11-DSL查询语法-全文检索查询
酒店数据的索引库结构

#酒店 mapping POST /hotle { "mappings": { "properties": { "id": { "type": "keyword" }, "name":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "copy_to": "all" }, "address":{ "type": "keyword", "index": false }, "price":{ "type": "integer" }, "score":{ "type": "integer" }, "brand":{ "type": "keyword", "copy_to": "all" }, "city":{ "type": "keyword", "copy_to": "all" }, "starName":{ "type": "keyword" }, "business":{ "type": "keyword" }, "location":{ "type": "geo_point" }, "pic":{ "type": "keyword", "index": false }, "all":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } }
下面例子将围绕此结构讲解
全文检索查询
全文检索查询的基本流程如下:
(1)对用户搜索的内容做分词,得到词条。
(2)根据词条去倒排索引库中匹配,得到文档id。
(3)根据文档id找到文档,返回给用户。
比较常用的场景包括:
(1)商城的输入框搜索。
(2)百度输入框搜索。
因为是拿着词条去匹配,因此参与搜索的字段也必须是可分词的text类型的字段。
基本语法
常见的全文检索查询包括:
(1)match查询:单字段查询。
(2)multi_match查询:多字段查询,任意一个字段符合条件就算符合查询条件。
match查询语法如下:

mulit_match语法如下:

