多级缓存优化实践
一、分布式部署
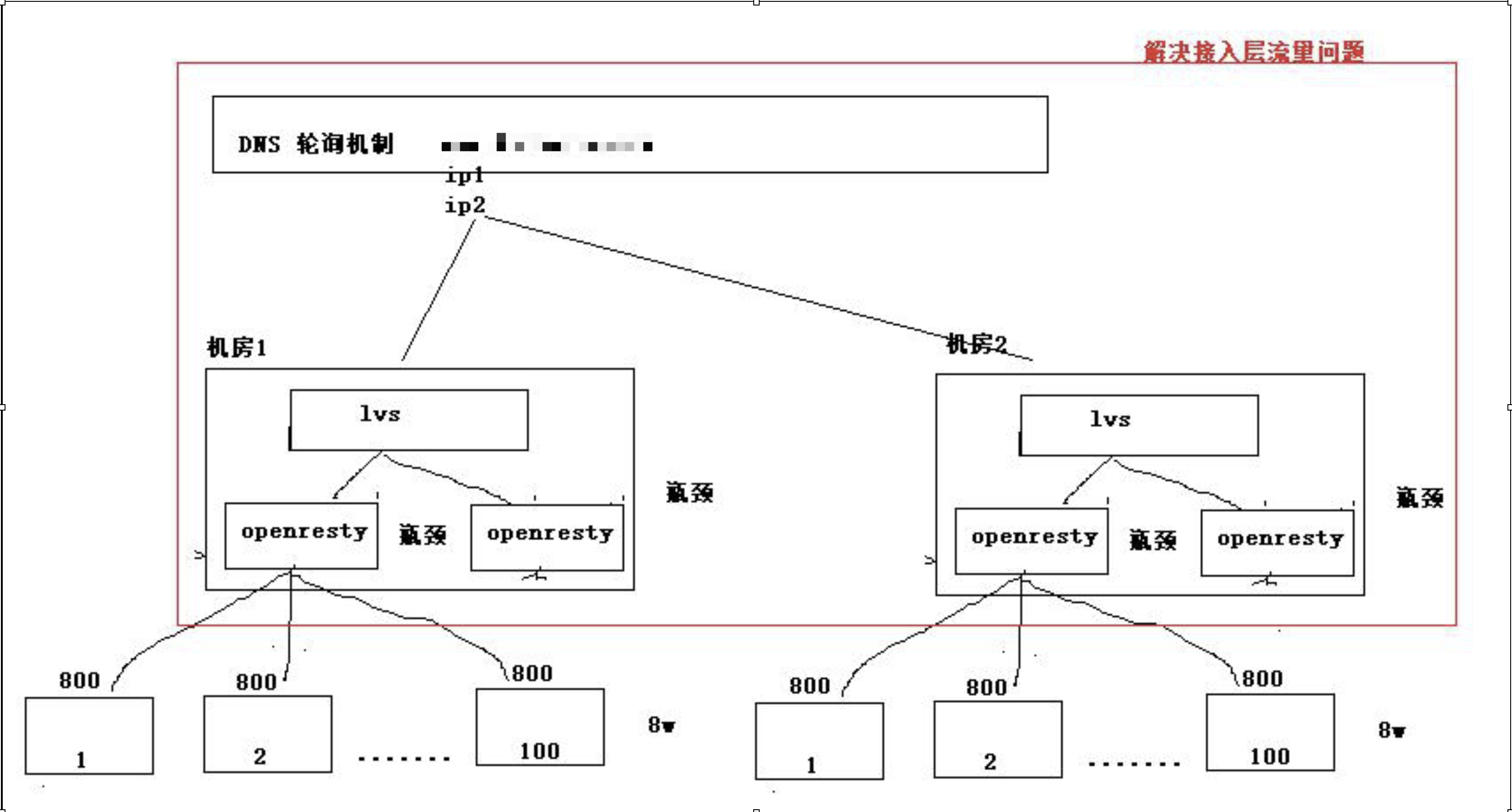
在分布式部署项目时一般部署结果如下图所示:
应用程序,使用集群部署,解决服务层的性能瓶颈
入口层,使用 LVS + Openresty(Nginx)来解决入口层瓶颈问题
入口层,使用DNS多机房部署,解决接入层流量问题。
在解决了服务层面的平静后,数据库就成为了需要解决的性能瓶颈,一般的解决方案:
1、分表分库(根据业务进行分库,分表)
2、冷热分离(把热点数据放入一个库,把冷数据放入另一个库,数据归档)
3、数据库设计(防止多表查询,冗余设计)
4、防止慢查询 SQL 语句
5、防止大表,大事务
6、缓存(多级缓存)----- 落在数据库上请求非常少,90%+请求命中缓存数据,不在访问数据库了;
分布式部署后,压测结果如下

然后从多级缓存来优化项目。
二、本地缓存&分布式缓存
1、缓存架构
(1)项目进程内部缓存:jvm 堆内存缓存 ,缓存在项目运行本地服务器
(2)分布式缓存 : redis 实现分布式缓存
(3)openresty 接入层缓存: 内存字典
(4)openresty+redis+lua 实现接入层缓存

