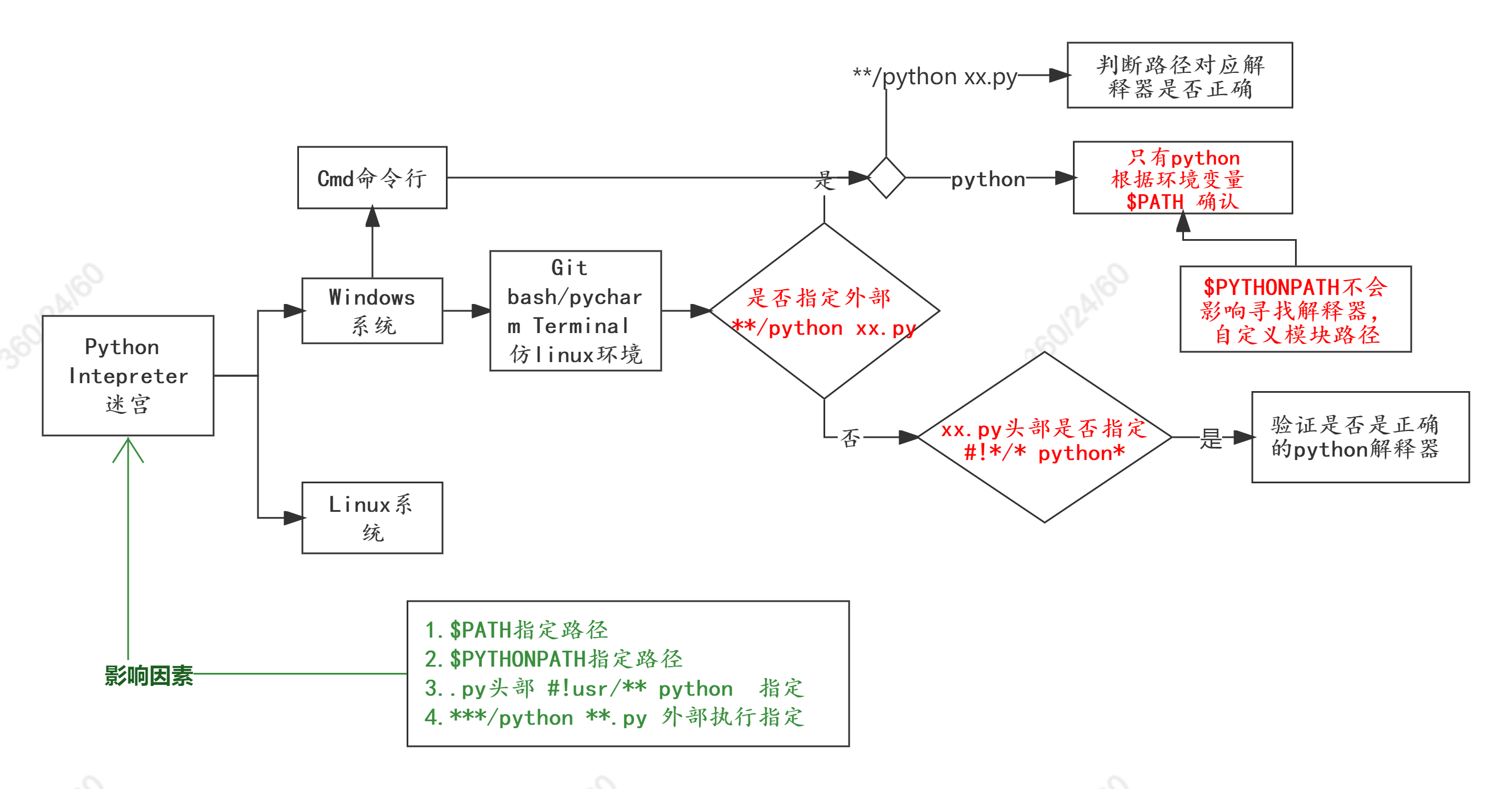
Python解释器路径寻找规则
Python编辑器路径寻址总结
-
Python寻找解释器顺序
Python编程优化
这场表演邀请了三位角色:run.sh、main.py、path.sh,拍摄场地选在了 Windows -> Git Bash
群演1号 run.sh
#!/usr/bin bash
. ./path.sh || exit -1
# demo.py无法直接找到是因为 $PATH中已经没有 工作目录
python demo.py
跳转到的地方
群演2号 path.sh
export PYTHONPATH=$PWD/define_module
export PATH="/d/Anaconda"
#export PATH="/d/Anaconda":$PWD
群演3号 demo.py
#coding=utf-8
import sys
# sys.path.append("/d/Anaconda/envs/py39/Lib/site-package/torch")
# print(sys.version, sys.path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print('demo')
python 寻找解释器顺序:
- 外层指定:
**/**/python *.py文件 则前面路径的python则为使用的解释器 !usr/bin/python如果上述解释器未指定,则从执行py文件头部这行代码(如果有的话)进行寻找$PYTHONPATH(寻找python模块的地方) windows则在环境变量中查找- 报错
not found Module,可以在$PYTHONPATH中加入相应的自定义模块路径
- 报错
Python编程优化
文件 IO对象嵌套
import io
with open(path , mode , encoding) as fin:
with open(path2 , mode , encoing ) as fout :
for line in fin :
...
