算法--数组、链表、栈、队列
一、数组
1、删除有序数组中的重复项(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/
给你一个 升序排列 的数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。
由于在某些语言中不能改变数组的长度,所以必须将结果放在数组nums的第一部分。更规范地说,如果在删除重复项之后有 k 个元素,那么 nums 的前 k 个元素应该保存最终结果。
将最终结果插入 nums 的前 k 个位置后返回 k 。
不要使用额外的空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
判题标准:
系统会用下面的代码来测试你的题解:
int[] nums = [...]; // 输入数组
int[] expectedNums = [...]; // 长度正确的期望答案
int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // 调用
assert k == expectedNums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
}
如果所有断言都通过,那么您的题解将被 通过。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]
输出:2, nums = [1,2,_]
解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2 ,并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2 。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
输出:5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4]
解释:函数应该返回新的长度 5 , 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104 -
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104 -
nums已按 升序 排列
解答
主要使用双指针
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || nums.length==1){
return nums.length;
}
int j = 0;
for(int i =1; i< nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] != nums[j]){
nums[++j] = nums[i];
}
}
return j+1;
}
}
2、移动零(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [0]
输出: [0]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
解答
仍然使用双指针即可
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int j = 0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] != 0){
nums[j] = nums[i];
j++;
}
}
while(j < nums.length){
nums[j++] = 0;
}
}
}
3、合并两个有序数组(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-sorted-array/
给你两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。
请你 合并 nums2 到 nums1 中,使合并后的数组同样按 非递减顺序 排列。
注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组 nums1 中。为了应对这种情况,nums1 的初始长度为 m + n,其中前 m 个元素表示应合并的元素,后 n 个元素为 0 ,应忽略。nums2 的长度为 n 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6]
解释:需要合并 [1,2,3] 和 [2,5,6] 。
合并结果是 [1,2,2,3,5,6] ,其中斜体加粗标注的为 nums1 中的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
输出:[1]
解释:需要合并 [1] 和 [] 。
合并结果是 [1] 。
示例 3:
输入:nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
输出:[1]
解释:需要合并的数组是 [] 和 [1] 。
合并结果是 [1] 。
注意,因为 m = 0 ,所以 nums1 中没有元素。nums1 中仅存的 0 仅仅是为了确保合并结果可以顺利存放到 nums1 中。
提示:
nums1.length == m + nnums2.length == n0 <= m, n <= 2001 <= m + n <= 200-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
进阶:你可以设计实现一个时间复杂度为 O(m + n) 的算法解决此问题吗?
解答
这道题仍然使用双指针,还有一个重要的点,就是从后往前循环,这样不会涉及数据的移动,时间复杂度为O(n+m),如果从前往后循环,会存在单个数组中中间插入的情况,时间复杂度为O(n+logn*m)
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m-1, j = n-1, k = m+n-1;
while(j >= 0){
if(i < 0){
nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
continue;
}
if(nums1[i] >= nums2[j]){
nums1[k--] = nums1[i--];
}else{
nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
}
}
4、加一(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/plus-one/description/
给定一个由 整数 组成的 非空 数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。
你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
示例 1:
输入:digits = [1,2,3]
输出:[1,2,4]
解释:输入数组表示数字 123。
示例 2:
输入:digits = [4,3,2,1]