缓存的使用流程:
首先查询OpenResty内存字典,如果有数据就返回;
OpenResty内存字典没有数据,查询jvm堆内缓存,如果有就返回;
jvm堆内缓存没有数据,查询分布式缓存redis,如果有数据就返回;
如果redis中没有数据,就查询数据库。
说明一点:缓存设计原则,缓存离请求距离越近,缓存性能就越好;
2、缓存实现
public TbSeckillGoods findOneByCache(Integer id){ //1、先从jvm堆缓存中读取数据,使用guva缓存 TbSeckillGoods seckillGoods = (TbSeckillGoods) guavaCahce.getIfPresent("seckill_goods_"+id); //判断jvm堆内缓存是否存在 if(seckillGoods == null){ //2、从分布式缓存中查询 seckillGoods = (TbSeckillGoods) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("seckill_goods_"+id); //判断 if(seckillGoods == null){ //3、直接从数据库查询 seckillGoods = seckillGoodsMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id); if(seckillGoods != null && seckillGoods.getStatus() == 1){ //添加缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("seckill_goods_"+id,seckillGoods,1,TimeUnit.HOURS); } } //添加guava缓存 guavaCahce.put("seckill_goods_"+id,seckillGoods); } //如果缓存存在,返回Redis缓存 return seckillGoods; }
缓存代码逻辑实现非常之简单的,就是先查询堆内存缓存,然后查询分布式缓存,如果以上 2 级缓存都未命中的话,那么就查询数据库,然后把数据放入分布式缓存,及堆内存缓存即可实现;
其中本地缓存使用了谷歌提供的GuavaCache,配置如下:
@Configuration public class GuavaCacheConfig { //定义一个guavacache对象 private Cache<String,Object> commonCache = null; @PostConstruct public void init(){ commonCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() .initialCapacity(10) // 设置缓存中最大的支持存储缓存的key, 超过100个,采用LRU淘汰策略淘汰缓存 .maximumSize(100) // 设置缓存写入后过期时间 .expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); } @Bean public Cache<String,Object> getCommonCache(){ return commonCache; }
那么其实有个问题,就是时候可以使用Map作为本地缓存的问题,其实是不可以的。
(1)因为虽然Map也是 K-V 结构,但是其对数据脏读问题,对脏数据极度不敏感,通俗的讲,就是不能删除缓存;
(2)还有一个比较重要的问题,JVM 内存资源非常宝贵,(java 对象,jvm 信息),不能把大量数据放入 jvm 堆内存中,如果使用Map,其实无法管理内存的大小,最终会影响服务性能。
那么GuavaCache就对此做了很好的处理:
(1)guavacache 工具可以给堆内存缓存设置过期时间;
(2)把热点数据放入堆内存缓存;(可以设置缓存的数量,尽量保证热点数据在缓存中)
使用了本地缓存 + 分布式缓存后,压测结果如下:

三、接入层缓存
(一)Openresty 使用简述
内存字典: openresy 服务器内存实现缓存 (openresty + lua 共同实现的)
安装:http://openresty.org/cn/linux-packages.html
安装完毕后,安装目录在:/usr/local/openresty,openresty是集成了nginx和lua,因此它的配置项其实就是nginx的配置项,可以修改nginx/conf/nginx.conf
对于nginx的配置,有两种方式,分别是使用content_by_lua直接配置输出和使用content_by_lua_file来配置文件
http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen 80; server_name lclpc; location /lua1 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua 'ngx.say("hello lua ......")'; } location /lua2 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua_file lua/test.lua; } location /lua3 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua_file lua/detail.lua; } location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; }
配置完毕后,启动
PATH=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin:$PATH
export PATH
nginx -c conf/nginx.conf
1、使用lua语句
location /lua1 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua 'ngx.say("hello lua ......")'; }
验证 /lua1

2、使用lua文件
nginx配置
location /lua2 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua_file lua/test.lua; }
编辑 lua/test.lua
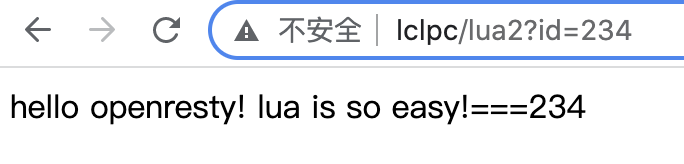
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
ngx.say("hello openresty! lua is so easy!==="..args.id)
验证
3、使用lua文件转发请求
编辑lua/detail.lua文件,让其转发到后端服务器
ngx.exec('/seckill/goods/detail/1');
nginx配置
upstream BACKEND { server 172.20.10.2:9000; server 172.20.10.3:9000; } server { listen 80; server_name lclpc; location /lua3 { default_type text/html; content_by_lua_file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/lua/detail.lua; }
验证

4、更多的lua脚本接入方式可以参考:https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/modules/lua/#directives
(二)Openstry内存字典缓存
1、开启Openstry内存字典
修改nginx配置,开启一个名为ngx_cache的128m的内存字典
lua_shared_dict ngx_cache 128m;

