ThreadLocal--介绍、常用场景
什么是ThreadLocal?
官方介绍

/** * This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from * their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its * {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized * copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private * static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., * a user ID or Transaction ID). * * <p>For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each * thread. * A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()} * and remains unchanged on subsequent calls. * <pre> * import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; * * public class ThreadId { * // Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned * private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0); * * // Thread local variable containing each thread's ID * private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId = * new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { * @Override protected Integer initialValue() { * return nextId.getAndIncrement(); * } * }; * * // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary * public static int get() { * return threadId.get(); * } * } * </pre> * <p>Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local * variable as long as the thread is alive and the {@code ThreadLocal} * instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of * thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other * references to these copies exist). * * @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea * @since 1.2 */ public class ThreadLocal<T> { ...... }
我们可以得知 ThreadLocal 的作用是:提供线程内的局部变量,不同的线程之间不会相互干扰,这种变量在线程的生命周期内起作用,减少同一个线程内多个函数或组件之间一些公共变量传递的复杂度。
总结
1. 线程并发: 在多线程并发的场景下.
2. 传递数据: 我们可以通过ThreadLocal在同一线程,不同组件中传递公共变量.
3. 线程隔离: 每个线程的变量都是独立的,不会互相影响.
《Java并发编程之美》中介绍
我们知道一个对象的所有线程共享它的全局变量,所以这些变量是非线程安全的,我们可以使用同步技术。但是当我们不想使用同步的时候,我们可以选择ThreadLocal变量。每个线程都会拥有他们自己的Thread变量,它们可以使用get()/set()方法去获取他们的默认值或者在线程内部改变他们的值。
ThreadLocal属于线程安全的实现方法—无同步方案的一种。ThreadLocal是JDK包提供的,它提供了线程本地变量,也就是如果你创建了一个ThreadLocal变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的本地副本,多个线程操作这个变量的时候,实际是操作自己本地内存里面的变量,从而避免了线程安全问题。
示例
示例一
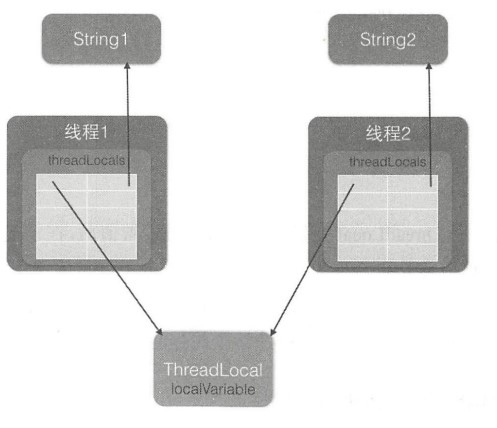
开启两个线程,在每个线程内部设置了本地变量的值,然后调用print方法打印当前本地变量的值。如果在打印之后调用本地变量的remove方法会删除本地内存中的变量。

1 public class ThreadLocalTest { 2 static void print(String str) { 3 //打印当前线程本地内存中localVariable变量的值 4 System.out.println(str + ":" + localVariable.get()); 5 //清除当前线程本地内存中的localVariable的值 6 localVariable.remove(); 7 } 8 9 //创建ThreadLocal变量 10 static ThreadLocal<String> localVariable = new ThreadLocal<String>(); 11 12 //创建线程one 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Thread threadOne = new Thread(new Runnable() { 15 @Override 16 public void run() { 17 //设置线程One中本地变量loalVariable的值 18 localVariable.set("threadOne local variable"); 19 //调用打印函数 20 print("threadOne"); 21 //打印本地变量值 22 System.out.println("threadOne remove after" + ":" + localVariable.get()); 23 } 24 }); 25 //创建线程two 26 Thread threadTwo = new Thread(new Runnable() { 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 //设置线程Two中本地变量loalVariable的值 30 localVariable.set("threadTwo local variable"); 31 //调用打印函数 32 print("threadTwo"); 33 //打印本地变量值 34 System.out.println("threadTwo remove after" + ":" + localVariable.get()); 35 } 36 }); 37 //启动线程 38 threadOne.start(); 39 threadTwo.start(); 40 } 41 42 }
示例二

