pytest夹具fixture、常用插件和allure报告
1.pytest夹具fixture
夹具:在用例执行之前,执行之后,自动的运行代码
1.1 创建fixture
- python函数+fixture装饰器
前后之分:yield
1 import pytest 2 3 @pytest.fixture 4 def func(): 5 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 6 yield 7 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】')
1.2 使用fixture
1 def test_A(func): 2 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 3 assert 1==1 4 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器
1.3 fixture的作用范围
pytest的fixture,支持5级作用域(unittest支持3级),让用例共享fixture
- function:每个用例不共享fixture的返回值,默认
- class:每个类中的用例,共享fixture
- module:每个模块(文件)中的用例,共享fixture
- package:每个包(目录)中的用例,共享fixture
- session:所有的用例,共享fixture
1.3.1 function
1 import pytest 2 3 @pytest.fixture(scope="function") 4 def func(): 5 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 6 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 7 yield 8 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 9 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】') 10 11 12 @pytest.mark.skip 13 def test_A(func): 14 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 15 assert 1==1 16 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 17 18 @pytest.mark.skip 19 def test_B(func): 20 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 21 assert 1 == 2 22 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 23 24 @pytest.mark.skip 25 def test_C(func): 26 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 27 assert 3 == 3 28 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接

1.3.2 class
1 import pytest 2 3 @pytest.fixture(scope="class") 4 def func(): 5 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 6 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 7 yield 8 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 9 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】') 10 11 12 @pytest.mark.skip 13 def test_A(func): 14 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 15 assert 1==1 16 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 17 18 @pytest.mark.skip 19 def test_B(func): 20 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 21 assert 1 == 2 22 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 23 24 @pytest.mark.skip 25 def test_C(func): 26 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 27 assert 3 == 3 28 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 29 30 31 class TestA: 32 def test_a(self,func): 33 pass 34 35 def test_b(self,func): 36 pass
