k8s创建rabbitmq集群
新建文件rabbitmq.yaml
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: test-rabbitmq --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rabbitmq-config namespace: test-rabbitmq data: enabled_plugins: | [rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_peer_discovery_k8s]. rabbitmq.conf: | ## Cluster formation. See https://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html to learn more. cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_k8s cluster_formation.k8s.host = kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local ## Should RabbitMQ node name be computed from the pod's hostname or IP address? ## IP addresses are not stable, so using [stable] hostnames is recommended when possible. ## Set to "hostname" to use pod hostnames. ## When this value is changed, so should the variable used to set the RABBITMQ_NODENAME ## environment variable. cluster_formation.k8s.address_type = hostname ## How often should node cleanup checks run? cluster_formation.node_cleanup.interval = 30 ## Set to false if automatic removal of unknown/absent nodes ## is desired. This can be dangerous, see ## * https://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html#node-health-checks-and-cleanup ## * https://groups.google.com/forum/#!msg/rabbitmq-users/wuOfzEywHXo/k8z_HWIkBgAJ cluster_formation.node_cleanup.only_log_warning = true cluster_partition_handling = autoheal ## See https://www.rabbitmq.com/ha.html#master-migration-data-locality queue_master_locator=min-masters ## This is just an example. ## This enables remote access for the default user with well known credentials. ## Consider deleting the default user and creating a separate user with a set of generated ## credentials instead. ## Learn more at https://www.rabbitmq.com/access-control.html#loopback-users loopback_users.guest = false --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: rabbitmq namespace: test-rabbitmq --- kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: rabbitmq-peer-discovery-rbac namespace: test-rabbitmq rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["endpoints"] verbs: ["get"] # - apiGroups: [""] # resources: ["events"] # verbs: ["create"] --- kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: rabbitmq-peer-discovery-rbac namespace: test-rabbitmq subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: rabbitmq roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: rabbitmq-peer-discovery-rbac --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: namespace: test-rabbitmq name: rabbitmq labels: app: rabbitmq type: LoadBalancer spec: type: NodePort ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 15672 targetPort: 15672 nodePort: - name: amqp protocol: TCP port: 5672 targetPort: 5672 nodePort: selector: app: rabbitmq --- apiVersion: apps/v1 # See the Prerequisites section of https://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html#peer-discovery-k8s. kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: rabbitmq