Netty编码示例(RPC & WbeSocket & Tomcat)
一、Netty实现Dubbo RPC
(一)RPC 基本介绍
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)—远程过程调⽤,是⼀个计算机通信协议。该协议允许运⾏于⼀台计算机的程序调⽤另⼀台计算机的⼦程序,⽽程序员⽆需额外地为这个交互作⽤编程两个或多个应⽤程序都分布在不同的服务器上,它们之间的调⽤都像是本地⽅法调⽤⼀样。

PRC 调⽤流程说明:
1、服务消费⽅(client)以本地调⽤⽅式调⽤服务
2、client stub 接收到调⽤后负责将⽅法、参数等封装成能够进⾏⽹络传输的消息体
3、client stub 将消息进⾏编码并发送到服务端
4、server stub 收到消息后进⾏解码
5、server stub 根据解码结果调⽤本地的服务
6、本地服务执⾏并将结果返回给 server stub
7、server stub 将返回导⼊结果进⾏编码并发送⾄消费⽅
8、client stub 接收到消息并进⾏解码
9、服务消费⽅(client)得到结果
总结:RPC 的⽬标就是将 2 - 8 这些步骤都封装起来,⽤户⽆需关⼼这些细节,可以像调⽤本地⽅法⼀样即可完成远程服务调⽤
(二)实现RPC设计
设计说明:
(1)创建⼀个接⼝,定义抽象⽅法。⽤于消费者和提供者之间的约定。
(2)创建⼀个提供者,该类需要监听消费者的请求,并按照约定返回数据。
(3)创建⼀个消费者,该类需要透明的调⽤⾃⼰不存在的⽅法,内部需要使⽤netty请求提供者返回数据
(三)实现RPC代码
1、公共代码:
(1)定义统⼀的接⼝
客户端直接调用接口即可,服务端需要对接口进行实现
public interface CityService { String getName(String mes); }
(2)定义协议标识
为了判断是否是安全的请求,这里简单模拟一下,以指定字符串开头的,就认为是安全的请求。
public class Constant { public static final String protocolName = "cityService#name#"; }
2、服务端代码
(1)提供⽅:接⼝实现
public class CityServiceImpl implements CityService { private int count = 0; @Override public String getName(String mes) { System.out.println("收到客户端消息=" + mes); //根据mes 返回不同的结果 if (mes != null) { return "你好客户端, 我已经收到你的消息 [" + mes + "] 第" + (++count) + " 次"; } else { return "你好客户端, 我已经收到你的消息 "; } } }
(2)Netty的服务端的处理handler
这个比较简单,主要就是需要校验一下协议(是否是按照指定的字符串开头),然后获取真正的请求参数(去掉请求内容中固定的协议字符串),然后调用实现类,最终返回数据。
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private CityService cityService = null; public NettyServerHandler(CityService cityService ){ this.cityService = cityService; } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //获取客户端发送的消息,并调用服务 System.out.println("msg=" + msg); //客户端在调用服务器的api时,我们需要定义一个协议 //比如我们要求 每次发消息是都必须以某个字符串开头 "cityService#name##你好" if (msg.toString().startsWith(Constant.protocolName)) { String result = cityService.getName(msg.toString().substring(Constant.protocolName.length())); ctx.writeAndFlush(result); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
(3)Netty服务端启动
主要就是启动一个NettyServer,并添加处理的handler
public class NettyServer { public static void startServer(String hostName, int port) { startServer0(hostName, port); } //编写一个方法,完成对NettyServer的初始化和启动 private static void startServer0(String hostname, int port) { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { CityService cityService = new CityServiceImpl(); ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler(cityService)); //业务处理器 } } ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(hostname, port).sync(); System.out.println("server is ready"); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
(4)服务提供者启动类
public class ServerBootstrap { public static void main(String[] args) { NettyServer.startServer("127.0.0.1", 7000); } }
3、客户端代码
(1)Netty的客户端的处理handler
这里需要多说一点,该handler中有三个属性,分别为context上下文、请求参数、返回结果。
对于方法,在channelActive中(该方法在客户端与服务端建立连接后就会调用),初始化了context上下文;在setPara方法中对请求参数做了初始化;在execptionCaught方法中关闭了与服务端的连接。
最重要的两个方法是channelRead和call方法,因为handler不但继承了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,而且还实现了Callable接口,那么如果在异步提交线程时,就会调用call方法,而服务端返回结果时,就会调用channelRead方法,基于此,在提交任务会触发的call方法中,向服务端发起了请求,同时调用wait方法将线程挂起。当服务端返回结果时,channelRead方法执行,获取返回结果并对结果属性赋值,最后调用notify方法唤醒处于等待的call线程,最终由call线程返回调用结果。