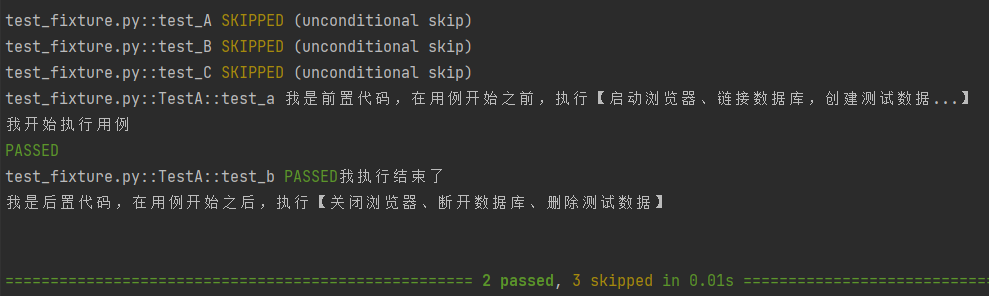
1.3.3 module
1 import pytest 2 3 @pytest.fixture(scope="module") 4 def func(): 5 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 6 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 7 yield 8 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 9 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】') 10 11 12 def test_A(func): 13 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 14 assert 1==1 15 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 16 17 def test_B(func): 18 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 19 assert 1 == 2 20 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 21 22 def test_C(func): 23 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 24 assert 3 == 3 25 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 26 27 28 class TestA: 29 def test_a(self,func): 30 pass 31 32 def test_b(self,func): 33 pass

1.3.4 package
注意:需要把夹具文件conftest放在你需要的用例的目录,如果放在项目根路径,那package作用域和seesion作用域功能是一样的
1 #test_abc.py 2 3 import pytest 4 5 6 class TestABC: 7 @pytest.mark.ut 8 def test_ok(self,func): 9 assert 1 == 1 10 11 @pytest.mark.ut 12 def test_fail(self,func): 13 assert 1 == 2 14 15 @pytest.mark.skip #无条件跳过 16 @pytest.mark.ui 17 def test_web(self): 18 assert 1==3 19 20 @pytest.mark.api 21 def test_api(self): 22 assert 2 23 24 @pytest.mark.skipif(True,reason='为真时跳过') #无条件跳过 25 @pytest.mark.ui 26 def test_UI(self): 27 assert 3 28 29 @pytest.mark.ui 30 @pytest.mark.xfail #预期失败 31 def test_app(self): 32 assert 4 33 34 #test_add.py 35 36 import pytest 37 38 39 def add(a, b): # 计算a+b的结果 40 return a + b 41 42 43 @pytest.mark.parametrize( 44 "a,b", 45 [ 46 (1, 1), 47 (3, 5), 48 ('3', '5'), 49 (None, '5'), 50 (None, False) 51 ] 52 ) 53 def test_1(a, b,func): 54 # a = 1 55 # b = 1 56 c = add(a, b) 57 assert c == a + b 58 59 #test_fixture.py 60 61 import pytest 62 63 def test_A(func): 64 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 65 assert 1==1 66 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 67 68 def test_B(func): 69 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 70 