Java核心技术(初阶)知识点复习——[10]Java异常和异常处理
1.异常与异常处理的概念
[1]程序不正常的行为或者状态称为异常;常见的包括数学上的错误(如5/0)、空指针、数组越界访问、读取不存在的文件等;
[2]Java的异常处理机制使得程序返回到安全状态,即1)允许用户保存当前运行结果;
2)抓住异常,分析异常内容;
3)并以适当的方式安全的关闭程序(如,弹出错误警告而不是直接死机);
2.异常分类
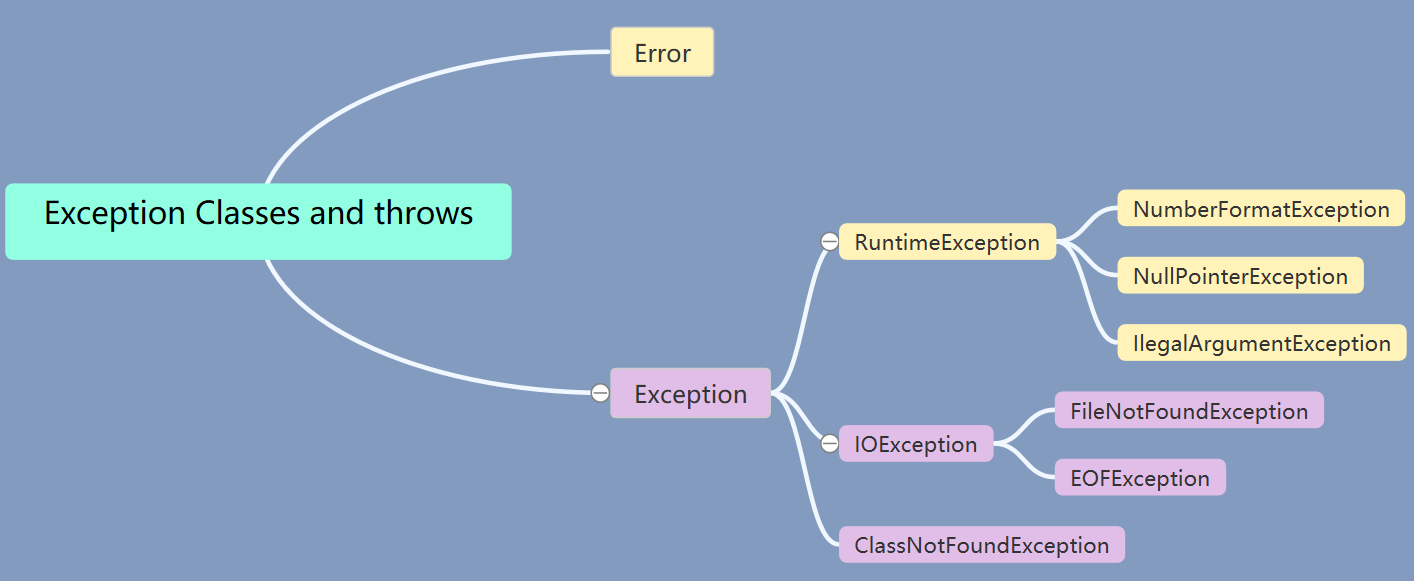
[1]Throwable是所有类的祖先;
Error系统内部错误或资源耗尽,不管它;
Exception是程序有关异常,重点关注,
1) 又分为RuntimeException是程序运行时自身的错误(1.2.):为编译器不辅助检查的Unchecked Exception,即不强制要求必须出现处理此类Exception的代码;
2) IOException程序运行时外界的错误(3.4.):为编译器辅助检查的Checked Exception,即编译器强制要求程序中有处理此类的代码;
3.Java异常处理机制*2
[1]try+catch/finally结构:
try{}内:正常业务逻辑代码;
catch{}内:当try{}内发生异常时,执行catch{}内代码,若整个运行期间都无异常,绕开(相当于没有何时类型的实参传入形参);
进入一个catch{}后,不会再返回到try{}内发生异常的位置,即try{}内发生异常位置之后的代码都不会被执行;
一个异常只能进入一个catch{}内,即进入一个catch{}后,后续的catch{}都不会执行,直接跳到finally{};
因此,当用多个catch{}时,一场子类必须写在它们任何父类之前,否则,这个语句块永远不会使用,编译会报错;
finally{}内:当try{}/catch{}执行结束后,必须要执行finally{}中的最终处理代码;
[2]throws关键字重新抛出异常:
某方法可能出现异常语句,但不在此处处理,即添加“try+catch/finally结构”,而是用throws关键字来声明异常;
调用带有throws异常(checked exception)的方法,必须出现以下两种语句之一:1)通过try+catch/finally结构处理这些异常;
2)再次throws这些异常,直到main函数为止;
1 public class IntegerReader{ 2 private static BufferedReader stdIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 3 private static PrintWriter stdErr = new PrintWriter(System.err, true); 4 private static PrintWriter stdOut = new PrintWriter(System.out, true); 5 6 public static void main (String[] args){ 7 stdOut.println("The value is:" + readInteger()); 8 } 9 10 public static int readInteger() throws IOException, NemberFormatException{ 11 stdErr.print("Enter an integer >"); 12 stdErr.flush(); 13 return Integer.parseInt(stdIn.readLine()); 14 } 15 }
4.自定义异常
[1]必须继承自Exception类或其子类:
继承自Exception,就是一个Checked Exception;
继承自RuntimeException,就是一个Unchecked Exception;
[2]自定义重点在构造函数:
调用父类Exception的message构造函数;
可以自定义自己的成员变量;
