spring源码分析之事务源码分析
系列文章目录
文章目录
事务源码分析
<!-- 启用事务注解 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
与AOP的标签解析相同,tx:annotation-driven标签也是自定义标签,http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx找到对应的handler是TxNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/tx=org.springframework.transaction.config.TxNamespaceHandler
TxNamespaceHandler
执行init方法
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
在解析tx:annotation-driven标签时使用AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser来进行解析
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
registerTransactionalEventListenerFactory(parserContext);
String mode = element.getAttribute("mode");
if ("aspectj".equals(mode)) {
// mode="aspectj"
registerTransactionAspect(element, parserContext);
}
else {
// mode="proxy"
AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator(element, parserContext);
}
return null;
}
configureAutoProxyCreator
public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 注册了InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
// org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor
String txAdvisorBeanName = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME;
if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) {
Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSource definition.
// 创建TransactionAttributeSource的bean
RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition(
"org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource");
sourceDef.setSource(eleSource);
sourceDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 注册TransactionAttributeSource的bean
String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef);
// Create the TransactionInterceptor definition.
// 创建TransactionInterceptor的bean
RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class);
interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource);
interceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef);
interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
// 注册TransactionInterceptor的bean
String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor definition.
// 创建TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor的bean
RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
advisorDef.setSource(eleSource);
advisorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 将TransactionAttributeSource的bean注入到transactionAttributeSource属性中
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
// // 将TransactionInterceptor的bean注入到adviceBeanName属性中
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName);
if (element.hasAttribute("order")) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order"));
}
// 注册的bean的名称是org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef);
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource);
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName));
parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef);
}
}
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
来先看一下InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的结构,发现和之前解析AOP时的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator很像
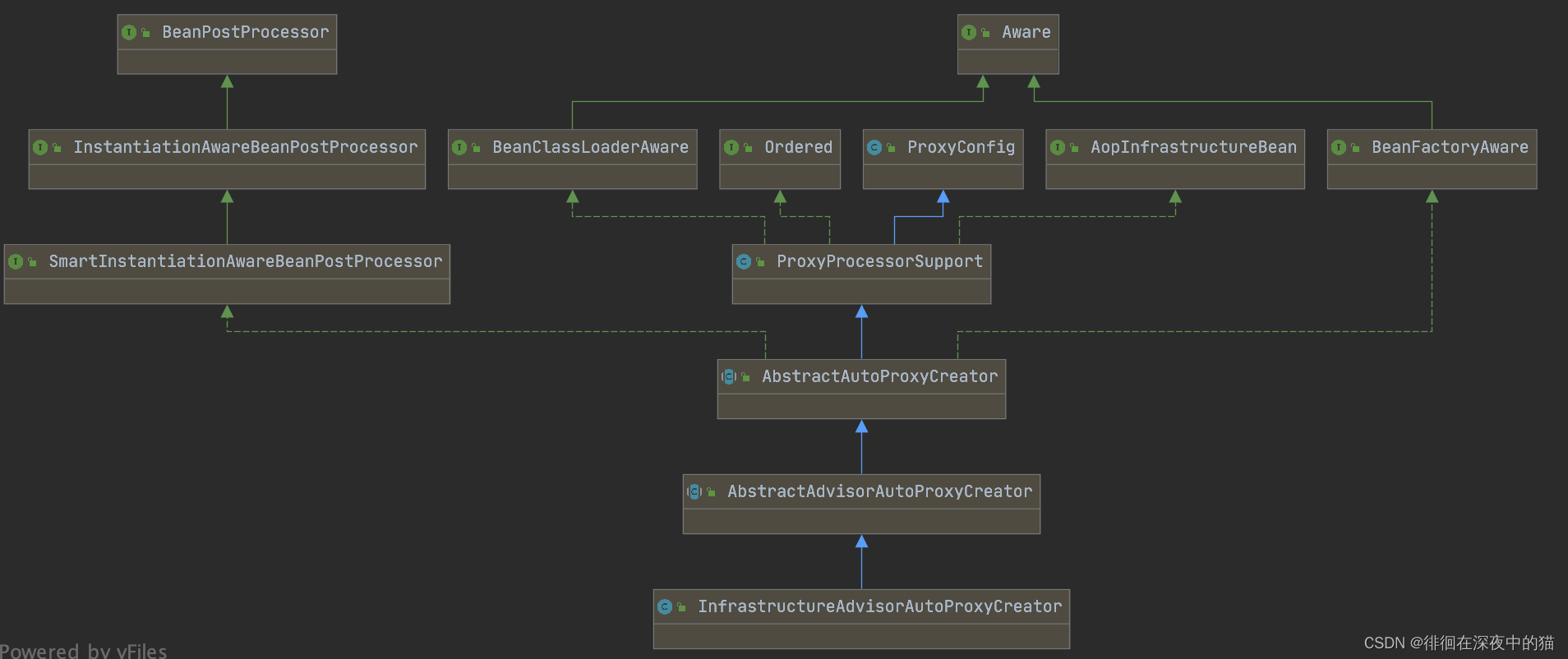
而且继承的类也是一样的,都是AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,之后的逻辑就与AOP的很是相似了,找Advisor类的bean,是有一个的,注册BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
public class BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
/**
* Set the transaction attribute source which is used to find transaction
* attributes. This should usually be identical to the source reference
* set on the transaction interceptor itself.