assert 1 == 2 71 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 72 73 def test_C(func): 74 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 75 assert 3 == 3 76 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 77 78 79 class TestA: 80 def test_a(self,func): 81 pass 82 83 def test_b(self,func): 84 pass 85 86 #conftest.py 87 88 import pytest 89 90 @pytest.fixture(scope="package") 91 def func(): 92 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 93 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 94 yield 95 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 96 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】

1.3.5 session
1 #test_abc.py 2 3 import pytest 4 5 6 class TestABC: 7 @pytest.mark.ut 8 def test_ok(self,func): 9 assert 1 == 1 10 11 @pytest.mark.ut 12 def test_fail(self,func): 13 assert 1 == 2 14 15 @pytest.mark.skip #无条件跳过 16 @pytest.mark.ui 17 def test_web(self): 18 assert 1==3 19 20 @pytest.mark.api 21 def test_api(self): 22 assert 2 23 24 @pytest.mark.skipif(True,reason='为真时跳过') #无条件跳过 25 @pytest.mark.ui 26 def test_UI(self): 27 assert 3 28 29 @pytest.mark.ui 30 @pytest.mark.xfail #预期失败 31 def test_app(self): 32 assert 4 33 34 #test_add.py 35 36 import pytest 37 38 39 def add(a, b): # 计算a+b的结果 40 return a + b 41 42 43 @pytest.mark.parametrize( 44 "a,b", 45 [ 46 (1, 1), 47 (3, 5), 48 ('3', '5'), 49 (None, '5'), 50 (None, False) 51 ] 52 ) 53 def test_1(a, b,func): 54 # a = 1 55 # b = 1 56 c = add(a, b) 57 assert c == a + b 58 59 #test_fixture.py 60 61 import pytest 62 63 def test_A(func): 64 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 65 assert 1==1 66 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 67 68 def test_B(func): 69 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 70 assert 1 == 2 71 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 72 73 def test_C(func): 74 #print('我开始执行用例') #连接数据库 75 assert 3 == 3 76 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭数据库连接 77 78 79 class TestA: 80 def test_a(self,func): 81 pass 82 83 def test_b(self,func): 84 pass 85 86 #conftest.py 87 88 import pytest 89 90 @pytest.fixture(scope="session") 91 def func(): 92 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 93 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 94 yield 95 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 96 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】')

