python学习第一天笔记
本节内容
- Python介绍
- 发展史
- Python 2 or 3?
- 安装
- Hello World程序
- 变量
- 用户输入
- 模块初识
- .pyc是个什么鬼?
- 数据类型初识
- 数据运算
- 表达式if ...else语句
- 表达式for 循环
- break and continue
- 表达式while 循环
- 作业需求
一、 Python介绍
python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum)。1989年的圣诞节期间,吉多·范罗苏姆为了在阿姆斯特丹打发时间,决心开发一个新的脚本解释程序,作为ABC语言的一种继承。
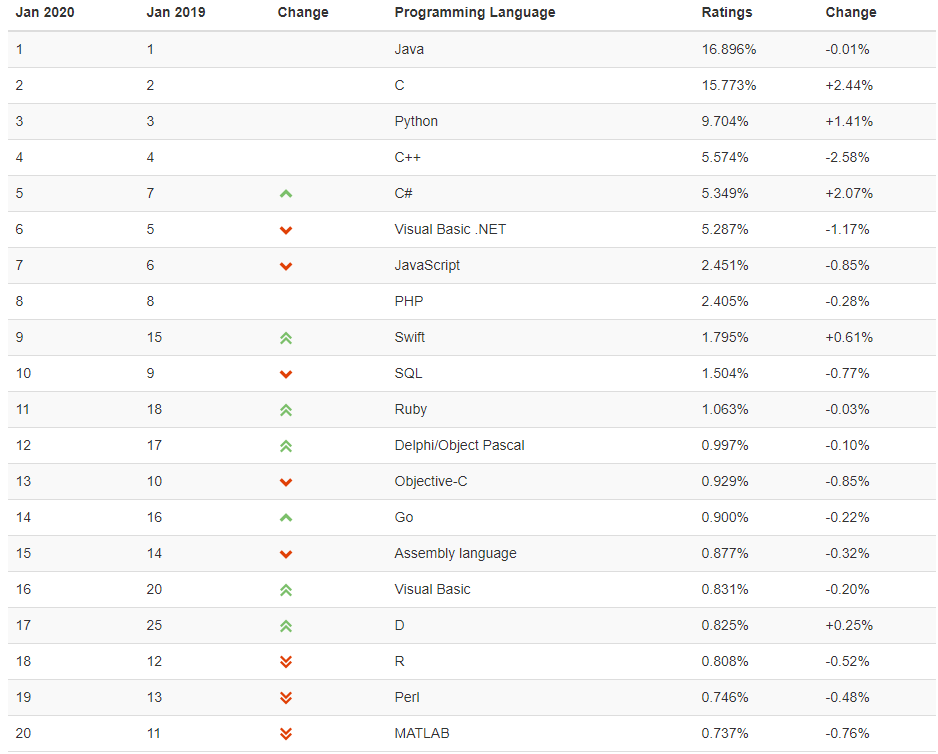
最新的TIOBE排行榜,Python赶超PHP占据第三, Python崇尚优美、清晰、简单,是一个优秀并广泛使用的语言。
截止2020年1月,python排名第三。
https://www.tiobe.com/tiobe-index/
二、 Python发展史
- 1989年,为了打发圣诞节假期,Guido开始写Python语言的编译器。Python这个名字,来自Guido所挚爱的电视剧Monty Python's Flying Circus。他希望这个新的叫做Python的语言,能符合他的理想:创造一种C和sell之间,功能全面,易学易用,可拓展的语言。
- 1991年,第一个Python的编译器诞生。它是用C语言实现的,并能够调用C语言的库文件。从一出生,Python已经具有了:类,函数,异常处理,包含表和词典在内的核心数据库类型,以及模块为基础的拓展系统。
- Granddaddy of Python web frameworks,Zone 1 was released in 1999
- Python 1.0 - January 1994 增加了 lambda,map,filter and reduce.
- Python 2.0 - October 16,2000, 加入了内存回收机制,构成了现在Python语言框架的基础
- Python 2.4 - November 30 2004,同年目前最流行的WEB框架Django诞生
- Python 2.5 - September 19 2006
- Python 2.6 -October 1,2008
- Python 2.7 - July 3,2010In November 2014, it was announced that Python 2.7 would be supported until 2020, and reaffirmed that there would be no 2.8 release as users were expected to move to Python 3.4+ as soon as possible
- Python 3.0 - December 3, 2008
- Python 3.1 - June 27,2009
- Python 3.2 - February 20,2011
- Python 3.3 - September 29,2012
- Python 3.4 - March 16, 2014
- Python 3.5 -September 13,2015
三、python应用
Web Programming:Django,Pyramid,Bottle,Tornado,Flask,web2py(web开发)
GUI Development: wxPython,tklnter,PyGtk,PyGObject,PyQt(图形GUI)
Scientific and Numeric: SciPy,Pandas,Ipython(科学计算,人工智能)
Software Development: Buildbot,Trac,Roundup(软件开发)
