SIMD---AVX系列
AVX全称Advanced Vcetor Extension,是对SSE的后续扩展,主要分为AVX、AVX2、AVX512三种。在目前常见的机器上,大多只支持到AVX系列,因此其他SIMD扩展指令我们就先不学习了。
1. AVX系列
1.1 AVX
AVX使用了16个YMM寄存器,主要针对的是浮点数计算优化,支持32位单精度和64位双精度。AVX将打包长度由SSE的128位扩展为256位。
AVX主要有两个改进:
- 256位浮点打包数据长度。
- 三位操作数:计算形式可以由先前的A = A + B改为A = B + C。
AVX使用了SSE的128的寄存器,YMM寄存器的低位部分是XMM寄存器:
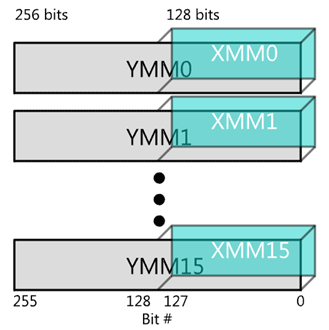
1.2 AVX2
AVX2是AVX指令的扩展,主要在整形数据方面做了完善:
- 256位整形打包数据。
- 算数运算支持完善。
1.3 AVX-512
AVX-512指令扩展主要把256位数据扩展到512位,在数据级并行又迈进了一步。AVX-512扩展包含好几个部分:
- AVX-512 Foundation
- AVX-512 Conflict Detection Instructions (CD)
- AVX-512 Exponential and Reciprocal Instructions (ER)
- AVX-512 Prefetch Instructions (PF)
- AVX-512 Vector Length Extensions (VL)
- AVX-512 Byte and Word Instructions (BW)
- AVX-512 Doubleword and Quadword Instructions (DQ)
- AVX-512 Integer Fused Multiply Add (IFMA)
- AVX-512 Vector Byte Manipulation Instructions (VBMI)
- AVX-512 Vector Neural Network Instructions Word variable precision (4VNNIW)
- AVX-512 Fused Multiply Accumulation Packed Single precision (4FMAPS)
- AVX-512 Vector Neural Network Instructions (VNNI)
- AVX-512 Galois Field New Instructions(GFNI)
- AVX-512 Vector AES instructions (VAES)
- AVX-512 Vector Byte Manipulation Instructions 2 (VBMI2)
- AVX-512 Bit Algorithms (BITALG)
但是只有Foundation部分是各实现保证支持的。
2. AVX功能支持检测
不是所有机型都通用的指令集需要调用cpuid指令来检测:
push ecx
mov eax, 0
cpuid
cmp ecx, 1
jb notSupported // check if supports EAX=1 when using CPUID
mov eax, 1
cpuid
and ecx, 0x18000000 // clear non-related bits
cmp ecx, 0x18000000 // check OSXSAVE and avx
jne notSupported
mov ecx, 0
XGETBV // get XCR0 register value
and eax, 0x6
cmp eax, 0x6 // check XMM and YMM state
jne notSupported
mov eax, 1
jmp done
notSupported:
mov eax, 0
done:
pop ecx
根据Intel开发者指南,我们需要检测OSXSAVE、AVX、XMM state、YMM state这四个功能。cpuid隐式使用eax寄存器作为指令参数执行:当eax位0时,cpuid返回eax可传入最大值;传入1时,返回功能标记为,这时候我们通过检查ecx寄存器的第28、29位就可以判断是否分别支持OSXSAVE和AVX功能;之后我们要给ecx赋值0来作为参数调用XGETBV指令,这个指令返回结果的第2、3位表明XMM、YMM状态是否开启。
3. AVX优化使用
与之前的随笔一样,我们对10000000个单精度浮点数进行加操作,但是我电脑机型不支持AVX2,因此无法演示AVX系列的整数优化操作:
__m256 step = _mm256_set_ps(10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0,
10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0);
__m256* dst = reinterpret_cast<__m256*>(data);
for (unsigned i = 0; i < count; i += 8)
{
__m256 sum = _mm256_add_ps(*dst, step);
*dst++ = sum;
}
4. 运行结果
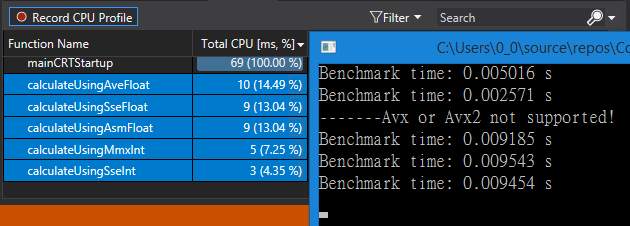
这个运行时间表明,有时候简单的使用AVX来进行计算优化并不一定会提升程序的运行效率,得深入分析,完整代码见链接。



