apache 基本配置
1.1 ServerRoot 配置
【ServerRoot "" 主要用于指定Apache的安装路径,此选项参数值在安装Apache时系统会自动把Apache的路径写入。Windows安装时,该选项的值为Windows安装的路径,Linux安装时该选项值为编译时选择的路径】
1.2 Mutex default:logs
互斥:允许你为多个不同的互斥对象设置互斥机制【mutex mechanism】和互斥文件目录,或者修改全局默认值
如果互斥对象是基于文件的以及默认的互斥文件目录不在本地磁盘或因为其它原因而不适用,那么取消注释并改变目录。
【下面这个命令是改变互斥对象的目录】
1.3 Listen 配置
【Listen主要侦听web服务端口状态,默认为:80,即侦听所有的地址的80端口,注意这里也可以写成IP地址的侦听形式,不写即默认的地址:0.0.0.0】
1.4 Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support(动态共享对象支持)
【主要用于添加Apache一些动态模块,比如php支持模块。重定向模块,认证模块支持,注意如果需要添加某些模块支持,只需把相关模块前面注释符号取消掉。如图所示,要对Apache添加某个功能模块,把前面的注释符号去掉就行】
1.5 Apache运行用户配置
【此选项主要用指定Apache服务的运行用户和用户组,默认为:daemon,如图所示下】
1.6 Apache服务默认管理员地址设置
【此选项主要用指定Apache服务管理员通知邮箱地址,选择默认值即可,如果有真实的邮箱地址也可以设置此值】
1.7 Apache的默认服务名及端口设置
【此选项主要用指定Apache默认的服务器名以及端口,默认参数值设置为:ServerName localhost:80即可】
1.8 Apache的根目录访问控制设置
【此选项主要是针对用户对根目录下所有的访问权限控制,默认Apache对根目录访问都是拒绝访问。后面会继续讲到】
1.6 Apache的默认网站根目录设置及访问控制
【此区域的配置文件,主要是针对Apache默认网站根目录的设置以及相关的权限访问设置,默认对网站的根目录具有访问权限,此选项默认值即可】
1.9 Apache的默认首页设置
【此区域文件主要设置Apache默认支持的首页,默认只支持:index.html首页,如要支持其他类型的首页,需要在此区域添加:如index.php表示支持index.php类型首页】
1.10 Apache关于.ht文件访问配置
【此选项主要是针对.ht文件访问控制,默认为具有访问权限,此区域文件默认即可】
1.11 Apache关于日志文件配置
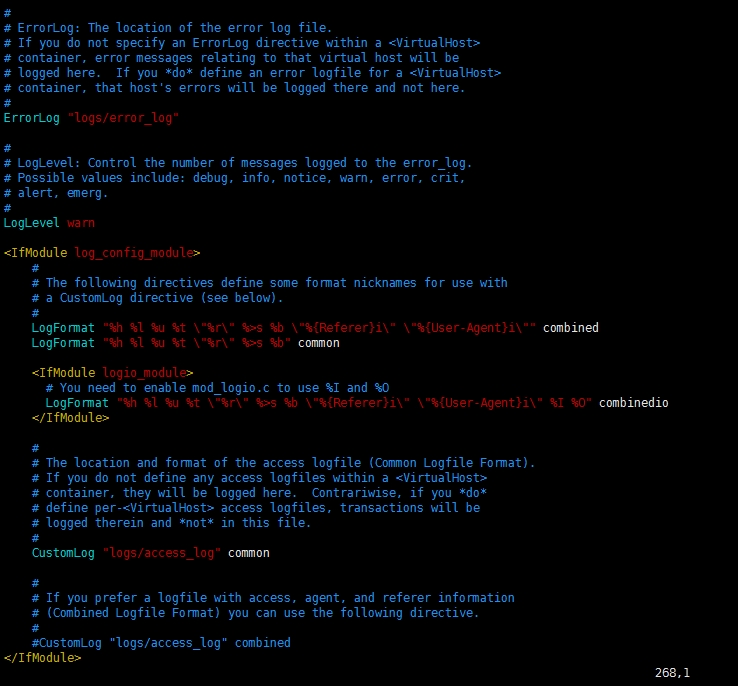 【此区域文件主要是针对Apache默认的日志级别,默认的访问日志路径,默认的错误日志路径等相关设置,此选项内容默认即可】
【此区域文件主要是针对Apache默认的日志级别,默认的访问日志路径,默认的错误日志路径等相关设置,此选项内容默认即可】
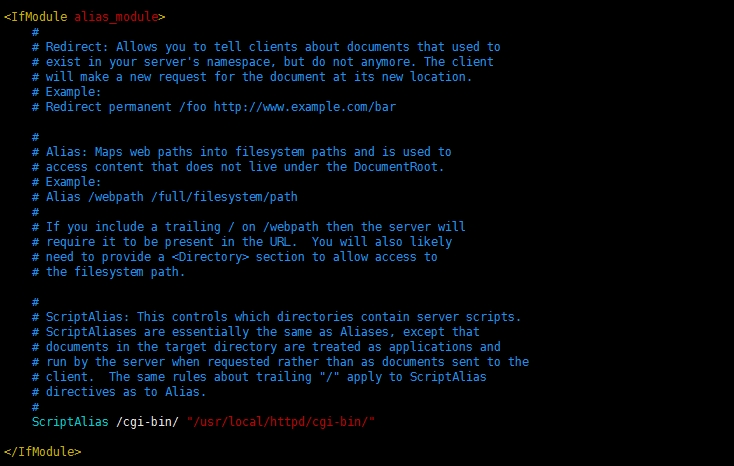
1.11 URL重定向,cgi模块配置说明
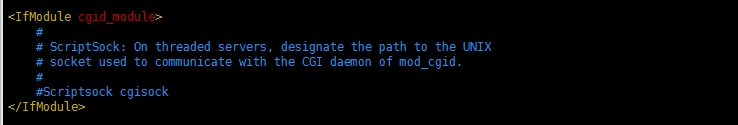
【此区域文件主要包含一些URL重定向,别名,脚本别名等相关设置,以及一些特定的处理程序,比如cgi设置说明。后期会继续说道】
1.12 MIME媒体文件,以及相关http文件解析配置说明