fout.write()
数组 List
pop(index) # index不指定,则删除最后一个
from functools import reduce
reduce(func , iterable , initializer=None) # func常以lambda展示 iterable可迭代对象 initializer不指定则以迭代对象第一个值为初始值
双向队列 Queue使用,来自于标准库collections.deque
from collections import deque
#初始化
d = deque('init') | d = deque(['i','n','i','t'])
# 新增API
pop()/popleft() append()/appendleft() extendleft
交换两变量值a,b = b,a
python 字符串替换(正则)
# 正则方式
import re
re.sub(r'匹配规则source', after_str , target_str , count=0 )
#replace
new_str = target_str.replace('匹配项', '替换项' , count=-1)
# count 代表替换的次数,-1代表替换所有的 符合的字符串
3种for循环遍历list 方式:
for item in list:
for index in range(len(list)):
for item,index in enumerate(list):
3种for循环遍历 dict 方式:
for key in dict:
for key in dict.keys():
for value in dict.values():
for item in dict.items():
for key,item in dict.items():
pycharm配置远程调试 : https://www.cnblogs.com/lhx9527/p/16023075.html
python多线程打印:
import multiprocessing
import time
import os
def func(args):
print("in func :", os.getpid())
time.sleep(1)
return args * args
def func2(nn):
print(nn, "in func2 :", os.getpid())
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = multiprocessing.Pool(5)
for i in range(10):
p.apply_async(func, args=(i, ), callback=func2)
p.close()
p.join()
由于GML锁的缘故,python多线程适用于IO任务多于CPU任务的情况,可以使用多进程:
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
# 子进程要执行的代码
def run_proc(name):
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
if __name__=='__main__':
print('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
print('Child process will start.')
p.start() # 开始执行子进程,异步执行
print('Other task RUN')
p.join() # 恢复同步
print('Child process end.')
如何在shell中运行python字符串代码:
python -c '''
import random
from sys import argv
for f in [1,2]:
arr = open(argv[f]).readlines()
random.Random(argv[3]).shuffle(arr)
with open(argv[f] + "-sf", "w", encoding = "utf8") as fout:
for line in arr:
fout.write(line)
''' $scp $text $4
-
str.split() # 当不指定分隔符时,以空格类字符(space ,tab等)最大数量分割
-
join两种用法:- '连接符'.join(数组) 返回数组元素相连的字符串
- '连接符'.join(字符串) 在字符串相邻字符中插入连接符
-
dict按序遍历:
sorted(d.items() , key= lambda kv: (kv[1] , kv[0]))
参考:
https://jarvisma.gitbook.io/pythonlearn/5.4-python-mo-kuai-hua/chapter5.4.2
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38156052/article/details/81130117
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27825451/article/details/100552739
https://blog.csdn.net/NeverLate_gogogo/article/details/107615838
http://www.coolpython.net/python_senior/module_concept/modify-sys-path.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人