android之Fragment基础详解(一)
一、Fragment的设计哲学
Android在3.0中引入了fragments的概念,主要目的是用在大屏幕设备上——例如平板电脑上,支持更加动态和灵活的UI设计。平板电脑的屏幕比手机的大得多,有更多的空间来放更多的UI组件,并且这些组件之间会产生更多的交互。
针对屏幕尺寸的差距,很多情况下,都是先针对手机开发一套App,然后拷贝一份,修改布局以适应平板神马超级大屏的。难道无法做到一个App可以同时适应手机和平板么,当然了,必须有啊。Fragment的出现就是为了解决这样的问题。你可以把Fragment当成Activity的一个界面的一个组成部分,甚至Activity的界面可以完全有不同的Fragment组成,更帅气的是Fragment拥有自己的生命周期和接收、处理用户的事件,这样就不必在Activity写一堆控件的事件处理的代码了。更为重要的是,你可以动态的添加、替换和移除某个Fragment。
下图是文档中给出的一个Fragment分别对应手机与平板间不同情况的处理图:


PS:简单的新闻浏览页面,使用两个Fragment分别显示新闻列表与新闻内容;
Fragment在应用中应当是一个模块化和可重用的组件,因为Fragment定义了他自己的布局,以及通过使用他自己的生命周期回调方法定义了他自己的行为,可以将Fragment包含到多个Activity中。
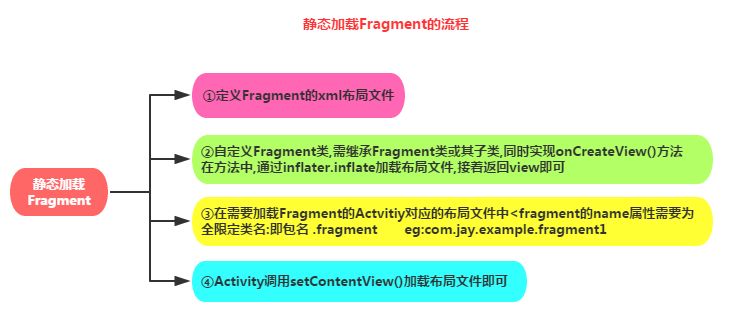
二、静态加载Fragment
Fragment知识概要:
-
- Fragment 可以作为Activity界面的一部分组成出现(不能单独使用)
- 可以在一个Activity中同时出现多个fragment,并且一个fragment也可以在多个activity中使用
- 在activity运行过程中,可以添加、一处或替换fragment
- fragment可以响应自己的输入事件,并且有自己的生命周期,他们的生命周期会受宿主activity的生命周期影响,比如Activity被destory销毁了,他也会跟着销毁
onCreateView()方法
Fragment第一次绘制它的用户界面的时候,系统会调用此方法,未来绘制Fragment的UI,此方法必须返回一个View,如果不显示UI,返回NULL即可。
在activity的layout文件中声明Fragment,需要特别注意的是<fragment>中的android: name 属性指定了在layout中实例化的Fragment类
标识Fragment的方法:
android:id 属性提供一个唯一的ID
android:tag 属性提供一个唯一字符串
1、fragment布局文件,显示fragment显示内容控件

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <TextView 8 android:id="@+id/text" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 ></TextView> 12 13 <Button 14 android:id="@+id/button" 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 17 18 /> 19 </LinearLayout>
2、自定义一个Fragment类,需要继承Fragment或者他的子类,重写onCreateView()方法 在该方法中调用:inflater.inflate()方法加载Fragment的布局文件,接着返回加载的view对象

1 package com.example.fragment; 2 3 import android.app.Fragment; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.view.LayoutInflater; 6 import android.view.View; 7 import android.view.ViewGroup; 8 import android.widget.TextView; 9 10 public class MyFragment extends Fragment{ 11 @Override 12 public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, 13 Bundle savedInstanceState) { 14 15 //layout布局文件转换成view对象 16 /** 17 * resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件 18 * root:加载layout的父ViewGroup 19 * attachToRoot:flase,不反回父ViewGroup 20 */ 21 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment, container, false); 22 TextView text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text); 23 text.setText("加载静态Fragment"); 24 return view ; 25 26 } 27 }
3、在需要加载Fragment的Activity对应的布局文件中添加fragment的标签, 记住,name属性是全限定类名哦,就是要包含Fragment的包名

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <fragment 8 android:id="@+id/fragment" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:name="com.example.fragment.MyFragment" 12 /> 13 </LinearLayout>
4、 Activity在onCreate( )方法中调用setContentView()加载布局文件即可!(可添加事件)