其中TEXT为搜索的内容,FIELD为搜索的字段。
示例

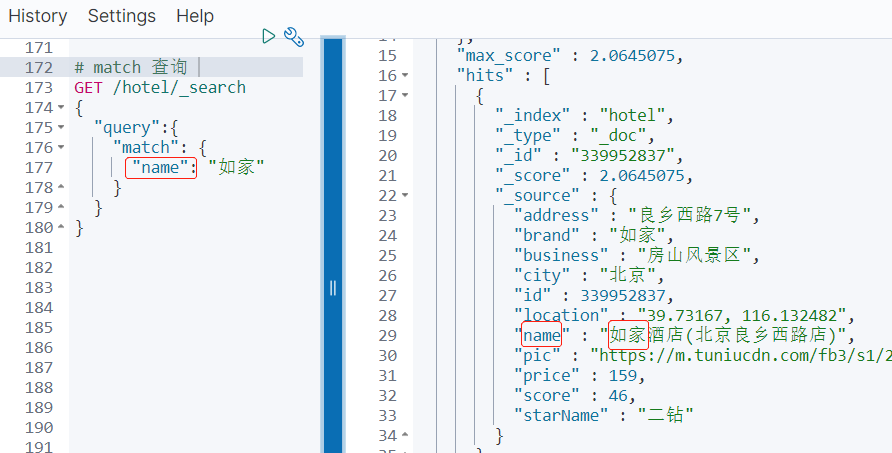
1 # match 查询 2 GET /hotel/_search 3 { 4 "query":{ 5 "match": { 6 "name": "如家" 7 } 8 } 9 } 10 11 # multi_match查询 12 GET /hotel/_search 13 { 14 "query":{ 15 "multi_match": { 16 "query": "外滩如家", 17 "fields": ["name","brand","business"] 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 GET /hotel/_search 23 { 24 "query":{ 25 "match": { 26 "all": "外滩如家" 27 } 28 } 29 }
match查询
mulit_match查询
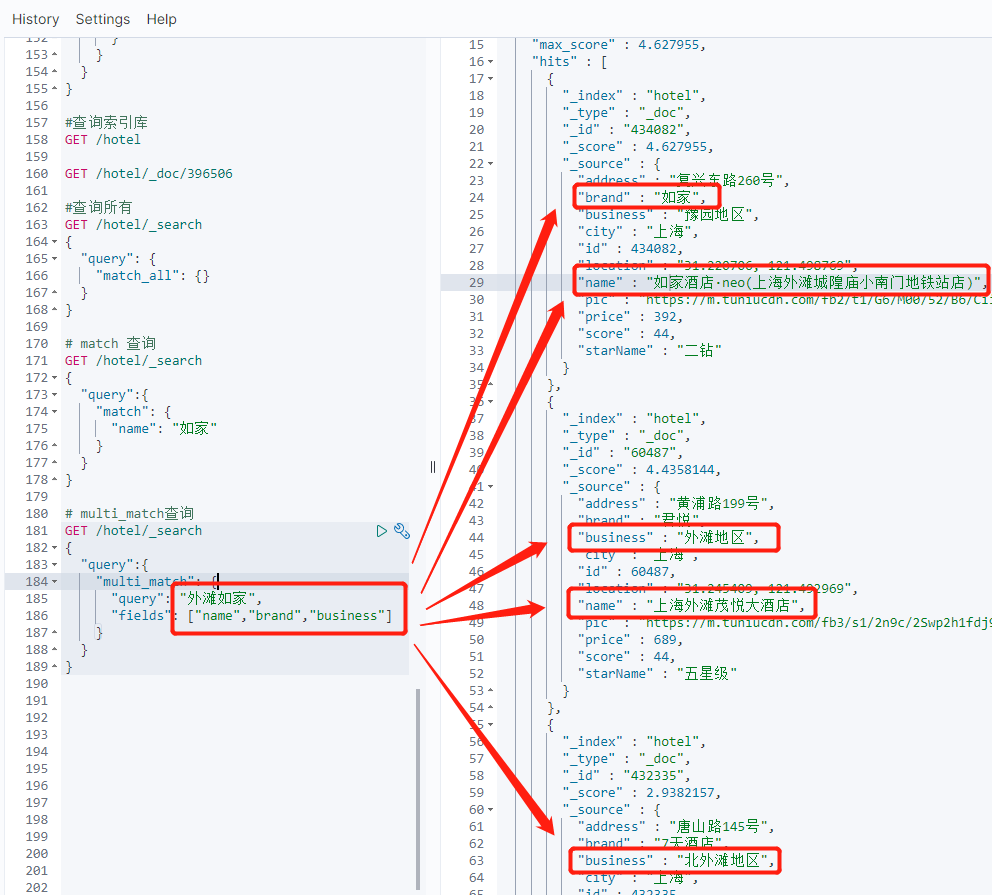
上面的multi_match查询和下面的单字段all查询的结果是一样的,但是,搜索字段越多,对查询性能影响越大,因此建议采用copy_to,然后单字段查询的方式。
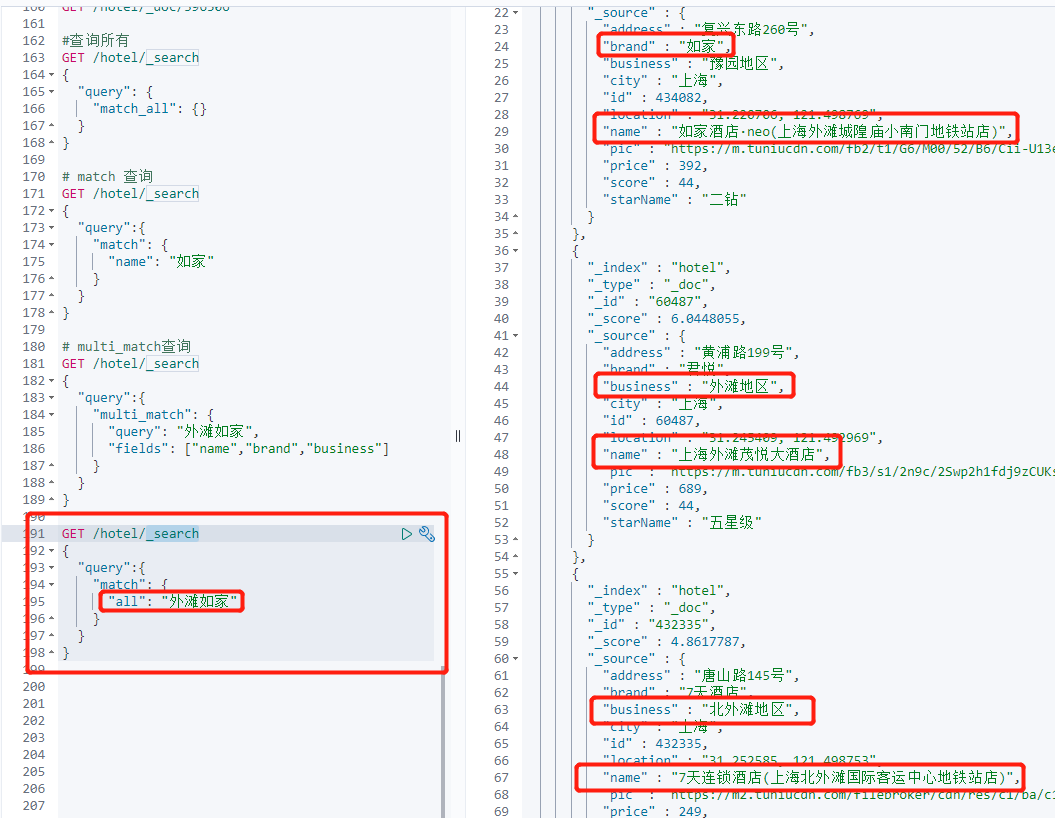
(1)match:根据一个字段查询
(2)multi_match:根据多个字段查询,参与查询字段越多,查询性能越差
希望本文章对您有帮助,您的转发、点赞是我的创作动力,十分感谢。更多好文推荐,请关注我的微信公众号--JustJavaIt