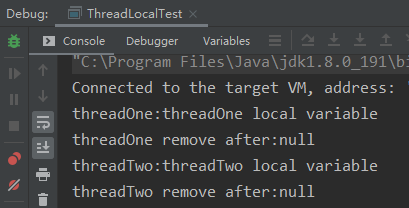
1 /** 2 * 未使用ThreadLocal 3 * @author JustJavaIt 4 * @date 2022/6/18 15:00 5 */ 6 public class MyDemo { 7 private String content; 8 9 private String getContent() { 10 return content; 11 } 12 13 private void setContent(String content) { 14 this.content = content; 15 } 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 MyDemo demo = new MyDemo(); 19 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 20 Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据"); 24 System.out.println("-----------------------"); 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent()); 26 } 27 }); 28 thread.setName("线程" + i); 29 thread.start(); 30 } 31 } 32 }
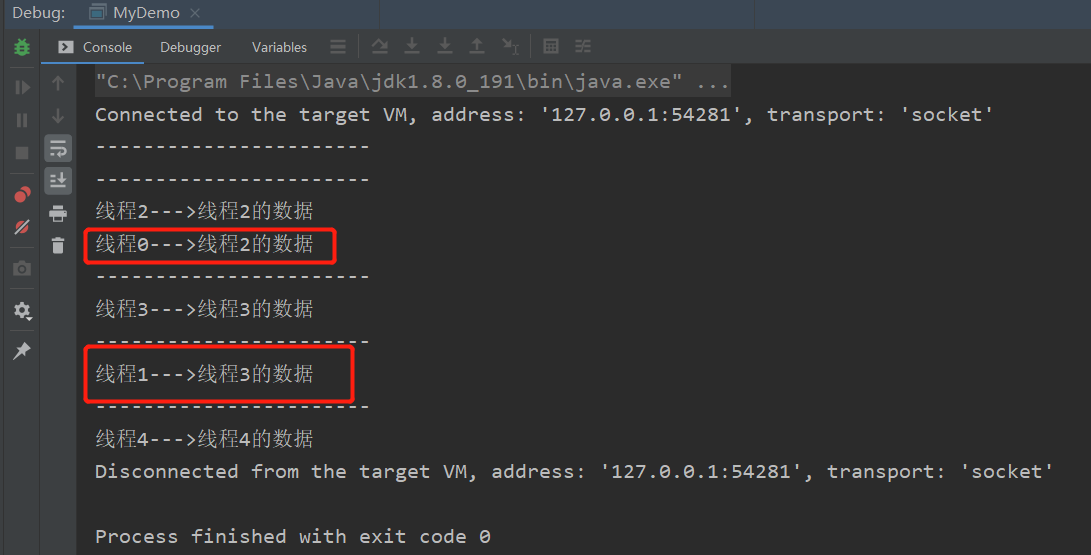

1 /** 2 * 采用 ThreadLocal 的方式 3 * @author justJavaIt 4 * @date 2022/6/18 15:10 5 */ 6 public class MyThreadLocalDemo { 7 private static ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal<>(); 8 9 private String content; 10 11 private String getContent() { 12 return tl.get(); 13 } 14 15 private void setContent(String content) { 16 tl.set(content); 17 } 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 MyThreadLocalDemo demo = new MyThreadLocalDemo(); 21 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 22 Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据"); 26 System.out.println("-----------------------"); 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent()); 28 } 29 }); 30 thread.setName("线程" + i); 31 thread.start(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
ThreadLocal两种典型的使用场景
场景1,ThreadLocal 用作保存每个线程独享的对象,为每个线程都创建一个副本,这样每个线程都可以修改自己所拥有的副本, 而不会影响其他线程的副本,确保了线程安全。
场景2,ThreadLocal 用作每个线程内需要独立保存信息,以便供其他方法更方便地获取该信息的场景。每个线程获取到的信息可能都是不一样的,前面执行的方法保存了信息后,后续方法可以通过 ThreadLocal 直接获取到,避免了传参,类似于全局变量的概念。
典型场景1
这种场景通常用于保存线程不安全的工具类,典型的使用的类就是 SimpleDateFormat。
假如需求为1000 个线程都要用到 SimpleDateFormat,使用线程池来实现线程的复用,否则会消耗过多的内存等资源,如果我们每个任务都创建了一个 simpleDateFormat 对象,也就是说,1000 个任务对应 1000 个 simpleDateFormat 对象,那么运行结果正确,但是这么多对象的创建是有开销的,并且在使用完之后的销毁同样是有开销的,而且这么多对象同时存在在内存中也是一种内存的浪费。我们可以将simpleDateFormat 对象给提取了出来,变成 static 静态变量,但是这样一来就会有线程不安全的问题。我们希望达到的效果是,既不浪费过多的内存,同时又想保证线程安全。经过思考得出,可以让每个线程都拥有一个自己的 simpleDateFormat 对象来达到这个目的,这样就能两全其美了。要想达到这个目的,我们就可以使用 ThreadLocal。
ThreadLocal不支持继承