共享fixture好处:
- 节省fixture的执行时间
- 每一个用例都启动浏览器,然后关闭浏览器 4000个用例*7秒=28000秒
- 全局只启动一次浏览器,供每个用例使用:1*7s=7s
- 用例之间传递数据
1 import pytest 2 3 def test_A(func): 4 #print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 5 assert 1==1 6 func.id=15 7 #print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 8 9 10 class TestA: 11 def test_a(self,func): 12 id=func.id 13 print(id) 14 func.id+=1 15 16 def test_b(self,func): 17 id=func.id 18 print(id) 19 20 import pytest 21 22 class clazz1: 23 pass 24 25 @pytest.fixture(scope="session") 26 def func(): 27 print('我是前置代码,在用例开始之前,执行【启动浏览器、链接数据库,创建测试数据...】') 28 print('我开始执行用例') #启动浏览器 29 yield clazz1() 30 print('我执行结束了') #关闭浏览器 31 print('我是后置代码,在用例开始之后,执行【关闭浏览器、断开数据库、删除测试数据】')

共享fixture弊端:
- 共享之后,不会重复执行(例如,用例执行过程中,浏览器意外关闭,就不会再次启动浏览器)
1.4 conftest.py
从名字上看:测试配置文件(代码版)
从功能上看:可以被所有的用例自动导入,用来存放跨文件的fixture、hook
每个目录,都可以创建一个conftest.py,可以屏蔽上级目录的conftest.py
哪个conftest.py离测试用例越近,影响力越大
应该在根目录创建通用的conftest
然后在个别目录,创建特殊的conftest
1.5 fixture的其他写法

https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iMQfm_7jwVFWD9cY2r94TA
2.pytest常用插件
有的插件,安装之后,自动启用
有的插件,安装之后,配置后才启用
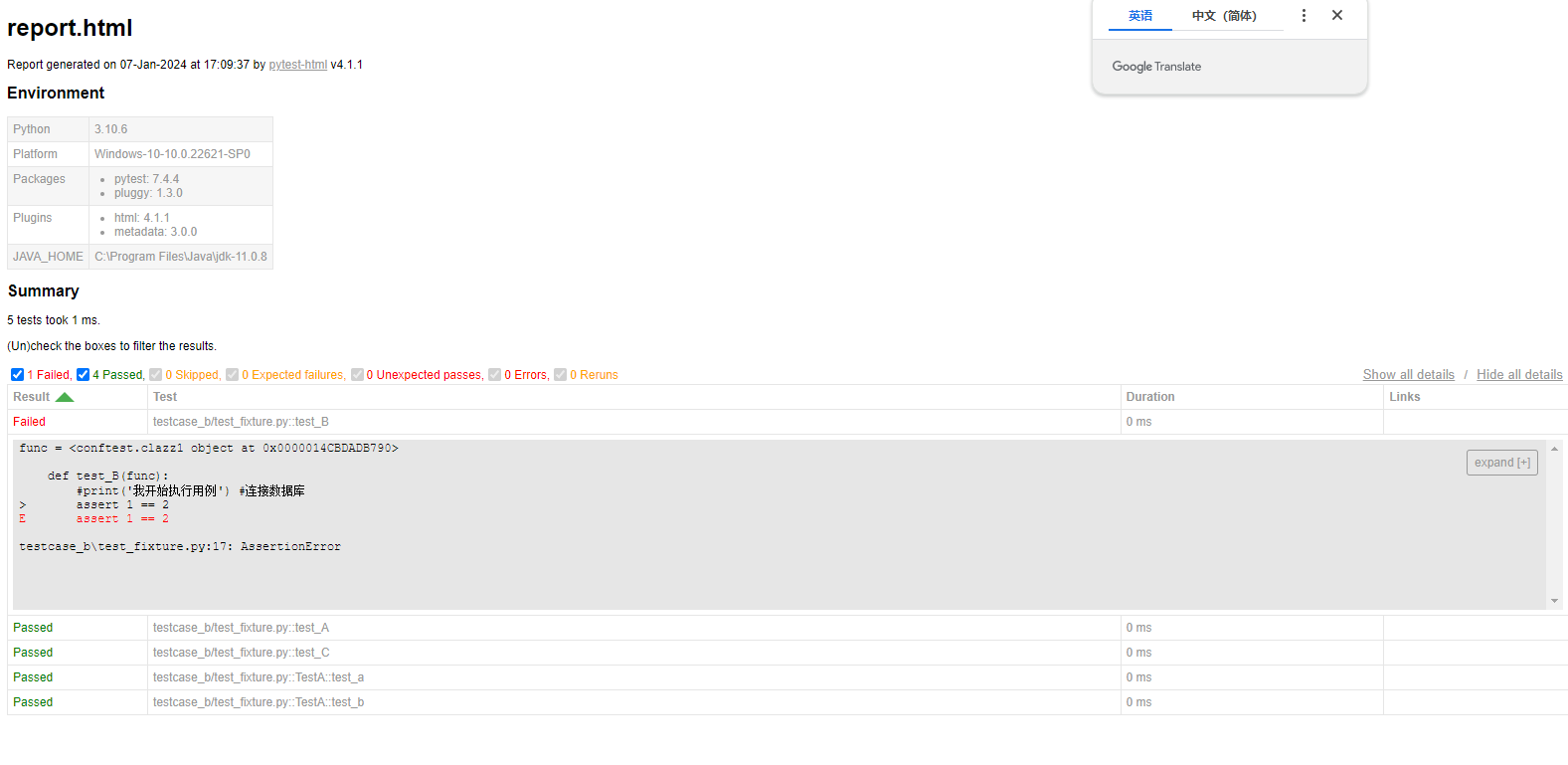
2.1 pytest-html
用途:生成html报告
安装:pip install pytest-html
配置:
addopts= --html=report.html --self-contained-html
2.2 pytest-xdist
用途:并法执行用例
安装:pip install pytest-xdist
配置:
[pytest] addopts= -n 4 addopts= -n auto addopts=-n 0
- 0 不使用并发
- 4 创建4个进程并发
- auto 创建和cpu相同数量的进程并发
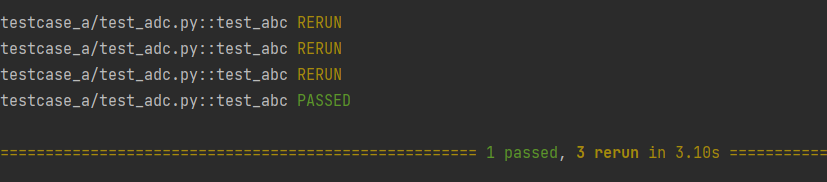
2.3 pytest-rerunfailures
用途:用例失败之后,重新运行
安装:pip install pytest-rerunfailures
配置:
[pytest]
addopts= --reruns 5 --reruns-delay 1
1 import random 2 3 4 def test_abc(): 5 a = random.randint(1, 5) 6 b = 5 7 assert a == b
2.4 pytest-order
用途:自定义用例执行顺序
安装:pip install pytest-order
1 #test_order.py 2 3 import pytest 4 5 @pytest.mark.order(1) 6 def test_a(): 7 pass 8 9 @pytest.mark.order(3) 10 def test_b(): 11 pass 12 13 #test_new_order.py 14 import pytest 15 16 @pytest.mark.order(2) 17 def test_c(): 18 pass 19 20 @pytest.mark.order(4) 21 def test_d(): 22 pass
预期效果:a,c,b,d
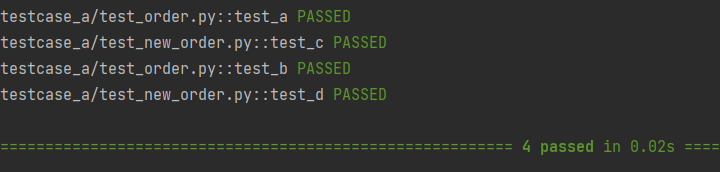
排序规则:
- 先执行有order标记的用例,后执行没有order标记的用例
- order标记越小,顺序越靠前
2.5 pytest-result-log