1 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 2 import android.widget.Button; 3 import android.widget.TextView; 4 5 public class MainActivity2 extends Activity{ 6 7 private TextView tv; 8 9 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 10 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 11 12 setContentView(R.layout.main2); 13 14 Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button); 15 tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text); 16 button.setText("改变"); 17 button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { 18 19 @Override 20 public void onClick(View v) { 21 tv.setText("TextView改变了"); 22 } 23 }); 24 } 25 }
三、动态加载
撰写代码将Fragmen添加到一个Activity layout 中
add():添加一个Fragment(指定要添加的fragment 和 要插入的View)
与此类似的还有remove() 、替换()
处理Frament事务
格局用户的交互情况,对Fragment进行添加、移除、替换,以及执行其他动作,提交给Activity的每一套变化被称作一个事务
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
每一个事务都是同时执行一套变化,可以在一个事务中设置所有想执行的变化,包括add()、remove()、replace()、然后提交给Activity,必须调用commit()方法
如果允许用户通过按下back按键返回到前一个Fragment状态,调用commit()之前可以加入addToBackStack()方法

MyFragment2.xml

1 package com.example.fragment; 2 3 import android.app.Fragment; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.view.LayoutInflater; 6 import android.view.View; 7 import android.view.ViewGroup; 8 import android.widget.TextView; 9 10 public class MyFragment2 extends Fragment{ 11 @Override 12 public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, 13 Bundle savedInstanceState) { 14 15 //layout布局文件转换成view对象 16 /** 17 * resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件 18 * root:加载layout的父ViewGroup 19 * attachToRoot:flase,不反回父ViewGroup 20 */ 21 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment, container, false); 22 TextView text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text); 23 text.setText("动态加载Fragment"); 24 return view ; 25 26 } 27 }
主要代码

Fragment与activity通信
生命周期图:
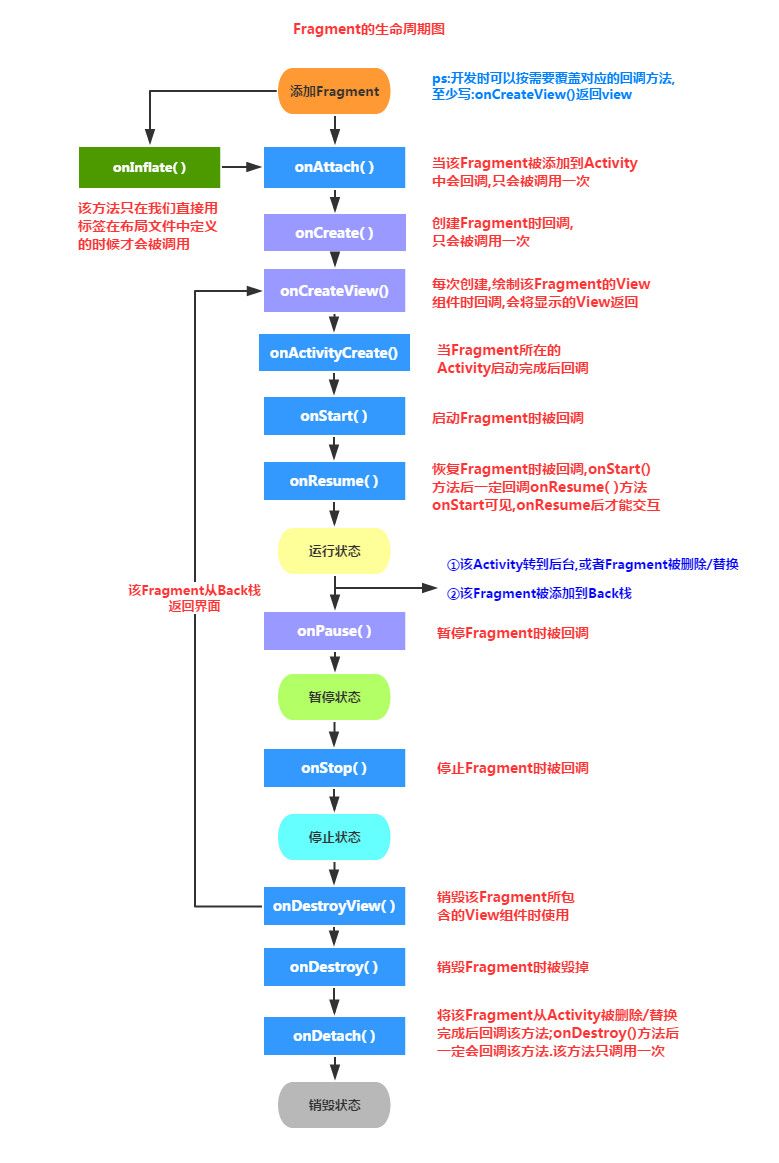
探究fragment生命周期案例:

1 package com.example.fragment; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.app.FragmentManager; 5 import android.app.FragmentTransaction; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.View; 8 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 9 import android.widget.Button; 10 11 public class MainActivity3 extends Activity { 12 13 private Button button; 14 private boolean flag = true; 15 16 17 @Override 18 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 19 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 20 setContentView(R.layout.main3); 21 init(); 22 button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button); 23 button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { 24 25 @Override 26 public void onClick(View v) { 27 FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager(); 28 FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); 29 30 if (flag) { 31 MyFragment4 frag4=new MyFragment4(); 32 beginTransaction.replace(R.id.layout, frag4); 33 flag=false; 34 } else { 35 MyFragment3 frag3=new MyFragment3(); 36 beginTransaction.replace(R.id.layout, frag3); 37 flag=true; 38 39 } 40 41 beginTransaction.commit(); 42 } 43 }); 44 45 } 46 47 private void init() { 48 FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager(); 49 FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); 50 MyFragment3 frag3 = new MyFragment3(); 51 beginTransaction.add(R.id.layout,frag3); 52 beginTransaction.commit(); 53 } 54 55 }