这也就是上面图片中有线程挂起等待(wait)的原因,就是call线程挂起,等待channelRead线程唤醒。
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter implements Callable { private ChannelHandlerContext context;//上下文 private String result; //返回的结果 private String para; //客户端调用方法时,传入的参数 //与服务器的连接创建后,就会被调用, 这个方法是第一个被调用(1)/(2) @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelActive call,thread="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); context = ctx; //因为我们在其它方法会使用到 ctx } //收到服务器的数据后,调用方法 (4) // @Override public synchronized void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelRead call,thread="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); result = msg.toString(); notify(); //唤醒等待的线程 } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } //被代理对象调用, 发送数据给服务器,-> wait -> 等待被唤醒(channelRead) -> 返回结果 (3)-》5 @Override public synchronized Object call() throws Exception { System.out.println("before send,thread="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); context.writeAndFlush(para); //进行wait wait(); //等待channelRead 方法获取到服务器的结果后,唤醒 System.out.println("after send,thread="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); return result; //服务方返回的结果 } void setPara(String para) { System.out.println("setPara,thread="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); this.para = para; } }
(2)Netty客户端
如果是第一次调用,就需要初始化一个clientHandler,初始化逻辑就是一个简单的初始化,没有太多可说的,这里需要说的是,使用了代理模式,将请求参数加上了协议固定的字符串,从而符合服务端的协议校验,然后就是使用了线程池,使用submit向线程池中提交任务,从而执行上面handler中的call方法,然后使用了get方法阻塞获取调用结果。
public class NettyClient { //创建线程池 private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()); private static NettyClientHandler nettyClientHandler; private int count = 0; //编写方法使用代理模式,获取一个代理对象 public Object getBean(final Class<?> serivceClass, final String providerName) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{serivceClass}, (proxy, method, args) -> { System.out.println("(proxy, method, args) 进入...." + (++count) + " 次"); //{} 部分的代码,客户端每调用一次 hello, 就会进入到该代码 if (nettyClientHandler == null) { initNettyClientHandler(); } System.out.println("method:"+method.getName()); //设置要发给服务器端的信息 //providerName 协议头 args[0] 就是客户端调用api getName(???), 参数 nettyClientHandler.setPara(providerName + args[0]); return executor.submit(nettyClientHandler).get(); }); } //初始化客户端 private static void initNettyClientHandler() { nettyClientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(); //创建EventLoopGroup NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .handler( new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(nettyClientHandler); } } ); try { bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 7000).sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //重要!不要关闭 // group.shutdownGracefully(); } }
(9)服务消费者启动类
这里没有什么可说的,就是循环调用了十次。