输出:[4,3,2,2]
解释:输入数组表示数字 4321。
示例 3:
输入:digits = [0]
输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= digits.length <= 1000 <= digits[i] <= 9
解答
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
for(int i=digits.length-1; i>= 0;i--){
k = i == digits.length-1 ? 1 : 0;
int sum = digits[i] + j + k;
if(sum == 10){
digits[i] = 0;
j = 1;
}else{
digits[i] = sum;
j = 0;
break;
}
}
if(j != 0){
digits = new int[digits.length+1];
digits[0] = 1;
}
return digits;
}
}
二、链表
1、反转链表(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
解答
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode preNode = head;
ListNode node = head.next;
preNode.next = null;
while(node != null){
ListNode nextNode = node.next;
node.next = preNode;
preNode = node;
node = nextNode;
}
return preNode;
}
}
2、K 个一组翻转链表(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/description/
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
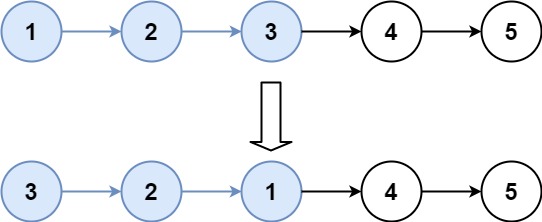
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
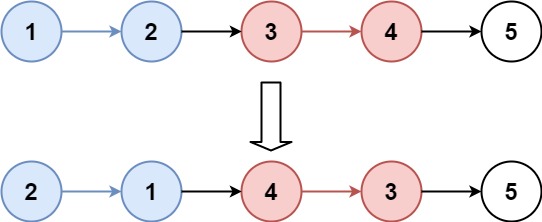
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
进阶:你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
解答
解题思路:
1、先分组
2、对于每一组进行翻转
3、对组进行前后关系设置
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode protectNode = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode preHead = protectNode;
while(head != null){
ListNode end = getEndNode(head, k);
if(end == null){
break;
}
ListNode nextHead = end.next;
reverse(head, nextHead);
preHead.next = end;
head.next = nextHead;
preHead = head;
head = nextHead;
}
return protectNode.next;
}
private ListNode getEndNode(ListNode head, int k){
int i=1;
while(i<k && head != null){
head = head.next;
i++;
}
return head;
}
private void reverse(ListNode head, ListNode end){
ListNode pre = null;
while(head != null && head != end){
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
}
}
3、环形链表(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
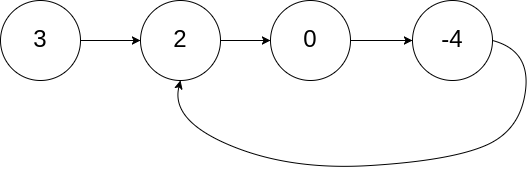
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
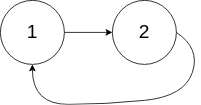
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 104] -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
进阶:你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
解答
主要用到快慢指针,如果快慢指针走到同一个位置,说明有循环链表,否则就不存在
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
4、环形链表2(中等)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
进阶:你是否可以使用 O(1) 空间解决此题?
解答
这道题主要是解题思路,代码并不难
首先定义几个变量,x:表示环形链表前的长度,y:表示从环形链表开始到快慢指针相遇的长度,r:表示环形链表的长度
那么,快指针走的长度为:fast = x + mr+y,满指针走的长度为:slow= x + nr+y,其中m和n分别表示快慢指针循环环形链表的次数
由于快指针走的速度是满指针的2倍,因此就有 fast = 2slow,移动后 x = (m-2n)r - y,也就是从环形链表相遇的节点开始到环形链表的开始节点的长度 与 链表头结点到环形链表节点开始节点长度一致
基于以上分析,解题思路如下:
1、首先使用快慢指针找到相同节点
2、再用两个指针,一个从环形链表相遇节点往后递进,一个从链表头结点向前递进,最终汇合的节点就是环形链表的开始节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode meetNode = null;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
meetNode = fast;
break;
}
}
if(meetNode == null){
return null;
}
while(meetNode != head){
head = head.next;
meetNode = meetNode.next;
}
return meetNode;
}
}
5、合并两个有序链表(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
解答:
比较简单,就不做说明了,这里说一个易错点,while(list1 != null || list2 != null)特别容易写成while(list1 != null && list2 != null),需要注意
另外可以把 if(list1 == null){ 与 if(list1.val <= list2.val) 合并到一个分支为 if(list2 == null || (list1 != null && list1.val <= list2.val)),不过这样如果 list2 为 null,仍然需要循环 list1 的长度,如果直接设置完 break,就不需要循环。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode protectNode = new ListNode();
ListNode head = protectNode;
while(list1 != null || list2 != null){
if(list1 == null){
head.next = list2;
break;
}
if(list2 == null){
head.next = list1;
break;
}
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
head.next = list1;
ListNode temp = list1.next;
list1.next = null;
list1 = temp;
}else{
head.next = list2;
ListNode temp = list2.next;
list2.next = null;
list2 = temp;
}
head = head.next;
}
return protectNode.next;
}
}
三、栈与队列
0、概述
栈对先进后出,队列时先进先出,比较简单,没什么可说的
1、有效的括号(简单)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
解答
使用栈先进先出的特性
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();
for(char c : s.toCharArray()){
if(c == '(' || c== '[' || c == '{'){
stack.push(c);
}else{
if(stack.isEmpty()){
return false;
}
char top = stack.pop();
if(c == ')' && '(' != top
|| c == ']' && '[' != top
|| c == '}' && '{' != top){
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
2、最小栈(中等)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/description/
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack()初始化堆栈对象。void push(int val)将元素val推入堆栈。void pop()删除堆栈顶部的元素。int top()获取堆栈顶部的元素。int getMin()获取堆栈中的最小元素。
示例 1:
输入:
["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
[[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
输出:
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
解释:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
提示:
-231 <= val <= 231 - 1pop、top和getMin操作总是在 非空栈 上调用push,pop,top, andgetMin最多被调用3 * 104次
解答
要求最小值,那么就需要额外的空间进行存储,就定义一个 minStack
最小值栈的存储,每一次 push 时,都记录当前的最小值,例如上面的 -2,0,-3 的顺序
push -2 时,最小值栈为空,最小值为 -2
push 0 时,最小值为 -2
push -3 时,最小值为 -3
因此就可以定义一个最小值栈,每一次 push 时,存储的是原栈中的最小值,那么每一次 pop 原栈时,就需要把最小值栈也 pop 一次。
注:之前想过使用三个栈,原栈还存在,另外有一个最小值栈和一个临时栈,临时栈完全作为新来数据时,最小值栈为了重新排序而设定的一个临时存储空间。这样思路也没问题,但是当代码提交时,提示超出了运行时间,看来这样方式的效率还是不行。
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack();
minStack = new Stack();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
val = minStack.isEmpty() ? val : Math.min(val, minStack.peek());
minStack.push(val);
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(val);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
3、逆波兰表达式求值(中等)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/description/
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
注意 两个整数之间的除法只保留整数部分。
可以保证给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
输入:tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"]
输出:9
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
示例 2:
输入:tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"]
输出:6
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
示例 3:
输入:tokens = ["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"]
输出:22
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22
提示:
1 <= tokens.length <= 104tokens[i]是一个算符("+"、"-"、"*"或"/"),或是在范围[-200, 200]内的一个整数
逆波兰表达式:
逆波兰表达式是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指算符写在后面。
- 平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如
( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 )。 - 该算式的逆波兰表达式写法为
( ( 1 2 + ) ( 3 4 + ) * )。
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
- 去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成
1 2 + 3 4 + *也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。 - 适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中
解答
用到了栈,如果不是运算符,就往栈里添加,如果是运算符,就从栈里面获取两个数据进行运算,再把运算结果放入栈中
易错点:pop 的时候要注意两个值的先后顺序,第一个 pop 的是运算符后面的数据,第二个 pop 的数据是运算符前面的数据,对于减法和除法要特别注意。
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack();
for(String s : tokens){
if(s.equals("+") || s.equals("-") || s.equals("*") || s.equals("/")){
int y = numStack.pop();
int x = numStack.pop();
if(s.equals("+")){
numStack.push(x + y);
}
if(s.equals("-")){
numStack.push(x - y);
}
if(s.equals("*")){
numStack.push(x * y);
}
if(s.equals("/")){
numStack.push(x / y);
}
}else{
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
}
}
return numStack.pop();
}
}
4、面试题 16.26. 计算器(中等)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/calculator-lcci/description/
给定一个包含正整数、加(+)、减(-)、乘(*)、除(/)的算数表达式(括号除外),计算其结果。
表达式仅包含非负整数,+, - ,*,/ 四种运算符和空格 。 整数除法仅保留整数部分。
示例 1:
输入: "3+2*2"
输出: 7
示例 2:
输入: " 3/2 "
输出: 1
示例 3:
输入: " 3+5 / 2 "
输出: 5
说明:
- 你可以假设所给定的表达式都是有效的。
- 请不要使用内置的库函数
eval。
解答
解题思路:
1、中缀转后缀:可以将中缀表达式改为后缀表达式,即上面的逆波兰表达式,就是将运算符放入两个需要运算的数据之后,然后出一个运算符,就接着出两个数字,运算完毕后将数据再让进去。
2、定义两个栈分别存储数字和运算符:那么为了更好的获取数字和获取运算符,就需要使用两个栈,一个存储数据,一个存储运算符,即循环字符,如果是数字的就放入数字的栈,如果是运算符的就放入运算符的栈
3、运算符优先级:由于运算符有优先级,因此不能无脑的将数字和运算符放入栈中,如果新来的运算符优先级小于等于栈中已有的优先级,则先将栈中的运算符计算
4、最后出栈:在全部循环完毕后,有可能符号栈中还有运算符没有出栈,因此需要再判断将运算符栈中数据出栈完
5、结束控制:由于可能出现两位及以上的数字,因此在判断数字时,使用的是字符判断,每次和之前的相加,直到遇到非数字才停止,并将该数字入栈,那么就存在最后一个数字没法入栈的情况;另外题目中提示可能有空格,那么就取个巧,在字符串的最后加上一个空格,保证最后一个数值可以入栈。
取巧点:字符串后加空格保证最后一个数值入栈
易错点:在判断符号优先级时,有两个点容易出错:
1、第一个是优先级的判断,必须是前面的优先级大于等于当前准备入栈的优先级,就需要先计算前面的结果,必须包含等于,因为不包含的话,就可能出现 1-1+1=-1的情况(因为这两个服务的优先级一样,没有先做前面的运算,而都放入了栈中,最后使用后缀表达式,先算后面再算前面)
2、第二个 for 循环中的 while,这里比较容易被误用 if,如果使用 if,就可能出现 2-3/4+5=-3的情况,因为 if 只判断一次,那么第一个减号,直接入栈,第二个除号,比之前的优先极高,也入栈,到了加号,比之前的优先级低,那么优先算 3/4,但是由于 if 只判断了一次,就会变为 2-0+5,根据后缀表达式,就会产生 -3 的结果,使用 while 可以一直向前判断,在 3/4 算完后,继续使用加号和之前的运算符比较(减号),仍然是小于等于,那么之前的继续运算,最后就会得到 2+5 ,最终值为7
class Solution {
public int calculate(String s) {
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack();
Stack<Character> opsStack = new Stack();
s += " ";
String numStr = "";
for(char ch : s.toCharArray()){
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
numStr += ch;
continue;
}else if(!"".equals(numStr)){
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(numStr));
numStr = "";
}
if(ch == ' '){
continue;
}
while(!opsStack.isEmpty() && getRange(opsStack.peek()) >= getRange(ch)){
numStack.push(grtResult(numStack.pop(), numStack.pop(), opsStack.pop()));
}
opsStack.push(ch);
}
while(!opsStack.isEmpty()){
numStack.push(grtResult(numStack.pop(), numStack.pop(), opsStack.pop()));
}
return numStack.pop();
}
private int getRange(char ch){
if(ch == '*' || ch == '/'){return 2;}
if(ch == '+' || ch == '-'){return 1;}
return 0;
}
private int grtResult(int val1, int val2, char ops){