【此区域文件主要包含一些mime文件支持,以及添加一些指令在给定的文件扩展名与特定的内容类型之间建立映射关系,比如添加对php文件扩展名映射关系。】
1.13 服务器页面提示设置
【此区域可定制的访问错误响应提示,支持三种方式:1明文 ,2本地重定向 3,外部重定向;另外还包括内存映射或“发送文件系统调用”可被用于分发文件等配置】
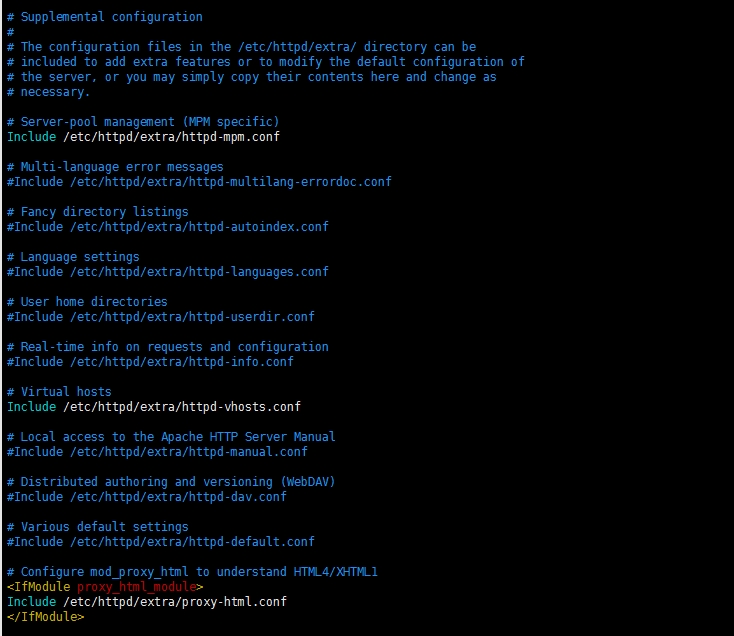
1.14 Apache服务器补充设置
【此区域主要包括:服务器池管理,多语言错误消息,动态目录列表形式配置,语言设置,用户家庭目录,请求和配置上的实时信息,虚拟主机,Apache Http Server手册,分布式创作和版本控制,多种类默认设置,mod_proxy_html,使其支持HTML4/XHTML1等等补充配置的补充】
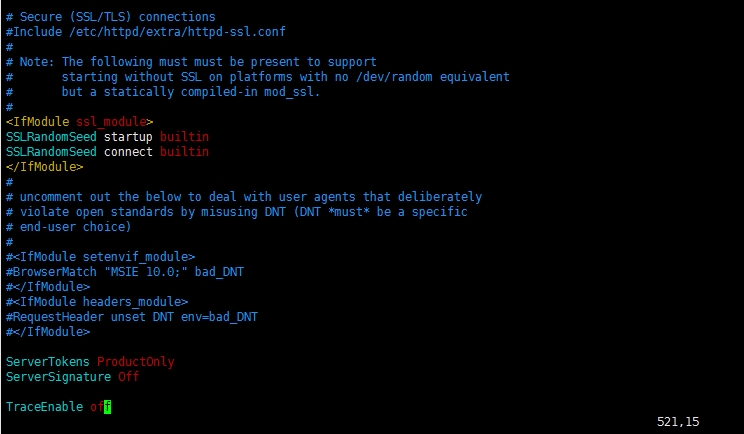
1.15 Apache服务器安全连接设置
【此区域主要是关于服务器安全连接设置,用于使用https连接服务器等设置的地方】
Apache常用配置详解
Apache配置文件:conf/httpd.conf。(注意:表示路径时使用‘/’而不使用‘\’,注释使用‘#’)
1. ServerRoot:服务器根目录,也就是Apache的安装目录,其他的目录配置若是使用相对路径,都是相对于服务器根目录的。
配置示例:
ServerRoot “D:/wamp/bin/Apache2.4.23”
2. Listen:服务器监听的端口,可以只配置端口,也可以同时指定IP地址和端口,还可以指定使用的协议。(可配置多个端口)
完整配置示例:
Listen 127.0.0.1:80 http
3. DocumentRoot:网站的根目录,也就是放置网站文件的地方。
配置示例:
DocumentRoot = “D:/wamp/www”
4. LoadModule:加载特定的DSO模块,这些已编译的DSO模块存放于Apache安装目录下的modules目录中。
配置示例:
LoadModule actions_module modules/mod_actions.so
5. User:设置实际提供服务的子进程的用户。
配置示例:
User daemon
6. Group:设置提供服务的Apache子进程运行时的用户组。
配置示例:
Group daemon
7. ServerAdmin:设置在所有返回给客户端的错误信息中包含的管理员的邮件地址。(也可以使用URL)
配置示例:
ServerAdmin 23423423@qq.com
8. ServerName:设置服务器用于识别自己的主机名和端口号。如果没有指定端口号,服务器会使用接受请求的那个端口。
配置示例:
ServerName localhost:80
9. <Directory>:和</Directory>一起用于封装一组指令,使之仅对某个目录及其子目录生效。该指令不能被嵌套使用,也不能出现
在<Limit>或<LimitExcept>配置段中。
配置示例:
<Directory “D:/wamp/www”>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews Includes IncludesNOEXEC ExecCGI
AllowOverride None
Order allow, deny
allow from all
</Directory>
指令及其参数说明:
(1)Options:控制在特定目录中将使用哪些服务器特性。