public class ClientBootstrap { //这里定义协议头 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建一个消费者 NettyClient customer = new NettyClient(); //创建代理对象 CityService service = (CityService) customer.getBean(CityService.class, Constant.protocolName); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ //通过代理对象调用服务提供者的方法(服务) String res = service.getName("hello bejing-"+i); System.out.println("调用的结果 res= " + res); Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); } } }
4、代码输出结果
(1)服务端输出
msg=cityService#name#hello bejing-0 收到客户端消息=hello bejing-0 msg=cityService#name#hello bejing-1 收到客户端消息=hello bejing-1 msg=cityService#name#hello bejing-2 收到客户端消息=hello bejing-2 msg=cityService#name#hello bejing-3 收到客户端消息=hello bejing-3
(2)客户端输出
(proxy, method, args) 进入....1 次 method:getName channelActive call,thread=nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 setPara,thread=main before send,thread=pool-1-thread-1 channelRead call,thread=nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 after send,thread=pool-1-thread-1 调用的结果 res= 你好客户端, 我已经收到你的消息 [hello bejing-0] 第1 次 (proxy, method, args) 进入....2 次 method:getName setPara,thread=main before send,thread=pool-1-thread-2 channelRead call,thread=nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 after send,thread=pool-1-thread-2 调用的结果 res= 你好客户端, 我已经收到你的消息 [hello bejing-1] 第2 次 (proxy, method, args) 进入....3 次 method:getName setPara,thread=main before send,thread=pool-1-thread-3 channelRead call,thread=nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 after send,thread=pool-1-thread-3 调用的结果 res= 你好客户端, 我已经收到你的消息 [hello bejing-2] 第3 次
二、Netty实现Websocket
(一)WebSocket协议介绍
HTTP协议的主要弊端:
半双⼯协议:可以在客户端和服务端2个⽅向上传输,但不能同时传输。同⼀时刻,只能在⼀个⽅向传输。
HTTP消息冗⻓:相⽐于其他⼆进制协议,有点繁琐。
⿊客攻击,例如⻓时间轮询。现在很多⽹站的消息推送都是使⽤轮询,即客户端每隔1S或者其他时间给服务器发送请求,然后服务器返回最新的数据给客户端。HTTP协议中的Header⾮常冗⻓,因此会占⽤很多的带宽和服务器资源。
为了解决这个问题,HTML5定义的WebSocket协议。
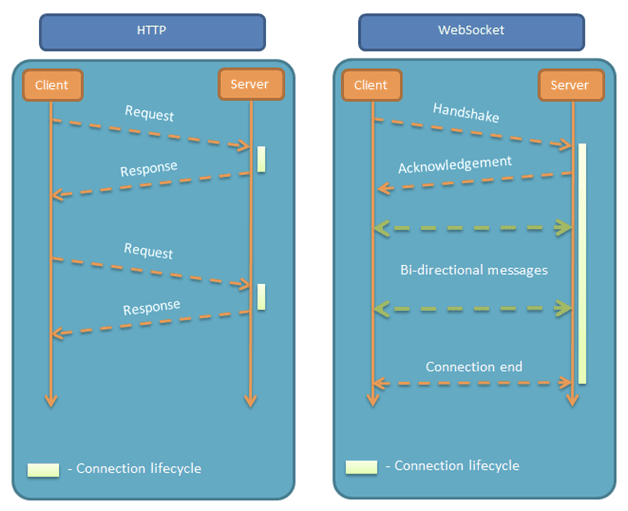
WebSocket协议在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要⼀个握⼿的动作,然后,浏览器和服务器之间就形成了⼀条快速通道,两者就可以直接互相传送数据了。
WebSocket基于TCP双向全双⼯协议,即在同⼀时刻,即可以发送消息,也可以接收消息,相⽐于HTTP协议,是⼀个性能上的提升。特点:
单⼀的TCP连接,全双⼯;
对代理、防⽕墙和路由器透明;
⽆头部信息、Cookie和身份验证;
⽆安全开销;
通过"ping/pong"帧保持链路激活;
服务器可以主动传递消息给客户端,不再需要客户端轮询;
拥有以上特点的WebSocket就是为了取代轮询和Comet技术,使得客户端浏览器具备像C/S架构下桌⾯系统⼀样的实时能⼒。浏览器通过js建⽴⼀个WebSocket的请求,连接建⽴后,客户端和服务器端可以通过TCP直接交换数据。
因为WebSocket本质上是⼀个TCP连接,稳定,所以在Comet和轮询⽐拥有性能优势。
(二)实现WebSocket
1、服务端启动
public class MyWebSocketServer { int port; public MyWebSocketServer(int port) { this.port = port; } public void start() { ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { bootstrap.group(boss, work) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new WebSocketServerInitializer()); ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)).sync(); System.out.println("server started . port : " + port); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); work.shutdownGracefully(); } } public void pushMsg(){ //模拟异步发送推送消息 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1); scheduledThreadPool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> { TextWebSocketFrame tws = new TextWebSocketFrame("server push message,this time:"+ LocalDateTime.now()); // 群发 ChannelSupervise.send2All(tws); }, 0,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyWebSocketServer server = new MyWebSocketServer(8081);// 8081为启动端口 // server.pushMsg(); server.start(); } }