namespace: test-rabbitmq spec: serviceName: rabbitmq # Three nodes is the recommended minimum. Some features may require a majority of nodes # to be available. replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: rabbitmq template: metadata: labels: app: rabbitmq spec: serviceAccountName: rabbitmq terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10 nodeSelector: # Use Linux nodes in a mixed OS kubernetes cluster. # Learn more at https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubernetes-api/labels-annotations-taints/#kubernetes-io-os kubernetes.io/os: linux containers: - name: rabbitmq-k8s image: rabbitmq:3.8 volumeMounts: - name: config-volume mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq # Learn more about what ports various protocols use # at https://www.rabbitmq.com/networking.html#ports ports: - name: http protocol: TCP containerPort: 15672 - name: amqp protocol: TCP containerPort: 5672 livenessProbe: exec: # This is just an example. There is no "one true health check" but rather # several rabbitmq-diagnostics commands that can be combined to form increasingly comprehensive # and intrusive health checks. # Learn more at https://www.rabbitmq.com/monitoring.html#health-checks. # # Stage 2 check: command: ["rabbitmq-diagnostics", "status"] initialDelaySeconds: 60 # See https://www.rabbitmq.com/monitoring.html for monitoring frequency recommendations. periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 15 readinessProbe: exec: # This is just an example. There is no "one true health check" but rather # several rabbitmq-diagnostics commands that can be combined to form increasingly comprehensive # and intrusive health checks. # Learn more at https://www.rabbitmq.com/monitoring.html#health-checks. # # Stage 2 check: command: ["rabbitmq-diagnostics", "status"] # To use a stage 4 check: # command: ["rabbitmq-diagnostics", "check_port_connectivity"] initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 10 imagePullPolicy: Always env: - name: MY_POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: apiVersion: v1 fieldPath: metadata.name - name: MY_POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace - name: RABBITMQ_USE_LONGNAME value: "true" # See a note on cluster_formation.k8s.address_type in the config file section - name: K8S_SERVICE_NAME value: rabbitmq - name: RABBITMQ_NODENAME value: rabbit@$(MY_POD_NAME).$(K8S_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_POD_NAMESPACE).svc.cluster.local - name: K8S_HOSTNAME_SUFFIX value: .$(K8S_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_POD_NAMESPACE).svc.cluster.local - name: RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE value: "mycookie" volumes: - name: config-volume configMap: name: rabbitmq-config items: - key: rabbitmq.conf path: rabbitmq.conf - key: enabled_plugins path: enabled_plugins
在服务器上执行:kubectl apply -f rabbitmq.yaml
等所有pod全部启动成功后,进入管理界面查看
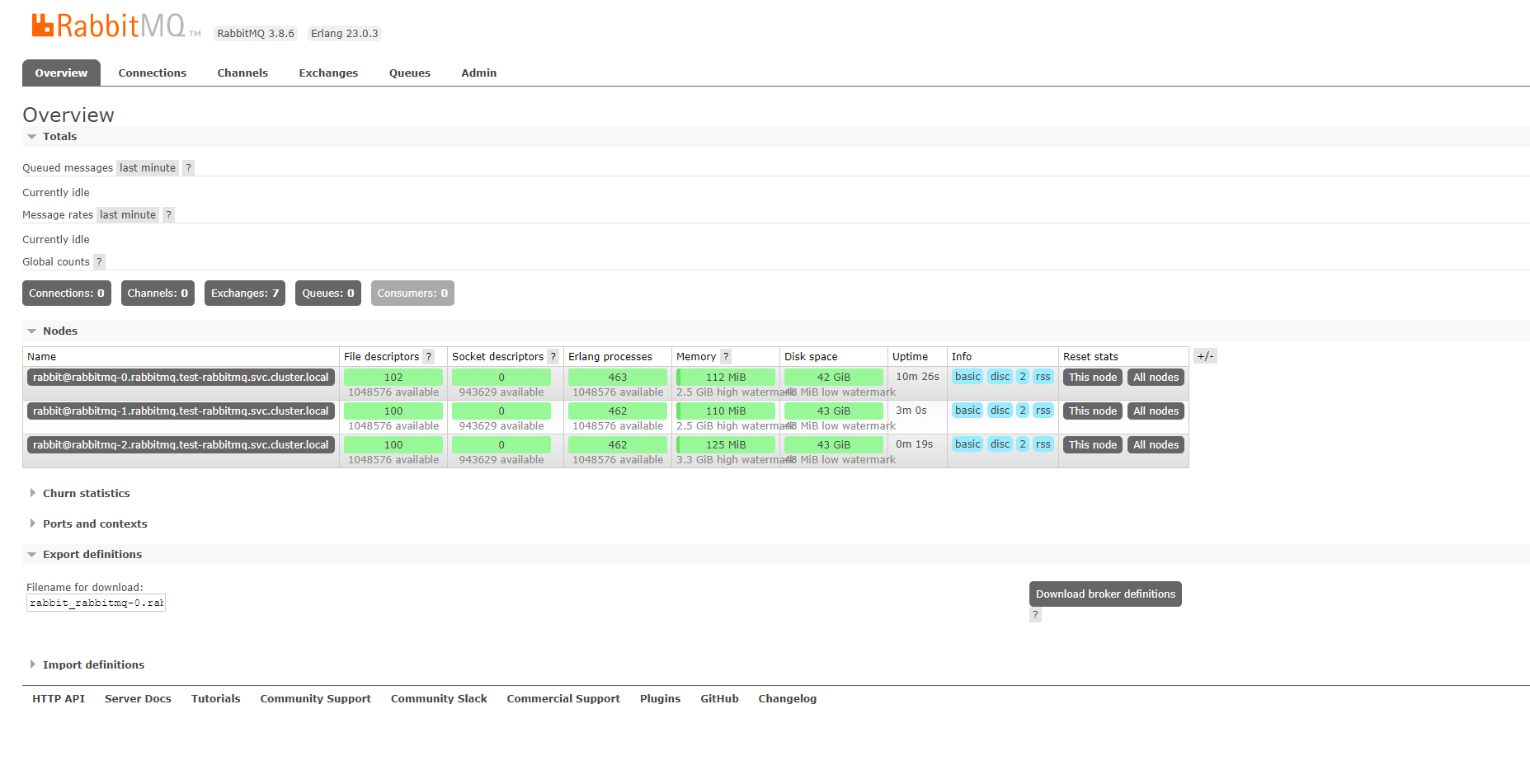
rabbitmq集群部署成功,这里只是内存模式,如果要挂载存储,请添加相应的配置