1 public class DevideByMinusException extends Exception{ 2 int divisor; 3 public DivideByMinusException(String msg, int divisor) 4 { 5 super(msg);//1.调用父类msg构造函数 6 this.divisor = divisor; 7 } 8 public int getDevisor() 9 { 10 return this.getDevisor(); 11 } 12 }
注1.:必须重写的构造方法为以下四种之一
[1]Exception()
构造zd详细消息为 null 的新异常。
[2]Exception(String message)
构造带指定详细消息的新异常。
[3]Exception(String message, Throwable cause)
构造带指定详细消息和原因的新异常。
[4]Exception(Throwable cause)
根据回指定的原因和 (cause==null ? null : cause.toString()) 的详细消息构造新异常(它通常包答含 cause 的类和详细消息)
1 public class Student{ 2 public int divide(int x, int y) 3 { 4 return x/y;//2.编译通过,因为被除数异常属于Unchecked Exception,可以对比4.更深刻理解这个Unchecked Exception是有多么的Unchecked 5 } 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws DivideByMinusException{ 7 Student newton = new Student(); 8 newton.divide5(5, -2); 9 } 10 11 public int divide2(int x, int y) 12 { 13 int result; 14 try 15 { 16 result = x/y; 17 } 18 catch(ArithmeticException e) 19 { 20 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 21 } 22 catch(Exception e) 23 { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 return result; 27 }
1 public int divide3(int x, int y)throws ArithmeticException 2 { 3 return x/y; 4 } 5 6 public int divide4(int x, int y)//3.尽管divide3声明throws了一个异常,但divide可以不用处理,因为是Unchecked Exception 7 { 8 // try 9 // { 10 // return divide3(x, y) 11 // } 12 // catch(ArithmeticException e) 13 // { 14 // e.printStackTrace(); 15 // } 16 return divide3(x, y) 17 }
1 public int divide5(int x, int y)throws DivideByMinusException 2 { 3 try 4 { 5 if(y<0) 6 { 7 throw new DivideByException("The divisor is negative", y); 8 } 9 return divide3(x, y); 10 } 11 catch(ArithmeticException e) 12 { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 }//4.如果此时divide4调用了divide5,则必须对他进行处理
[3]必须且只能使用throw(注意和上面throws区分!!!)关键字“主动”抛出异常
异常对象生成的方式为:1)由Java虚拟机在运行时系统生成;(Unchecked Exception)
2)由Java类库中的某些类生成;(Checked Exception)
3)自己生成的异常对象;(可以不是真的出现了异常,而只是抛出下看看……理解可能有问题,先一搁置)
注:throw抛出的异常必须时Throwable的子类,这里和[1]中的要求也契合;


