Mysql的安装和还原-免安装版
1 | 下载资源:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/操作方法 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | 1.环境变量path 中加入 解压后的MySQL文件目录至bin目录2.添加 my.ini文件【一定注意,My.ini识别圆角半角等特殊字符】3.初始化mysqld --initialize-insecure4.注册MySQL服务mysqld -install5.启动MySQL服务net start mysql6.修改默认账户密码mysqladmin -u root password lhl@1237.登录MySQLmysql -uroot -plhl@123-- ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'lhl@123';8.卸载MySQ8.1、停止服务net stop mysql8.2、执行删除mysqld -remove mysql8.3、删除环境变量 |
1 |
安装完成后需要执行【UPDATE mysql.`user` SET `Host`='%' WHERE `User`='root'】,否则其他服务器无法访问
1 | |
下载安装包:

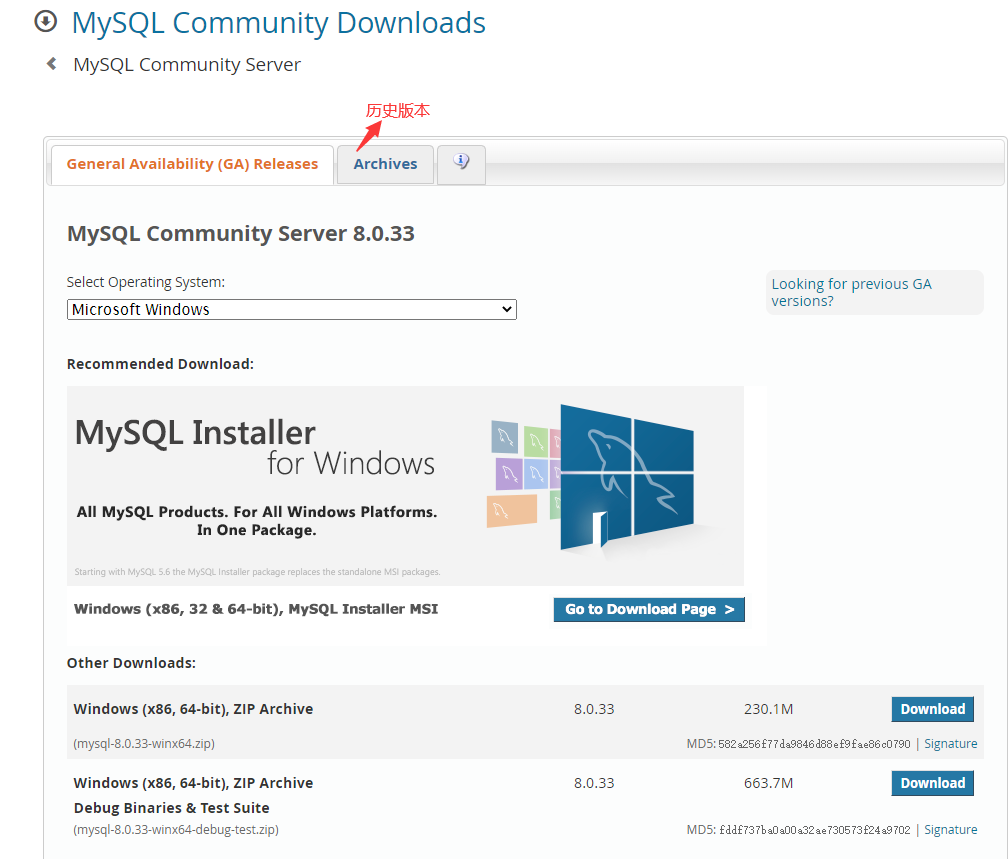
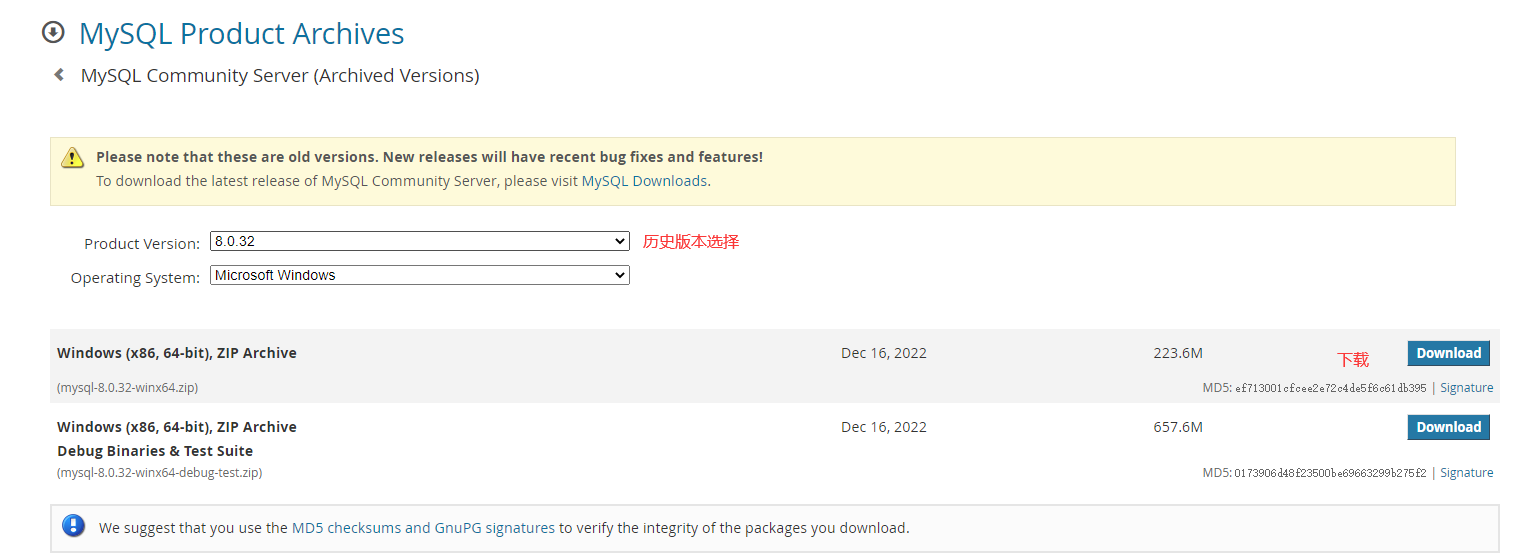