2、lua 脚本的方式实现内存字典缓存
修改nginx配置文件
location /goods/get { default_type application/json; content_by_lua_file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/lua/lua_share.lua; }
新增lua_share.lua文件
-- 基于内存字典实现缓存 -- 添加缓存方法 function set_to_cache(key,value,expritime) if not expritime then expritime = 0 end -- 获取本地内存字典对象 local ngx_cache = ngx.shared.ngx_cache -- 添加本地缓存数据 local succ,err,forcible = ngx_cache:set(key,value,expritime) return succ end -- 获取缓存方法 function get_from_cache(key) -- 获取本地内存字典对象 local ngx_cache = ngx.shared.ngx_cache -- 从本地内存字典中获取数据 local value = ngx_cache:get(key) return value end -- 实现缓存业务 -- 判断本地内存字典是否具有缓存数据,如果没有访问后端服务 -- 先获取请求参数 local params = ngx.req.get_uri_args() local id = params.id -- 先从本地内存字典获取缓存数据 local goods = get_from_cache("seckill_goods_"..id) -- 如果内存字典缓存数据不存在 if goods == nil then -- 从后端服务器查询 local res = ngx.location.capture("/seckill/goods/detail/"..id) -- 获取请求数据body
goods = res.body -- 添加本地缓存数据 set_to_cache("seckill_goods_"..id,goods,60) end -- 返回缓存结构 ngx.say(goods)
验证

压测:

(三)Redis + Lua
1、缓存架构
原来设计的结构是首先查询Opensty内存字典缓存,如果没有数据,就会走后端项目,然后后端项目再去查询redis数据库。前面提到,离请求越近,缓存效果越好,那么就可以直接在OpenStry中操作redis,如果其内存字典中没有数据,则直接查询redis数据库,如果redis数据库没有数据,再请求到后端服务器。

Openresty+lua 集成了 Redis lua 库,使用 Redis+lua 访问方式,只需要引入 redis 的 lua 库即可。
可以在/usr/local/openresty/lualib/resty中查看Openstry集成的库,可以发现,Openstry集成了redis、mysql、memcached等

引入redis库:require "resty.redis"
2、编写lua脚本
处理逻辑就是先查询本地内存字典,如果没有数据,在查询redis,没有数据,在查询后端服务。
-- 引入 redis.lua local redis = require "resty.redis" -- new 一个 redis 对象 local red = redis:new() -- 基于内存字典实现缓存 -- 添加缓存方法 function set_to_cache(key,value,expritime) if not expritime then expritime = 0 end -- 获取本地内存字典对象 local ngx_cache = ngx.shared.ngx_cache -- 添加本地缓存数据 local succ,err,forcible = ngx_cache:set(key,value,expritime) return succ end -- 获取缓存方法 function get_from_cache(key) -- 获取本地内存字典对象 local ngx_cache = ngx.shared.ngx_cache -- 从本地内存字典中获取数据 local value = ngx_cache:get(key) if not value then -- 从 redis 获取缓存数据 local rev,err = get_from_redis(key) if not rev then ngx.say("redis cache not exsists",err) return end -- 添加本地缓存数据 set_to_cache(key,rev,60) end return value end -- 向 redis 添加缓存 function set_to_redis(key,value) -- 设置 redis 超时时间 red:set_timeout(100000) -- 连接 redis 服务器 local ok,err = red:connect("172.20.10.14",6379) -- 判断连接是否 OK if not ok then ngx.say("failed to connect:",err) return end -- 向 redis 添加缓存数据 local ok,err = red:set(key,value) if not ok then ngx.say("failed set to redis:",err) return end return ok; end -- 从 redis 获取缓存数据 function get_from_redis(key) -- 设置 redis 超时时间 red:set_timeout(100000) -- 连接 redis 服务器 local ok,err = red:connect("172.20.10.14",6379) -- 判断连接是否 OK if not ok then ngx.say("failed to connect:",err) return end -- 从 redis 获取缓存数据 local res,err = red:get(key) if not res then ngx.say("failed get to redis:",err) return end -- 打印 ngx.say("get cache data from redis...............") return res end -- 实现缓存业务 -- 判断本地内存字典是否具有缓存数据,如果没有访问后端服务 -- 先获取请求参数 local params = ngx.req.get_uri_args() local id = params.id -- 先从本地内存字典获取缓存数据 local goods = get_from_cache("seckill_goods_"..id) -- 如果内存字典缓存数据不存在 if goods == nil then -- 从后端服务器查询 local res = ngx.location.capture("/seckill/goods/detail/"..id) -- 获取请求数据body goods = res.body -- 添加本地缓存数据 set_to_cache("seckill_goods_"..id,goods,60) end -- 返回缓存结构 ngx.say(goods)
3、验证
重新加载nginx配置后,访问接口,可以看到,第一次是直接从redis中查询的,后面的访问直接走的本地内存字典。

4、压测
这个压测结果与上面的压测结果基本一致,是因为上面用的就是内存字典,因此差异不大。

-----------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------
朦胧的夜 留笔~~



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号