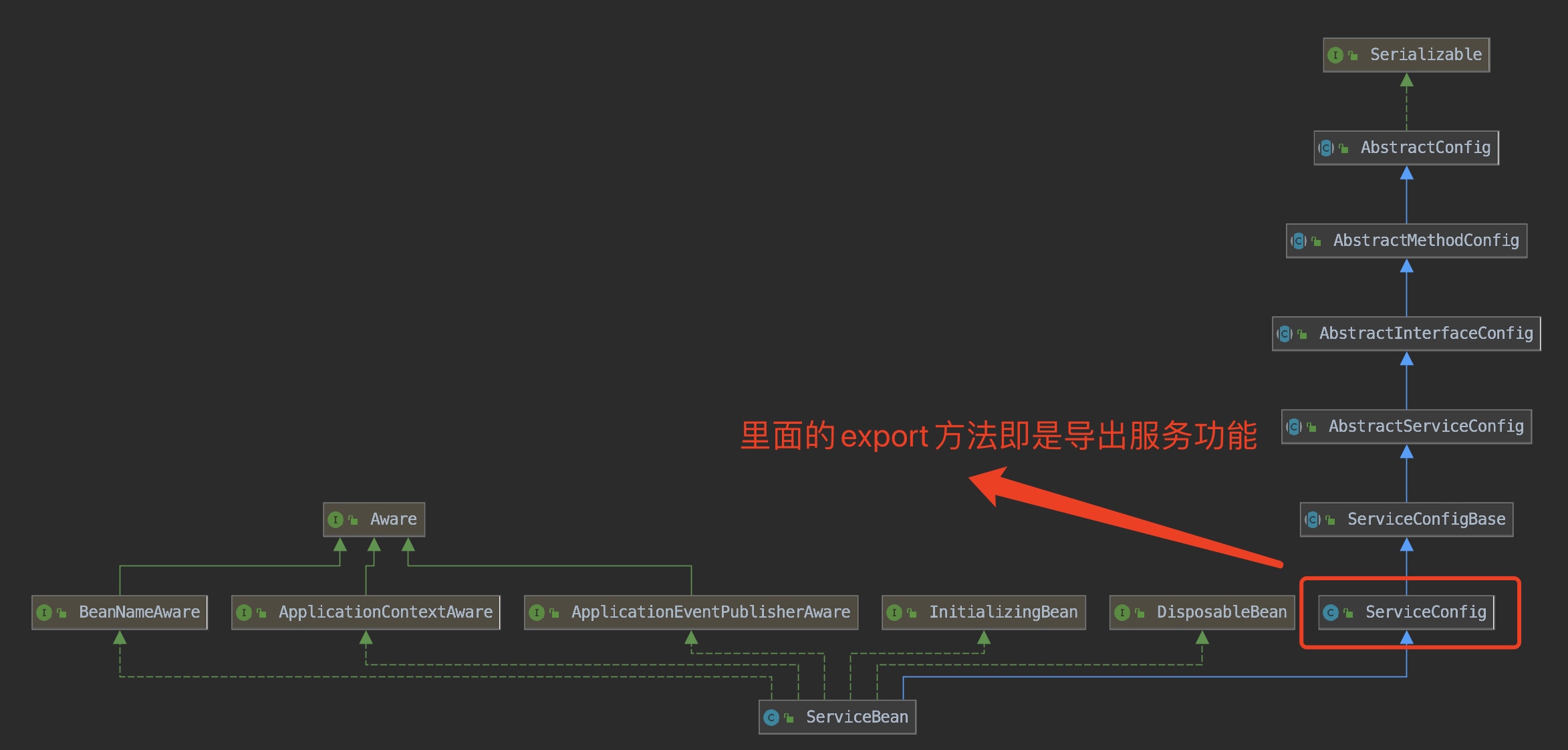
服务导出也是是一个繁琐的过程,所以在后面的章节进行详细的探讨,本章我们只要知道其服务导出引入与注册中心交互。
5、dubbo启动引导其服务导出。
DubboBootstrap是一个dubbo框架启动的帮助类,他有一个start()方法,在该方法的内部就会调用exportServices()用于导出服务,和调用referServices()进行引用服务。那么DubboBootstrap的start()方法是被谁调用?
一般使用dubbo框架的都会引入Spring框架,Spring框架有一个事件监听机制,dubbo正是监听Spring的上下文刷新事件ContextRefreshedEvent,来启动Dubbo服务的。这个服务监听类就是DubboBootstrapApplicationListener。
DubboBootstrapApplicationListener是如何注册到Spring中的呢?
