spring boot+mybatis整合
spring boot+mybatis整合
LZ今天自己搭建了下Spring boot+Mybatis,比原来的Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis简单好多。其实只用Spring boot也可以开发,但是对于多表多条件分页查询,Spring boot就有点力不从心了,所以LZ把Mybatis整合进去,不得不说,现在的框架搭建真的是方便。话不多说,进入正题。
一、java web开发环境搭建
网上有很多教程,参考教程:http://www.cnblogs.com/Leo_wl/p/4752875.html
二、Spring boot搭建
1、Intellij idea菜单栏File->new->project。
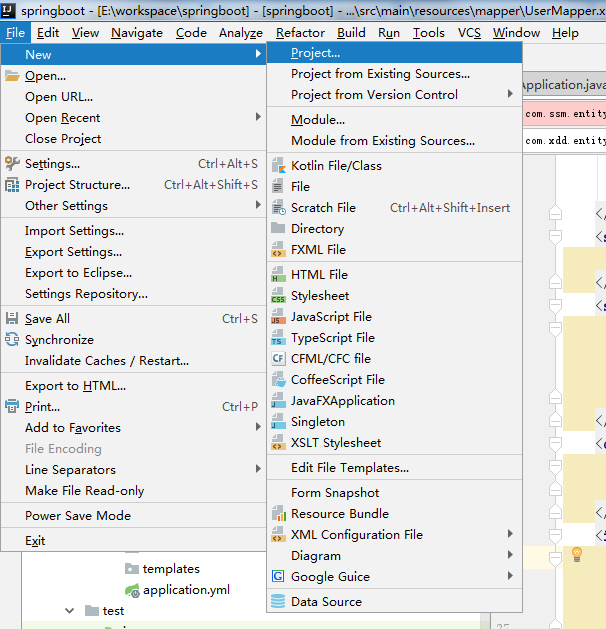
2、选择左侧栏中spring initializr,右侧选择jdk版本,以及默认的Service URL,点击next。

/3、然后填写项目的Group、Artifact等信息,helloworld阶段选默认就可以了,点击next。

4、左侧点击Web,中间一侧选择Web,然后左侧选择SQL,中间一侧选择JPA、Mybatis、MYSQL(LZ数据库用的是mysql,大家可以选择其他DB),点击next。

5、填写Project name 等信息,然后点击Finish。
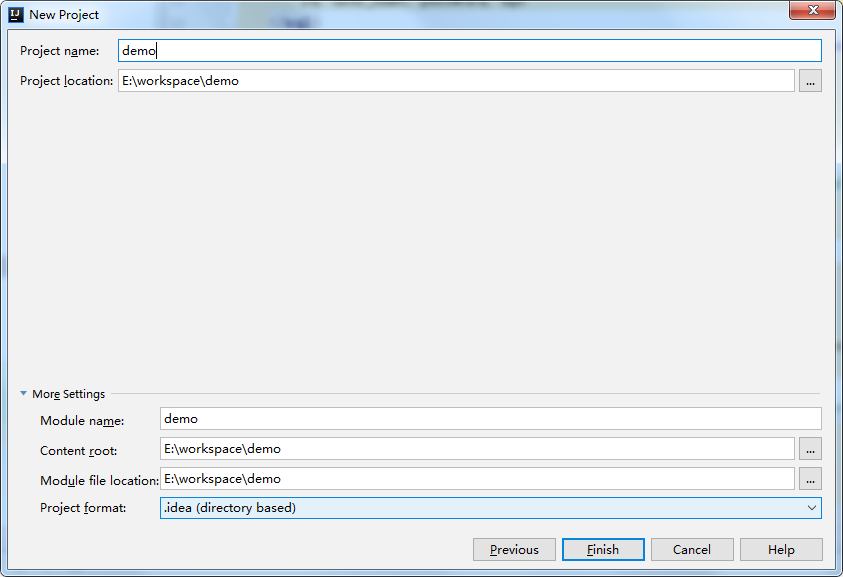
至此,一个maven web项目就创建好了,目录结构如下:
这样,Spring boot就搭建好了,pom.xml里已经有了Spring boot的jar包,包括我们的mysql数据连接的jar包。Spring boot内置了类似tomcat这样的中间件,所以,只要运行DemoApplication中的main方法就可以启动项目了。我们测试一下。
在src/main/java下新建目录com/demo/entity/User。
package com.demo.entity;
public class User {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
相同目录下新建com/demo/controller/TestBootController。
package com.demo.controller;
import com.demo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@RequestMapping("/testboot")
public class TestBootController {
@RequestMapping("getuser")
public User getUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("test");
return user;
}
}
spring boot启动DemoAplication是需要扫描它下面的Controller等类的,所以将DemoApplication移动到com/demo目录下。还有就是Spring boot启动默认是要加载数据源的,所以我们在src/main/resources下新建application.yml:
#默认使用配置
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
#公共配置与profiles选择无关
mybatis:
typeAliasesPackage: com.xdd.entity
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
---
#开发配置
spring:
profiles: dev
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
或者将pom.xml中加载数据源的jar包先注释掉也可以。
/*<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency>*/
最终的目录结构如下,