System Administration: Ansible,Salt,OpenStack(系统运维)
四、Python在一些公司的应用:
- 谷歌:Google App Engine 、code.google.com 、Google earth 、谷歌爬虫、Google广告等项目都在大量使用Python开发
- CIA: 美国中情局网站就是用Python开发的
- NASA: 美国航天局(NASA)大量使用Python进行数据分析和运算
- YouTube:世界上最大的视频网站YouTube就是用Python开发的
- Dropbox:美国最大的在线云存储网站,全部用Python实现,每天网站处理10亿个文件的上传和下载
- Instagram:美国最大的图片分享社交网站,每天超过3千万张照片被分享,全部用python开发
- Facebook:大量的基础库均通过Python实现的
- Redhat: 世界上最流行的Linux发行版本中的yum包管理工具就是用python开发的
- 豆瓣: 公司几乎所有的业务均是通过Python开发的
- 知乎: 国内最大的问答社区,通过Python开发(国外Quora)
- 春雨医生:国内知名的在线医疗网站是用Python开发的
- 除上面之外,还有搜狐、金山、腾讯、盛大、网易、百度、阿里、淘宝 、土豆、新浪、果壳等公司都在使用Python完成各种各样的任务。
五、python中的变量与赋值
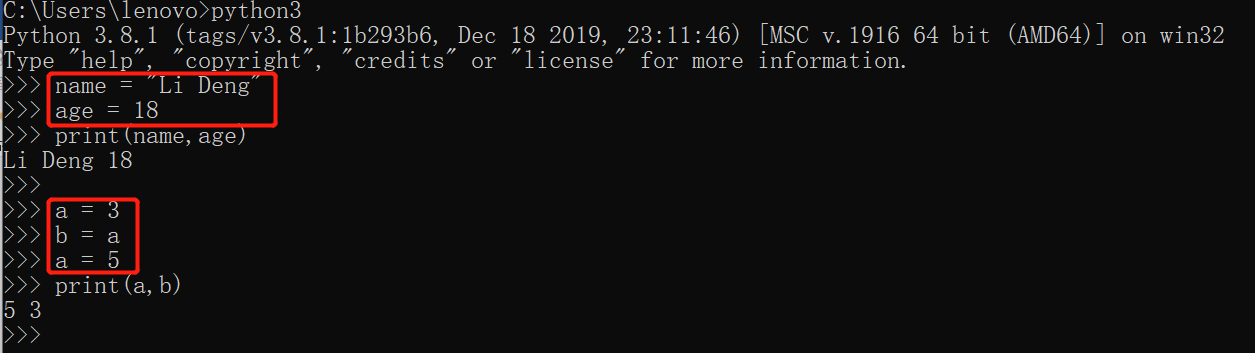
变量定义时的字符串必须加引号,如果不加会提示错误,或是将字符串当做变量重新定义
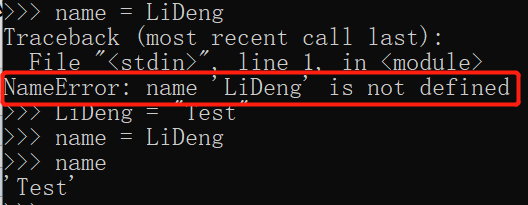
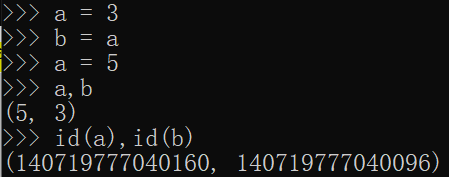
通过id查看变量的python中的内存地址
六、变量起名
1.显式
2. nums_of_alex_gf = 19
3. NumsOfAlexGf = 2
4.变量名只能是字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
5.变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
6.变量名中不能有特殊字符
7.python中的关键字不能声明为变量名
七、用户交互
八、python中的数据类型
- 数字
- Int
- Float
- Long
- 布尔
- 字符串
- 列表
- 元组
- 字典
1、 初识数据类型
2 是一个整数的例子。
长整数 不过是大一些的整数。
3.23和52.3E-4是浮点数的例子。E标记表示10的幂。在这里,52.3E-4表示52.3 * 10-4。
(-5+4j)和(2.3-4.6j)是复数的例子,其中-5,4为实数,j为虚数,数学中表示复数是什么?。
int(整型)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
long(长整型)
跟C语言不同,Python的长整数没有指定位宽,即:Python没有限制长整数数值的大小,但实际上由于机器内存有限,我们使用的长整数数值不可能无限大。
注意,自从Python2.2起,如果整数发生溢出,Python会自动将整数数据转换为长整数,所以如今在长整数数据后面不加字母L也不会导致严重后果了。
float(浮点型)
浮点数用来处理实数,即带有小数的数字。类似于C语言中的double类型,占8个字节(64位),其中52位表示底,11位表示指数,剩下的一位表示符号。
complex(复数)
复数由实数部分和虚数部分组成,一般形式为x+yj,其中的x是复数的实数部分,y是复数的虚数部分,这里的x和y都是实数。
注:Python中存在小数字池:-5 ~ 257
2、布尔值
真或假
1或0
0 == False
1 == True
3、字符串
"hello world"

