Spring容器基础xmlbeanfactory(一起看源码)
在spring中,如果你想创建容器少不了使用常见的xmlbeanfactory,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,在这里,不介绍后两者。即使xmlbeanfactory已经过时了,但是有必要还是说一说。创建容器的代码:BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContextIOC.xml"));发现这里的构造函数中的参数是ClassPathResource类,这个类的作用就是加载配置文件,也就是说spring的配置文件的加载少不了这个类。这个类它是怎样加载文件的,我们一起追踪它的执行流程。

Resource是ClassPathResource实现的接口,Resource继承了InputStreamSource接口。在InputStreamSource这个接口里面只有一个方法,一起来看一下。

这说明拿到了输入流,这样我们就可以对文件做操作。此时,Resource接口有这些方法。
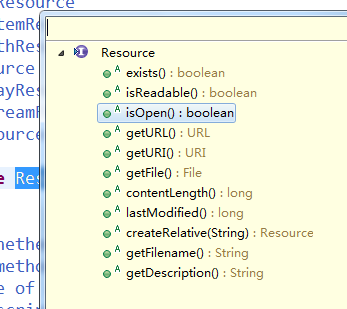
足以说明Resource接口封装底层资源,这些方法这里不过多介绍了。其中,exists,isReadable,isOpen是判断当前资源状态的方法。通过以上完成了对配置文件的封装,接下来介绍XmlBeanFactory的初始化过程。XmlBeanFactory类的构造函数有这样几个:
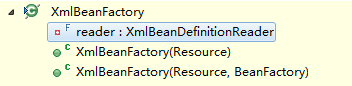
这里使用构造函数参数为Resource,进入这个方法后,看到这样的一串代码
我们点进去this(resource,null),调用的是XmlBeanFactory(Resource, BeanFactory)这个构造函数。
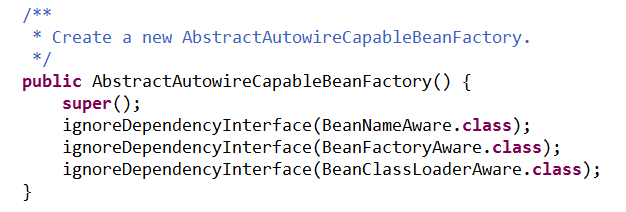
通过追踪super(parentBeanFactory);可以猜到使用ignoreDependencyInterface忽略了给定接口的自动装配功能。源码如下:
在XmlBeanFactory构造函数中,资源加载的核心代码是:this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);资源加载完成之后,接下来就是读取,在XmlBeanFactory构造函数中调用了this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);再一次追踪一下这串代码: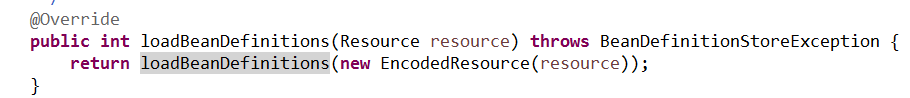
可以大致猜到以上代码主要作用对资源文件的编码进行处理,追踪loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)):
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
以上源码中,红色才是核心所在。追踪此代码:
/** * Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #doLoadDocument * @see #registerBeanDefinitions */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
以上代码其实就是要拿到Document,通过Document注册Bean信息。再一次追踪源代码:
/** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
追踪documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
/** * This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD * (or DTD, historically). * <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings * specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions. */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); }
最后一句代码doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);开始进行对XML解析,核心源码有必要给大家看一下:
/** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. */ protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { return; } } } preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
解析并注册BeanDefinitions,源代码如下:
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
到此,整个过程才结束。经过这样的漫长的过程的学习,理解设计的思路,这样才能对spring有更好的理解与看法。希望大家给出宝贵建议,我们一起探讨,一起进步。感谢大家的支持,你的支持是我最大的动力。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号