kubelet分析-pvc扩容源码分析
存储的扩容分为controller端操作与node端操作两大步骤,controller端操作由external-resizer来调用ceph完成,而node端操作由kubelet来完成,下面来分析下kubelet中有关存储扩容的相关代码。
基于tag v1.17.4
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases/tag/v1.17.4
controller端存储扩容作用
将底层存储扩容,如ceph rbd扩容,则会让ceph集群中的rbd image扩容。
controller端存储扩容分析请看external-resizer 源码分析/pvc 扩容分析
node端存储扩容作用
在pod所在的node上做相应的操作,让node感知该存储已经扩容,如ceph rbd filesystem扩容,则会调用node上的文件系统扩容命令让文件系统扩容。
某些存储无需进行node端扩容操作如cephfs。
存储扩容大致过程
(1)更改pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage,触发扩容
(2)controller端存储扩容:external-resizer watch pvc对象,当发现pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage比pvc.Status.Capacity.storgage大,于是调csi plugin的ControllerExpandVolume方法进行 controller端扩容,进行底层存储扩容,并更新pv.Spec.Capacity.storgage。
(3)node端存储扩容:kubelet发现pv.Spec.Capacity.storage大于pvc.Status.Capacity.storage,于是调csi node端扩容,对dnode上文件系统扩容,成功后kubelet更新pvc.Status.Capacity.storage。
存储扩容详细流程
下面以ceph rbd存储扩容为例,对详细的存储扩容过程进行分析。
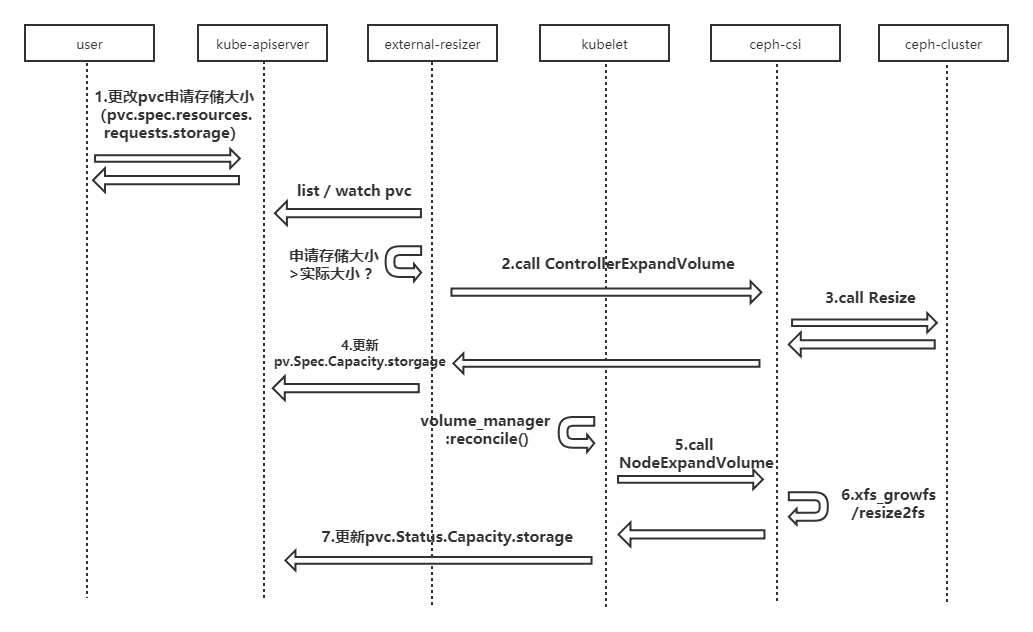
(1)修改pvc对象,修改申请存储大小(pvc.spec.resources.requests.storage);
(2)修改成功后,external-resizer监听到该pvc的update事件,发现pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage比pvc.Status.Capacity.storgage大,于是调ceph-csi组件进行 controller端扩容;
(3)ceph-csi组件调用ceph存储,进行底层存储扩容;
(4)底层存储扩容完成后,external-resizer组件更新pv对象的.Spec.Capacity.storgage的值为扩容后的存储大小;
(5)kubelet的volume manager在reconcile()调谐过程中发现pv.Spec.Capacity.storage大于pvc.Status.Capacity.storage,于是调ceph-csi组件进行 node端扩容;
(6)ceph-csi组件对node上存储对应的文件系统扩容;
(7)扩容完成后,kubelet更新pvc.Status.Capacity.storage的值为扩容后的存储大小。
下面主要对kubelet中的存储扩容相关的代码进行分析,controller端存储扩容分析将在后续分析external-resizer时进行分析。
volumeManager.Run
关于存储扩容,主要看到两个主要方法:
(1)vm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Run:主要负责找到并标记需要扩容的存储;
(2)vm.reconciler.Run:主要负责对需要扩容的存储触发进行扩容操作。
func (vm *volumeManager) Run(sourcesReady config.SourcesReady, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
go vm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Run(sourcesReady, stopCh)
klog.V(2).Infof("The desired_state_of_world populator starts")