1 name = raw_input("name:") 2 age = raw_input("age:") 3 job = raw_input("job:") 4 5 print("Information of []:" + name + "\nName:[]" +name +"\nAge:[]" +age +"\nJob:[]" +job) 6 7 msg = ''' 8 Information of %s: 9 Name:%s 10 Age:%s 11 Age:%s 12 ''' %(name,name,age,job) 13 print(msg) 14 15 16 17 print("Information of %s:\nName:%s\nAge:%s\nAge:%s" %(name,name,age,job))
运行结果:
name:Rain age:19 job:IT Information of []:Rain Name:[]Rain Age:[]19 Job:[]IT
PS: 字符串是 %s;整数 %d;浮点数%f
- 移除空白
- 分割
- 长度
- 索引
- 切片

1 name = raw_input("name:") 2 age = int(raw_input("age:")) 3 job = raw_input("job:") 4 5 #print("Information of []:" + name + "\nName:[]" +name +"\nAge:[]" +age +"\nJob:[]" +job) 6 7 # %d 8 # %f 9 msg = ''' 10 Information of %s: 11 Name:%s 12 Age:%d 13 Age:%s 14 ''' %(name,name,age,job) 15 print(msg) 16 17 #print("Information of %s:\nName:%s\nAge:%s\nAge:%s" %(name,name,age,job))
strip默认去除空格,可以去除任意字符

1 name = raw_input("name:").strip() 2 age = int(raw_input("age:")) 3 job = raw_input("job:").strip() 4 5 #print("Information of []:" + name + "\nName:[]" +name +"\nAge:[]" +age +"\nJob:[]" +job) 6 7 # %d 8 # %f 9 msg = ''' 10 Information of %s: 11 Name:%s 12 Age:%d 13 Age:%s 14 ''' %(name,name,age,job) 15 print(msg)
>>> name_list = ["alex","65brother","tenglan"] >>> name_list ['alex', '65brother', 'tenglan']
列表的作用,在一个变量中容易的存取多个信息
>>> name_list[1] '65brother' >>> name_list[0] 'alex' >>> name_list[2] 'tenglan'
基本操作:
- 索引
- 切片
- 追加
- 删除
- 长度
- 切片
- 循环
- 包含
查看列表中有什么方法:

1 >>> help(name_list) 2 Help on list object: 3 4 >>> dir(name_list) 5 'append', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort'] 6 7 >>> name_list.append("Eric") 8 >>> name_list 9 ['alex', '65', 'it', 'Eric']
索引

1 >>> name_list[1] 2 '65brother' 3 >>> name_list[0] 4 'alex' 5 >>> name_list[2] 6 'tenglan' 7 >>> name_list.index("65brother") 8 9 1
追加

1 >>> name_list.append("ERIC") 2 >>> name_list 3 ['alex', '65brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC'] 4 5 >>> name_list.append("65brother") 6 >>> name_list 7 ['alex', '65brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC', '65brother']
计数
>>> name_list.count("65brother")
2
插入:
在索引2的位置插入一条记录
>>> name_list.insert(2,"66brother") >>> name_list ['alex', '65brother', '66brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC', '65brother']
删除
删除最后一条记录
>>> name_list.pop() '65brother' >>> name_list ['alex', '65brother', '66brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC']
删除指定的值
>>> name_list.remove("66brother")
>>> name_list
['alex', '65brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC']
反转:
>>> name_list ['alex', '65brother', 'tenglan', 'ERIC'] >>> name_list.reverse() >>> name_list ['ERIC', 'tenglan', '65brother', 'alex']
排序:

1 >>> name_list 2 3 ['ERIC', 'tenglan', '65brother', 'alex'] 4 5 >>> name_list.sort() 6 7 >>> name_list 8 9 ['65brother', 'ERIC', 'alex', 'tenglan'] 10 11 12 13 >>> name_list.insert(5,'65brother') 14 15 >>> name_list.insert(2,'65brother') 16 17 >>> name_list 18 19 [55, 99, '65brother', '!', '*', '65brother', '65brother', 'Eric', '_', 'alex', 'it']
删除多个同样的值:
>>> for i in range(name_list.count('65brother')):
... name_list.remove('65brother')
...
>>> name_list
[55, 99, '!', '*', 'Eric', '_', 'alex', 'it']
切片:

1 >>> a = [1,2,3,'a','b'] 2 3 >>> a.sort() 4 5 Traceback (most recent call last): 6 7 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 8 9 TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'int' 10 11 12 13 >>> a.insert(2,4) 14 15 >>> a.insert(1,6) 16 17 >>> a 18 19 [1, 6, 2, 4, 3, 'a', 'b']
切片是顾首不顾尾

1 >>> a[0:2] 2 3 [1, 6] 4 5 >>> a[0:3] 6 7 [1, 6, 2] 8 9 >>> a[0:5] 10 11 [1, 6, 2, 4, 3] 12 13 >>> a[1:5] 14 15 [6, 2, 4, 3] 16 17 >>> a[2:5] 18 19 [2, 4, 3] 20 21 22 23 >>> a[0:5:2] 24 25 [1, 2, 3] 26 27 28 29 >>> a 30 31 [1, 6, 2, 4, 3, 'a', 'b'] 32 33 >>> a[-1] #取最后一个 34 35 'b' 36 37 >>> a[-2] #取倒数第二个 38 39 'a' 40 41 >>> a[-2:] #取倒数第二个到结束 42 43 ['a', 'b'] 44 45 >>> a[:3] #取第一个到第三个 46 47 [1, 6, 2] 48 49 50 51 52 53 >>> b=a[0:5] 54 55 >>> b 56 57 [1, 6, 2, 4, 3] 58 59 >>> b.sort() 60 61 >>> b 62 63 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6]
扩展

