flex布局详解

一、Flex布局是什么?🔥
Flex 是 Flexible Box 的缩写,意为"弹性布局",用来为盒状模型提供最大的灵活性。
.box{
display: flex;
}
行内元素也可以使用 Flex 布局:
.box{
display: inline-flex;
}
Webkit 内核的浏览器,必须加上-webkit前缀:
.box{
display: -webkit-flex; /* Safari */
display: flex;
}
🌀Flex布局与传统布局对比:
传统布局:
- 兼容性好
- 布局繁琐
- 局限(不能在移动端很好的布局)
FLex布局:
- 操作方便,布局简单,移动端广泛应用
- PC端浏览器支持较差
- IE11或更低版本不支持或部分支持
🌀Flex布局原理:
--通过给父元素添加flex属性来控制子元素的位置和排列方式
🔺注意:设为 Flex 布局以后,子元素的float、clear和vertical-align属性将失效。
二、基本概念🔥
采用 Flex 布局的元素,称为 Flex 容器(flex container),简称"容器"。它的所有子元素自动成为容器成员,称为 Flex 项目(flex item),简称"项目"。
容器默认存在两根轴:水平的主轴(main axis)和垂直的交叉轴(cross axis)。主轴的开始位置(与边框的交叉点)叫做main start,结束位置叫做main end;交叉轴的开始位置叫做cross start,结束位置叫做cross end、
项目默认沿主轴排列,单个项目占据的主轴空间叫做main size,占据的交叉轴空间叫做cross size

三、容器属性🔥
1)flex-direction:设置主轴方向
2)justify-content:设置主轴上的子元素排列方式
3)flex-wrap:设置子元素是否换行
4)align-content:设置侧轴上子元素排列方式(多行)
5)align-items:设置侧轴上子元素排列方式(单行)
6)flex-flow:复合属性,同时设置了flex-direction和flex-wrap
3.1 flex-direction🚩
flex-direction属性决定主轴的方向(即项目的排列方向)
语法:
.box {
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
}
属性值:
row:默认值,主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿。column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。

完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:


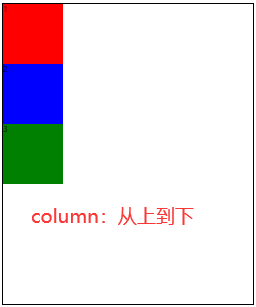

3.2 flex-wrap🚩
默认情况下,项目都排在一条线(又称"轴线")上。
flex-wrap属性定义,如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
语法:
.box{ flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse; }
属性值:
nowrap(默认):不换行wrap:换行,第一行在上方wrap-reverse:换行,第一行在下方

完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: nowrap|wrap|wrap-reverse; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } .yellow{ background-color: yellow; } .orange{ background-color: orange; } .pink{ background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> <div class="box yellow">4</div> <div class="box orange">5</div> <div class="box pink">6</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:



3.3 flex-flow🚩
flex-flow属性是flex-direction属性和flex-wrap属性的简写形式,默认值为row nowrap
语法:
.box { flex-flow: <flex-direction> || <flex-wrap>; }
.box{ flex-direction: row; flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; /* 等同于 */ flex-flow:row wrap-reverse }
3.4 justify-content🚩
justify-content属性定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式
语法:
.box { justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around; }
属性值:
flex-start(默认值):左对齐flex-end:右对齐center: 居中space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍space-evenly:均匀排列每个元素,每个元素之间的间隔相等
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: wrap; /* 定义项目在主轴上的对齐方式 */ justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:


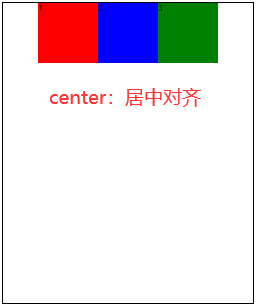

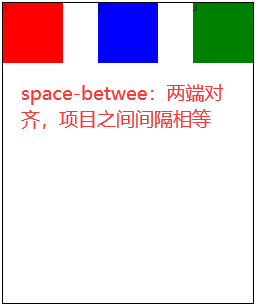

3.5 align-items🚩
align-items属性定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐
语法:
.box { align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch; }
属性值:
flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐。flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐。center:交叉轴的中点对齐。baseline: 项目的第一行文字的基线对齐。stretch(默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为auto,将占满整个容器的高度。
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: wrap; /* 定义项目在交叉轴上的对齐方式 */ align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } /* .yellow{ background-color: yellow; } .orange{ background-color: orange; } .pink{ background-color: pink; } */ </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> <!-- <div class="box yellow">4</div> <div class="box orange">5</div> <div class="box pink">6</div> --> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:

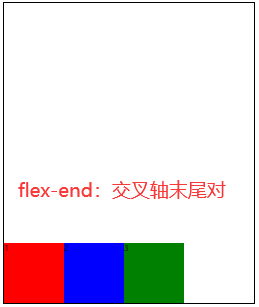
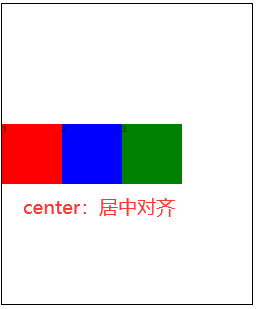