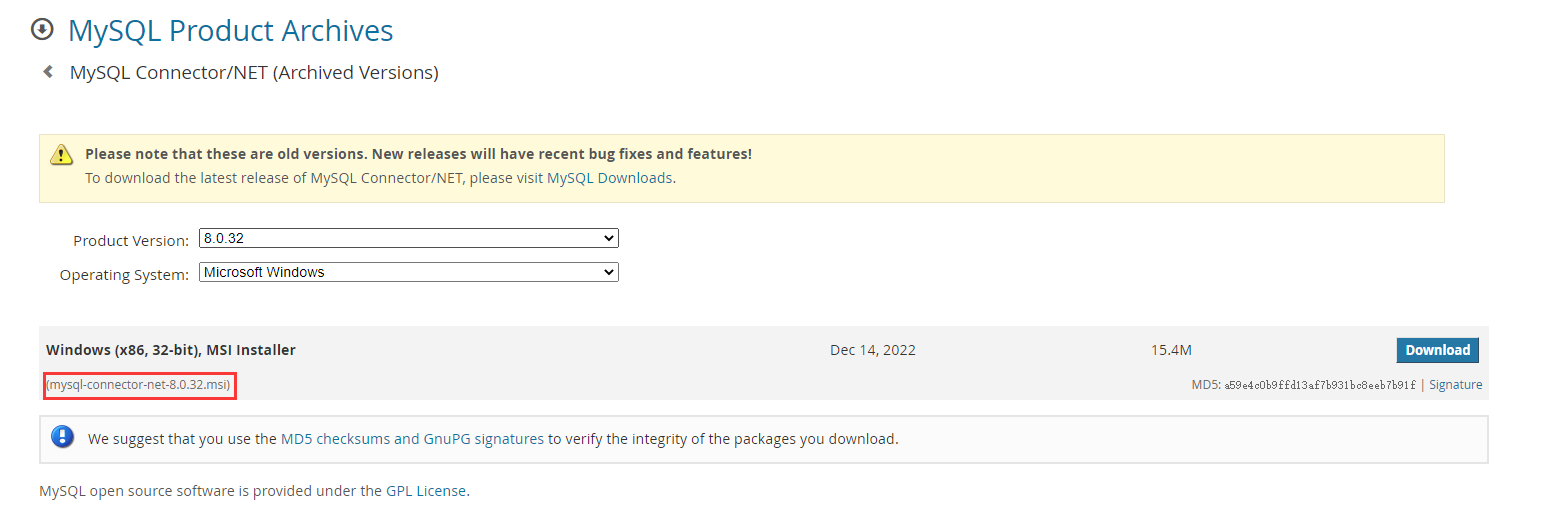

安装步骤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | 1.环境变量path 中加入 解压后的MySQL文件目录至bin目录2.添加 my.ini文件<br>CMD 》管理员运行 》 cd 安装包路径3.初始化mysqld --initialize-insecure4.注册MySQL服务mysqld -install5.启动MySQL服务net start mysql6.修改默认账户密码mysqladmin -u root password 1234567.登录MySQLmysql -uroot -p123456 |
1. 将下载的免安装包解压到系统
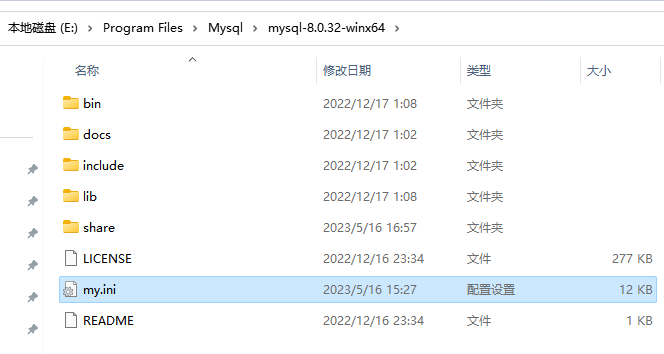
1.环境变量
path 中加入 解压后的MySQL文件目录至bin目录
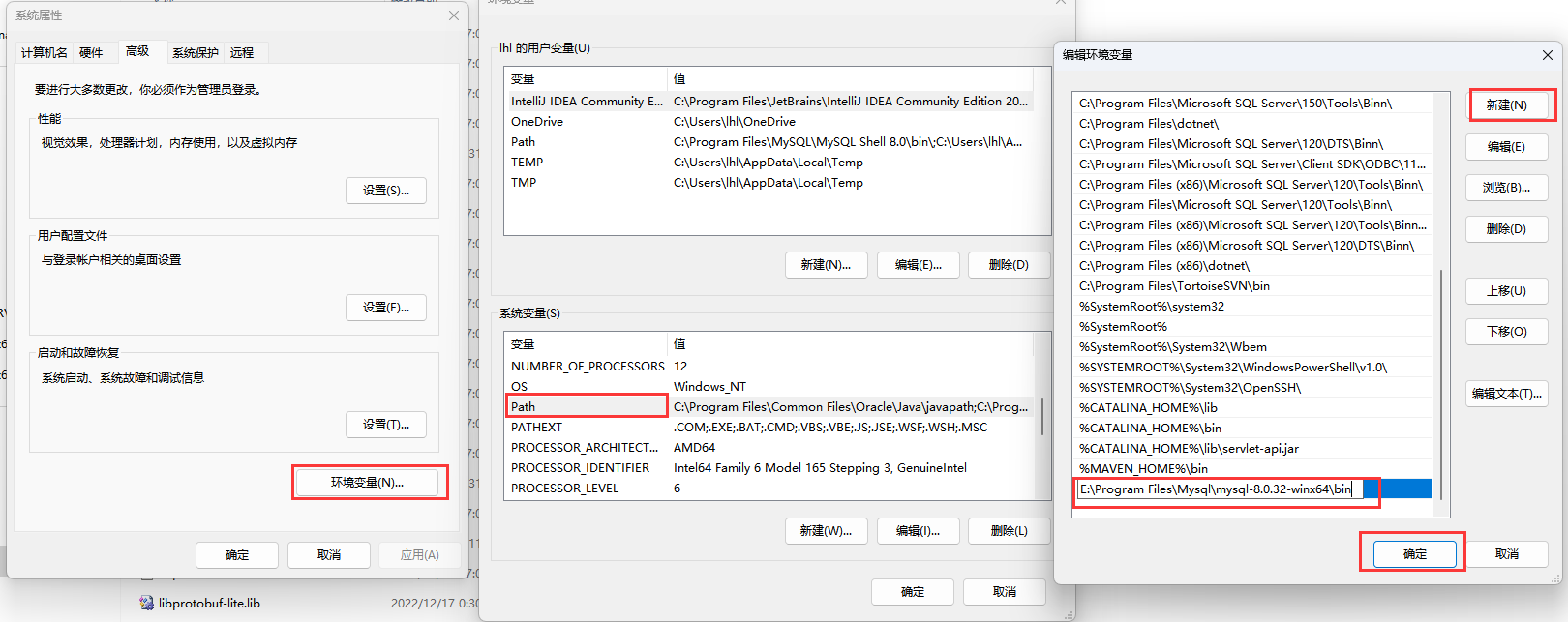
或者
添加系统变量: mysql_home 路径【D:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL Server 8.0】
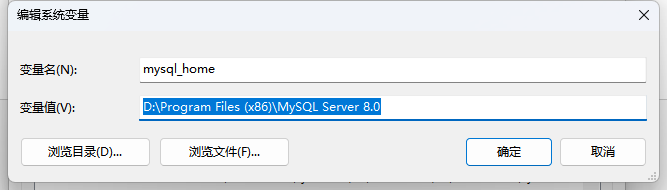
Path: 添加 : %mysql_home%\bin