if(ops == '+'){return val2 + val1;}
if(ops == '-'){return val2 - val1;}
if(ops == '*'){return val2 * val1;}
return val2 / val1;
}
}
5、基本计算器(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/basic-calculator/description/
给你一个字符串表达式 s ,请你实现一个基本计算器来计算并返回它的值。
注意:不允许使用任何将字符串作为数学表达式计算的内置函数,比如 eval() 。
示例 1:
输入:s = "1 + 1"
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:s = " 2-1 + 2 "
输出:3
示例 3:
输入:s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)"
输出:23
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105s由数字、'+'、'-'、'('、')'、和' '组成s表示一个有效的表达式- '+' 不能用作一元运算(例如, "+1" 和
"+(2 + 3)"无效) - '-' 可以用作一元运算(即 "-1" 和
"-(2 + 3)"是有效的) - 输入中不存在两个连续的操作符
- 每个数字和运行的计算将适合于一个有符号的 32位 整数
解答
这道题和上面题有两个大的区别,一个是有括号,一个是可能存在负号,而上面的题有乘除,这道题没有,则不用考虑,那么直接把上面问题的解答拿下来,针对这两个大的区别点做针对的修改。
1、有括号:主要添加对于括号的判断,如果是左括号,直接放入符号栈中,如果是右括号,则直接向前进行处理,直到遇到一个左括号
2、负值:其实这道题出的有问题,并没有描述存在负号的情况,但是在提交的时候会又能相关的测试用例,导致提交不成功。
对于负号的问题,可以通过在负号前补零来处理,那么就要看哪些场景需要补零了。
补零的场景:如果负号在左括号后面,或者在加减号后面,都是需要补零的,那么就可以设置一个标志,在这两个场景时,将该标志设置为true,但是如果实在数字之后,就不需要补零。
标记设置完成后,如果需要补零,并且当前符号为符号,那就需要在前面补零,即往数值栈中添加一个零。
class Solution {
public int calculate(String s) {
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack();
Stack<Character> opsStack = new Stack();
s += " ";
String numStr= "";
boolean needZero = true;
for(char ch : s.toCharArray()){
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
numStr += ch;
needZero = false;
continue;
}else if(!"".equals(numStr)){
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(numStr));
numStr = "";
}
if(ch == ' '){
continue;
}
if(ch == '('){
opsStack.push(ch);
needZero = true;
continue;
}
if(ch == ')') {
while(opsStack.peek() != '('){
numStack.push(getResult(numStack.pop(), numStack.pop(), opsStack.pop()));
}
opsStack.pop();
continue;
}
if(ch == '-' && needZero){
numStack.push(0);
}
while(!opsStack.isEmpty() && getRange(ch) <= getRange(opsStack.peek())){
numStack.push(getResult(numStack.pop(), numStack.pop(), opsStack.pop()));
}
needZero = true;
opsStack.push(ch);
}
while(!opsStack.isEmpty()){
numStack.push(getResult(numStack.pop(), numStack.pop(), opsStack.pop()));
}
return numStack.pop();
}
private int getRange(char ch){
if(ch == '+' || ch == '-') {return 1;}
if(ch == '*' || ch == '/') {return 2;}
return 0;
}
private int getResult(int v1, int v2, char ops){
if(ops == '+') { return v2 + v1;}
if(ops == '-') { return v2 - v1;}
if(ops == '*') { return v2 * v1;}
return v2 / v1;
}
}
7、设计循环双端队列(中等)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-deque/
设计实现双端队列。
实现 MyCircularDeque 类:
MyCircularDeque(int k):构造函数,双端队列最大为k。boolean insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回true,否则返回false。boolean insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回true,否则返回false。boolean deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回true,否则返回false。boolean deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回true,否则返回false。int getFront()):从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回-1。int getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回-1。boolean isEmpty():若双端队列为空,则返回true,否则返回false。boolean isFull():若双端队列满了,则返回true,否则返回false。
示例 1:
输入