klog.Infof("Starting Kubelet Volume Manager")
go vm.reconciler.Run(stopCh)
metrics.Register(vm.actualStateOfWorld, vm.desiredStateOfWorld, vm.volumePluginMgr)
if vm.kubeClient != nil {
// start informer for CSIDriver
vm.volumePluginMgr.Run(stopCh)
}
<-stopCh
klog.Infof("Shutting down Kubelet Volume Manager")
}
1.vm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Run
主要是对dswp.populatorLoop的调用
func (dswp *desiredStateOfWorldPopulator) Run(sourcesReady config.SourcesReady, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// Wait for the completion of a loop that started after sources are all ready, then set hasAddedPods accordingly
klog.Infof("Desired state populator starts to run")
wait.PollUntil(dswp.loopSleepDuration, func() (bool, error) {
done := sourcesReady.AllReady()
dswp.populatorLoop()
return done, nil
}, stopCh)
dswp.hasAddedPodsLock.Lock()
dswp.hasAddedPods = true
dswp.hasAddedPodsLock.Unlock()
wait.Until(dswp.populatorLoop, dswp.loopSleepDuration, stopCh)
}
populatorLoop中调用dswp.findAndAddNewPods
func (dswp *desiredStateOfWorldPopulator) populatorLoop() {
dswp.findAndAddNewPods()
// findAndRemoveDeletedPods() calls out to the container runtime to
// determine if the containers for a given pod are terminated. This is
// an expensive operation, therefore we limit the rate that
// findAndRemoveDeletedPods() is called independently of the main
// populator loop.
if time.Since(dswp.timeOfLastGetPodStatus) < dswp.getPodStatusRetryDuration {
klog.V(5).Infof(
"Skipping findAndRemoveDeletedPods(). Not permitted until %v (getPodStatusRetryDuration %v).",
dswp.timeOfLastGetPodStatus.Add(dswp.getPodStatusRetryDuration),
dswp.getPodStatusRetryDuration)
return
}
dswp.findAndRemoveDeletedPods()
}
findAndAddNewPods中主要看到dswp.processPodVolumes
// Iterate through all pods and add to desired state of world if they don't
// exist but should
func (dswp *desiredStateOfWorldPopulator) findAndAddNewPods() {
// Map unique pod name to outer volume name to MountedVolume.