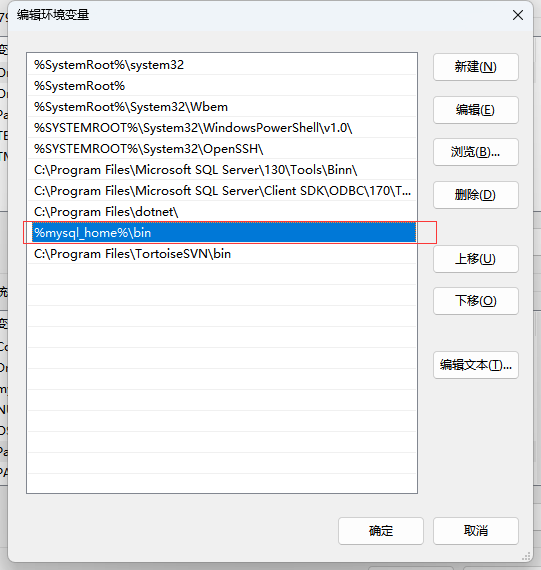
2.添加 my.ini文件,以下为参考示例
[mysqld]
max_allowed_packet=128M
#feedback=off
#设置3306端口
port = 3306
# 设置mysql的安装目录
basedir=D:\Program Files\MySql\mysql-8.0.11-winx64
# Path to the database root
# datadir=D:\Program Files\MySql\mysql-5.7.31-winx64\Data
# datadir=D:\Program Files (x86)\mysql-8.0.11-winx64\Data
datadir=D:\Program Files\MySql\mysql-8.0.11-winx64\Data
# datadir=C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data
# Secure File Priv.
# secure-file-priv=D:\Program Files (x86)\mysql-8.0.11-winx64/Uploads
# 允许最大连接数
max_connections=200
# 服务端使用的字符集默认为8比特编码的latin1字符集
# character-set-server=utf8
# 创建新表时将使用的默认存储引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# The default character set that will be used when a new schema or table is
# created and no character set is defined
# character-set-server=
# The default authentication plugin to be used when connecting to the server
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
# The default storage engine that will be used when create new tables when
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# Set the SQL mode to strict
sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION"
# General and Slow logging.
log-output=FILE
general-log=0
general_log_file="MysqlPc.log"
slow-query-log=1
slow_query_log_file="MysqlPc-slow.log"