用途:将用例的名称和结果,保存到日志文件
安装:pip install pytest-result-log
配置:
[pytest]
log_file_level= info
log_file_format= %(levelname)-8s %(asctime)s [%(name)s:%(lineno)s] : %(message)s
log_file_date_format=%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
result_log_level_verbose=info
2.6 allure-pytest
allure是一个Java测试报告框架
allure-pytest:是allure支持pytest插件
用途:生成allure能够识别的数据文件
安装:pip install allure-pytest
配置:
[pytest]
addopts=--alluredir=./temp --clean-alluredir
3.allure企业级测试报告
allure:是一个java测试报告框架
3.1 搭建java的jdk环境
JDK+Java源程序
JDK:
- 使用Pycharm自带的java.exe
- 如果单独安装。建议使用JDK17+
- 设置环境变量:JAVA_HONE,PATH
- 命令可以执行java.exe
E:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm Community Edition 2023.1.2\jbr\bin
环境变量:
JAVA_HONE =E:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm Community Edition 2023.1.2\jbr
PATH=PATH;E:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm Community Edition 2023.1.2\jbr\bin
验证:
命令行窗口输入:java,能显示如截图一样的信息,说明环境变量设置成功
3.2 Allure环境搭建
1.解压 allure安装包
2.环境变量配置:PATH=PATH;D:\allure-2.24.1\bin\
3.命令行验证:allure
pycharm分别执行:java和allure
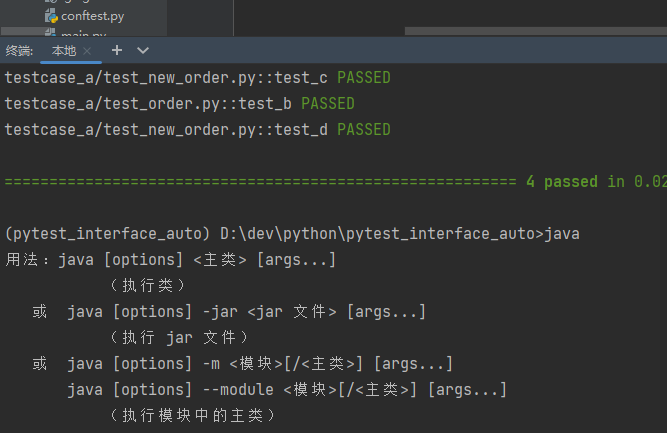
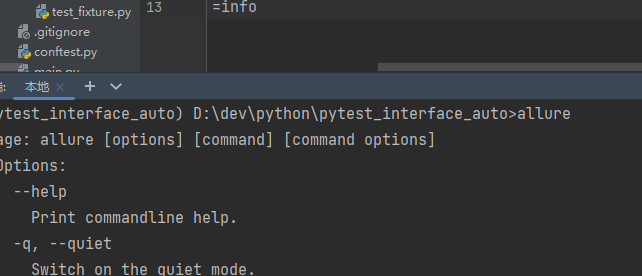
3.3 生成报告
allure generate -c -o report temps
根据temps目录中的数据,生成报告并放在report目录中
allure seve temps
根据temps目录中的数据,生成报告并直接展示
3.4 内容定制
3.4.1 logo定制
3.4.1.1 启用插件
D:\allure-2.18.1\config\allure.yml
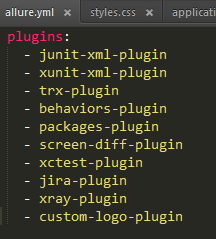
3.4.1.2 修改logo
D:\allure-2.18.1\plugins\custom-logo-plugin\static\styles.css
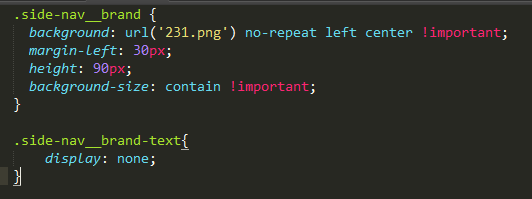
url('要修改的文件.png')
文件放入styles.css同一目录
重新生成报告
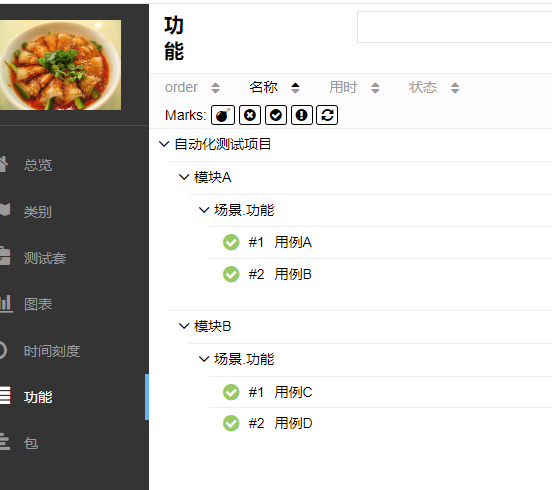
3.4.2 内容定制
1 import pytest 2 import allure 3 4 @allure.epic('自动化测试项目') 5 @allure.feature('模块A') 6 @allure.story('场景.功能') 7 @allure.title('用例A') 8 @pytest.mark.order(1) 9 def test_a(): 10 pass 11 12 @allure.epic('自动化测试项目') 13 @allure.feature('模块A') 14 @allure.story('场景.功能') 15 @allure.title('用例B') 16 @pytest.mark.order(3) 17 def test_b(): 18 pass 19 20 @allure.epic('自动化测试项目') 21 @allure.feature('模块B') 22 @allure.story('场景.功能') 23 @allure.title('用例C') 24 @pytest.mark.order(1) 25 def test_c(): 26 pass 27 28 @allure.epic('自动化测试项目') 29 @allure.feature('模块B') 30 @allure.story('场景.功能') 31 @allure.title('用例D') 32 @pytest.mark.order(3) 33 def test_d(): 34 pass




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)