2、服务端ChannelInitializer
这里说明一下,用到了几个Netty内置的handler:
HttpServerCodec:http编解码器
HttpObjectAggregator:可以将多段聚合的处理器,因为http在传输过程中是分段传输的,如果一次的请求太大,浏览器就会分多次发送,而该处理器就是将多段数据做聚合。
ChunkedWriteHandler:以块的方式写,支持发送大的流码,但是不会占用过多的内存,防止java内存溢出。
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler:将http协议升级为websocket协议,保持长链接
public class WebSocketServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) { ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline(); //因为基于http协议,使用http的编码和解码器 pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec())// http 编解器 /* 说明 1. http数据在传输过程中是分段, HttpObjectAggregator ,就是可以将多个段聚合 2. 这就是为什么,当浏览器发送大量数据时,就会发出多次http请求 */ .addLast("httpAggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(512 * 1024)) //是以块方式写,添加ChunkedWriteHandler处理器,支持异步发送大的码流(大的文件传输),但不占用过多的内存,防止java内存溢出 .addLast("http-chunked", new ChunkedWriteHandler()) //WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 核心功能是将 http协议升级为 ws协议 , 保持长连接 .addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/websocket66")) .addLast(new WebSocketRequestHandler());// 请求处理器 } }
3、服务端处理
这里没有什么太多要说的,就是重新相关的方法即可。
public class WebSocketRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Object> { private WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("receive msg:" + msg); if (msg instanceof FullHttpRequest) { System.out.println("FullHttpRequestMessage"); //以http请求形式接入,但是走的是websocket // handleHttpRequest(ctx, (FullHttpRequest) msg); } else if (msg instanceof WebSocketFrame) { System.out.println("WebSocketFrameMessage"); //处理websocket客户端的消息 handlerWebSocketFrame(ctx, (WebSocketFrame) msg); } } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //id 表示唯一的值,LongText 是唯一的 ShortText 不是唯一 System.out.println("client connect:longId:" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText()); System.out.println("client connect:shortId:"+ ctx.channel().id().asShortText()); ChannelSupervise.addChannel(ctx.channel()); } @Override public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //断开连接 //id 表示唯一的值,LongText 是唯一的 ShortText 不是唯一 System.out.println("client leave:longId:" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText()); System.out.println("client leave:shortId:"+ ctx.channel().id().asShortText()); ChannelSupervise.removeChannel(ctx.channel()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { System.out.println("exception: " + cause.getMessage()); ctx.close(); //关闭连接 } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.flush(); } /* 对WebSocket请求进行处理 */ private void handlerWebSocketFrame(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, WebSocketFrame frame) { //处理客户端请求并返回应答消息 String meessage = ((TextWebSocketFrame) frame).text(); System.out.println("receive:" + meessage); ctx.channel().writeAndFlush( new TextWebSocketFrame("time:" + LocalDateTime.now() + ",message:" + meessage)); } /** * http请求 * 该方法用于处理websocket握手请求 */ private void handleHttpRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req) { //如果HTTP解码失败,返回异常。