Indexs:若访问目录下无index文件,则准许显示该目录下的文件列表以供选择。
FollowSymLinks:准许在目录中使用符号链接到其他目录。
MultiViews:准许内容协商的“多重视图”。如果客户端请求的路径可能对应多种类型的文件,服务器将根据客户端请求的具体情
况自动选择一个最匹配客户端要求的文件。例如只在地址栏输入index也可以访问到index.php页面。
Includes:准许SSI。
IncludesNOEXEC:准许SSI,但不可使用exec和include功能。
ExecCGI:准许在该目录下使用CGI。
All:表示除了MultiViews之外的所有特性。
None:表示不启用任何的服务器特性。
注意:如果一个目录被多次设置了options,则最特殊的一个会被完全接受。
(2)AllowOverrid:是否准许文件“.htaccess”中设定的权限覆盖“access.conf”文件中设定的权限。
All:准许覆盖。
None:不准许覆盖。
AuthConfig:允许使用与认证授权相关的指令。
FileInfo:允许使用控制文档类型的指令、控制文档元数据的指令、mod_rewrite中的指令、mod_actions中的Action指令。
Indexs:允许使用控制目录索引的指令。
Limit:允许使用控制主机访问的指令。
(3)Order:控制默认的访问状态和allow、deny指令生效的顺序。
allow:允许访问。
deny:拒绝访问。
这两个参数由最后一个出现的参数决定,如“Order allow,deny”默认拒绝了所有的意思(中间有且只有一个逗号),但最终的判断
结果还要总下面的allow、deny语句中各自所包含的范围(如果有的话),这两个语句后面都一定接着“from”,否则Apache
会无法启动。“Order allow,deny”表示先判断allow语句再判断deny语句。
注意:上面的Order和allow、deny语句是针对Apache2.2的配置,Apache2.4的客户端访问控制由Require语句来配置。
区别示例:
拒绝所有请求:
2.2配置:
Order deny,allow
deny from all
2.4配置:
Require all denied
允许所有请求:
2.2配置:
Order allow,deny
allow from all
2.4配置:
Require all granted
只允许某个特定IP的访问:
2.2配置:
Order deny,allow
deny from all
allow IP-address
2.4配置
Require host IP-addres
10. <Files>:提供基于文件名的访问控制。<Files>段将根据他们在配置文件中出现的顺序被处理:在<Directory>段和.htaccess文件被处理之后,但在<Location>段之前。<Files>能嵌
入到<Directory>段中以限制它们作用的文件范围。也可用于.htaccess文件当中,以允许用户在文件层面上控制对文件的访问。
配置示例:
<Files ".ht*">
Require all denied
</Files>
11. <IfModule>:封装根据指定的模块是否启用而决定是否生效的指令。
配置示例:
<IfModule http2_module>
ProtocolsHonorOrder On
Protocols h2 h2c http/1.1
</IfModule>
12. DirectoryIndex:当客户端请求一个目录时寻找的资源列表。
