【Java基础总结】IO流

字节流
1. InputStream 字节输入流

代码演示
1 InputStream in = System.in; 2 3 System.out.println("int read(byte b) 方法演示"); 4 //int read() 5 int bt = 0; 6 while((bt=in.read())>0){ 7 System.out.print(bt+" "); 8 if(bt == 10){ //回车\r(13) 换行\n(10) 9 break; 10 } 11 } 12 System.out.println("\n\rint read(byte[] buffer) 方法演示"); 13 14 //int read(byte[] buffer) 15 int length = 0; 16 byte[] buffer = new byte[10]; 17 while((length=in.read(buffer)) != 0){ 18 for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ 19 System.out.print(buffer[i]+" "); 20 } 21 break; 22 } 23 24 System.out.println("\n\rint read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int len) 方法演示"); 25 26 //int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int len) 27 int len = 1024; 28 int count = 0; 29 byte[] buf = new byte[len]; 30 while((count=in.read(buf, 0, len))>0){ 31 for(int i=0; i<count; i++){ 32 System.out.print(buf[i]+" "); 33 } 34 break; 35 } 36 in.close();
2. OutputStream 字节输出流
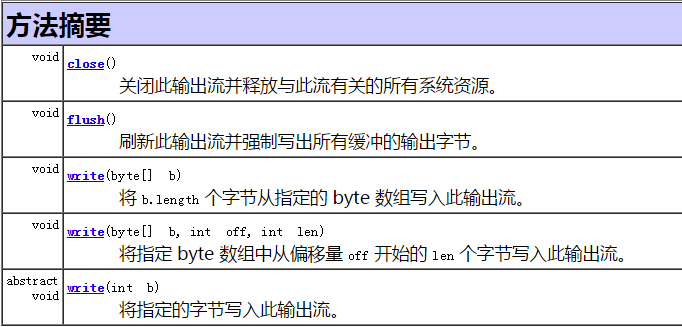
代码演示
1 OutputStream out = System.out; 2 //void write(int b) 3 out.write(65); //字符A 4 5 out.write(13); //回车 \r 6 out.write(10); //换行 \n 7 8 //flush() 9 out.flush(); 10 11 //write(byte[] bytes) 12 byte[] bytes = new String("张晓明").getBytes(); 13 out.write(bytes); 14 15 out.write(13); //回车 \r 16 out.write(10); //换行 \n 17 18 //write(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) 19 bytes = new String("zhangxiaoming").getBytes(); 20 out.write(bytes, 5, 8); 21 22 out.close();
字符流
1. Reader 字符输入流
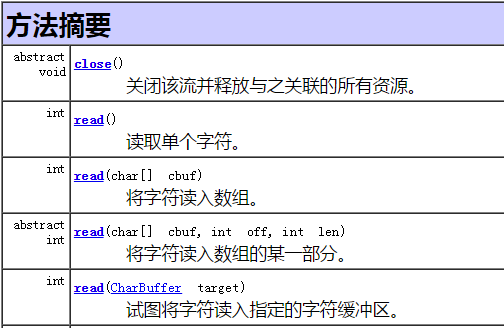
代码演示
1 Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in); 2 3 //int read() 4 System.out.println("int read() 方法演示"); 5 int c; 6 while((c=reader.read()) != 13){ 7 System.out.print((char)c); 8 } 9 reader.read(); 10 11 //int read(char[] buf) 12 System.out.println("\n\rint read(char[] buf) 方法演示"); 13 int count = 0; 14 char[] buf = new char[1024]; 15 while((count=reader.read(buf)) > 0){ 16 String str = new String(buf, 0, count); 17 if(str.indexOf("stop")>=0) break; 18 System.out.print(str); 19 } 20 21 //int read(char[] buffer, int offset, int len) 22 System.out.println("\n\rint read(char[] buffer, int offset, int len) 方法演示"); 23 int length = 1024; 24 char[] buffer = new char[length]; 25 while((count=reader.read(buffer, 0, length)) > 0){ 26 String str = new String(buffer, 0, count); 27 if(str.indexOf("stop")>=0) break; 28 System.out.print(str); 29 }
2. Writer 字符输出流
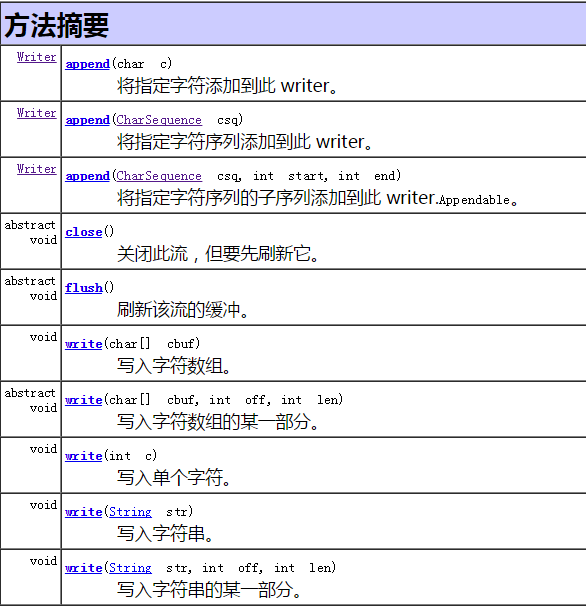
代码演示
1 Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out); 2 String str = "中国"; 3 4 //write(String str) 写入字符串 5 writer.write(str); 6 7 //write(int c) 写入单个字符 8 writer.write(10); //换行符 9 10 //write(String str, int offset, int length) 写入部分字符串 11 writer.write(str, 0, 1); 12 13 writer.write(10); 14 15 //write(char[] buf) 写入字符数组 16 char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); 17 writer.write(chars); 18 19 writer.write(10); 20 21 //write(char[] buf, int offset, int length) 写入部分字符数组 22 writer.write(chars, 0, 1); 23 writer.write(10); 24 25 writer.flush(); 26 27 //append(char c) 追加字符 28 writer.append('z'); 29 writer.write(10); 30 31 String str2 = "中华人民共和国"; 32 //append(CharSequence csq) 33 writer.append(str2); 34 writer.write(10); 35 36 //append(CharSequence csq, int offset, int length) 37 writer.append(str2, 0, 4); 38 39 writer.close();

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号