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:id="@+id/layout" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical" > 7 8 <Button 9 android:text="切换Fragment" 10 android:id="@+id/button" 11 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 13 </Button> 14 15 </LinearLayout>

1 package com.example.fragment; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.app.Fragment; 5 import android.os.Bundle; 6 import android.util.Log; 7 import android.view.LayoutInflater; 8 import android.view.View; 9 import android.view.ViewGroup; 10 import android.widget.TextView; 11 12 public class MyFragment3 extends Fragment { 13 14 /** 15 * 每次创建都会绘制Fragment的View组件 16 */ 17 @Override 18 public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, 19 Bundle savedInstanceState) { 20 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false); 21 TextView tv = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text); 22 tv.setText("第一个ragment"); 23 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onCreateView()"); 24 return view; 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * 当fragment被添加Activity时候慧回调此方法,并且只调用一次 29 */ 30 @Override 31 public void onAttach(Activity activity) { 32 super.onAttach(activity); 33 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onAttach()"); 34 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 创建Fragment时回调 39 */ 40 @Override 41 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 42 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 43 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onCreate()"); 44 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * 当Fragment所长的activity启动完成后调用 49 */ 50 @Override 51 public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 52 super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState); 53 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onActivityCreated()"); 54 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * 启动Fragment 59 * 60 */ 61 @Override 62 public void onStart() { 63 super.onStart(); 64 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onStart()"); 65 66 } 67 68 /** 69 * 恢复Fragment时会被回调,调用onStart()方法后 一定调用onResume()方法 70 */ 71 @Override 72 public void onResume() { 73 super.onResume(); 74 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onResume()"); 75 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * 暂停Fragment 80 */ 81 @Override 82 public void onPause() { 83 super.onPause(); 84 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onPause()"); 85 86 } 87 88 /** 89 * 停止Fragment 90 */ 91 @Override 92 public void onStop() { 93 super.onStop(); 94 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onStop()"); 95 96 } 97 98 /** 99 *销毁 Fragment所包含的View组件 100 */ 101 @Override 102 public void onDestroyView() { 103 super.onDestroyView(); 104 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDestroyView()"); 105 106 } 107 108 /** 109 * 销毁Fragment是被回调 110 */ 111 @Override 112 public void onDestroy() { 113 super.onDestroy(); 114 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDestroy()"); 115 116 } 117 118 /** 119 * Fragment从Activity中删除时会回调该方法,只会调用一次 120 */ 121 @Override 122 public void onDetach() { 123 super.onDetach(); 124 Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDetach()"); 125 } 126 }
 MyFragment4.java
MyFragment4.java
测试顺序:启动fragment—>回到桌面—>回到应用—>切换fragment—>退出fragment
日志打印:
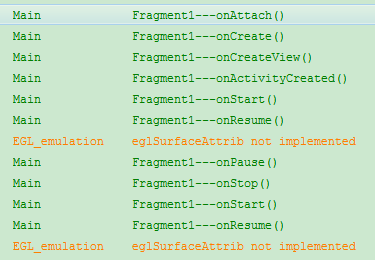
总结:
1)启动fragment
onAttach()—>onCreat()—>onCreateView()—>onActivityCreated()—>onStart()—>onResume()
2)锁屏
onPause()—>onStop()
3)解锁
onStart()—>onResume()
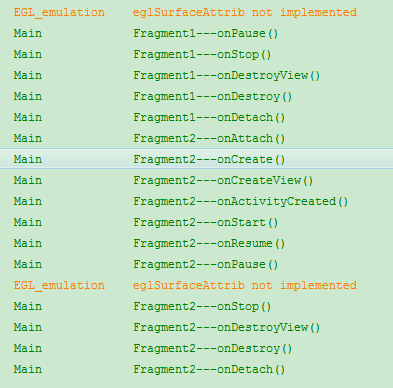
4)切换到其他的Fragment
第一个:onPause()—>onStop()—>onDestroyView()—>onDestroy()—>onDetach
第二个:onAttach()—>onCreat()—>onCreateView()—>onActivityCreated()—>onStart()—>onResume()
Fragment 与Activity通信
1)Fragment可调用getActivity()方法获取它所在的Activity
2)Activity可调用FragmentManager的findFragmentById()或findFragmentByTag()方法获取Fragment
Activity——>Fragment:在Activity中创建Bundle数据包,并调用Fragment的setArguments(Bundle bundle)方法
Fragment——>Activity:需要在Fragment中定义一个内部回调接口,再让包含该Fragment的Activity实现该回调接口。这样Fragment可调用该回调方法将数据传递给Activity



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号