mountedVolumesForPod := make(map[volumetypes.UniquePodName]map[string]cache.MountedVolume)
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandInUsePersistentVolumes) {
for _, mountedVolume := range dswp.actualStateOfWorld.GetMountedVolumes() {
mountedVolumes, exist := mountedVolumesForPod[mountedVolume.PodName]
if !exist {
mountedVolumes = make(map[string]cache.MountedVolume)
mountedVolumesForPod[mountedVolume.PodName] = mountedVolumes
}
mountedVolumes[mountedVolume.OuterVolumeSpecName] = mountedVolume
}
}
processedVolumesForFSResize := sets.NewString()
for _, pod := range dswp.podManager.GetPods() {
if dswp.isPodTerminated(pod) {
// Do not (re)add volumes for terminated pods
continue
}
dswp.processPodVolumes(pod, mountedVolumesForPod, processedVolumesForFSResize)
}
}
processPodVolumes主要是调用dswp.checkVolumeFSResize对需要扩容的存储进行标记
// processPodVolumes processes the volumes in the given pod and adds them to the
// desired state of the world.
func (dswp *desiredStateOfWorldPopulator) processPodVolumes(
pod *v1.Pod,
mountedVolumesForPod map[volumetypes.UniquePodName]map[string]cache.MountedVolume,
processedVolumesForFSResize sets.String) {
......
expandInUsePV := utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandInUsePersistentVolumes)
// Process volume spec for each volume defined in pod
for _, podVolume := range pod.Spec.Volumes {
......
if expandInUsePV {
dswp.checkVolumeFSResize(pod, podVolume, pvc, volumeSpec,
uniquePodName, mountedVolumesForPod, processedVolumesForFSResize)
}
}
......
}
1.1 checkVolumeFSResize
主要逻辑:
(1)调用volumeRequiresFSResize判断是否需要扩容;
(2)调用dswp.actualStateOfWorld.MarkFSResizeRequired做进标记处理。
// checkVolumeFSResize checks whether a PVC mounted by the pod requires file
// system resize or not. If so, marks this volume as fsResizeRequired in ASW.
// - mountedVolumesForPod stores all mounted volumes in ASW, because online
// volume resize only considers mounted volumes.
// - processedVolumesForFSResize stores all volumes we have checked in current loop,
// because file system resize operation is a global operation for volume, so
// we only need to check it once if more than one pod use it.
func (dswp *desiredStateOfWorldPopulator) checkVolumeFSResize(
pod *v1.Pod,
podVolume v1.Volume,
pvc *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
volumeSpec *volume.Spec,
uniquePodName volumetypes.UniquePodName,
mountedVolumesForPod map[volumetypes.UniquePodName]map[string]cache.MountedVolume,
processedVolumesForFSResize sets.String) {
if podVolume.PersistentVolumeClaim == nil {
// Only PVC supports resize operation.
return
}
uniqueVolumeName, exist := getUniqueVolumeName(uniquePodName, podVolume.Name, mountedVolumesForPod)
if !exist {
// Volume not exist in ASW, we assume it hasn't been mounted yet. If it needs resize,
// it will be handled as offline resize(if it indeed hasn't been mounted yet),
// or online resize in subsequent loop(after we confirm it has been mounted).
return
}
if processedVolumesForFSResize.Has(string(uniqueVolumeName)) {
// File system resize operation is a global operation for volume,
// so we only need to check it once if more than one pod use it.
return
}
// volumeSpec.ReadOnly is the value that determines if volume could be formatted when being mounted.
// This is the same flag that determines filesystem resizing behaviour for offline resizing and hence
// we should use it here. This value comes from Pod.spec.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.readOnly.
if volumeSpec.ReadOnly {
// This volume is used as read only by this pod, we don't perform resize for read only volumes.