["MyCircularDeque", "insertLast", "insertLast", "insertFront", "insertFront", "getRear", "isFull", "deleteLast", "insertFront", "getFront"]
[[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
输出
[null, true, true, true, false, 2, true, true, true, 4]
解释
MyCircularDeque circularDeque = new MycircularDeque(3); // 设置容量大小为3
circularDeque.insertLast(1); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertLast(2); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(3); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 已经满了,返回 false
circularDeque.getRear(); // 返回 2
circularDeque.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.deleteLast(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 返回 true
circularDeque.getFront(); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= k <= 10000 <= value <= 1000insertFront,insertLast,deleteFront,deleteLast,getFront,getRear,isEmpty,isFull调用次数不大于2000次
解答:
没什么可说的
class MyCircularDeque {
ListNode headNode;
ListNode endNode;
int count;
int limit;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
headNode = new ListNode();
endNode = new ListNode();
headNode.next = endNode;
endNode.pre = headNode;
count = 0;
limit = k;
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if(count == limit){
return false;
}
count += 1;
ListNode tempNode = headNode.next;
ListNode thisNode = new ListNode(value);
headNode.next = thisNode;
thisNode.pre = headNode;
thisNode.next = tempNode;
tempNode.pre = thisNode;
return true;
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if(count == limit){
return false;
}
count += 1;
ListNode tempNode = endNode.pre;
ListNode thisNode = new ListNode(value);
tempNode.next = thisNode;
thisNode.pre = tempNode;
thisNode.next = endNode;
endNode.pre = thisNode;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if(count == 0){
return false;
}
count -= 1;
ListNode tempNode = headNode.next.next;
headNode.next = tempNode;
tempNode.pre = headNode;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if(count == 0){
return false;
}
count -= 1;
ListNode tempNode = endNode.pre.pre;
endNode.pre = tempNode;
tempNode.next = endNode;
return true;
}
public int getFront() {
return count == 0 ? -1 : headNode.next.val;
}
public int getRear() {
return count == 0 ? -1 : endNode.pre.val;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return count == limit;
}
}
class ListNode{
public ListNode next;
public ListNode pre;
public int val;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(){
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/
四、单调栈与单调队列
0、概述
单调队列和单调栈并非一种数据结构,而是为了解题而出现的一种思路,将不规则的线性结构转变为单调递增或者单调递减的规则线性结构,进而可以更好计算结果。
单调栈和单调队列的解题套路:
(1)for 循环每一个选项
(2)while(栈顶与新元素不满足单调性){弹栈,更新答案,累加"宽度"}
(3)入栈
1、柱状图中最大的矩形(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
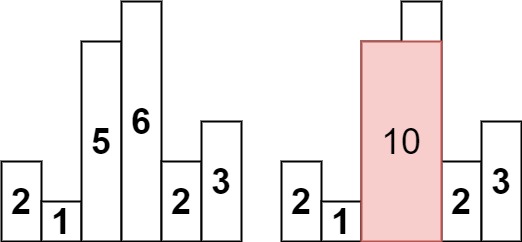
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
示例 2:
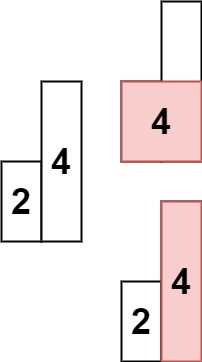
输入: heights = [2,4]
输出: 4
提示:
1 <= heights.length <=1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
解答
解题思路:
1、为什么选择单调栈:如果数组(柱子)是单调递增,那么就比较好处理:
如果从左开始,第 i 跟柱子时,height*(length-i),那么循环每一根柱子,在每一跟柱子时计算面积,然后和既往最大值对比即可
其中 i 为当前节点的位置,length 为数组长度,height 为 第 i 跟柱子的高度
如果从右开始,计算出当前节点的面积后,将高度设置为和前面的高度一致,再计算前面的高度
2、如何变为单调栈