3.6 align-content🚩
align-content属性定义了多根轴线的对齐方式。如果项目只有一根轴线,该属性不起作用
语法:
.box {
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch;
}
属性值:
flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: wrap; /* 定义多根轴线的对齐方式(只有一行不起作用) */ align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; font-size: 25px; } .blue{ background-color: blue; font-size: 30px; } .green{ background-color: green; font-size: 45px; } .yellow{ background-color: yellow; } .orange{ background-color: orange; } .pink{ background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">A</div> <div class="box blue">贰</div> <div class="box green">3</div> <div class="box yellow">4</div> <div class="box orange">5</div> <div class="box pink">6</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:






四、项目属性🔥
orderflex-growflex-shrinkflex-basisflexalign-self
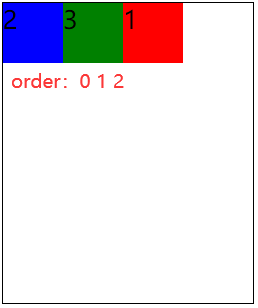
4.1 order🚩
order属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为0
语法:
.item {
order: <integer>;
}
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: wrap; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; } .red{ background-color: red; /* order数值越小项目越靠前 */ order: 2; } .blue{ background-color: blue; order: 0; } .green{ background-color: green; order: 1; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:
4.2 flex-grow🚩
flex-grow属性定义项目的放大比例,默认为0
语法:
.item { flex-grow: <number>; /* default 0 */ }
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; /* 设置容器内部元素排列方向 */ flex-direction: row; /* 设置容器内部元素如何换行 */ flex-wrap: wrap; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; font-size: 50px; } .red{ /* flex-grow:定义项目的放大比例,默认为0 */ background-color: red; flex-grow: 1; /* 红色将剩余空间占据 */ } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:

总结:
- 如果所有项目的flex-grow属性都为1,则所有项目平等分剩余空间。
- 如果一个项目的flex-grow属性为2,其他项目为1,则前者占据的剩余空间将比其他多一倍
4.3 flex-shrink🚩
flex-shrink属性定义项目的缩小比例,默认值为1,即如果空间不足,则当前项目缩小
语法:
.item { flex-shrink: <number>; /* default 1 */ }
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; } .box{ width: 230px; height: 120px; font-size: 50px; } .red{ background-color: red; } .blue{ background-color: blue; /* 定义项目的缩小比例,值为0则不缩小 */ flex-shrink: 0; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:
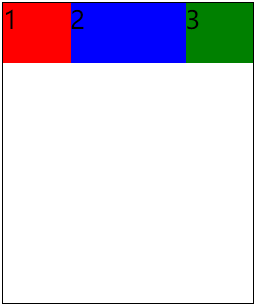
蓝色div设置flex-shrink属性为0,其他div默认为1,空间不足时该蓝色div不会被压缩
总结:
- 如果所有项目的flex-shrink属性都为1,当空间不足时都将等比例缩小
- 如果一个项目的flex-shrink属性为0,其他项目都为1,则空间不足时前者不会被缩小
- 负值对该属性无效
4.4 flex-basis🚩
flex-basis属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间。它的默认值为auto,即项目的本来大小
设置元素固定或自动空间的占比!
语法:
.item { flex-basis: <length> | auto; /* default auto */ }
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; font-size: 50px; } .red{ background-color: red; /* 设置元素固定空间占比 */ flex-basis: 15rem; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:

设置红色div剩余空间占比为15rem,也可以设置为px,这样就可以不用占据所有剩余空间
4.5 flex🚩
flex属性是flex-grow,flex-shrink和flex-basis的简写,默认值为0 1 auto。后两个属性可选
语法:
.item { flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ] }
一般放大比例直接设置:
.item { flex: 1 }
该属性有两个快捷值:auto (1 1 auto) 和 none (0 0 auto)。
建议优先使用这个属性,而不是单独写三个分离的属性,因为浏览器会推算相关值。
4.6 align-self🚩
align-self属性允许 单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖align-items属性。
默认值为auto,表示继承父元素的align-items属性,如果没有父元素,则等同于stretch。
语法:
.item { align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch; }
完整示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ border: 1px solid #000000; width: 500px; height: 600px; margin: 0 auto; /* 定义flex容器 */ display: flex; } .box{ width: 120px; height: 120px; font-size: 50px; } .red{ background-color: red; align-self: flex-end; } .blue{ background-color: blue; } .green{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box red">1</div> <div class="box blue">2</div> <div class="box green">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例效果:

设置红色div的align-self属性为flex-end,则它将在交叉轴的终点对齐
该属性可能取6个值,除了auto,其他都与align-items属性完全一致
参考文章:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/07/flex-grammar.html?utm_source=tuicool
本文来自博客园,作者:不知名前端李小白,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/libo-web/p/15705585.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号