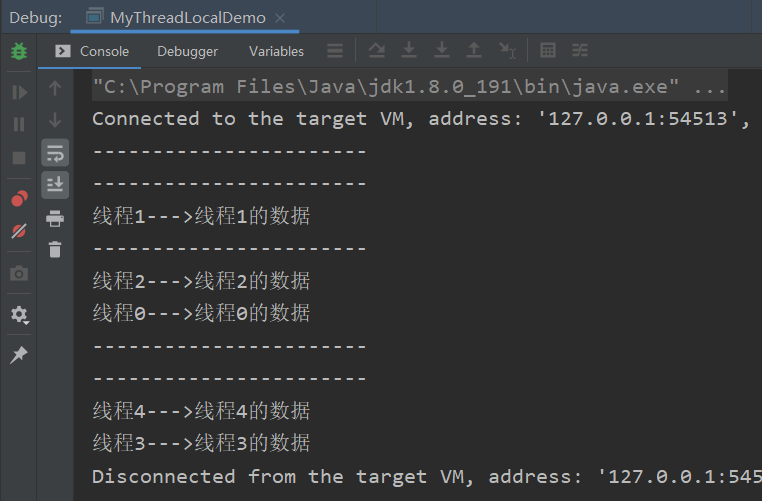
1 public class TestThreadLocal { 2 3 // (1) 创建线程变量 4 public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); 5 //测试InheritableThreadLocal让子线程可以访问在父程序中设置的本地变量。 6 //public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(); 7 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // (2) 设置线程变量 11 threadLocal.set("hello world"); 12 // (3) 启动子线程 13 Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { 14 // (4) 子线程输出线程变量的值 15 System.out.println("thread: " + threadLocal.get()); 16 }); 17 18 thread.start(); 19 // (5) 主线程获取并输出threadLocal的值 20 System.out.println("main: " + threadLocal.get()); 21 } 22 }
运行结果:
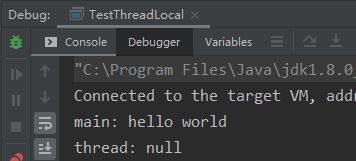
同一个ThreadLocal变量在父线程中设置值后,在子线程是取不到的。这是正常现象。因为子线程thread里面调用get方法时当前线程为thread线程,而这里调用set方法设置的变量时main线程,两者是不同线程,自然子线程访问时放回null。
InheritableThreadLocal
为了解决ThreadLocal不支持继承的问题,InheritableThreadLocal应运而生。InheritableThreadLocal继承自ThreadLocal,其提供了一个特性,就是让子线程可以访问在父线程中设置的本地变量。
示例只需把ThreadLocal不支持继承中示例的11行注释后打开13行即可。运行结果:
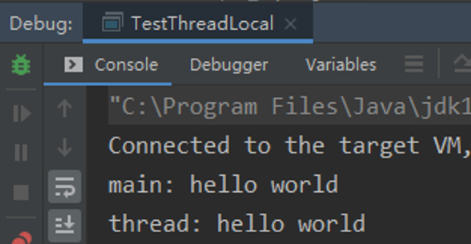
可以看到现在可以从子线程正常获取到线程变量的值了。
原理
InheritableThreadLocal 类通过重写getMap()和 createMap()方法 让本地变量保存到了具体线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量里面,那么线程再通过InheritableThreadLocal类实例的set或get方法设置变量时,就会创建当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量。当父线程创建子线程时,构造函数会把父线程中inheritableThreadLocals变量里面的本地变量复制一份保存到子线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量里面。
使用场景
那么在什么情况下需要子线程可以获取父线程的threadLocal变量呢?还挺多比如,子线程需要拿到存放在threadLocal变量中的用户登录信息,有的中间件需要把统一的id追踪到的整个调用链路记录下来。其实子线程使用父线程中的threadLocal方法由多种方式,比如创建线程时传入父线程中的变量,并将其复制到子线程中,或者在父线程中构造一个map作为参数传递给子线程,但是这些都改变了我们的使用习惯,所以在这些情况下InheritableThreadLocal就显得比较有用了。
感谢您的阅读,如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮。本文欢迎各位转载,但是转载文章之后必须在文章页面中给出作者和原文连接。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具
2020-06-18 接口的不同写法在Swagger上的不同