long_query_time=10
# Binary Logging.
# log-bin=
#日志文件的存放时间是7天
expire_logs_days=7
sync_binlog=1
binlog_cache_size=4M
max_binlog_size=1024M
max_binlog_cache_size=256M
lower_case_table_names=1
# Error Logging.
log-error="MysqlPc.err"
# Server Id.
# server-id=1
# The number of open tables for all threads. Increasing this value
# increases the number of file descriptors that mysqld requires.
# Therefore you have to make sure to set the amount of open files
# allowed to at least 4096 in the variable "open-files-limit" in
# section [mysqld_safe]
table_open_cache=256
# Maximum size for internal (in-memory) temporary tables. If a table
# grows larger than this value, it is automatically converted to disk
# based table This limitation is for a single table. There can be many
# of them.
tmp_table_size=16M
# How many threads we should keep in a cache for reuse. When a client
# disconnects, the client's threads are put in the cache if there aren't
# more than thread_cache_size threads from before. This greatly reduces
# the amount of thread creations needed if you have a lot of new
# connections. (Normally this doesn't give a notable performance
# improvement if you have a good thread implementation.)
thread_cache_size=10
# *** MyISAM Specific options
# The maximum size of the temporary file MySQL is allowed to use while
# recreating the index (during REPAIR, ALTER TABLE or LOAD DATA INFILE.
# If the file-size would be bigger than this, the index will be created
# through the key cache (which is slower).
myisam_max_sort_file_size=100G
# If the temporary file used for fast index creation would be bigger
# than using the key cache by the amount specified here, then prefer the
# key cache method. This is mainly used to force long character keys in
# large tables to use the slower key cache method to create the index.
myisam_sort_buffer_size=8M
# Size of the Key Buffer, used to cache index blocks for MyISAM tables.
# Do not set it larger than 30% of your available memory, as some memory
# is also required by the OS to cache rows. Even if you're not using
# MyISAM tables, you should still set it to 8-64M as it will also be
# used for internal temporary disk tables.
key_buffer_size=8M
# Size of the buffer used for doing full table scans of MyISAM tables.
# Allocated per thread, if a full scan is needed.
read_buffer_size=16M
read_rnd_buffer_size=0
# *** INNODB Specific options ***
# innodb_data_home_dir=
# Use this option if you have a MySQL server with InnoDB support enabled
# but you do not plan to use it. This will save memory and disk space
# and speed up some things.
# skip-innodb=
# If set to 1, InnoDB will flush (fsync) the transaction logs to the
# disk at each commit, which offers full ACID behavior. If you are
# willing to compromise this safety, and you are running small
# transactions, you may set this to 0 or 2 to reduce disk I/O to the
# logs. Value 0 means that the log is only written to the log file and
# the log file flushed to disk approximately once per second. Value 2
# means the log is written to the log file at each commit, but the log
# file is only flushed to disk approximately once per second.
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1
# The size of the buffer InnoDB uses for buffering log data. As soon as
# it is full, InnoDB will have to flush it to disk. As it is flushed
# once per second anyway, it does not make sense to have it very large
# (even with long transactions).
innodb_log_buffer_size=1M
# InnoDB, unlike MyISAM, uses a buffer pool to cache both indexes and
# row data. The bigger you set this the less disk I/O is needed to
# access data in tables. On a dedicated database server you may set this
# parameter up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. Do not set it
# too large, though, because competition of the physical memory may
# cause paging in the operating system. Note that on 32bit systems you
# might be limited to 2-3.5G of user level memory per process, so do not
# set it too high.
innodb_buffer_pool_size=8M
# Size of each log file in a log group. You should set the combined size
# of log files to about 25%-100% of your buffer pool size to avoid
# unneeded buffer pool flush activity on log file overwrite. However,
# note that a larger logfile size will increase the time needed for the
# recovery process.
innodb_log_file_size=48M
# Number of threads allowed inside the InnoDB kernel. The optimal value
# depends highly on the application, hardware as well as the OS
# scheduler properties. A too high value may lead to thread thrashing.
innodb_thread_concurrency=9
# The increment size (in MB) for extending the size of an auto-extend InnoDB system tablespace file when it becomes full.