klog.V(5).Infof("Skip file system resize check for volume %s in pod %s/%s "+
"as the volume is mounted as readonly", podVolume.Name, pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
return
}
if volumeRequiresFSResize(pvc, volumeSpec.PersistentVolume) {
dswp.actualStateOfWorld.MarkFSResizeRequired(uniqueVolumeName, uniquePodName)
}
processedVolumesForFSResize.Insert(string(uniqueVolumeName))
}
1.1.1 volumeRequiresFSResize
pv.Spec.Capacity.storage大小比pvc.Status.Capacity.storage大小要大时返回true
func volumeRequiresFSResize(pvc *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim, pv *v1.PersistentVolume) bool {
capacity := pvc.Status.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage]
requested := pv.Spec.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage]
return requested.Cmp(capacity) > 0
}
1.1.2 MarkFSResizeRequired
主要逻辑:
(1)获取volume对应的volumePlugin;
(2)调用volumePlugin.RequiresFSResize()判断plugin是否支持resize;
(3)plugin支持则设置podObj的fsResizeRequired属性为true。(reconcile中会根据podObj的fsResizeRequired属性为true来触发node端resize操作)
func (asw *actualStateOfWorld) MarkFSResizeRequired(
volumeName v1.UniqueVolumeName,
podName volumetypes.UniquePodName) {
asw.Lock()
defer asw.Unlock()
volumeObj, volumeExists := asw.attachedVolumes[volumeName]
if !volumeExists {
klog.Warningf("MarkFSResizeRequired for volume %s failed as volume not exist", volumeName)
return
}
podObj, podExists := volumeObj.mountedPods[podName]
if !podExists {
klog.Warningf("MarkFSResizeRequired for volume %s failed "+
"as pod(%s) not exist", volumeName, podName)
return
}
volumePlugin, err :=
asw.volumePluginMgr.FindNodeExpandablePluginBySpec(podObj.volumeSpec)
if err != nil || volumePlugin == nil {
// Log and continue processing
klog.Errorf(
"MarkFSResizeRequired failed to find expandable plugin for pod %q volume: %q (volSpecName: %q)",
podObj.podName,
volumeObj.volumeName,
podObj.volumeSpec.Name())
return
}
if volumePlugin.RequiresFSResize() {
if !podObj.fsResizeRequired {
klog.V(3).Infof("PVC volume %s(OuterVolumeSpecName %s) of pod %s requires file system resize",
volumeName, podObj.outerVolumeSpecName, podName)
podObj.fsResizeRequired = true
}
asw.attachedVolumes[volumeName].mountedPods[podName] = podObj
}
}
2.vm.reconciler.Run
func (rc *reconciler) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
wait.Until(rc.reconciliationLoopFunc(), rc.loopSleepDuration, stopCh)
}
func (rc *reconciler) reconciliationLoopFunc() func() {
return func() {
rc.reconcile()
// Sync the state with the reality once after all existing pods are added to the desired state from all sources.
// Otherwise, the reconstruct process may clean up pods' volumes that are still in use because
// desired state of world does not contain a complete list of pods.
if rc.populatorHasAddedPods() && !rc.StatesHasBeenSynced() {
klog.Infof("Reconciler: start to sync state")
rc.sync()
}
}
}
省略了部分代码,下面列出的是扩容相关代码。
扩容相关主要逻辑:
(1)调用rc.actualStateOfWorld.PodExistsInVolume;
(2)判断上一步骤的返回是否是IsFSResizeRequiredError,true时调用rc.operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume触发扩容操作。
func (rc *reconciler) reconcile() {
......
// Ensure volumes that should be attached/mounted are attached/mounted.
for _, volumeToMount := range rc.desiredStateOfWorld.GetVolumesToMount() {
volMounted, devicePath, err := rc.actualStateOfWorld.PodExistsInVolume(volumeToMount.PodName, volumeToMount.VolumeName)
volumeToMount.DevicePath = devicePath
if cache.IsVolumeNotAttachedError(err) {
......
} else if !volMounted || cache.IsRemountRequiredError(err) {
......
} else if cache.IsFSResizeRequiredError(err) &&
utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandInUsePersistentVolumes) {
klog.V(4).Infof(volumeToMount.GenerateMsgDetailed("Starting operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume", ""))
err := rc.operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume(
volumeToMount.VolumeToMount,
rc.actualStateOfWorld)
if err != nil &&
!nestedpendingoperations.IsAlreadyExists(err) &&
!exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff(err) {
// Ignore nestedpendingoperations.IsAlreadyExists and exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff errors, they are expected.