配置示例:
DirectoryIndex index.php index.htm index.html
(服务器将返回最先找到的那一个)
13. ErrorLog:指定当服务器遇到错误时记录错误日志的文件。
(若不是一个以“/”开头的绝对路径,则是一个相对于ServerRoot的相对路径)
配置示例:
ErrorLog "logs/error.log"
14. LogLevel:用于调整记录在错误日志中的信息的详细程度。
错误信息详细程度按重要性降序排列如下:
emerg:紧急(系统无法使用)
alert:必须立即采取措施。
crit:致命情况。
error:错误情况。
warn:警告情况。
notice:一般重要情况。
info:普通信息。
debug:调试信息。
(当指定了某个级别时,所有级别高于它的信息也会被同时记录)
配置示例:
LogLevel warn
15. LogFormat:定义访问日志的记录格式。
配置示例:
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
(其中common就是这种格式的标识符)
16. CustomLog:设定日志的文件名和格式。
配置示例:
CustomLog "logs/access.log" common
(使用标识符common定义的格式来记录logs/access.log这个日志文件)
17. TransferLog:指定日志文件的位置。
本指令除不允许直接定义日志格式或根据条件进行日志记录外,与CustomLog指令有完全相同的参数和功能。
18. Alias:映射URL到文件系统的特定区域。Alias指令使客户端可以访问到DocumentRoot以外的本地文件。
配置示例:
Alias /myphoto "E:/照片"
<Directory "E:/照片">
Options Indexes
Require all granted
</Directory>
目录/myphoto是相对于DocumentRoot的相对路径,甚至可以是一个不存在的目录,这时访问该目录就会映射到“E:/照片”目录中。
注意:一定要通过<Directory>段明确地对目标目录设定访问权限,否则会提示“forbidden”。
Redirect:将一个路径重定向到另一个路径下。
配置示例:
Redirect /haha /chsfc
(Redirect和Alias不同,配置中的两个路径都是在DocumentRoot目录下的)
注意:要使用Alias和Redirect都应该先开启alias_module模块功能。
19. ScriptAlias:映射一个URL到文件系统并视之为CGI脚本目录。
配置示例:
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "D:/wamp/bin/Apache2.4.23/cgi-bin"
20. DefaultType:当服务器无法确定一个文档的内容类型时发送的默认MIME内容类型。
配置示例:
DefaultType text/plain (纯文本,浏览器在内部打开)
DefaultType application/octet-stream (浏览器提示用户进行保存)
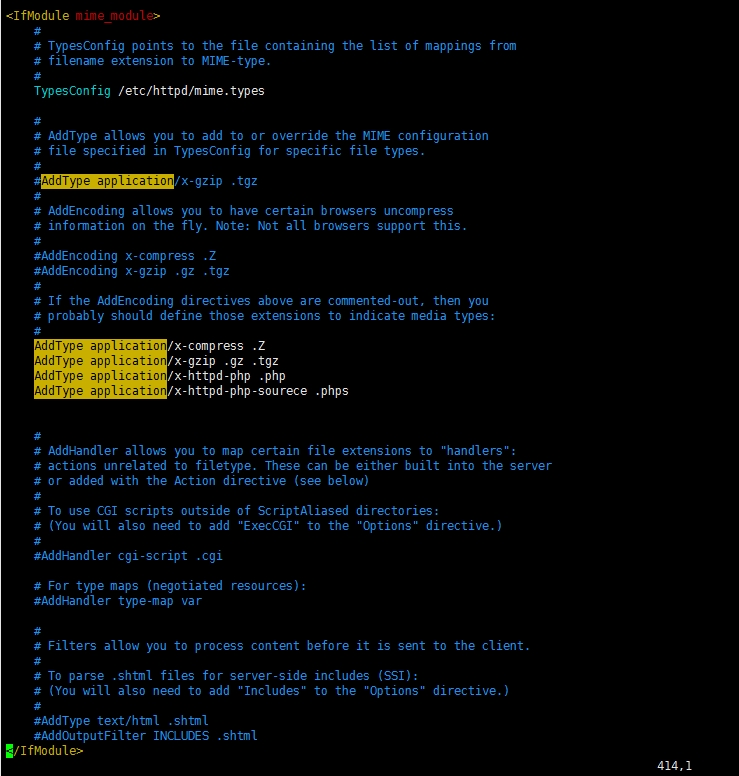
21. AddType:为特定后缀的文件指定MIME类型,这里的设置将覆盖mime.types中的设置。
配置示例:
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php .html .htm (前导点可带可不带)
