ArrayList集合详解
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
public interface RandomAccess { }
RandomAccess接口是一个标志接口(Marker),这个可以查看Collections的源码查看
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) { if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size()<BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD) return Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key); else return Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key); }
从上面源码可以得出结论:如果实现RandomAccess接口或者集合的实际存储值小于5000,就使用就采用 index 的方式遍历, 反之就采用 iterator 的方式遍历。
2、成员变量说明
/** * Default initial capacity. */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
没有给定集合长度默认是10
/** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */ private int size;
ArrayList实际存储的长度
protected transient int modCount = 0;
这个变量是定义在 AbstractList 中的。记录对 List 操作的次数。主要使用是在 Iterator,是防止在迭代的过程中集合被修改
/** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when * first element is added. */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
3、构造函数:
3.1、无参构造器
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
配合add的这段代码
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; }
注意:注释是说构造一个容量大小为 10 的空的 list 集合,但构造函数了只是给 elementData 赋值了一个空的数组,其实是在第一次添加元素时容量扩大至 10 的。
3.2、有参构造器
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } }
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; }
每次添加元素的时候都要确认容器的大小,拿实际存储的长度+1去和能够存储的长度elementData.length进行比较,如果实际长度大于能够存储的长度就会进行扩容,扩容的时候
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
newCapacity = (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 来扩容。然后将原数组中的数据复制到大小为 newCapacity 的新数组中,并将新数组赋值给 elementData。private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }
public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
参数:
src:要复制的数组(源数组)
srcPos:复制源数组的起始位置