innodb_autoextend_increment=64
# The number of regions that the InnoDB buffer pool is divided into.
# For systems with buffer pools in the multi-gigabyte range, dividing the buffer pool into separate instances can improve concurrency,
# by reducing contention as different threads read and write to cached pages.
innodb_buffer_pool_instances=8
# Determines the number of threads that can enter InnoDB concurrently.
innodb_concurrency_tickets=5000
# Specifies how long in milliseconds (ms) a block inserted into the old sublist must stay there after its first access before
# it can be moved to the new sublist.
innodb_old_blocks_time=1000
# It specifies the maximum number of .ibd files that MySQL can keep open at one time. The minimum value is 10.
innodb_open_files=300
# When this variable is enabled, InnoDB updates statistics during metadata statements.
innodb_stats_on_metadata=0
# When innodb_file_per_table is enabled (the default in 5.6.6 and higher), InnoDB stores the data and indexes for each newly created table
# in a separate .ibd file, rather than in the system tablespace.
innodb_file_per_table=1
# Use the following list of values: 0 for crc32, 1 for strict_crc32, 2 for innodb, 3 for strict_innodb, 4 for none, 5 for strict_none.
innodb_checksum_algorithm=0
# The number of outstanding connection requests MySQL can have.
# This option is useful when the main MySQL thread gets many connection requests in a very short time.
# It then takes some time (although very little) for the main thread to check the connection and start a new thread.
# The back_log value indicates how many requests can be stacked during this short time before MySQL momentarily
# stops answering new requests.
# You need to increase this only if you expect a large number of connections in a short period of time.
back_log=80
# If this is set to a nonzero value, all tables are closed every flush_time seconds to free up resources and
# synchronize unflushed data to disk.
# This option is best used only on systems with minimal resources.
flush_time=0
# The minimum size of the buffer that is used for plain index scans, range index scans, and joins that do not use
# indexes and thus perform full table scans.
join_buffer_size=256K
# The maximum size of one packet or any generated or intermediate string, or any parameter sent by the
# mysql_stmt_send_long_data() C API function.
# If more than this many successive connection requests from a host are interrupted without a successful connection,
# the server blocks that host from performing further connections.
max_connect_errors=100
# Changes the number of file descriptors available to mysqld.
# You should try increasing the value of this option if mysqld gives you the error "Too many open files".
open_files_limit=4161
# If you see many sort_merge_passes per second in SHOW GLOBAL STATUS output, you can consider increasing the
# sort_buffer_size value to speed up ORDER BY or GROUP BY operations that cannot be improved with query optimization
# or improved indexing.
sort_buffer_size=256K
# The number of table definitions (from .frm files) that can be stored in the definition cache.
# If you use a large number of tables, you can create a large table definition cache to speed up opening of tables.
# The table definition cache takes less space and does not use file descriptors, unlike the normal table cache.
# The minimum and default values are both 400.
table_definition_cache=1400
# Specify the maximum size of a row-based binary log event, in bytes.
# Rows are grouped into events smaller than this size if possible. The value should be a multiple of 256.
binlog_row_event_max_size=8K
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, a replication slave synchronizes its master.info file to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_master_info events.
sync_master_info=10000
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, the MySQL server synchronizes its relay log to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_relay_log writes to the relay log.
sync_relay_log=10000
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, a replication slave synchronizes its relay-log.info file to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_relay_log_info transactions.