1 >>> a 2 3 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 'a', 'b'] 4 5 >>> b 6 7 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6] 8 9 >>> a+b 10 11 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 'a', 'b', 1, 2, 3, 4, 6] 12 13 >>> a.extend(b) 14 15 >>> a 16 17 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 'a', 'b', 1, 2, 3, 4, 6] 18 19 20 21 22 23 >>> name = "Alex Li" 24 25 >>> a.extend(name) 26 27 >>> a 28 29 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 'a', 'b', 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 'A', 'l', 'e', 'x', ' ', 'L', 'i']
包含

1 >>> a 2 3 [1, 6, 4, 3, '65brother'] 4 5 >>> 4 in a 6 7 True 8 9 >>> if 4 in a: 10 11 print ("ddd") 12 13 14 15 ddd
5、元组
元组是只读的

1 >>> t = (1,2,3,4) 2 3 >>> t 4 5 (1, 2, 3, 4) 6 7 >>> dir(t) 8 9 ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', 10 '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', 11 '__repr__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'count', 'index']
查看类型
>>> type(t)
<type 'tuple'>
将元组转换成列表:
>>> list(t)
[1, 2, 3, 4]
将列表转换成元组:
>>> tuple(a)
(1, 6, 4, 3, '65brother')
基本操作
- 索引
- 切片
- 循环
- 长度
6.字典
十二、数据运算

比较运算:

赋值运算:

逻辑运算:


1 >>> sex = "m" 2 >>> age = 26 3 >>> if sex == 'm' and age >25: 4 print("time to get married!") 5 6 time to get married! 7 8 >>> names = ['alex','rain'] 9 >>> if 'jack' not in names: 10 print("invalid user") 11 12 13 invalid user
成员运算:

身份运算:


1 >>> type(names) 2 <type 'list'> 3 >>> type(names) is list 4 True 5 >>> type(names) is tuple 6 False 7 >>> type(3) is int 8 True
位运算:
a=60,b=13

128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 a=60 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 b=13 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 a&b=12 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 a|b=61 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 a^b=49 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 ~a=-61 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 a<<2=240 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 a>>2=15

1 >>> a = 60 2 >>> b = 13 3 >>> a&b 4 12 5 >>> a|b 6 61 7 >>> a^b 8 49 9 >>> ~a 10 -61 11 >>> a<<2 12 240 13 >>> a>>2 14 15
运算符优先级:

条件判断
IF ... ELSE和缩进
python2
lucky_num = 19
input_num = input("pls input your guess number:")
if input_num == lucky_num:
print("Bingo!")
elif input_num < lucky_num:
print("the real number is bigger")
else:
print("the real number is smallber")
python3
lucky_num = 19
input_num = int(input("pls input your guess number:"))
#int将字符串格式转换成数字格式
if input_num == lucky_num:
print("Bingo!")
elif input_num < lucky_num:
print("the real number is bigger")
else:
print("the real number is smallber")
循环
在程序里设定好你的年龄,然后启动程序让用户猜测,用户输入后,根据他的输入提示用户输入的是否正确,如果错误,提示是猜大了还是小了
while
1.

1 lucky_num = 19 2 while True: 3 input_num = input("pls input your guess number:") 4 5 if input_num == lucky_num: 6 print("Bingo!") 7 break 8 elif input_num < lucky_num: 9 print("the real number is bigger") 10 else: 11 print("the real number is smallber")
2.

1 lucky_num = 19 2 input_num = 0 3 while input_num != lucky_num: 4 input_num = int(input("Input the guess num:")) 5 #input_num = raw_input("Input the guess num:") 6 #if input_num == lucky_num: 7 # print("bingo!") 8 # break 9 if input_num > lucky_num: 10 print("the real number is smaller.") 11 else: 12 print("the real number is bigger.") 13 14 print("bingo!")
执行结果:
C:\Python27\python.exe D:/python/s12/day1/guess_lucky_num.py Input the guess num:22 the real number is smaller. Input the guess num:19 the real number is bigger. bingo! Process finished with exit code 0
第一次循环时,
lucky_num = 19
input_num = 0
lucky_num != input_num
进入循环,输入22,此时对lucky_num 和 input_num进行判断,
if input_num > lucky_num:
print("the real number is smaller")
因为22>19,所以此时打印the real number is smaller
然后进入下一轮循环,lucky_num = 19,input_num =22,再次输入19,因为此时已经进入循环, if input_num
> lucky_num:
print("the real number is smaller")
elif input_num
< lucky_num:
print("the real number is bigger")
根据以上条件判断,打印the real number is bigger,之后准备进入循环,由于不满足循环条件,lucky_num
!= input_num,因此打印bingo
所以此代码有bug修改为如下的代码
3.