22. ErrorDocument:批示当遇到错误的时候服务器将给客户端什么样的应答。
语法:
ErrorDocument error-code document
其中error-code时服务器返回的错误代码,document是回应的数据,可以是简单的文本,
本地网页,本地CGI程序,或远程主机上的网页。
配置示例:
ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo."
ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html
23. EnableMMAP:指示httpd在递送中如果需要读取一个文件的内容,是否可以使用内存映射。
配置示例:
EnableMMAP On
EnableMMAP Off
(这种内存映射有时会带来性能的提高,有时却会出现问题)
24. EnableSendfile:控制httpd是否可以使用操作系统内核的sendfile支持来将文件发送到户端。
配置示例:
EnableSendfile Off
(这个sendfile机制避免了分开的读和写操作以及缓冲区分配,但是在一些平台或文件系统上会引发一些问题)
25. include:在服务器配置文件中包含其他配置文件。
配置示例:
include conf/extra/httpd-autoindex.conf
在Apache安装目录下的conf/extra/目录中有一些补充配置文件,可以根据需要,通过配置将它们包含到主配置文件conf/httpd.conf文件中。
apache的httpd.conf翻译
# This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the
这是Apache HTTP Server的主配置文件。它包括了
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
配置指令【directives】,这些指令给服务器服务器指令【instructions】【】
# See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information.
查看<URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/>以取得更多信息
# In particular, see
# <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html>
# for a discussion of each configuration directive.
特别指出,查看<URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html>以得到关于每条配置命令的讨论
#
# Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding
# what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure
# consult the online docs. You have been warned.
不要只是简单阅读这里的每条指令而不理解它们的所做所为【真实含义】。这里只是一种提示和提醒。如果你不能确定【它们的含义】,请参阅在线文档。特此警告!
