19 深入特权级转移(中)
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/wanmeishenghuo/tag/%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F/
https://blog.51cto.com/13475106/category6.html
处理器通过什么规则判断资源请求或者代码跳转是否合法?
数据段的访问规则:(数据段无可执行属性)
访问者权限(CPL)高于或者等于数据段权限(DPL)
请求特权级(RPL)高于或者等于数据段权限(DPL)
即(CPL <= DPL)&& (RPL <= DPL)
上面的公式没有阐述CPL和RPL的关系,这是因为对数据段进行访问的时候CPL和RPL是没有关系的。
怎么判断一个段是不是数据段呢?
这就要根据有无可执行属性来判断了,无可执行属性就是数据段了。
访问示例:
CPL=2, RPL=1, DPL=3,是否合法?合法
CPL=0, RPL=3, DPL=2,是否合法?不合法
CPL=0, RPL=1, DPL=2,是否合法?合法
合法性的检查发生在对段寄存器赋值的时候,例如mov ds, ax。
每个特权级都有不同的栈,每个特权级只能使用自己特权级的栈,例如,0特权级只能使用0特权级的栈,3特权级只能使用3特权级的栈。
如果0特权级使用2特权级的栈,则在mov ss, ax的时候会报错。
对于栈来说段描述符的DPL也要和栈段选择子的RPL相等。
对于栈段来说:
当为ss寄存器赋值时,使用规则(CPL==RPL)&& (CPL==DPL)保证特权级的匹配。
定义栈的时候要让RPL和DPL的值相同。
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 | %include "inc.asm"org 0x9000jmp ENTRY_SEGMENT[section .gdt]; GDT definition; 段基址, 段界限, 段属性GDT_ENTRY : Descriptor 0, 0, 0CODE32_DESC : Descriptor 0, Code32SegLen - 1, DA_C + DA_32 + DA_DPL0VIDEO_DESC : Descriptor 0xB8000, 0x07FFF, DA_DRWA + DA_32 + DA_DPL3DATA32_DESC : Descriptor 0, Data32SegLen - 1, DA_DR + DA_32 + DA_DPL2STACK32_DESC : Descriptor 0, TopOfStack32, DA_DRW + DA_32 + DA_DPL0; GDT endGdtLen equ $ - GDT_ENTRYGdtPtr: dw GdtLen - 1 dd 0 ; GDT SelectorCode32Selector equ (0x0001 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL0VideoSelector equ (0x0002 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL3Data32Selector equ (0x0003 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL1Stack32Selector equ (0x0004 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL0; end of [section .gdt]; CPL = 2, RPL = 1, DPL = 3, 访问是否合法? ===> yes; CPL = 0, RPL = 3, DPL = 2, 访问是否合法? ===> no; CPL = 0, RPL = 1, DPL = 2, 访问是否合法? ===> yesTopOfStack16 equ 0x7c00[section .s16][bits 16]ENTRY_SEGMENT: mov ax, cs mov ds, ax mov es, ax mov ss, ax mov sp, TopOfStack16 ; initialize GDT for 32 bits code segment mov esi, CODE32_SEGMENT mov edi, CODE32_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, DATA32_SEGMENT mov edi, DATA32_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, STACK32_SEGMENT mov edi, STACK32_DESC call InitDescItem ; initialize GDT pointer struct mov eax, 0 mov ax, ds shl eax, 4 add eax, GDT_ENTRY mov dword [GdtPtr + 2], eax ; 1. load GDT lgdt [GdtPtr] ; 2. close interrupt cli ; 3. open A20 in al, 0x92 or al, 00000010b out 0x92, al ; 4. enter protect mode mov eax, cr0 or eax, 0x01 mov cr0, eax ; 5. jump to 32 bits code ; push Stack32Selector ; 目标栈段选择子 ; push TopOfStack32 ; 栈顶指针位置 ; push Code32Selector ; 目标代码段选择子 ; push 0 ; 目标代码段偏移 ; retf jmp word Code32Selector : 0; esi --> code segment label; edi --> descriptor labelInitDescItem: push eax mov eax, 0 mov ax, cs shl eax, 4 add eax, esi mov word [edi + 2], ax shr eax, 16 mov byte [edi + 4], al mov byte [edi + 7], ah pop