sync_relay_log_info=10000
# Load mysql plugins at start."plugin_x ; plugin_y".
# plugin_load=
# MySQL server's plugin configuration.
# loose_mysqlx_port=33060
#log-bin=mysql-bin
group_concat_max_len=1024000
server-id=1
log-bin=mysql-bin
#设置每用户最大的 连接数300
max_user_connections=300
#10分钟没有交互将关闭连接
wait_timeout = 600
#服务器关闭交互式连接前等待活动的秒数
interactive_timeout = 900
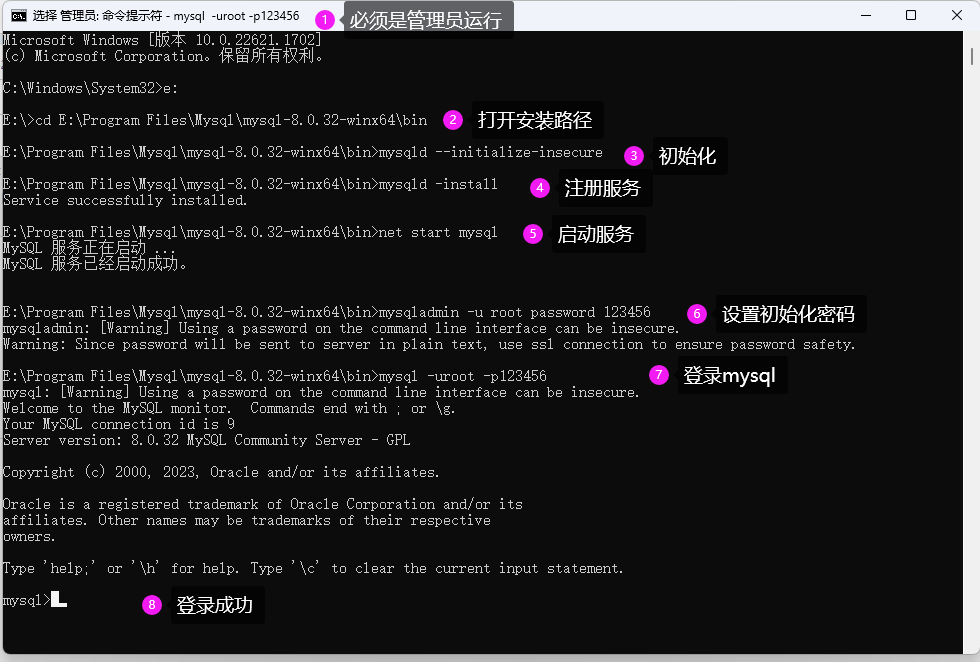
3.初始化
mysqld --initialize-insecure
执行成功后,会创建【datadir=E:\Program Files\Mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\Data 】文件夹,并且在文件夹中生成一些文件,如图:
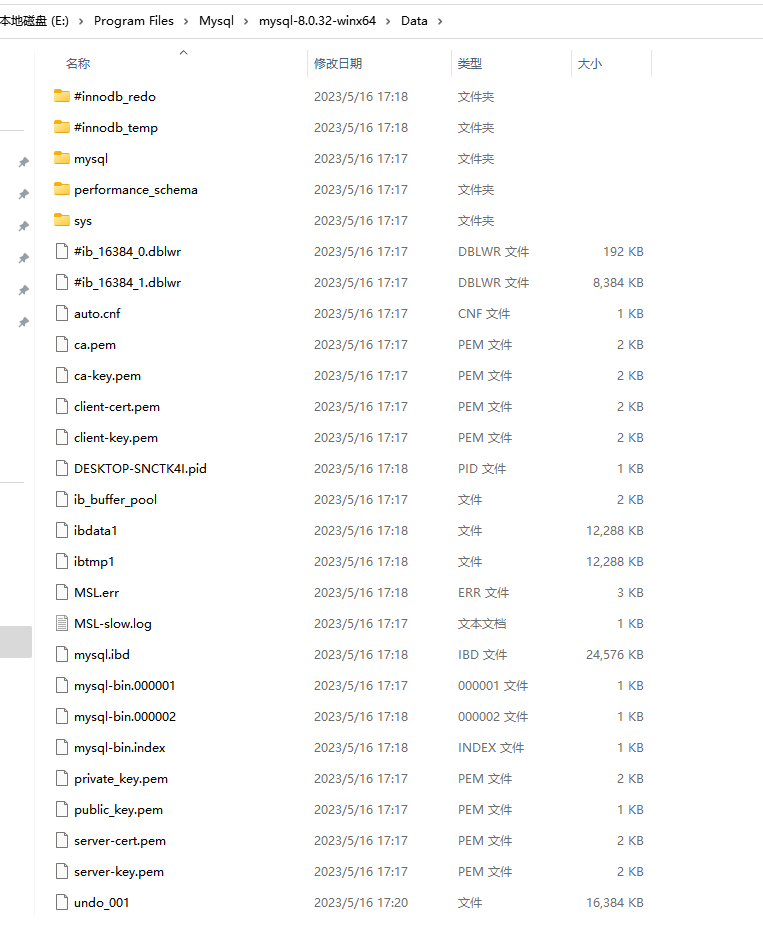
4.注册MySQL服务
mysqld -install
执行成功后,显示:【Service successfully installed.】
5.启动MySQL服务
net start mysql
执行成功后,显示:【MySQL 服务已经启动成功。】
6.修改默认账户密码
