扩展 IHttpModule
上篇提到请求进入到System.Web后,创建完HttpApplication对象后会执行一堆的管道事件,然后可以通过HttpModule来对其进行扩展,那么这篇文章就来介绍下如何定义我们自己的module来实现对项目的一些扩展。
先看一下IHttpModule的接口源码,只有Dispose()和Init(HttpApplication context)这两个方法,从方法名称我们就可以知道Dispose方法是用来释放资源的,而Init方法自然就是用来初始化的,一般仅用于给期望的HttpApplication事件注册方法。
using System; using System.Security.Permissions; namespace System.Web { /// <summary> /// Provides module initialization and disposal events to the implementing class. /// </summary> [AspNetHostingPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Level = AspNetHostingPermissionLevel.Minimal), AspNetHostingPermission(SecurityAction.InheritanceDemand, Level = AspNetHostingPermissionLevel.Minimal)] public interface IHttpModule { /// <summary> /// Initializes a module and prepares it to handle requests. /// </summary> /// <param name="context"> /// An <see cref="T:System.Web.HttpApplication" /> that provides access to the methods, properties, and events common to all application objects within an ASP.NET application /// </param> void Init(HttpApplication context); /// <summary> /// Disposes of the resources (other than memory) used by the module that implements <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpModule" />. /// </summary> void Dispose(); } }
Init方法拥有HttpApplication的参数,那么我们先来实现一个自己定义的HttpModule。实现自定义的httpmodule需要实现IHttpModule接口。
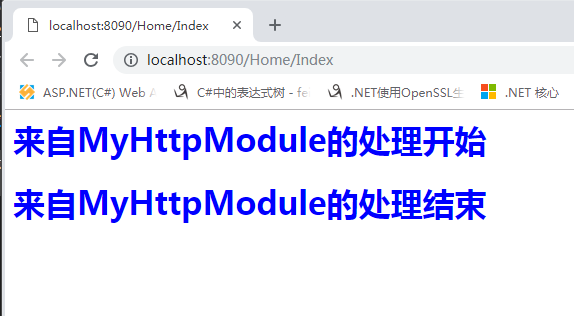
namespace Jesen.Web.Core { /// <summary> /// 自定义实现HttpModule,实现IHttpModule接口 /// </summary> public class MyHttpModule : IHttpModule { public void Dispose() { } public void Init(HttpApplication context) { //在此处添加管道事件的处理 context.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(Context_BeginRequest); context.EndRequest += new EventHandler(Context_EndRequest); } private void Context_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication context = sender as HttpApplication; context.Response.Write("<h1 style='color:#00f'>来自MyHttpModule的处理开始</h1>"); } private void Context_EndRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication context = sender as HttpApplication; context.Response.Write("<h1 style='color:#00f'>来自MyHttpModule的处理结束</h1>"); } } }
实现完IHttpModule接口后我们还需要对自定义的HttpModule进行注册,注册的方式是通过web.config来配置。
VS2013及以后/IIS7.0之后的集成模式的配置位置:
<system.webServer>
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="false">
<!--runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests处理静态文件的请求-->
<remove name="FormsAuthentication" />
<remove name="WindowsAuthentication" />
<remove name="PassportAuthentication" />
<remove name="RoleManager" />
<remove name="FileAuthorization" />
<remove name="UrlAuthorization" />
<add name="MyHttpModule" type="Jesen.Web.Core.MyHttpModule,Jesen.Web.Core"/>
</system.webServer>
如果是VS2013以前/IIS7.0之前和经典模式的配置位置:
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" />
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" />
<!--<httpModules>
<remove name="FormsAuthentication" />
<add name="MyHttpModule" type="Jesen.Web.Core.MyHttpModule,Jesen.Web.Core" />
<add name="ApplicationInsightsWebTracking" type="Microsoft.ApplicationInsights.Web.ApplicationInsightsHttpModule, Microsoft.AI.Web" />
</httpModules>
</system.web>
接着我们运行程序,浏览器访问结果如下,浏览器输出我们上面自定义的HttpModule处理事件的代码。
其实module对所有请求都起作用,在每次接收到请求的时候,都会有一堆的Module被执行,因为.Net框架已经在全局配置文件里面配好了一些必要的module,该配置文件地址:C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\Config\web.config,我们可以在自己的项目中的web.config文件中去移除一些不需要的module,例如上面的 <remove name="FormsAuthentication" />移除了Form表单验证。全局web.config配置文件对httpModule的配置如下:

至此我们可以总结一下module的作用,1、可以用来做权限认证;2、可以做Url转发;3、可以做性能监控;4、可以用来做反爬虫,检测同一个IP频繁的请求。当然,module不适合单独为某些请求而服务,因为它是针对所有请求的。
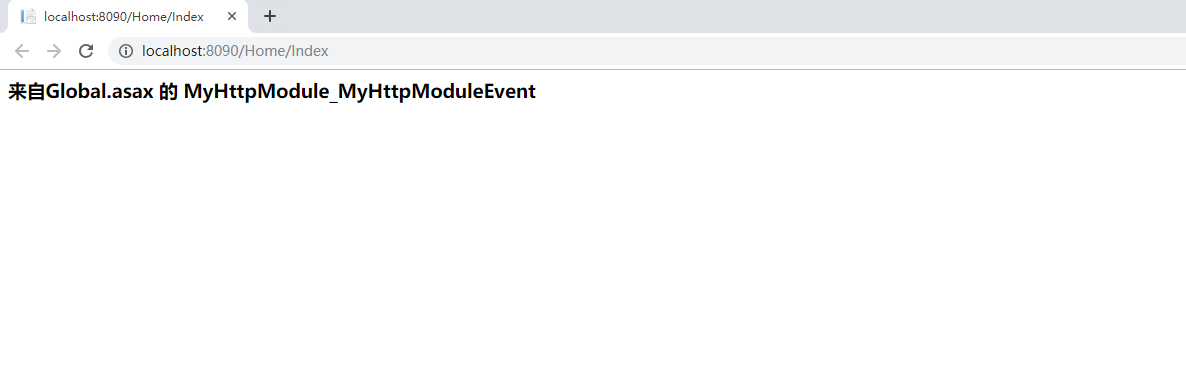
接下来我们来看下asp.net中的另一类事件,我们把代码改了一下,在我们自定义的Module里面我们定义了一个事件MyHttpModuleEvent,我们依然按照上面注册module的方法在web.config文件中注册好MyHttpModule。不同的是我们在项目启动文件Global.asax.cs文件中添加了 以web.config注册模块的名称_Module中的事件的一个方法。运行项目之后,我们发现该方法MyHttpModule_MyHttpModuleEvent被调用了。
