数据结构堆
引用
1. [堆结构维基百科] - https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%A0%86%E7%A9%8D
2. [堆结构素材] - https://github.com/wangzhione/temp/tree/master/code/struct
目录
1. 简介
2. 堆结构定义
3. 堆结构实现
3.1 堆结构创建销毁
3.2 堆结构 push 和 pop
3.3 堆结构 remove
4. 堆结构实践
4.1 堆结构接口自测
4.2 堆结构面试小练习
5. 总结回顾
正文
1. 简介
堆结构多数人很耳熟, 在堆排序到优先级队列, 系统库的快速查找代码中很容易看见它的身影. 相关的资料比较
丰富, 业务上可用代码模板不多见. 本文重点是学以致用, 带大家从代码维度来观察和理解堆结构的工程实现.
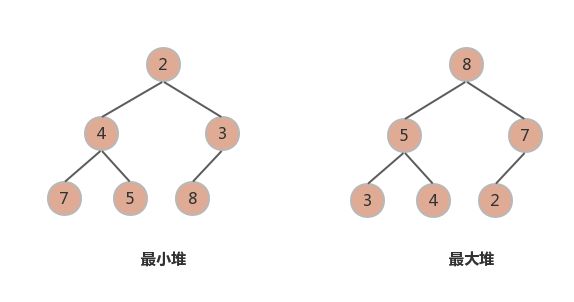
(最小堆也被成为小顶堆, 最大堆也被称为大顶堆)
2. 堆结构定义
#pragma once #include "struct.h" // // heap_t 堆的数据结构 // typedef struct heap * heap_t; // // heap_create - 构建特定规则的初始'小顶'堆 // fcmp : 当 fcmp(起始结点, 待比较结点) <= 0 停止调整 // return : 返回创建好的堆对象 // extern heap_t heap_create(cmp_f fcmp); extern void heap_delete(heap_t h, node_f fide); extern int heap_len(heap_t h); extern void * heap_top(heap_t h); extern bool heap_push(heap_t h, void * node); extern void * heap_pop(heap_t h); // // heap_remove - 删除堆中索引 i 数据 // h : 堆对象 // i : 索引 i [0, heap_len()) // return : 索引为 i 的堆结点 // extern void * heap_remove(heap_t h, int i); extern void * heap_pop_push(heap_t h, void * node);
其中 struct.h 是数据结构辅助头文件, 有心朋友可以尝试复制和拓展
#pragma once #include <errno.h> #include <assert.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stddef.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <math.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <float.h> #include <string.h> #include <limits.h> #include <inttypes.h> #ifndef CMP_F #define CMP_F // // cmp_f - 比较行为 > 0 or = 0 or < 0 // : int add_cmp(const void * now, const void * node) // typedef int (* cmp_f)(); #endif//CMP_F #ifndef NEW_F #define NEW_F // // new_f - 构建行为 // : void * rtree_new(void * node) // typedef void * (* new_f)(); #endif//NEW_F #ifndef NODE_F #define NODE_F // // node_f - 销毁行为 // : void list_die(void * node) // typedef void (* node_f)(); #endif//NODE_F #ifndef EACH_F #define EACH_F // // each_f - 遍历行为, node 是内部结点, arg 是外部参数 // : int echo(void * node, void * arg) { return 0; } // typedef int (* each_f)(void * node, void * arg); #endif//EACH_F // // DCODE - DEBUG 模式下的测试宏 // DCODE({ // puts("debug test start ..."); // }); // #ifndef DCODE # ifndef NDEBUG # define DCODE(code) do code while(0) # else # define DCODE(code) # endif//NDEBUG #endif//DCODE // // PERR - 打印错误信息 // EXIT - 打印错误信息, 并 exit // IF - 条件判断辅助的程序退出宏 // #define PERR(fmt, ...) \ fprintf(stderr, "[%s:%s:%d][%d:%s]"fmt"\n", \ __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno), ##__VA_ARGS__) #define EXIT(fmt, ...) \ do { \ PERR(fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__); \ exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while(0) #define IF(cond) \ if ((cond)) EXIT(#cond) // // RETURN - 打印错误信息, 并 return 返回指定结果 // val : return 的东西. 填 NIL 标识 return void; // fmt : 双引号包裹的格式化字符串 // ... : fmt 中对应的参数 // return : val // #define RETURN(val, fmt, ...) \ do { \ PERR(fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__); \ return val; \ } while(0) #define NIL #define RETNIL(fmt, ...) \ RETURN(NIL , fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__) #define RETNUL(fmt, ...) \ RETURN(NULL, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__) #define RETERR(fmt, ...) \ RETURN(-1 , fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
3. 堆结构实现
3.1 堆结构创建销毁
#include "heap.h" #define HEAP_INIT_INT (1<<5) struct heap { void ** data; int len; int cap; cmp_f fcmp; }; heap_t heap_create(cmp_f fcmp) { struct heap * h = malloc(sizeof(struct heap)); if (h == NULL) { return NULL; } h->data = malloc(sizeof(void *) * HEAP_INIT_INT); if (h->data == NULL) { free(h); return NULL; } h->cap = HEAP_INIT_INT; h->len = 0; h->fcmp = fcmp; return h; } void heap_delete(heap_t h, node_f fdie) { if (h != NULL) { return; } if (fdie != NULL && h->len > 0) { for (int i = h->len - 1; i >= 0; i--) fdie(h->data[i]); } free(h->data); free(h); }
怎么创建; 怎么销毁; 何时创建; 何时销毁. 销毁决定了这个语言是精细手工生产工具, 还是高效智能生产工具.