要求Upgrade为websocket,过滤掉get/Post if (!req.decoderResult().isSuccess() || (!"websocket".equals(req.headers().get("Upgrade")))) { //若不是websocket方式,则创建BAD_REQUEST(400)的req,返回给客户端 sendHttpResponse(ctx, req, new DefaultFullHttpResponse( HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST)); return; } // 构造握手响应返回,本机测试 WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory wsFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory( "ws://localhost:8080/websocket", null, false); //通过工厂来创建WebSocketServerHandshaker实例 handshaker = wsFactory.newHandshaker(req); if (handshaker == null) { WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory.sendUnsupportedVersionResponse(ctx.channel()); } else { /* 通过WebSocketServerHandshaker来构建握手响应消息返回给客户端。 同时将WebSocket相关编解码类添加到ChannelPipeline中,该功能需要阅读handshake的源码。 */ handshaker.handshake(ctx.channel(), req); } } /** * 拒绝不合法的请求,并返回错误信息 */ private static void sendHttpResponse(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req, DefaultFullHttpResponse res) { // 返回应答给客户端 if (res.status().code() != 200) { ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(res.status().toString(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8); res.content().writeBytes(buf); buf.release(); HttpUtil.setContentLength(res, res.content().readableBytes()); } ChannelFuture f = ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(res); // 如果是非Keep-Alive,关闭连接 if (!HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(req) || res.status().code() != 200) { f.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } } }
4、客户端(⻚⾯)
这里使用的js处理的Netty的相关方法,例如socket.open等价于java的channelActive,socket.onmessage等价于channelRead,socket.onclose等价于channelInactive,send方法等价于writeAndFlush。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>my websocket client</title> </head> <body> <textarea id="msgBoxs" style="height: 300px; width: 600px"></textarea> <br> 待发送消息:<input type="text" id="msg"> <input type="button" id="sendBtn" onclick="send()" value="发送"> <script type="application/javascript"> var socket ; if(!window.WebSocket){ window.WebSocket = window.MozWebSocket; } //判断当前浏览器是否支持websocket if(window.WebSocket){ var msgBoxs = document.getElementById("msgBoxs") //go on socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8081/websocket66") //相当于连接开启(感知到连接开启) socket.onopen = function (evt) { msgBoxs.value = "连接开启了.." console.log("Connection open ..."); } //相当于channelRead, ev 收到服务器端回送的消息 socket.onmessage = function (evt) { console.log("Received Message: ", evt.data) msgBoxs.value = msgBoxs.value + "\n" + evt.data } //相当于连接关闭(感知到连接关闭) socket.onclose = function (evt) { console.log("Connect closed."); msgBoxs.value = msgBoxs.value + "\n" + "连接关闭了.." } }else{ alert("ERROR:您的浏览器不支持WebSocket!!"); } function send() { if(!window.socket) { //先判断socket是否创建好 return; } if(socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) { var msg = document.getElementById("msg").value socket.send(msg) }else { alert("连接没有开启"); } //msgBox.value = "" } </script> </body> </html>
演示结果:
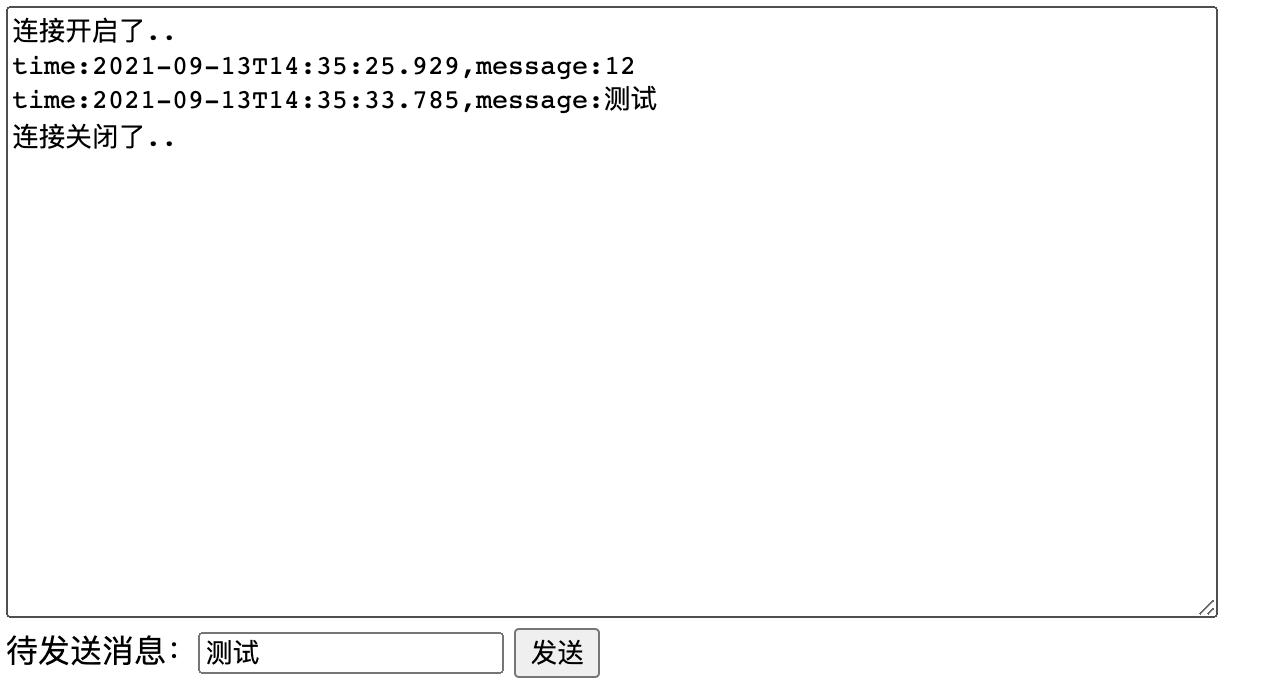
也可以看到,其最终的返回结果是websocket协议。
5、服务端推送消息
这个就比较简单,和之前的群聊一样,使用一个ChannelGroup存放所有的客户端连接,发送时循环客户端连接发送即可。在客户端连接上服务端时向channelGroup中添加连接,在断开是移除连接
public class ChannelSupervise { /** * ChannelGroup是netty提供用于管理web于服务器建立的通道channel的, * 其本质是一个高度封装的set集合,在服务器广播消息时, * 可以直接通过它的writeAndFlush将消息发送给集合中的所有通道中去 */ private static ChannelGroup GlobalGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE); /** * ChannelMap维护的是channelID和channel的对应关系,用于向指定channel发送消息 */ private static ConcurrentMap<String, ChannelId> ChannelMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public static void addChannel(Channel channel) { GlobalGroup.add(channel); ChannelMap.put(channel.id().asShortText(), channel.id()); } public static void removeChannel(Channel channel) { GlobalGroup.remove(channel); ChannelMap.remove(channel.id().asShortText()); } //找到某个channel来发送消息 public static Channel findChannel(String id) { return GlobalGroup.find(ChannelMap.get(id)); } public static void send2All(TextWebSocketFrame tws) { GlobalGroup.writeAndFlush(tws); } }
相关方法的调用在上面的WebSocketRequestHandler类中已经体现。
(三)实现WebSocket
netty的websocket协议是在HTTP协议基础之上完成的,要使⽤WebSocket协议,需要将HTTP请求头中添加 Upgrade:WebSocket
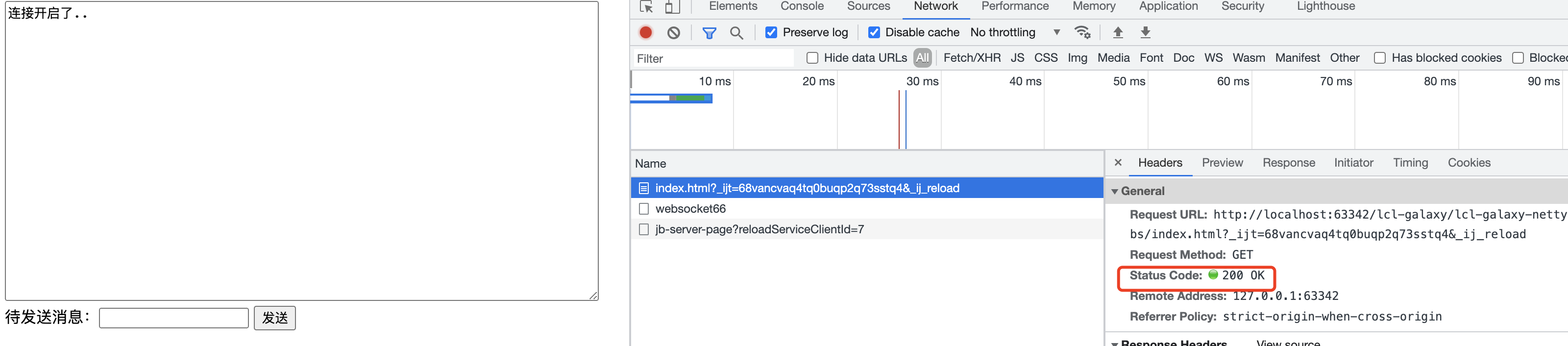
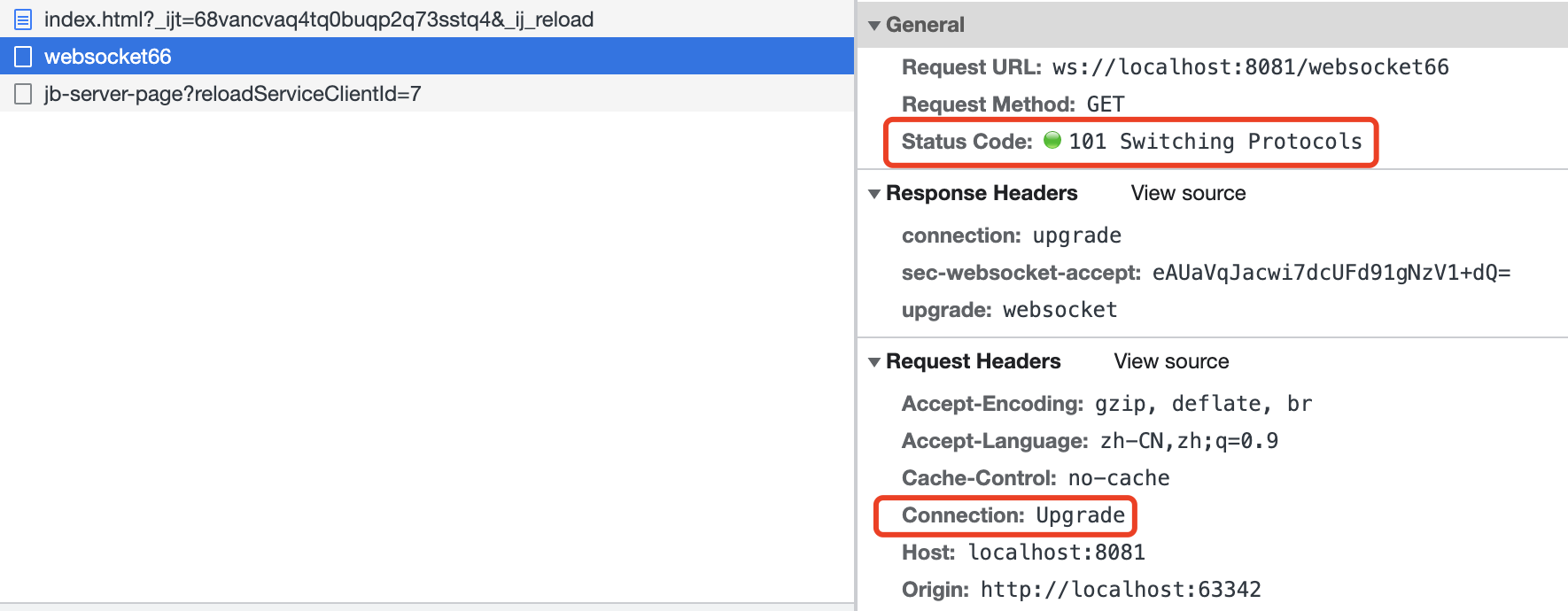
WebSocket相关的编解码
public abstract class WebSocketServerHandshaker { .... //WebSocket相关的编解码 public final ChannelFuture handshake(Channel channel, FullHttpRequest req, HttpHeaders responseHeaders, final ChannelPromise promise) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("{} WebSocket version {} server handshake", channel, version()); } //构造握⼿响应 FullHttpResponse response = newHandshakeResponse(req, responseHeaders); //下⾯将channelpipeline中的HttpObjectAggregator和HttpContentCompressor移除,并且添加WebSocket编解码器newWebSocketEncoder和newWebsocketDecoder ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); if (p.get(HttpObjectAggregator.class) != null) { p.remove(HttpObjectAggregator.class); } if (p.get(HttpContentCompressor.class) != null) { p.remove(HttpContentCompressor.class); } ChannelHandlerContext ctx = p.context(HttpRequestDecoder.class); final String encoderName; if (ctx == null) { // this means the user use an HttpServerCodec ctx = p.context(HttpServerCodec.class); if (ctx == null) { promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("No HttpDecoder and no HttpServerCodec in the pipeline")); return promise; } p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsencoder", newWebSocketEncoder()); p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsdecoder", newWebsocketDecoder()); encoderName = ctx.name(); } else { p.replace(ctx.name(), "wsdecoder", newWebsocketDecoder()); encoderName = p.context(HttpResponseEncoder.class).name(); p.addBefore(encoderName, "wsencoder", newWebSocketEncoder()); } //将response消息返回给客户端 channel.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (future.isSuccess()) { ChannelPipeline p = future.channel().pipeline(); p.remove(encoderName); promise.setSuccess(); } else { promise.setFailure(future.cause()); } } }); return promise; } ...