// Log all other errors.
klog.Errorf(volumeToMount.GenerateErrorDetailed("operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume failed", err).Error())
}
if err == nil {
klog.V(4).Infof(volumeToMount.GenerateMsgDetailed("operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume started", ""))
}
}
}
......
}
2.1 rc.actualStateOfWorld.PodExistsInVolume
扩容相关主要逻辑:
(1)从actualStateOfWorld中获取获取volumeObj;
(2)从volumeObj中获取podObj;
(3)判断podObj的fsResizeRequired属性,true时返回newFsResizeRequiredError。
func (asw *actualStateOfWorld) PodExistsInVolume(
podName volumetypes.UniquePodName,
volumeName v1.UniqueVolumeName) (bool, string, error) {
asw.RLock()
defer asw.RUnlock()
volumeObj, volumeExists := asw.attachedVolumes[volumeName]
if !volumeExists {
return false, "", newVolumeNotAttachedError(volumeName)
}
podObj, podExists := volumeObj.mountedPods[podName]
if podExists {
if podObj.remountRequired {
return true, volumeObj.devicePath, newRemountRequiredError(volumeObj.volumeName, podObj.podName)
}
if podObj.fsResizeRequired &&
utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandInUsePersistentVolumes) {
return true, volumeObj.devicePath, newFsResizeRequiredError(volumeObj.volumeName, podObj.podName)
}
}
return podExists, volumeObj.devicePath, nil
}
2.2 rc.operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume
调用oe.operationGenerator.GenerateExpandInUseVolumeFunc做进一步处理
func (oe *operationExecutor) ExpandInUseVolume(volumeToMount VolumeToMount, actualStateOfWorld ActualStateOfWorldMounterUpdater) error {
generatedOperations, err := oe.operationGenerator.GenerateExpandInUseVolumeFunc(volumeToMount, actualStateOfWorld)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return oe.pendingOperations.Run(volumeToMount.VolumeName, "", generatedOperations)
}
GenerateExpandInUseVolumeFunc中主要看到og.doOnlineExpansion
func (og *operationGenerator) GenerateExpandInUseVolumeFunc(
volumeToMount VolumeToMount,
actualStateOfWorld ActualStateOfWorldMounterUpdater) (volumetypes.GeneratedOperations, error) {
volumePlugin, err :=
og.volumePluginMgr.FindPluginBySpec(volumeToMount.VolumeSpec)
if err != nil || volumePlugin == nil {
return volumetypes.GeneratedOperations{}, volumeToMount.GenerateErrorDetailed("NodeExpandVolume.FindPluginBySpec failed", err)
}
fsResizeFunc := func() (error, error) {
var resizeDone bool
var simpleErr, detailedErr error
resizeOptions := volume.NodeResizeOptions{
VolumeSpec: volumeToMount.VolumeSpec,
}
attachableVolumePlugin, _ :=
og.volumePluginMgr.FindAttachablePluginBySpec(volumeToMount.VolumeSpec)
if attachableVolumePlugin != nil {
volumeAttacher, _ := attachableVolumePlugin.NewAttacher()
if volumeAttacher != nil {
resizeOptions.CSIVolumePhase = volume.CSIVolumeStaged
resizeOptions.DevicePath = volumeToMount.DevicePath
dmp, err := volumeAttacher.GetDeviceMountPath(volumeToMount.VolumeSpec)
if err != nil {
return volumeToMount.GenerateError("NodeExpandVolume.GetDeviceMountPath failed", err)
}
resizeOptions.DeviceMountPath = dmp
resizeDone, simpleErr, detailedErr = og.doOnlineExpansion(volumeToMount, actualStateOfWorld, resizeOptions)
if simpleErr != nil || detailedErr != nil {
return simpleErr, detailedErr
}
if resizeDone {
return nil, nil
}
}
}
// if we are here that means volume plugin does not support attach interface
volumeMounter, newMounterErr := volumePlugin.NewMounter(
volumeToMount.VolumeSpec,
volumeToMount.Pod,
volume.VolumeOptions{})
if newMounterErr != nil {
return volumeToMount.GenerateError("NodeExpandVolume.NewMounter initialization failed", newMounterErr)
}
resizeOptions.DeviceMountPath = volumeMounter.GetPath()
resizeOptions.CSIVolumePhase = volume.CSIVolumePublished
resizeDone, simpleErr, detailedErr = og.doOnlineExpansion(volumeToMount, actualStateOfWorld, resizeOptions)
if simpleErr != nil || detailedErr != nil {
return simpleErr, detailedErr
}
if resizeDone {
return nil, nil
}
// This is a placeholder error - we should NEVER reach here.