mysqladmin -u root password 123456
7.登录MySQL
mysql -uroot -p123456
执行成功后,显示:【mysql>】
安装成功验证:
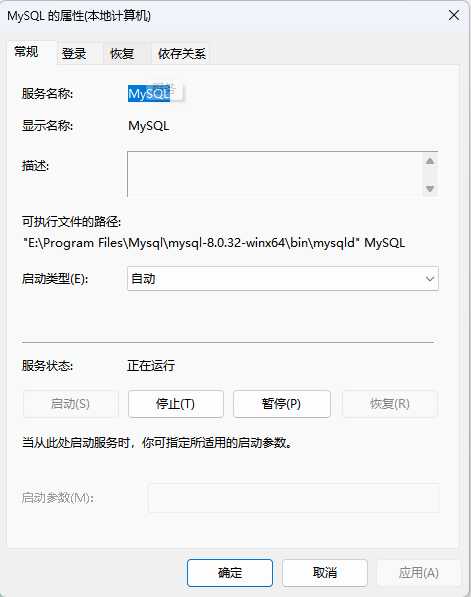
还原历史数据库数据
1.停止服务【MySql】
2.将历史数据库的文件【ibdata1,mysql.ibd】复制到路径【datadir=E:\Program Files\Mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\Data 】
3.将历史数据库的数据库文件复制到路径【datadir=E:\Program Files\Mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\Data 】
4.启动服务【MySql】
修改登录密码
未验证 https://blog.csdn.net/TH_NUM/article/details/71402801
进入mysql数据库
输入以下命令:mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p
执行上面的命令后,会提示输入密码,输入密码后回车,当显示下面的界面时表示成功链接到了mysql数据库。
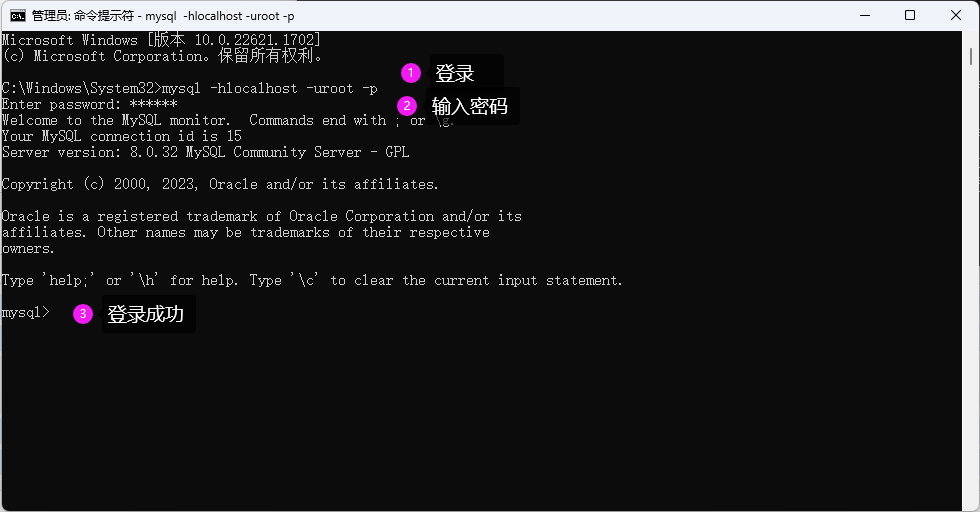



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2017-05-16 easyui 绑定下拉框,下拉框选择改变事件的触发方法
2017-05-16 easyui 改列名