eax ret[section .dat][bits 32]DATA32_SEGMENT: DTOS db "D.T.OS!", 0 DTOS_OFFSET equ DTOS - $$Data32SegLen equ $ - DATA32_SEGMENT [section .s32][bits 32]CODE32_SEGMENT: mov ax, VideoSelector mov gs, ax mov ax, Data32Selector mov ds, ax mov ax, Stack32Selector mov ss, ax mov eax, TopOfStack32 mov esp, eax mov ebp, DTOS_OFFSET mov bx, 0x0C mov dh, 12 mov dl, 33 call PrintString jmp $ ; ds:ebp --> string address; bx --> attribute; dx --> dh : row, dl : colPrintString: push ebp push eax push edi push cx push dx print: mov cl, [ds:ebp] cmp cl, 0 je end mov eax, 80 mul dh add al, dl shl eax, 1 mov edi, eax mov ah, bl mov al, cl mov [gs:edi], ax inc ebp inc dl jmp printend: pop dx pop cx pop edi pop eax pop ebp ret Code32SegLen equ $ - CODE32_SEGMENT[section .gs][bits 32]STACK32_SEGMENT: times 1024 * 4 db 0 Stack32SegLen equ $ - STACK32_SEGMENTTopOfStack32 equ Stack32SegLen - 1 |
结论:
选择子被段寄存器加载时,会进行保护模式的检查
检查选择子的下标是否合法(段描述符的合法性,前面博客写过)
检查特权级是否合法,(CPL & RPL <= DPL)
检查特权级时CPL和RPL之间不会进行比较(仅对普通数据段的访问成立,不包括栈段的使用)
代码段的分类:
非系统段(S=1)
一致性代码段
非一致性代码段
系统段(S=0)
LDT, TSS, 各种门结构
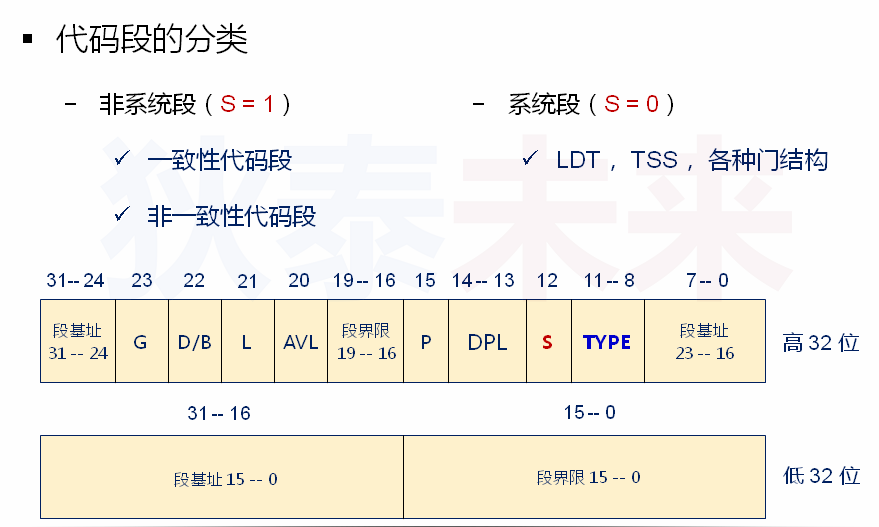
S是段描述符中的一个位域。
这里的系统不是指的操作系统,而是处理器本身。
LDT和TSS是用于多任务实现的结构,一般叫做系统段。
非系统段就是我们定义的数据段、代码段等。
代码段又分为两类,一致性代码段和非一致性代码段,这个概念就和段描述符中的TYPE位域有关了。

TYPE域有5位,A、R、C、X、S。
一致性代码段:X=1 C=1
非一致性代码段:X=1 C=0
一致性和非一致性有什么区别呢?
代码段之间的跳转规则(我们这里讲解的跳转是不借助门描述符的)

非一致性代码段
代码段之间只能平级转移(CPL==DPL, RPL<=DPL)CPL和RPL不用比较
一致性代码段
支持低特权级代码向高特权级代码的转移(CPL>=DPL),高跳到低不允许
虽然可以成功转移到高特权级代码段,但是当前特权级不变,特权级不变,栈就不变
非一致性代码段能跳转到一致性代码段,可以从低特权级的代码段跳转到高特权级代码段,高跳到低不允许
一致性代码段能跳到非一致性代码段(这时在一致性代码段中的特权级是由原来跳转到这个代码段时非一致性代码段的特权级决定的,因为上面我们说了特权级不变)
数据段只有一种,没有一致性和非一致性的区分,并且数据段不允许被低特权级的代码段访问。
降特权级跳转(retf)时,目标代码段特权级与目标栈段特权级必须完全相同,即(ss.rpl==cs.rpl)&& (ss.dpl==cs.rpl)
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 | %include "inc.asm"org 0x9000jmp ENTRY_SEGMENT[section .gdt]; GDT definition; 段基址, 段界限, 段属性GDT_ENTRY : Descriptor 0, 0, 0CODE32_DESC : Descriptor 0, Code32SegLen - 1, DA_C + DA_32 + DA_DPL1VIDEO_DESC : Descriptor 0xB8000, 0x07FFF, DA_DRWA + DA_32 + DA_DPL2DATA32_DESC : Descriptor 0, Data32SegLen - 1, DA_DR + DA_32 + DA_DPL2STACK32_DESC : Descriptor 0, TopOfStack32, DA_DRW + DA_32 + DA_DPL1FUNCTION_DESC : Descriptor 0, FunctionSegLen - 1, DA_C + DA_32 + DA_DPL1NEW_DESC : Descriptor 0, NewSegLen - 1, DA_CCO + DA_32 + DA_DPL0; GDT endGdtLen equ $ - GDT_ENTRYGdtPtr: dw GdtLen - 1 dd 0 ; GDT SelectorCode32Selector equ (0x0001 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL1VideoSelector equ (0x0002 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL2Data32Selector equ (0x0003 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL2Stack32Selector equ (0x0004 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL1FunctionSelector equ (0x0005 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL1NewSelector equ (0x0006 << 3) + SA_TIG + SA_RPL0; end of [section .gdt]TopOfStack16 equ 0x7c00[section .s16][bits 16]ENTRY_SEGMENT: mov ax, cs mov ds, ax mov es, ax mov ss, ax mov sp, TopOfStack16 ; initialize GDT for 32 bits code segment mov esi, CODE32_SEGMENT mov edi, CODE32_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, DATA32_SEGMENT mov edi, DATA32_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, STACK32_SEGMENT mov edi, STACK32_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, FUNCTION_SEGMENT mov edi, FUNCTION_DESC call InitDescItem mov esi, NEW_SEGMENT mov edi, NEW_DESC call InitDescItem ; initialize GDT pointer struct mov eax, 0 mov ax, ds shl eax, 4 add eax, GDT_ENTRY mov dword [GdtPtr + 2], eax ; 1. load GDT lgdt [GdtPtr] ; 2. close interrupt cli ; 3. open A20 in al, 0x92 or al, 00000010b out 0x92, al ; 4. enter protect mode mov eax, cr0 or eax, 0x01 mov cr0, eax ; 5. jump to 32 bits code push Stack32Selector ; 目标栈段选择子 push TopOfStack32 ; 栈顶指针位置 push Code32Selector ; 目标代码段选择子 push 0 ; 目标代码段偏移 retf; esi --> code segment label; edi --> descriptor labelInitDescItem: push eax mov eax, 0 mov ax, cs shl eax, 4 add eax, esi mov word [edi + 2], ax shr eax, 16 mov byte [edi + 4], al mov byte [edi + 7], ah pop eax ret[section .dat][bits 32]DATA32_SEGMENT: DTOS db "D.T.OS!", 0 DTOS_OFFSET equ DTOS - $$Data32SegLen equ $ - DATA32_SEGMENT [section .s32][bits 32]CODE32_SEGMENT: mov ax, VideoSelector mov gs, ax mov ax, Data32Selector mov ds, ax mov ax, Stack32Selector mov ss, ax mov eax, TopOfStack32 mov esp, eax ; mov ebp, DTOS_OFFSET ; mov bx, 0x0C ; mov dh, 12 ; mov dl, 33 ; call FunctionSelector : PrintString jmp NewSelector : 0 Code32SegLen equ $ - CODE32_SEGMENT[section .new][bits 32]NEW_SEGMENT: mov ebp, DTOS_OFFSET mov bx, 0x0C mov dh, 12 mov dl, 33 call FunctionSelector : PrintString jmp $ NewSegLen equ $ - NEW_SEGMENT[section .func][bits 32]FUNCTION_SEGMENT:; ds:ebp --> string address; bx --> attribute; dx --> dh : row, dl : colPrintStringFunc: push ebp push eax push edi push cx push dx print: mov cl, [ds:ebp] cmp cl, 0 je end mov eax, 80 mul dh add al, dl shl eax, 1 mov edi, eax mov ah, bl mov al, cl mov [gs:edi], ax inc ebp inc dl jmp printend: pop dx pop cx pop edi pop eax pop ebp retf PrintString equ PrintStringFunc - $$FunctionSegLen equ $ - FUNCTION_SEGMENT[section .gs][bits 32]STACK32_SEGMENT: times 1024 * 4 db 0 Stack32SegLen equ $ - STACK32_SEGMENTTopOfStack32 equ Stack32SegLen - 1 |
结论:
特权级降低转移时,retf指令会触发栈段的特权级检查(通过选择子中的rpl进行检查)
一致性代码段可以直接跳转到其他同级非一致性代码段执行
一致性代码段和非一致性代码段中的代码没有本质的区别,这两种代码段仅仅是跳转时使用的合法性判断规则不同,因此,一致性代码段到非一致性代码段的直接同级跳转是合法的。
小技巧:
大多数情况下,选择子中的RPL和对应段描述符中的DPL可设置为相同值。
小结:
CPL、RPL和DPL是处理器进行特权级保护的依据。
对于数据段,CPL<=DPL,RPL<=DPL
对于非一致性代码段,CPL==DPL,RPL<=DPL
对于一致性代码段,CPL>=DPL,转以后CPL不变。
posted on 2020-12-18 10:13 lh03061238 阅读(113) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)