24 单链表的遍历与优化
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanmeishenghuo/p/9650726.html 参考狄泰软件相关教程
问题:
如何遍历单链表中的每一个元素?
示例:
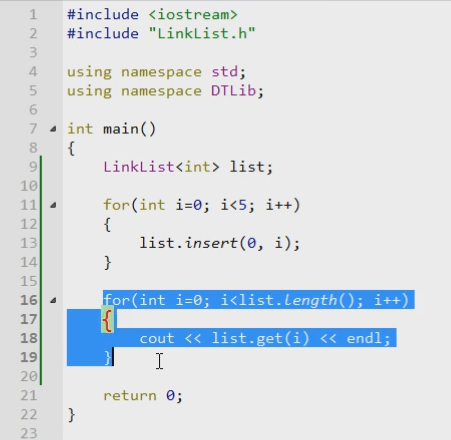

在头部插入元素时,时间复杂度是O(n)。 获取元素时,时间复杂度是O(n*n),因为内层定位位置时有一个O(n)复杂度。
从理论上来说遍历一个单链表,只需要线性的时间就够了。

设计思路:

提供一组相关的遍历函数,遍历时使用这些函数来操作:


move函数的i参数为目标位置,step参数为每次移动的节点数。
end用来判断当前的游标是否到达了单链表的尾部。
current返回当前游标指向的数据元素。
next移动游标,移动的次数根据move中的step的值来决定。
遍历时,这四个函数必须配合使用才能得到最大效率。
改进LinkList.h文件中的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 | #ifndef LINKLIST_H#define LINKLIST_H#include "List.h"#include "Exception.h"namespace DTLib{template < typename T >class LinkList : public List<T>{protected: struct Node : public Object { T value; Node* next; }; mutable struct : public Object { char reserved[sizeof(T)]; Node* next; }m_header; int m_length; int m_step; Node* m_current; Node* position(int i) const // O(n) { Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header); for(int p = 0; p < i; p++) { ret = ret->next; } return ret; }public: LinkList() { m_header.next = NULL; m_length = 0; m_step = 1; m_current = NULL; } bool insert(const T& e) { return insert(m_length, e); } bool insert(int i, const T& e) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length)); if( ret ) { Node* node = new Node(); if( node != NULL ) { Node* current = position(i); node->value = e; node->next = current->next; current->next = node; m_length++; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memery to insert new element..."); } } return ret; } bool remove(int i) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { Node* current = position(i); Node* toDel = current->next; current->next = toDel->next; delete toDel; m_length--; } return ret; } bool set(int i, const T& e) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { position(i)->next->value = e; } return ret; } T get(int i) const { T ret; if( get(i, ret) ) { return ret; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ..."); } return ret; } bool get(int i, T& e) const // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { e = position(i)->next->value; } return ret; } int find(const T& e) const // O(n) { int ret = -1; int i = 0; Node* node = m_header.next; while( node ) { if( node->value == e ) { ret = i; break; } else { node = node->next; i++; } } return ret; } int length() const // O(1) { return m_length; } void clear() // O(n) { while( m_header.next ) { Node* toDel = m_header.next; m_header.next = toDel->next; delete toDel; } m_length = 0; } bool move(int i, int step = 1) { bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0); if( ret ) { m_current = position(i)->next; m_step = step; } return ret; } bool end() { return (m_current == NULL); } T current() { if( !end() ) { return m_current->value; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ..."); } } bool next() //每次移动step步 { int i = 0; while((i < m_step) && !end()) { m_current = m_current->next; i++; } return (i == m_step); } ~LinkList() // O(n) { clear(); }};}#endif // LINKLIST_H |
第27、28行我们添加了两个成员变量,第185-226行添加了遍历需要的函数。
测试程序如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | #include <iostream>#include "LinkList.h"using namespace std;using namespace DTLib;int main(){ LinkList<int> list; for(int i = 0; i<5; i++) { list.insert(0,i); } //遍历时必须先调用move函数 for(list.move(0); !list.end(); list.next()) { cout << list.current() << endl; } return 0;} |
遍历list时必须先调用move函数,指定位置和步进值step,step是给next函数用的,例如:step为5,则每次调用next函数就会向后移动5个元素。
结果如下:
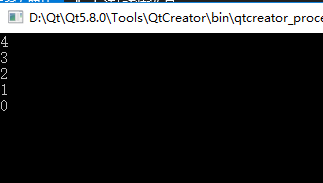
这时的遍历操作时间复杂度是O(n)。
步进值为2时,结果如下:
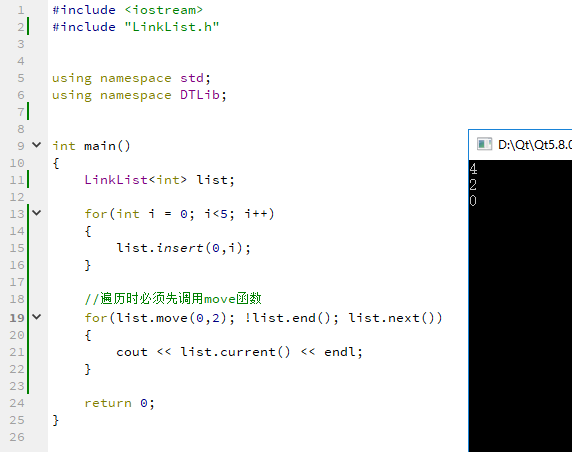
单链表内部封装:

程序改进:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 | #ifndef LINKLIST_H#define LINKLIST_H#include "List.h"#include "Exception.h"namespace DTLib{template < typename T >class LinkList : public List<T>{protected: struct Node : public Object { T value; Node* next; }; mutable struct : public Object { char reserved[sizeof(T)]; Node* next; }m_header; int m_length; int m_step; Node* m_current; Node* position(int i) const // O(n) { Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header); for(int p = 0; p < i; p++) { ret = ret->next; } return ret; } virtual Node* create() { return new Node(); } virtual void destroy(Node* pn) { delete pn; }public: LinkList() { m_header.next = NULL; m_length = 0; m_step = 1; m_current = NULL; } bool insert(const T& e) { return insert(m_length, e); } bool insert(int i, const T& e) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length)); if( ret ) { Node* node = create(); if( node != NULL ) { Node* current = position(i); node->value = e; node->next = current->next; current->next = node; m_length++; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memery to insert new element..."); } } return ret; } bool remove(int i) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { Node* current = position(i); Node* toDel = current->next; current->next = toDel->next; destroy(toDel); m_length--; } return ret; } bool set(int i, const T& e) // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { position(i)->next->value = e; } return ret; } T get(int i) const { T ret; if( get(i, ret) ) { return ret; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ..."); } return ret; } bool get(int i, T& e) const // O(n) { bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); if( ret ) { e = position(i)->next->value; } return ret; } int find(const T& e) const // O(n) { int ret = -1; int i = 0; Node* node = m_header.next; while( node ) { if( node->value == e ) { ret = i; break; } else { node = node->next; i++; } } return ret; } int length() const // O(1) { return m_length; } void clear() // O(n) { while( m_header.next ) { Node* toDel = m_header.next; m_header.next = toDel->next; destroy(toDel); } m_length = 0; } bool move(int i, int step = 1) { bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0); if( ret ) { m_current = position(i)->next; m_step = step; } return ret; } bool end() { return (m_current == NULL); } T current() { if( !end() ) { return m_current->value; } else { THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ..."); } } bool next() //每次移动step步 { int i = 0; while((i < m_step) && !end()) { m_current = m_current->next; i++; } return (i == m_step); } ~LinkList() // O(n) { clear(); }};}#endif // LINKLIST_H |
调用new生成Node的地方我们全换成了create函数,调用delete销毁Node的地方我们全换成了destroy函数。
问题:
封装这两个函数的意义是什么?
小结:

posted on 2020-06-08 10:14 lh03061238 阅读(248) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)