/// <summary> /// 自定义实现HttpModule,实现IHttpModule接口 /// </summary> public class MyHttpModule : IHttpModule { public event EventHandler MyHttpModuleEvent; public void Dispose() { } public void Init(HttpApplication context) { //在此处添加管道事件的处理 context.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(Context_BeginRequest); context.EndRequest += new EventHandler(Context_EndRequest); } private void Context_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication application = sender as HttpApplication; HttpContext context = application.Context;//Url重写 if (context.Request.Url.AbsolutePath.Equals("/Pipe/Some", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) context.RewritePath("/Pipe/Another"); if (MyHttpModuleEvent!= null) MyHttpModuleEvent.Invoke(this, e); } private void Context_EndRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication application = sender as HttpApplication; HttpContext context = application.Context; } }
protected void MyHttpModule_MyHttpModuleEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) { Response.Write("<h3>来自Global.asax 的 MyHttpModule_MyHttpModuleEvent</h2>"); }
那么为什么这个方法会被调用,这个其实是.Net框架约定俗成的。约定命名方式:HttpModule注册名称_事件名称,而这个事件的执行时机是由我们在自定义的module中确定的。
最后我们来看下Global.asax.cs文件中的一些方法。
/// <summary>
/// 网站启动时,响应第一次请求的执行的 /// 以后再以不执行了 /// 挺合适做一些初始化 /// </summary> protected void Application_Start() { AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();//注册区域路由 GlobalConfiguration.Configure(WebApiConfig.Register);//注册webapi路由 FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);//注册全局过滤器 RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);//注册路由 BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles); }
protected void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { //在应用程序关闭时运行的代码 logger.Info("Application_End"); } /// <summary> /// 请求出现异常,都可以处理 /// 也可以完成全局异常处理 /// filter只能处理控制器里面的异常 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> protected void Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e) { // 在出现未处理的错误时运行的代码 var error = Server.GetLastError(); logger.Info("Application_Error"); Response.Write("出错"); Server.ClearError(); } protected void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { // 在新会话启动时运行的代码 logger.Info("Session_Start"); } protected void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { // 在会话结束时运行的代码。 // 注意: 只有在 Web.config 文件中的 sessionstate 模式设置为 // InProc(默认内存里) 时,才会引发 Session_End 事件。如果会话模式设置为 StateServer // 或 SQLServer,则不会引发该事件。 logger.Info("Session_End"); }
从该文件中,我们可以看到Session_Start和Session_End两个方法,它们的调用也是.Net框架约定的,因为我们通过反射查看SessionStateModule的源码,可以看到其定义了Start和End两个事件。
public event EventHandler Start { add { this._sessionStartEventHandler = (EventHandler)Delegate.Combine(this._sessionStartEventHandler, value); } remove { this._sessionStartEventHandler = (EventHandler)Delegate.Remove(this._sessionStartEventHandler, value); } } public event EventHandler End { add { SessionOnEndTarget onEndTarget = this._onEndTarget; lock (onEndTarget) { if (this._store != null && this._onEndTarget.SessionEndEventHandlerCount == 0) { this._supportSessionExpiry = this._store.SetItemExpireCallback(new SessionStateItemExpireCallback(this._onEndTarget.RaiseSessionOnEnd)); } SessionOnEndTarget expr_4E = this._onEndTarget; int sessionEndEventHandlerCount = expr_4E.SessionEndEventHandlerCount + 1; expr_4E.SessionEndEventHandlerCount = sessionEndEventHandlerCount; } } remove { SessionOnEndTarget onEndTarget = this._onEndTarget; lock (onEndTarget) { SessionOnEndTarget expr_17 = this._onEndTarget; int sessionEndEventHandlerCount = expr_17.SessionEndEventHandlerCount - 1; expr_17.SessionEndEventHandlerCount = sessionEndEventHandlerCount; if (this._store != null && this._onEndTarget.SessionEndEventHandlerCount == 0) { this._store.SetItemExpireCallback(null); this._supportSessionExpiry = false; } } } }
需要注意的是在每处理一个Http请求时,应用程序事件都会触发一遍,但是Application_Start和 Application_End 例外,它仅在第一个资源文件被访问时被触发。Http Module无法注册和响应Session事件,对于Session_Start 和 Session_End,只能通过Glabal.asax来处理。