#
# Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many
# of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the
# server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin
# with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so "logs/access_log"
# with ServerRoot set to "/usr/local/apache2" will be interpreted by the
# server as "/usr/local/apache2/logs/access_log", whereas "/logs/access_log"
# will be interpreted as '/logs/access_log'.
#
关于配置文件和日志文件的名字:如果你使用了以斜杠“/“开始的指定了多个服务器控制文件名,那么服务器将使用那些绝对路径。
如 果你没有以斜杠“/“开始文件名,那么服务器根路径(ServerRoot)就是相对的---所以,像"logs/access_log"这样的服务器根 路径就将被服务器解释成加上"/usr/local/apache2"的"/usr/local/apache2/logs/access_log",反 之"/logs/access_log"将被服务器解释成"/logs/access_log"
# NOTE: Where filenames are specified, you must use forward slashes
# instead of backslashes (e.g., "c:/apache" instead of "c:\apache").
# If a drive letter is omitted, the drive on which httpd.exe is located
# will be used by default. It is recommended that you always supply
# an explicit drive letter in absolute paths to avoid confusion.
注意:在文件名被指定的地方,你必须用“前斜杠”【就是我们平时说的斜杠"/",与问号在同一个键,右手小指下的那个】代替后斜杠【即“反斜杠/】”(如:用"c:/apache"来代替"c:\apache")。
如果你省略了驱动器符号,那么httpd.exe将使用默认的驱动器。建议你总是在绝对路径中使用一个明确的驱动器符号,以避免混淆。
#
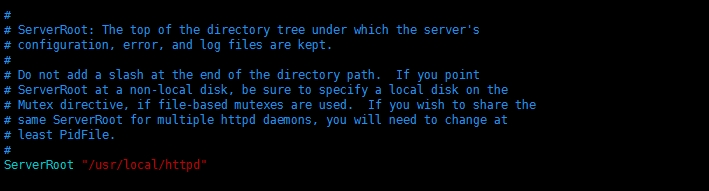
# ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's
# configuration, error, and log files are kept.
ServerRoot:目录树的顶级根目录,用来保存服务器配置、错误、日志文件
#
# Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point
# ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the
# Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the
# same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at
# least PidFile.
不要在路径的最后加斜杠“/“。如果你指定的ServerRoot不是本地磁盘,要确定用互斥指令【Mutex directive】指定一个本地磁盘,如果基于文件的互斥指令被使用【?】。
如果你希望共享在多个httpd守护进程【daemons】中共享相同的ServerRoot,你至少需要修改PidFile【?】
#【下面这个命令是指定服务器根目录】
ServerRoot "c:/Apache24"