err = fmt.Errorf("volume resizing failed for unknown reason")
return volumeToMount.GenerateError("NodeExpandVolume.NodeExpandVolume failed to resize volume", err)
}
eventRecorderFunc := func(err *error) {
if *err != nil {
og.recorder.Eventf(volumeToMount.Pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, kevents.VolumeResizeFailed, (*err).Error())
}
}
return volumetypes.GeneratedOperations{
OperationName: "volume_fs_resize",
OperationFunc: fsResizeFunc,
EventRecorderFunc: eventRecorderFunc,
CompleteFunc: util.OperationCompleteHook(util.GetFullQualifiedPluginNameForVolume(volumePlugin.GetPluginName(), volumeToMount.VolumeSpec), "volume_fs_resize"),
}, nil
}
og.doOnlineExpansion
doOnlineExpansion主要是调用og.nodeExpandVolume
func (og *operationGenerator) doOnlineExpansion(volumeToMount VolumeToMount,
actualStateOfWorld ActualStateOfWorldMounterUpdater,
resizeOptions volume.NodeResizeOptions) (bool, error, error) {
resizeDone, err := og.nodeExpandVolume(volumeToMount, resizeOptions)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("NodeExpandVolume.NodeExpandVolume failed : %v", err)
e1, e2 := volumeToMount.GenerateError("NodeExpandVolume.NodeExpandVolume failed", err)
return false, e1, e2
}
if resizeDone {
markFSResizedErr := actualStateOfWorld.MarkVolumeAsResized(volumeToMount.PodName, volumeToMount.VolumeName)
if markFSResizedErr != nil {
// On failure, return error. Caller will log and retry.
e1, e2 := volumeToMount.GenerateError("NodeExpandVolume.MarkVolumeAsResized failed", markFSResizedErr)
return false, e1, e2
}
return true, nil, nil
}
return false, nil, nil
}
og.nodeExpandVolume
og.nodeExpandVolume主要逻辑:
(1)获取扩容plugin;
(2)获取pv与pvc对象;
(3)当pv.Spec.Capacity比pvc.Status.Capacity大时,调用expandableVolumePlugin.NodeExpand进行扩容;
(4)扩容完成,调用util.MarkFSResizeFinished,更新PVC.Status.Capacity.storage的值为扩容后的存储大小值。
func (og *operationGenerator) nodeExpandVolume(volumeToMount VolumeToMount, rsOpts volume.NodeResizeOptions) (bool, error) {
if !utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandPersistentVolumes) {
klog.V(4).Infof("Resizing is not enabled for this volume %s", volumeToMount.VolumeName)
return true, nil
}
if volumeToMount.VolumeSpec != nil &&
volumeToMount.VolumeSpec.InlineVolumeSpecForCSIMigration {
klog.V(4).Infof("This volume %s is a migrated inline volume and is not resizable", volumeToMount.VolumeName)
return true, nil
}
// Get expander, if possible
expandableVolumePlugin, _ :=
og.volumePluginMgr.FindNodeExpandablePluginBySpec(volumeToMount.VolumeSpec)
if expandableVolumePlugin != nil &&
expandableVolumePlugin.RequiresFSResize() &&
volumeToMount.VolumeSpec.PersistentVolume != nil {
pv := volumeToMount.VolumeSpec.PersistentVolume
pvc, err := og.kubeClient.CoreV1().PersistentVolumeClaims(pv.Spec.ClaimRef.Namespace).Get(pv.Spec.ClaimRef.Name, metav1.GetOptions{})
if err != nil {
// Return error rather than leave the file system un-resized, caller will log and retry
return false, fmt.Errorf("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume get PVC failed : %v", err)
}
pvcStatusCap := pvc.Status.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage]