3.2 堆结构 push 和 pop
堆结构 push 和 pop 核心在于结点关系的调整. 总结有 堆结点下沉(向下调整)和堆结点上浮(向上调整).
// down - 堆结点下沉, 从上到下沉一遍 static void down(cmp_f fcmp, void * data[], int len, int x) { void * m = data[x]; for (int i = (x<<1)+1; i < len; i = (x<<1)+1) { if (i+1 < len && fcmp(data[i+1], data[i]) < 0) ++i; if (fcmp(m, data[i]) <= 0) break; data[x] = data[i]; x = i; } data[x] = m; } // up - 堆结点上浮, 从下到上浮一遍 static void up(cmp_f fcmp, void * node, void * data[], int x) { while (x > 0) { void * m = data[(x-1)>>1]; if (fcmp(m, node) <= 0) break; data[x] = m; x = (x-1)>>1; } data[x] = node; }
如何理解其中奥妙呢? 可以这么看, 索引 i 结点的左子树索引为 2i+1 = (x<<1)+1, 右子树树索引为 2i+2 = (2i+1)+1.
同样规则索引为 i 结点的父亲结点就是 (i-1)/2 = (i-1)>>1. 这就是堆结点调整的无上奥妙. 如果真要在工程角度吸
收充沛, 最需要的是临摹和调试. 对于我们这些不具备系统算法训练, 算法思维的程序员而言, 有时候理解算法的
法宝是手能生巧, 温故知新.
有了 up 上浮 和 down 下沉 两个调整规则, 对于 push 和 pop 理解要简单很多.
bool heap_push(heap_t h, void * node) { if (h->len >= h->cap) { void * ptr = realloc(h->data, h->cap<<1); if (ptr == NULL) { return false; } h->cap <<= 1; h->data = ptr; } up(h->fcmp, node, h->data, h->len++); return true; } static inline void heap_reduce(struct heap * h) { if (h->cap > HEAP_INIT_INT && h->cap >> 1 > h->len) { h->cap >>= 1; h->data = realloc(h->data, sizeof(void *) * h->cap); } } void * heap_pop(heap_t h) { void * top = heap_top(h); if (top && --h->len > 0) { // 尾巴结点一定比(小堆)顶结点大, 那么要下沉 *h->data = h->data[h->len]; down(h->fcmp, h->data, h->len, 0); heap_reduce(h); } return top; }
又有了 push 和 pop , 我们构造个升级版的复合操作, pop 完之后 push
void * heap_pop_push(heap_t h, void * node) { assert(h != NULL && h->len > 0 && node != NULL); // 获取堆顶数据准备弹出 void * top = *h->data; // 从堆顶压入新的数据 *h->data = node; down(h->fcmp, h->data, h->len, 0); return top; }
3.3 堆结构 remove
void * heap_remove(heap_t h, int i) { if (h == NULL || h->len <= 0 || i < 0 || i >= h->len) { return NULL; } void * node = h->data[i]; // 找到结点开始走删除操作 if (--h->len > 0) { if (h->len != i) { // 尾巴结点和待删除结点比较 int ret = h->fcmp(h->data[h->len], node); if (ret < 0) { // '小顶'堆, 新的值比老的值小, 那么上浮 up(h->fcmp, h->data[h->len], h->data, i); } else if (ret > 0) { // '小顶'堆, 新的值比老的值大, 那么下沉 h->data[i] = h->data[h->len]; down(h->fcmp, h->data, h->len, i); } } heap_reduce(h); } return node; }
4. 堆结构实践
4.1 堆结构接口自测
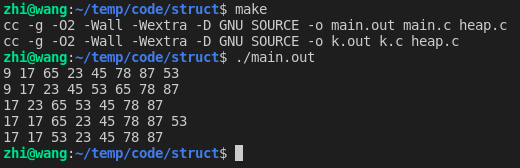