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributeSource
*/
public void setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
this.transactionAttributeSource = transactionAttributeSource;
}
/**
* Set the {@link ClassFilter} to use for this pointcut.
* Default is {@link ClassFilter#TRUE}.
*/
public void setClassFilter(ClassFilter classFilter) {
this.pointcut.setClassFilter(classFilter);
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
}
判断pointcut是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (targetClass != null && TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
// TransactionAttributeSource是上面进行创建的AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
// 获取事务属性
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
// 解析@Transactional注解 TransactionAttribute
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// Ignore CGLIB subclasses - introspect the actual user class.
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass);
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, userClass);
// If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method.
specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// First try is the method in the target class.
// 先尝试解析方法上有没有@Transactional注解
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
// 如果方法上没有,则解析类上的
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
方法增强
如果匹配到@Transactional注解就会使用上述注册的TransactionInterceptor来进行方法增强
TransactionInterceptor#invoke方法
对于事务方法的调用,最终会调用TransactionInterceptor#invoke方法,会根据不同的事务处理器以及事务配置情况来进行事务操作
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取代理的目标对象
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {
@Override
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
});
}
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)
throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// 获取事务属性
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// 事务管理器
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 方法的唯一标识
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 区分不同的事务管理器
// 对于CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager类型的事务管理器,需要回调函数来实现事务的创建和提交,即声明式事务
// 对于非CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager类型的,不需要通过回调函数来实现事务的创建和提交,即编程式事务
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建事务,同时把创建事务过程中得到的信息放到TransactionInfo中,保存当前事务状态
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 沿着处理器链进行调用,执行被增强方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 事务处理方法调用中出现异常,事务处理需要根据具体情况进行回滚或者提交
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 重置掉ThreadLocal中的信息transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo)
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 事务提交
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else { // 需要通过回调方法操作事务
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,
new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
事务创建方法createTransactionIfNecessary
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(
PlatformTransactionManager tm, TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
// 如果没有指定名字,则使用方法唯一标识来作为事务名
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 获取TransactionStatus
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
}
}
// 根据指定的属性和status准备一个TransactionInfo
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(PlatformTransactionManager tm,
TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification, TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
if (txAttr != null) {
// We need a transaction for this method...
// The transaction manager will flag an error if an incompatible tx already exists.
txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);
}
else {
// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only
// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.
}
// We always bind the TransactionInfo to the thread, even if we didn't create
// a new transaction here. This guarantees that the TransactionInfo stack
// will be managed correctly even if no transaction was created by this aspect.
// 将当前的TransactionInfo和线程进行绑定,同时TransactionInfo中由一个变量来保存以前的TransactionInfo,在请求事务时会创建TransactionInfo
txInfo.bindToThread();
return txInfo;
}
getTransaction获取事务
// 1、获取事务
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
// 从ConnectionHolder中进行获取,如果有则使用原本的连接,如果没有则进行创建
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 如果已经存在事务
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
// 事务超时
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
// 当前线程不存在事务,但是TransactionDefinition被声明为PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,则抛出异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// 当前线程不存在事务,但是TransactionDefinition被声明为PROPAGATION_REQUIRED或者PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW或者PROPAGATION_NESTED,则新建事务
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
// 空挂起
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开始创建事务,包括设置ConnectionHolder、隔离级别、timeout,如果是新连接,则绑定到当前线程
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 同步事务的设置
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw err;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
以DataSourceTransactionManager为例
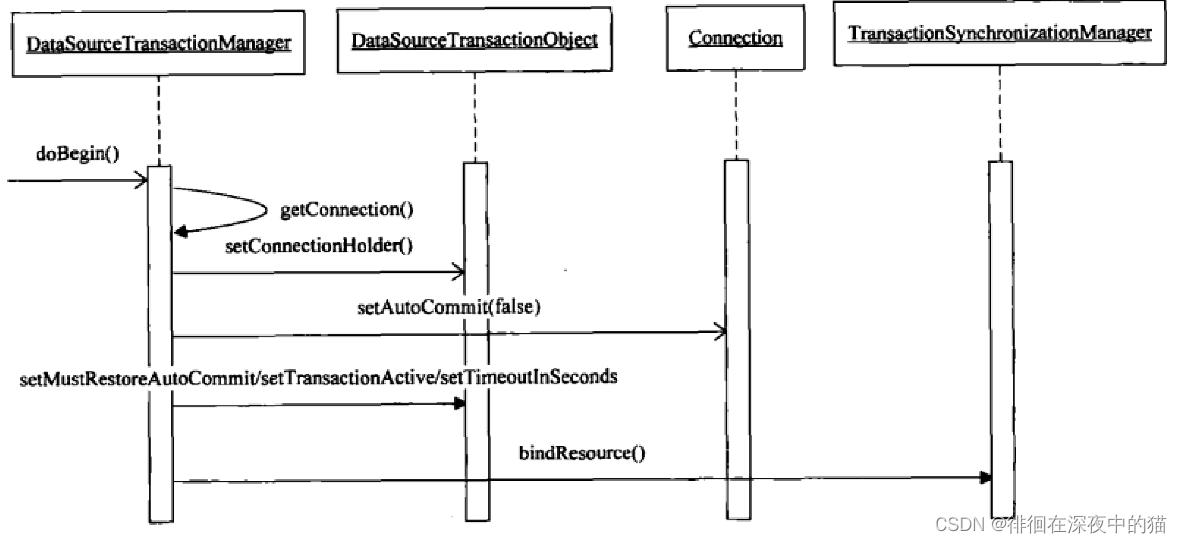
public class DataSourceTransactionManager extends AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
implements ResourceTransactionManager, InitializingBean {
// 注入的数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
private boolean enforceReadOnly = false;
public DataSourceTransactionManager() {
setNestedTransactionAllowed(true);
}
public DataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
this();
setDataSource(dataSource);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource instanceof TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) {
this.dataSource = ((TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) dataSource).getTargetDataSource();
}
else {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
}
/**
* Return the JDBC DataSource that this instance manages transactions for.