启动DemoApplication的main方法,访问http://localhost:8080/testboot/getuser即可。

三、整合Mybatis
1、集成druid,使用连接池。pom.xml中添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
最终的pom.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.arm</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
在application.yml中添加数据源、Mybatis的实体和配置文件位置。
#默认使用配置
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
#公共配置与profiles选择无关 mapperLocations指的路径是src/main/resources
mybatis:
typeAliasesPackage: com.xdd.entity
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
---
#开发配置
spring:
profiles: dev
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 使用druid数据源
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
就这样就整合完成了!我们测试一下。
用MyBatis Generator自动生成代码,参考博文:http://blog.csdn.net/zhshulin/article/details/23912615 这里列一下自动生成的代码。
import com.xdd.entity.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public interface UserDao {
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int insert(User record);
int insertSelective(User record);
User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(User record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(User record);
}
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.xdd.dao.UserDao" >
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.xdd.entity.User" >
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="user_name" property="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="password" property="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List" >
id, user_name, password, age
</sql>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" >
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from user_t
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" >
delete from user_t
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.xdd.entity.User" >
insert into user_t (id, user_name, password,
age)
values (#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{age,jdbcType=INTEGER})
</insert>
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.xdd.entity.User" >
insert into user_t
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," >
<if test="id != null" >
id,
</if>
<if test="userName != null" >
user_name,
</if>
<if test="password != null" >
password,
</if>
<if test="age != null" >
age,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," >
<if test="id != null" >
#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="userName != null" >
#{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="password != null" >
#{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="age != null" >
#{age,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.xdd.entity.User" >
update user_t
<set >
<if test="userName != null" >
user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="password != null" >
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="age != null" >
age = #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.xdd.entity.User" >
update user_t
set user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
age = #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER}
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
</mapper>
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private Integer age;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName == null ? null : userName.trim();
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password == null ? null : password.trim();
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
最后将DemoApplication.java修改一下,让其扫描dao层接口。
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.xdd.dao")
public class DemoApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class,args);
}
}
自己添加controller和service
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public interface UserService {
public User getUserById(int userId);
boolean addUser(User record);
}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
public User getUserById(int userId) {
return userDao.selectByPrimaryKey(userId);
}
public boolean addUser(User record){
boolean result = false;
try {
userDao.insertSelective(record);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/showUser")
@ResponseBody
public User toIndex(HttpServletRequest request, Model model){
int userId = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
User user = this.userService.getUserById(userId);
return user;
}
}
浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/user/showUser?id=1
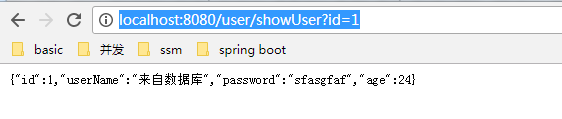
以前找别人的教程的时候总是嫌弃人家写的不详细,真的自己写的时候发现很多细节我也详细介绍不到,比如yml文件使用,比如数据库,看来还是要求别人容易,要求自己难。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号