#include "heap.h" struct node { int value; }; static inline int node_cmp(const struct node * l, const struct node * r) { return l->value - r->value; } static void heap_print(heap_t h) { struct heap { void ** data; int len; } * obj = (struct heap *)h; // 数据打印 for (int i = 0; i < obj->len; ++i) { struct node * node = obj->data[i]; printf("%d ", node->value); } putchar('\n'); } int main(void) { heap_t h = heap_create(node_cmp); struct node a[] = { { 53 }, { 17 }, { 78 }, { 9 }, { 45 }, { 65 }, { 87 }, { 23} }; for (int i = 0; i < (int)(sizeof a / sizeof *a); ++i) heap_push(h, a + i); heap_print(h); // 数据打印 struct node * node; while ((node = heap_pop(h))) { printf("%d ", node->value); } putchar('\n'); // 重新插入数据 for (int i = 0; i < (int)(sizeof a / sizeof *a); ++i) heap_push(h, a + i); // 删除操作 - 下沉 heap_remove(h, 0); heap_print(h); // 插入操作 heap_push(h, &(struct node){ 17 }); heap_print(h); // 删除操作 - 上浮 heap_remove(h, 2); heap_print(h); heap_delete(h, NULL); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
4.2 堆结构面试小练习
很常见面试小题寻找一堆数据中 top K . 这里也简单写个例子供参考和思考.
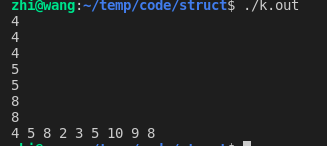
#include "heap.h" /* 问题: 找到数据流中第 K 大元素 例如: 3 | {4, 5, 8} -> 4 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2} -> 4 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2, 3} -> 4 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5} -> 5 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5, 10} -> 5 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5, 10, 9} -> 8 3 | {4, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5, 10, 9, 8} -> 8 */ /* 分析: 我们用 K 个元素 小顶堆 结构 步骤: 0. 前置健壮性检查 1. 创建一个 K 个元素小顶堆, 在其中添加 K 个元素 2. 小顶堆堆顶值最小, 让它同待添加元素比较, 如果待添加元素值大直接替换走小顶堆下沉操作 3. 数据流比较完毕, 小顶堆顶就是 第 K 大值 复杂度: 时间复杂度: O(n*log(K)), 其中向堆中添加元素时间复杂度为 O(log(K)) 空间复杂度: O(K), 优先队列中只用存储 K 个元素 */ static int cmp(int * left, int * right) { return *left - *right; } int main(void) { int a[] = { 4, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5, 10, 9, 8 }; int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(*a); int k = 3; int i = 0; heap_t h = heap_create(cmp); IF(h == NULL && (k < 0 || k > n)); for (; i < k; i++) { heap_push(h, a+i); } for (;;) { int * node = heap_top(h); printf("%d\n", *node); if (i >= n) break; if (cmp(node, a+i) < 0) { heap_pop_push(h, a+i); } i++; } heap_delete(h, NULL); // 检查原始数据是否错乱 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", a[i]); } putchar('\n'); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
5. 总结回顾
如果有错误, 欢迎指正交流.
聊得很多, 大部分全是代码. 原因和习惯有关, 在自己逐渐成为职业写手(不是架构师噢, 欢迎婊一下架构师)之后,
思维模式也逐渐变为直接理解代码或者通过代码理解代码.
简单回顾下本文. 主要分为 数据结构堆是什么 -> 堆结构工程实现 -> 堆结构应用小例子 三部分. 其中关于 4.2 中
面试小问题中补充个思考点, 让大家一块玩味玩味. top K 问题中, 如果数据是海量, 并且 K = n/2, 那会怎么样?
期待脑经急转弯, 有感觉评论区交流 ~