*/
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return this.dataSource;
}
public void setEnforceReadOnly(boolean enforceReadOnly) {
this.enforceReadOnly = enforceReadOnly;
}
public boolean isEnforceReadOnly() {
return this.enforceReadOnly;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (getDataSource() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'dataSource' is required");
}
}
@Override
public Object getResourceFactory() {
return getDataSource();
}
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
// 事务工作是由Connection来完成的,把数据库的Connection放入到ConnectionHolder中,然后封装到DataSourceTransactionObject对象中
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(this.dataSource);
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
// 判断是否存在事务,由ConnectionHolder的isTransactionActive来决定
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
// 事务开始
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = this.dataSource.getConnection();
// 设置ConnectionHolder
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
// 设置隔离级别
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
// 需要把自动提交事务关闭,由spring控制提交
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务的依据
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
// 如果是新开的连接,需要把Connection和线程绑定
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
@Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.dataSource);
}
@Override
protected void doResume(Object transaction, Object suspendedResources) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(this.dataSource, suspendedResources);
}
// 事务提交
@Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
try {
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
// 事务回滚
@Override
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
try {
con.rollback();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
@Override
protected void doSetRollbackOnly(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
txObject.setRollbackOnly();
}
@Override
protected void doCleanupAfterCompletion(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
// Remove the connection holder from the thread, if exposed.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.dataSource);
}
// Reset connection.
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
try {
if (txObject.isMustRestoreAutoCommit()) {
con.setAutoCommit(true);
}
DataSourceUtils.resetConnectionAfterTransaction(con, txObject.getPreviousIsolationLevel());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().clear();
}
/**
* Prepare the transactional {@code Connection} right after transaction begin.
* <p>The default implementation executes a "SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY" statement
* if the {@link #setEnforceReadOnly "enforceReadOnly"} flag is set to {@code true}
* and the transaction definition indicates a read-only transaction.
* <p>The "SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY" is understood by Oracle, MySQL and Postgres
* and may work with other databases as well. If you'd like to adapt this treatment,
* override this method accordingly.
* @param con the transactional JDBC Connection
* @param definition the current transaction definition
* @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC API
* @since 4.3.7
* @see #setEnforceReadOnly
*/
protected void prepareTransactionalConnection(Connection con, TransactionDefinition definition)
throws SQLException {
if (isEnforceReadOnly() && definition.isReadOnly()) {
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
try {
stmt.executeUpdate("SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY");
}
finally {
stmt.close();
}
}
}
/**
* DataSource transaction object, representing a ConnectionHolder.
* Used as transaction object by DataSourceTransactionManager.
*/
private static class DataSourceTransactionObject extends JdbcTransactionObjectSupport {
private boolean newConnectionHolder;
private boolean mustRestoreAutoCommit;
public void setConnectionHolder(ConnectionHolder connectionHolder, boolean newConnectionHolder) {
super.setConnectionHolder(connectionHolder);
this.newConnectionHolder = newConnectionHolder;
}
public boolean isNewConnectionHolder() {
return this.newConnectionHolder;
}
public void setMustRestoreAutoCommit(boolean mustRestoreAutoCommit) {
this.mustRestoreAutoCommit = mustRestoreAutoCommit;
}
public boolean isMustRestoreAutoCommit() {
return this.mustRestoreAutoCommit;
}
public void setRollbackOnly() {
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
}
@Override
public boolean isRollbackOnly() {
return getConnectionHolder().isRollbackOnly();
}
@Override
public void flush() {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerFlush();
}
}
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:拾光师,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/life-time/p/17864331.html 个人博客-> https://zhhll.icu



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号