pvSpecCap := pv.Spec.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage]
if pvcStatusCap.Cmp(pvSpecCap) < 0 {
// File system resize was requested, proceed
klog.V(4).Infof(volumeToMount.GenerateMsgDetailed("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume entering", fmt.Sprintf("DevicePath %q", volumeToMount.DevicePath)))
if volumeToMount.VolumeSpec.ReadOnly {
simpleMsg, detailedMsg := volumeToMount.GenerateMsg("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume failed", "requested read-only file system")
klog.Warningf(detailedMsg)
og.recorder.Eventf(volumeToMount.Pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, kevents.FileSystemResizeFailed, simpleMsg)
og.recorder.Eventf(pvc, v1.EventTypeWarning, kevents.FileSystemResizeFailed, simpleMsg)
return true, nil
}
rsOpts.VolumeSpec = volumeToMount.VolumeSpec
rsOpts.NewSize = pvSpecCap
rsOpts.OldSize = pvcStatusCap
resizeDone, resizeErr := expandableVolumePlugin.NodeExpand(rsOpts)
if resizeErr != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume failed : %v", resizeErr)
}
// Volume resizing is not done but it did not error out. This could happen if a CSI volume
// does not have node stage_unstage capability but was asked to resize the volume before
// node publish. In which case - we must retry resizing after node publish.
if !resizeDone {
return false, nil
}
simpleMsg, detailedMsg := volumeToMount.GenerateMsg("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume succeeded", "")
og.recorder.Eventf(volumeToMount.Pod, v1.EventTypeNormal, kevents.FileSystemResizeSuccess, simpleMsg)
og.recorder.Eventf(pvc, v1.EventTypeNormal, kevents.FileSystemResizeSuccess, simpleMsg)
klog.Infof(detailedMsg)
// File system resize succeeded, now update the PVC's Capacity to match the PV's
err = util.MarkFSResizeFinished(pvc, pvSpecCap, og.kubeClient)
if err != nil {
// On retry, NodeExpandVolume will be called again but do nothing
return false, fmt.Errorf("MountVolume.NodeExpandVolume update PVC status failed : %v", err)
}
return true, nil
}
}
return true, nil
}
expandableVolumePlugin.NodeExpand
NodeExpand中会调用util.CheckVolumeModeFilesystem来检查volumemode是否是block,如果是block,则不用进行node端扩容操作。
func (c *csiPlugin) NodeExpand(resizeOptions volume.NodeResizeOptions) (bool, error) {
klog.V(4).Infof(log("Expander.NodeExpand(%s)", resizeOptions.DeviceMountPath))
csiSource, err := getCSISourceFromSpec(resizeOptions.VolumeSpec)
if err != nil {
return false, errors.New(log("Expander.NodeExpand failed to get CSI persistent source: %v", err))
}
csClient, err := newCsiDriverClient(csiDriverName(csiSource.Driver))
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
fsVolume, err := util.CheckVolumeModeFilesystem(resizeOptions.VolumeSpec)
if err != nil {
return false, errors.New(log("Expander.NodeExpand failed to check VolumeMode of source: %v", err))
}
return c.nodeExpandWithClient(resizeOptions, csiSource, csClient, fsVolume)
}
MarkFSResizeFinished
更新PVC对象,将.Status.Capacity.storage的值为扩容后的存储大小值
// MarkFSResizeFinished marks file system resizing as done
func MarkFSResizeFinished(