dest:目标数组
destPos:目标数组的下标位置
length:要复制的长度
remove 操作
public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }
当调用 remove(int index) 时,首先会检查 index 是否合法,然后再判断要删除的元素是否位于数组的最后一个位置。如果 index 不是最后一个,就再次调用 System.arraycopy() 方法拷贝数组。然后将数组的最后一个位置空,size - 1;
当调用remove(Object o)时,首先判断o是否为null,如果为null,就在elementData寻找值为null的,然后调用fastRemove删除,过程和remove(int index) 差不多。
get过程
public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
首先判断数组有没有越界,如果没有直接根据下标获取数据返回。
5、迭代器 iterator
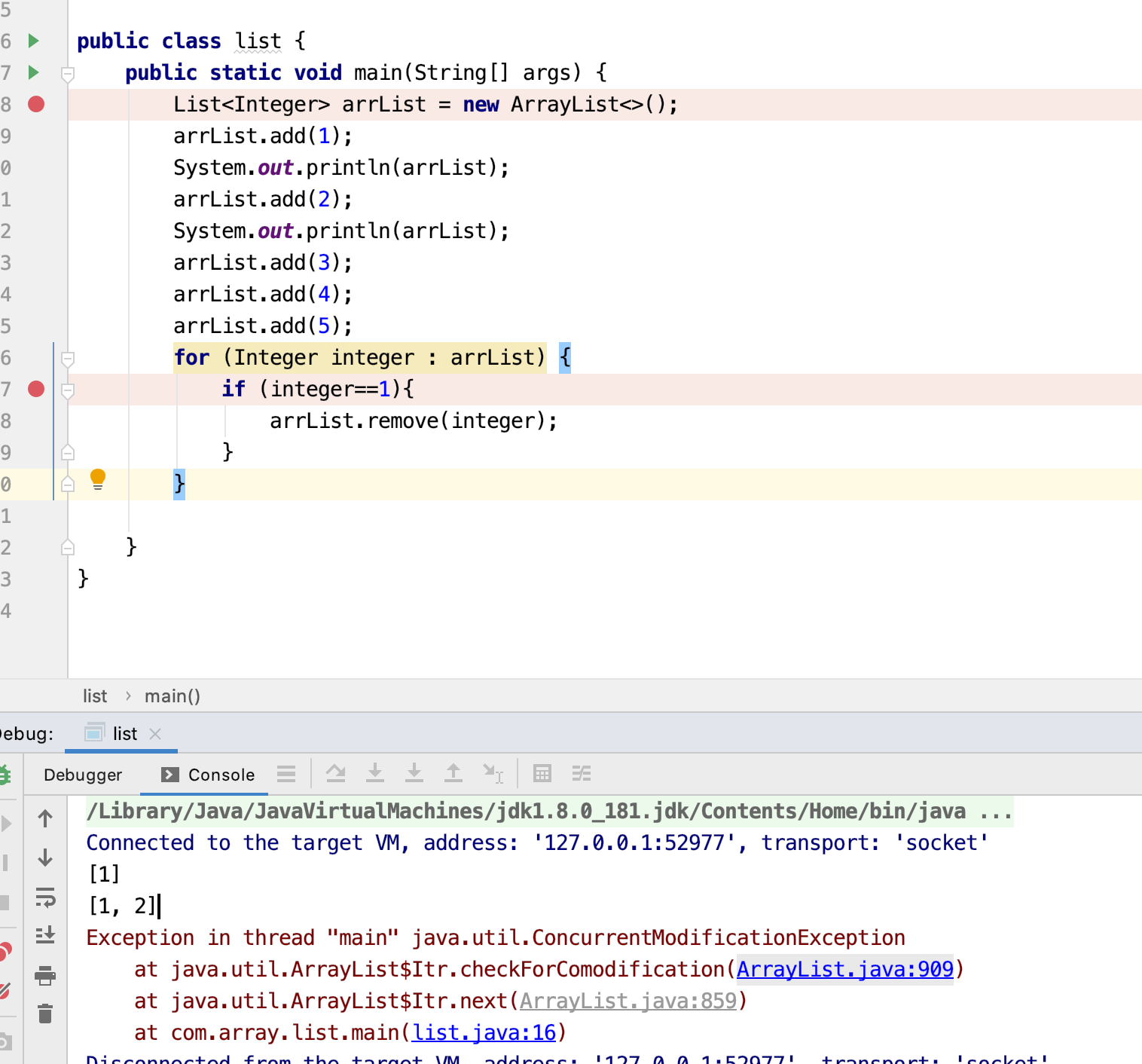
在用 增强for 遍历集合的时候是不可以对集合进行 remove操作的,因为 remove 操作会改变集合的大小。从而容易造成结果不准确甚至数组下标越界,更严重者还会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。
5、迭代器 iterator
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
cursor:代表下一个要访问的元素下标。 lastRet:代表当前访问的元素的下标,刚开始默认是-1。 expectedModCount:代表对 ArrayList 修改次数的期望值,初始值为 modCount
下面看看 Itr 的三个主要函数
hasNext 如果下一个元素的下标等于集合的大小 ,就证明到最后了
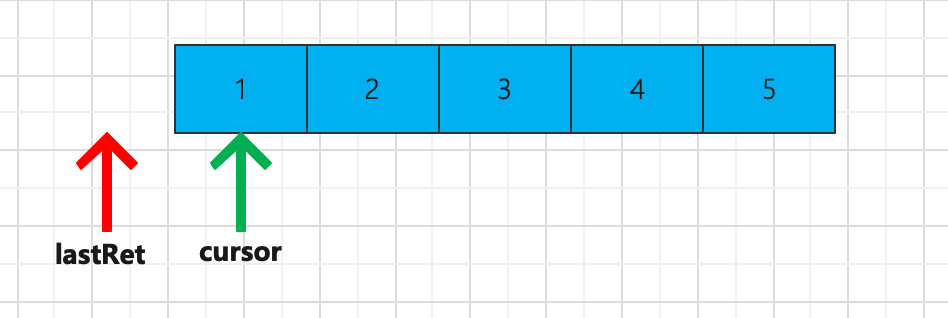
当调用next的时候lastRet变为0而cursor变为1,当0的位置的值为1的时候,执行ArrayList的remove,这时候modCount+1,而expectedModCount不变,这时候modCount和expectedModCount不相等
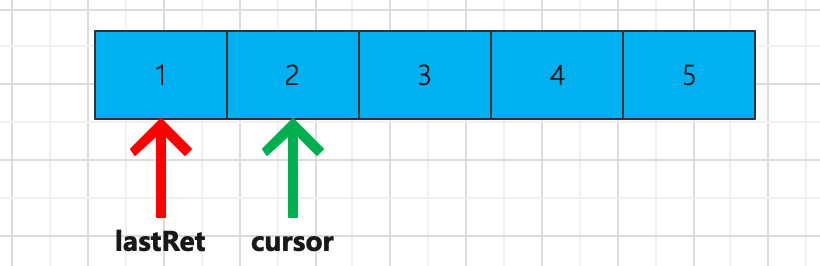
当调用next的时候,首先检查modCount和expectedModCount是否相等,如果不相等就报错:ConcurrentModificationException
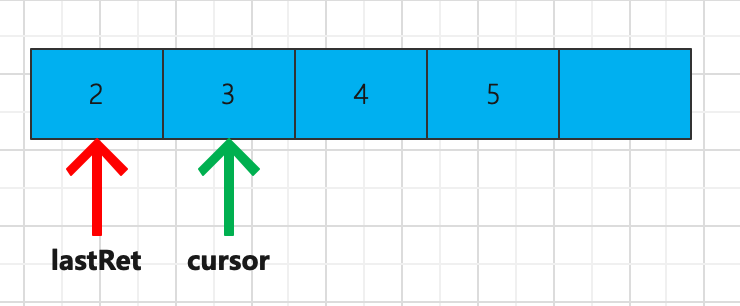
直接调用 iterator.remove() 即可。因为在该方法中增加了 expectedModCount = modCount 操作
但是这个 remove 方法也有弊端。
- 只能进行remove操作,add、clear 等 Itr 中没有。
- 调用 remove 之前必须先调用 next。因为 remove 开始就对 lastRet 做了校验。而 lastRet 初始化时为 -1。
- next 之后只可以调用一次 remove。因为 remove 会将 lastRet 重新初始化为 -1
newCapacity = (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 来扩容。 扩容之后是通过数组的拷贝来确保元素的准确性的,所以尽可能减少扩容操作。 ArrayList 的最大存储能力:Integer.MAX_VALUE。 size 为集合中存储的元素的个数。elementData.length 为数组长度,表示最多可以存储多少个元素。 如果需要边遍历边 remove ,必须使用 iterator。且 remove 之前必须先 next,next 之后只能用一次 remove。 





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构