1、如果是通过注解@DubboService,就是通过ServiceClassPostProcessor类,该类是实现了Spring的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。所以通过registerBeans进行注册。在@EnableDubbo注解上有一个@DubboComponentScan注解,该注解上的@export注解就会导入DubboComponentScanRegistrar类,在该类中完成DubboBootstrapApplicationListener的注册。
2、如果是通过<dubbo:service />的方式,我们知道Spring对于自定义的标签,需要自已提供一个NamespaceHanlder的实现类来协助解析自定义标签。而dubbo的NamespaceHanlder实现类为DubboNamespaceHandler。DubboNamespaceHandler该类就有该监听器的注入。
并且classpath下的META-INF下新增spring.hanlders和spring.schemes。内容如下:
spring.shemes :
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/dubbo.xsd
说明dubbo的命名空间文件位置
spring.handler:
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo=org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
说明处理该命名空间下的自定义标签通过DubboNamespaceHandler.
3、具体的Spring 自定义标签运用可以参考Netty自娱自乐之类Dubbo RPC 框架设计构想 【上篇】。
特征测试
在经过以上的基础铺垫之后,我们对Registry和RegistryProtocol协议进行测试。
本章主要主要的关注点在注册上,把目光移到RegistryProtocol的registry方法上。
private void register(URL registryUrl, URL registeredProviderUrl) {
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(registryUrl);
registry.register(registeredProviderUrl);
}
其中,
registryUrl 为注册的URL,例如:zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&export=dubbo://192.168.0.105:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&bind.ip=192.168.0.105&bind.port=20880&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&metadata-type=remote&methods=sayHello,sayHelloAsync&pid=9990&release=&side=provider×tamp=1596943034484&pid=9990®istry_protocol=zookeeper×tamp=1596943034477
registeredProviderUrl 为服务提供者需要被注册的URL。例如:dubbo://192.168.0.105:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&metadata-type=remote&methods=sayHello,sayHelloAsync&pid=9990&release=&side=provider×tamp=1596943034484
从上面的样例可以知道,registeredProviderUrl就是registryUrl 中参数export中的值。
test1
@Test
public void testRegistry(){
// 根据SPI 获取RegistryFactory 自适应注册工厂
RegistryFactory registryFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
//通过url.getProtocol 和registryFactory得到 zookeeper注册中心
URL registryUrl=URL.valueOf("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&export=dubbo://192.168.0.105:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&bind.ip=192.168.0.105&bind.port=20880&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&metadata-type=remote&methods=sayHello,sayHelloAsync&pid=9990&release=&side=provider×tamp=1596943034484&pid=9990®istry_protocol=zookeeper×tamp=1596943034477");
Registry zookeeperRegistry = registryFactory.getRegistry(registryUrl);
//根据zookeeperRegistry注册中心注册,需要的服务providerRegistryURL
URL providerRegistryURL=URL.valueOf("dubbo://192.168.0.105:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&metadata-type=remote&methods=sayHello,sayHelloAsync&pid=9990&release=&side=provider×tamp=1596943034484");
zookeeperRegistry.register(providerRegistryURL);
}
源码跟踪
registry方法定位到FailbackRegistry,主要作用当服务注册失败后,可以在后端线程重试。
public void register(URL url) {
// 判断该注册中心能接受的协议
if (!acceptable(url)) {
logger.info("URL " + url + " will not be registered to Registry. Registry " + url + " does not accept service of this protocol type.");
return;
}
// 调用AbstractRegistry的register(),主要是吧注册的URL放入registered集合中,说明该URL已经要被注册
super.register(url);
removeFailedRegistered(url); // 当前URL需要被注册,所以把它从注册失败列表里移除,因为可能是重试注册。
removeFailedUnregistered(url); // 当前URL需要被注册,所以把它从注销失败列表里移除,因为可能是重试注册。
try {
//调用子类的具体doRegister,模板方法
doRegister(url);
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e;
// If the startup detection is opened, the Exception is thrown directly.
// 查看是否check字段是否设置为true.
boolean check = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true)
&& url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true)
&& !CONSUMER_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol());
boolean skipFailback = t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException;
//如果需要严格检测的话,直接抛异常
if (check || skipFailback) {
if (skipFailback) {
t = t.getCause();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register " + url + " to registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
} else {
logger.error("Failed to register " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
// 否则把注册失败的URL 添加到failedRegistered,注册失败列表
addFailedRegistered(url);
}
}
private void addFailedRegistered(URL url) {
//获取该注册URL是否已经存在在注册失败列表里,存在直接返回
FailedRegisteredTask oldOne = failedRegistered.get(url);
if (oldOne != null) {
return;
}
// 否则创建一个失败注册重试任务FailedRegisteredTask,放入failedRegistered中。
FailedRegisteredTask newTask = new FailedRegisteredTask(url, this);
oldOne = failedRegistered.putIfAbsent(url, newTask);
if (oldOne == null) {
// 然后把该失败注册任务放入daemon线程retryTimer,定式重新注册
retryTimer.newTimeout(newTask, retryPeriod, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
由于章节篇幅限时,具体的doRegistry方法在后面章节分享。在下一个章节详细分析AbstractRegistry 的作用和FailbackRegistry的重试机制,并且详细剖析ZookeeperRegistry。