pvc *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
newSize resource.Quantity,
kubeClient clientset.Interface) error {
newPVC := pvc.DeepCopy()
newPVC.Status.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage] = newSize
newPVC = MergeResizeConditionOnPVC(newPVC, []v1.PersistentVolumeClaimCondition{})
_, err := PatchPVCStatus(pvc /*oldPVC*/, newPVC, kubeClient)
return err
}
// PatchPVCStatus updates PVC status using PATCH verb
// Don't use Update because this can be called from kubelet and if kubelet has an older client its
// Updates will overwrite new fields. And to avoid writing to a stale object, add ResourceVersion
// to the patch so that Patch will fail if the patch's RV != actual up-to-date RV like Update would
func PatchPVCStatus(
oldPVC *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
newPVC *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
kubeClient clientset.Interface) (*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim, error) {
patchBytes, err := createPVCPatch(oldPVC, newPVC)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("patchPVCStatus failed to patch PVC %q: %v", oldPVC.Name, err)
}
updatedClaim, updateErr := kubeClient.CoreV1().PersistentVolumeClaims(oldPVC.Namespace).
Patch(oldPVC.Name, types.StrategicMergePatchType, patchBytes, "status")
if updateErr != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("patchPVCStatus failed to patch PVC %q: %v", oldPVC.Name, updateErr)
}
return updatedClaim, nil
}
总结
存储的扩容分为controller端操作与node端操作两大步骤,controller端操作由external-resizer来调用ceph完成,而node端操作由kubelet来完成。
controller端存储扩容作用
将底层存储扩容,如ceph rbd扩容,则会让ceph集群中的rbd image扩容。
node端存储扩容作用
在pod所在的node上做相应的操作,让node感知该存储已经扩容,如ceph rbd filesystem扩容,则会调用node上的文件系统扩容命令让文件系统扩容。
某些存储无需进行node端扩容操作如cephfs。
存储扩容大致过程
(1)更改pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage,触发扩容
(2)controller端存储扩容:external-resizer watch pvc对象,当发现pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage比pvc.Status.Capacity.storgage大,于是调csi plugin的ControllerExpandVolume方法进行 controller端扩容,进行底层存储扩容,并更新pv.Spec.Capacity.storgage。
(3)node端存储扩容:kubelet发现pv.Spec.Capacity.storage大于pvc.Status.Capacity.storage,于是调csi node端扩容,对dnode上文件系统扩容,成功后kubelet更新pvc.Status.Capacity.storage。
存储扩容整体流程

如图,整体的存储扩容步骤如下:
(1)修改pvc对象,修改申请存储大小(pvc.spec.resources.requests.storage);
(2)修改成功后,external-resizer监听到该pvc的update事件,发现pvc.Spec.Resources.Requests.storgage比pvc.Status.Capacity.storgage大,于是调ceph-csi组件进行 controller端扩容;
(3)ceph-csi组件调用ceph存储,进行底层存储扩容;
(4)底层存储扩容完成后,ceph-csi组件更新pv对象的.Spec.Capacity.storgage的值为扩容后的存储大小;
(5)kubelet的volume manager在reconcile()调谐过程中发现pv.Spec.Capacity.storage大于pvc.Status.Capacity.storage,于是调ceph-csi组件进行 node端扩容;
(6)ceph-csi组件对node上存储对应的文件系统扩容;
(7)扩容完成后,kubelet更新pvc.Status.Capacity.storage的值为扩容后的存储大小。
node端(kubelet)存储扩容调用链
vm.reconciler.Run --> rc.operationExecutor.ExpandInUseVolume --> oe.operationGenerator.GenerateExpandInUseVolumeFunc --> og.doOnlineExpansion --> og.nodeExpandVolume --> expander.NodeExpand (pkg/volume/csi/expander.go) --> csClient.NodeExpandVolume



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号