三、Netty实现Tomcat
1、编解码器
这里主要使用了一些Netty自带handler。
HttpServerCodec:Http编解码器。其实也可以使用HttpRequestDecoder & HttpResponseEncoder,HttpRequestDecoder 可以把 ByteBuf 解码到 HttpRequest 和 HttpContent。HttpResponseEncoder 可以把 HttpResponse 或 HttpContent 编码到 ByteBuf。而HttpServerCodec 即是 HttpRequestDecoder 和 HttpResponseEncoder 的结合。
HttpObjectAggregator:可以将多段聚合的处理器,因为http在传输过程中是分段传输的,如果一次的请求太大,浏览器就会分多次发送,而该处理器就是将多段数据做聚合。
HttpServerExpectContinueHandler:这个方法的作用是: http 100-continue用于客户端在发送POST数据给服务器前,征询服务器情况,看服务器是否处理POST的数据,如果不处理,客户端则不上传POST数据,如果处理,则POST上传数据。在现实应用中,通过在POST大数据时,才会使用100-continue协议。
public class HttpHelloWorldServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); /** * 或者使用HttpRequestDecoder & HttpResponseEncoder * HttpRequestDecoder 即把 ByteBuf 解码到 HttpRequest 和 HttpContent。 * HttpResponseEncoder 即把 HttpResponse 或 HttpContent 编码到 ByteBuf。 * HttpServerCodec 即 HttpRequestDecoder 和 HttpResponseEncoder 的结合。 */ p.addLast(new HttpServerCodec()); /** * 在处理POST消息体时需要加上 */ p.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1024*1024)); //这个方法的作用是: http 100-continue用于客户端在发送POST数据给服务器前, // 征询服务器情况,看服务器是否处理POST的数据, // 如果不处理,客户端则不上传POST数据,如果处理,则POST上传数据。 // 在现实应用中,通过在POST大数据时,才会使用100-continue协议 // p.addLast(new HttpServerExpectContinueHandler()); p.addLast(new HttpHelloWorldServerHandler()); } }
2、handler处理类
这里关键点在于对于get和post请求的处理,而delete实际上类似于get,put类似于post。
如果是get请求,直接获取参数即可,然后根据参数进行逻辑处理。
如果是post请求,由于请求的内容在body中,因此需要先将请求内容转换为FullHttpRequest,FullHttpRequest 包含了 HttpRequest 和 FullHttpMessage,是⼀个 HTTP 请求的完全体。然再根据contentType来处理不同的请求数据,例如如果请求格式是json,那么就需要将content转换为JsonObject,然后遍历JsonObject进行取值。
public class HttpHelloWorldServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> { private HttpHeaders headers; private HttpRequest request; private FullHttpRequest fullRequest; private static final AsciiString CONTENT_TYPE = AsciiString.cached("Content-Type"); private static final AsciiString CONTENT_LENGTH = AsciiString.cached("Content-Length"); private static final AsciiString CONNECTION = AsciiString.cached("Connection"); private static final AsciiString KEEP_ALIVE = AsciiString.cached("keep-alive");
@Override public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception { User user = new User(); user.setDate(new Date()); if (msg instanceof HttpRequest){ request = (HttpRequest) msg; headers = request.headers(); String uri = request.uri(); System.out.println("http uri: "+ uri); HttpMethod method = request.method(); //localhost:8888/user?name=北京 if (method.equals(HttpMethod.GET)){ QueryStringDecoder queryDecoder = new QueryStringDecoder(uri, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); Map<String, List<String>> uriAttributes = queryDecoder.parameters(); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> attr : uriAttributes.entrySet()) { for (String attrVal : attr.getValue()) { System.out.println(attr.getKey() + "=" + attrVal); user.setUserName(attrVal); } } user.setMethod("get"); }else if (method.equals(HttpMethod.POST)){ //POST请求,由于你需要从消息体中获取数据,因此有必要把msg转换成FullHttpRequest //即 FullHttpRequest 包含了 HttpRequest 和 FullHttpMessage,是一个 HTTP 请求的完全体。 