这里选择单调递增,那么就是循环数组,如果当前节点满足单调性,就入栈,如果不满足单调性,就进行处理(根据具体的题意进行处理,修正、抛弃、调整前一个等)让其单调性成立,在这道题里,就把之前满足的做一个处理,保证之前节点的高度都小于当前节点的高度
由于是要计算最大面积,因此之前的抛弃时,要先计算之前的面积,例如现在是 2,3,4,1,那么在 1 这个节点
之前的4已经不满足单调性,那么就应该把 4 抛弃,但是需要计算一下当前节点的最大面积,高度为4,宽度为1,面积为4
再继续,3也不满足单调性,抛弃3,在这时,高为3,宽为2(因为之前的4虽然抛弃,但是宽度仍然在),面积为6
再继续,2也不满足单调性,抛弃2,在这时,高为2,宽为3,面积为6
最终 2,3,4 都被抛弃,需要将 1 放入栈,放入的是高为 1,宽为 4 的节点(宽需要加上之前抛弃的所有节点的宽)
3、特殊处理
上面方法实际是保证了栈的单调性,但是最终的数据没有处理,例如最终的单调栈为 2,3,4,5,那么都是push到栈中了,并没有计算最大值,或者没有计算完毕,就需要从前或者从后再计算一遍。
为了避免上述再来一次循环导致代码臃肿,可以取个巧,就是在数组的最后加一个0,让其在最后的节点不满足单调性,就会把之前的都计算了,所以,在 for 循环的判断里,使用了 i<= heights.leng 的条件(加上了等号),并且取第 i 个节点的高度时,如果是第 heights.length时,height 设置为 0,让其前面的所有都不满足单调性。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
Stack<Rect> stack = new Stack();
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<= heights.length;i++){
int height = i== heights.length ? 0 : heights[i];
int sumWeight = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().height >= height){
Rect rect = stack.pop();
sumWeight += rect.weight;
ans = Math.max(ans, sumWeight*rect.height);
}
stack.push(new Rect(sumWeight+1, height));
}
return ans;
}
}
class Rect{
public int weight;
public int height;
public Rect(int weight, int height){
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
}
2、滑动窗口最大值(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3
输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 1041 <= k <= nums.length
解答
题目分析:
以示例1为例,循环每一个节点:
i=0,值为1,可能最大值为1
i=1,值为3,由于1和3肯定在一组,因此1就没有作用,最大值为3
i=2,值为-1,由于可能存在1,3,-1,-2,-3的情况,因此-1有可能成为后续的最大值
i=3,值为-3,与上面一样,可能存在其为最大值的情况
i=4,值为5,那么往前推两位(k=3),前面两位分别是-1和-3,那么-1和-3就不可能成为最大值
综上分析,如果使用一个单调队列,保证其为单调递减,那么每一个节点都有可能成为后续的最大值,这个队列是从后面添加数据的,但是还要保证取数据的区间为k的限制,如果头结点的位置超过了当前节点与k的范围,就要移除,也就是说,从而保证一定取到的是k范围内的最大值。
解题:
由于要从两端操作单调栈,那么就可以使用一个双端队列,同时为了判断最大值的位置,则双端队列中存储的是最大值的下标,同时单调栈中保持单调递减,那么套用单调栈的套路,解题思路如下:
for 循环
如果单调栈中的头结点超出了范围,就剔除头结点
while 判断,对于不满足单调性的节点处理,使其满足单调性
获取头结点放入结果集
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] ans = new int[nums.length-k+1];
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(!deque.isEmpty() && i-k >= deque.getFirst()){
deque.removeFirst();
}
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.getLast()] <= nums[i]){
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(i);
if(i>=k-1){
ans[i-k+1] = nums[deque.getFirst()];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
3、接雨水(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
提示:
n == height.length1 <= n <= 2 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
解答1:单调栈
分析思路:雨水可以向左或向右流动,直到碰到比他高的节点就会停止,如果两端都碰到比他高的节点,那么当前节点的水就能被收集,如果是这样,保证单调递减,那么从第二个节点开始,都是有盛水的可能的,那么如果碰到了不满足单调递减的节点,就可以去计算一次盛水量,因此本题可以采用单调递减的方式处理。
解题套路仍然一样,先循环所有节点,如果满足单调性,则push,不满足单调性,则针对该题的特殊场景做处理
不满足单调性处理:不满足单调性,说明前一个节点比当前节点低,那么就要算出来前一个节点能存多少水,公式为:(Math.min(stack.peek().height, height) - rect.height) * sumWeight,其中stack.peek().height表示要前一个节点再之前一个节点的高度,height表示当前节点的高度,rect.height表示前一个节点的高度,sumWeight表示前一个节点的宽度。
可能描述起来比较绕口,举例,5,3,6这个场景,到了6,是不满足单调性的,因此就要计算当前节点(6)之前节点(3)可以盛多少水,那么其可以盛3左右高低低的那一个,然后再减去3本身的高度,就可以计算其盛水高度,宽度即为3这个节点本身的宽度。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] heights) {
Stack<Rect> stack = new Stack();
int ans = 0;
for(int height : heights){