1 lucky_num = 19 2 input_num = 0 3 while lucky_num != input_num: 4 input_num = input("pls input your guess number:") 5 6 # if input_num == lucky_num: 7 # print("Bingo!") 8 #break 9 if input_num > lucky_num: 10 print("the real number is smaller") 11 elif input_num < lucky_num: 12 print("the real number is bigger") 13 14 print("Bingo")

1 lucky_num = 19 2 input_num = 0 3 guess_count = 0 4 # while lucky_num != input_num and guess_count < 3: 5 while guess_count < 3: 6 input_num = input("pls input your guess number:") 7 8 if input_num > lucky_num: 9 print("the real number is smaller") 10 elif input_num < lucky_num: 11 print("the real number is bigger") 12 #guess_count = guess_count + 1 13 else: 14 print("Bingo") 15 break 16 guess_count += 1 17 else: 18 print("Too many retry")
循环如果正常退出(不满足while的条件),则执行最后一个else,如果未正常退出,则不执行
全选ctrl+/可以多行注释
for 循环

1 lucky_num = 19 2 input_num = 0 3 guess_count = 0 4 for i in range(3): 5 input_num = input("pls input your guess number:") 6 7 if input_num > lucky_num: 8 print("the real number is smaller") 9 elif input_num < lucky_num: 10 print("the real number is bigger") 11 #guess_count = guess_count + 1 12 else: 13 print("Bingo") 14 break 15 else: 16 print("Too many retry") 17 18 19 20 for i in range(10): 21 if i % 2 == 0: 22 continue 23 print i
详细关于循环的文档:http://www.python-course.eu/python3_loops.php
contiue结束本次循环,进入下一次循环
break跳出一层循环
for i in range(10):
if i <5:
continue
print(i)
for j in range(5):
for i in range(10):
if i <5:
continue
if i >8:
break
print(i)
for j in range(5):
for i in range(10):
if i <5:
continue
if j >3:
break
print(i)
十六、作业
作业一:博客
作业二:编写登陆接口
- 输入用户名密码
- 认证成功后显示欢迎信息
- 输错三次后锁定
- 三级菜单
- 可依次选择进入各子菜单
- 所需新知识点:列表、字典

1 dic = { 2 "陕西省":{ 3 "西安市":{'雁塔区','莲湖区','碑林区'}, 4 "咸阳市":{"秦都区",'渭城区'} 5 }, 6 "北京市":{ 7 "海淀区":{"万寿路","永定路"}, 8 "昌平区":{"沙河","回龙观"} 9 } 10 } 11 for k in dic.keys(): 12 print(k) 13 while True: 14 c1 = input("Pls input your choice1:\n") 15 if c1 in dic.keys(): 16 for i in dic[c1].keys(): 17 print(i.center(10,'*')) 18 c2 = input("Pls input your choice2:\n") 19 if c2 in dic[c1].keys(): 20 for j in dic[c1].get(c2): 21 print(j.center(18,'*')) 22 print("--------------------") 23 elif c2 == "b": 24 for i in dic[c1].keys(): 25 print(i) 26 continue 27 elif c2 == "q": 28 exit(1) 29 else: 30 print("Your input error") 31 exit(2) 32 elif c1 == "b": 33 for k in dic.keys(): 34 print(k.center(24,'*')) 35 print("--------------------") 36 continue 37 elif c1 == "q": 38 exit(3) 39 else: 40 print("Your input error") 41 exit(4) 42 for k in dic.keys(): 43 print(k)