fullRequest = (FullHttpRequest)msg; //根据不同的Content_Type处理body数据 String result = dealWithContentType(); user.setMethod("post"); user.setUserName(result); } byte[] content =JSON.toJSONBytes(user); FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(content)); response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain"); response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, response.content().readableBytes()); boolean keepAlive = HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(request); if (!keepAlive) { ctx.write(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } else { response.headers().set(CONNECTION, KEEP_ALIVE); ctx.write(response); } } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ctx.flush(); } /** * 简单处理常用几种 Content-Type 的 POST 内容(可自行扩展) * @throws Exception */ private String dealWithContentType() throws Exception{ String result = ""; String contentType = getContentType(); //可以使用HttpJsonDecoder if(contentType.equals("application/json")){ String jsonStr = fullRequest.content().toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8); JSONObject obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr); for(Map.Entry<String, Object> item : obj.entrySet()){ System.out.println(item.getKey()+"="+item.getValue().toString()); result = item.getValue().toString(); } }else if(contentType.equals("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")){ //方式一:使用 QueryStringDecoder String jsonStr = fullRequest.content().toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8); QueryStringDecoder queryDecoder = new QueryStringDecoder(jsonStr, false); Map<String, List<String>> uriAttributes = queryDecoder.parameters(); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> attr : uriAttributes.entrySet()) { for (String attrVal : attr.getValue()) { System.out.println(attr.getKey() + "=" + attrVal); } } }else if(contentType.equals("multipart/form-data")){ //TODO 用于文件上传 }else{ //do nothing... } return result; } private String getContentType(){ String typeStr = headers.get("Content-Type").toString(); String[] list = typeStr.split(";"); return list[0]; } }
3、启动类
public final class HttpHelloWorldServer { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpHelloWorldServer.class); static final int PORT = 8888; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Configure the server. EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024); b.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true); b.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) .childHandler(new HttpHelloWorldServerInitializer()); Channel ch = b.bind(PORT).sync().channel(); logger.info("Netty http server listening on port "+ PORT); ch.closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
4、验证
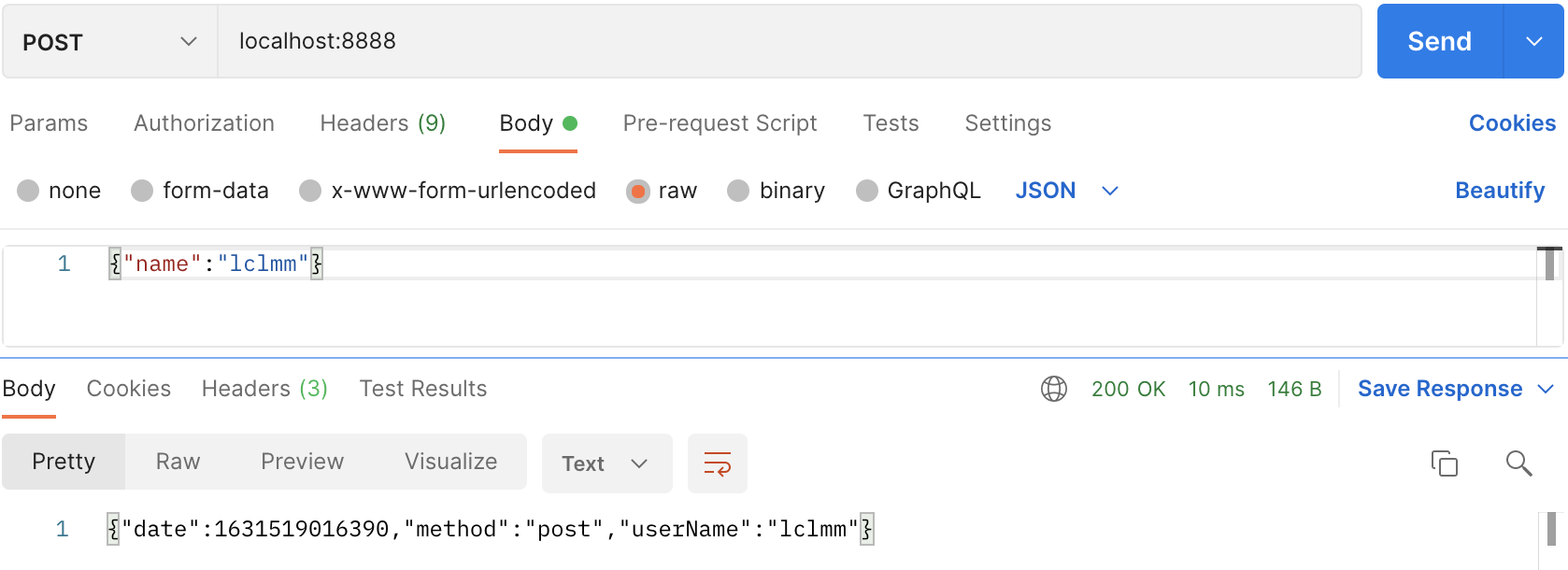
-----------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------
朦胧的夜 留笔~~




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号