int sumWeight = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().height <= height){
Rect rect = stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()){
continue;
}
sumWeight += rect.weight;
ans += (Math.min(stack.peek().height, height) - rect.height) * sumWeight;
}
stack.push(new Rect(sumWeight+1, height));
}
return ans;
}
}
class Rect{
public int weight;
public int height;
public Rect(int weight, int height){
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
}
解答2:前缀最大值
一个更好理解的观点:到一个节点后,查看其前后的最大值,那么最大值中的最小值如果大于当前节点的高度,则可以盛水,盛水的容量为左右最大值的小者与当前节点的高度差。
public int trap(int[] heights) {
int ans = 0;
int[] preMax = new int[heights.length];
int[] suffMax = new int[heights.length];
for(int i=1;i<heights.length;i++){
preMax[i] = Math.max(preMax[i-1], heights[i-1]);
}
for(int i = heights.length-2;i>=0;i--){
suffMax[i] = Math.max(suffMax[i+1], heights[i+1]);
System.out.println(suffMax[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<heights.length-1;i++){
if(suffMax[i] > heights[i] && preMax[i] > heights[i]){
ans += Math.min(suffMax[i], preMax[i]) - heights[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
4、最大矩形(困难)
题目地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-rectangle/
给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 、大小为 rows x cols 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
示例 1:

输入:matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]]
输出:6
解释:最大矩形如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:matrix = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:matrix = [["0"]]
输出:0
示例 4:
输入:matrix = [["1"]]
输出:1
示例 5:
输入:matrix = [["0","0"]]
输出:0
提示:
rows == matrix.lengthcols == matrix[0].length1 <= row, cols <= 200matrix[i][j]为'0'或'1'
解答
这道题是第一题的一个扩展,循环每一行,将每一行变更为柱形数组即可,那么解题思路就变成了以下三步
1、循环每一行,将每一行变为一个柱形数组:int[] heights = geneHeight(i, matrix);
2、计算每一行柱形数组能得到的最大面积:max = getMax(heights)
3、比较每一行的最大面积,从主取出最大值:ans = Math.max(ans, max)
第2点,完成照搬第一题即可,第三点没什么可说的,就单独说一下第一点
循环每一列,行都是从固定行开始,如果当前列的当前行不为1,当前柱形的高就加一,然后继续向上递归,直到碰到0或者到了第一行,就计算出了当前列的高。
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<matrix.length;i++){
int[] heights = geneHeight(i, matrix);
ans = Math.max(ans, getMax(heights));
}
return ans;
}
private int[] geneHeight(int row, char[][] matrix){
int col = matrix[row].length;
int[] heights = new int[col];
for(int i=0; i<col; i++){
int height = 0;
int rowTemp = row;
while(rowTemp >=0 && matrix[rowTemp][i] != '0'){
height++;
rowTemp--;
}
heights[i] = height;
}
return heights;
}
private int getMax(int[] heights){
Stack<Rect> stack = new Stack();
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=heights.length;i++){
int height = i == heights.length ? 0 : heights[i];
int sumWeight = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().height >= height){
Rect rect = stack.pop();
sumWeight += rect.weight;
ans = Math.max(ans, sumWeight*rect.height);
}
stack.push(new Rect(sumWeight+1, height));
}
return ans;
}
}
class Rect{
public int weight;
public int height;
public Rect(int weight, int height){
this.weight = weight;
this.height = height;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------
朦胧的夜 留笔~~



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号