#
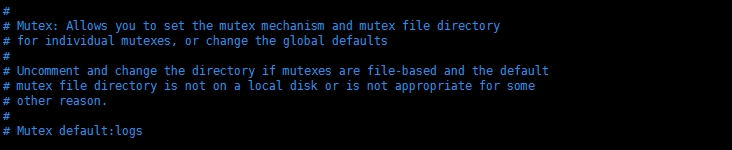
# Mutex: Allows you to set the mutex mechanism and mutex file directory
# for individual mutexes, or change the global defaults
互斥:允许你为多个不同的互斥对象设置互斥机制【mutex mechanism】和互斥文件目录,或者修改全局默认值
#
# Uncomment and change the directory if mutexes are file-based and the default
# mutex file directory is not on a local disk or is not appropriate for some
# other reason.
如果互斥对象是基于文件的以及默认的互斥文件目录不在本地磁盘或因为其它原因而不适用,那么取消注释并改变目录。
#【下面这个命令是改变互斥对象的目录】
# Mutex default:logs
#
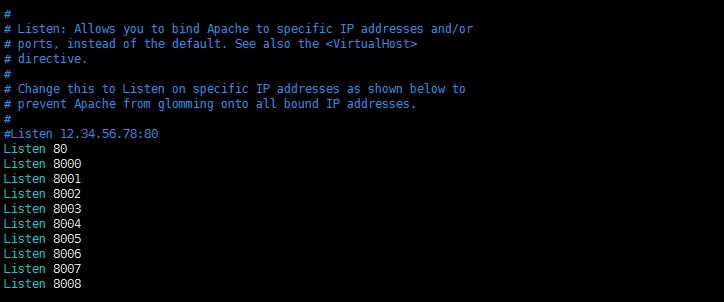
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost>
# directive.
侦听:允许你绑定Apache服务器到指定ip地址和/或端口,用来代替默认值。参见<VirtualHost>指令。
#
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
# prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses.
修改这个指令以侦听下面指定的ip地址,避免Apache服务器抓取全部绑定的IP地址
#【下面这个指令是80端口的IP地址,主网站IP就在这里配置】
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 80
#
# Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support 动态共享对象支持
#
# To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you
# have to place corresponding `LoadModule' lines at this location so the
# directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used.
# Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l') do not need
# to be loaded here.
为了能够使用一个作为DSO创建的模块【modules】的功能,你需要放置相应的【corresponding】`LoadModule'行在这个位置,这样在你使用之前,这些指令就包含在模块中了。
#
# Example:
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
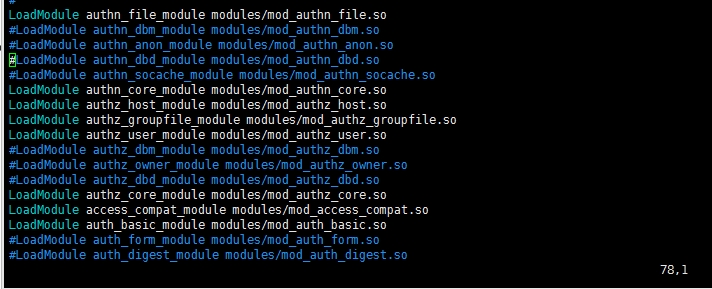
LoadModule access_compat_module modules/mod_access_compat.so
LoadModule actions_module modules/mod_actions.so
LoadModule alias_module modules/mod_alias.so
LoadModule allowmethods_module modules/mod_allowmethods.so
LoadModule asis_module modules/mod_asis.so
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
#LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so
#LoadModule auth_form_module modules/mod_auth_form.so
#LoadModule authn_anon_module modules/mod_authn_anon.so
LoadModule authn_core_module modules/mod_authn_core.so
#LoadModule authn_dbd_module modules/mod_authn_dbd.so
#LoadModule authn_dbm_module modules/mod_authn_dbm.so
LoadModule authn_file_module modules/mod_authn_file.so
#LoadModule authn_socache_module modules/mod_authn_socache.so
#LoadModule authnz_ldap_module modules/mod_authnz_ldap.so
LoadModule authz_core_module modules/mod_authz_core.so
#LoadModule authz_dbd_module modules/mod_authz_dbd.so
#LoadModule authz_dbm_module modules/mod_authz_dbm.so
LoadModule authz_groupfile_module modules/mod_authz_groupfile.so
LoadModule authz_host_module modules/mod_authz_host.so
#LoadModule authz_owner_module modules/mod_authz_owner.so
LoadModule authz_user_module modules/mod_authz_user.so
LoadModule autoindex_module modules/mod_autoindex.so
#LoadModule buffer_module modules/mod_buffer.so
#LoadModule cache_module modules/mod_cache.so
#LoadModule cache_disk_module modules/mod_cache_disk.so
#LoadModule cache_socache_module modules/mod_cache_socache.so
#LoadModule cern_meta_module modules/mod_cern_meta.so
LoadModule cgi_module modules/mod_cgi.so
#LoadModule charset_lite_module modules/mod_charset_lite.so
#LoadModule data_module modules/mod_data.so
#LoadModule dav_module modules/mod_dav.so
#LoadModule dav_fs_module modules/mod_dav_fs.so
#LoadModule dav_lock_module modules/mod_dav_lock.so
#LoadModule dbd_module modules/mod_dbd.so
#LoadModule deflate_module modules/mod_deflate.so
LoadModule dir_module modules/mod_dir.so
#LoadModule dumpio_module modules/mod_dumpio.so
LoadModule env_module modules/mod_env.so
#LoadModule expires_module modules/mod_expires.so
#LoadModule ext_filter_module modules/mod_ext_filter.so
#LoadModule file_cache_module modules/mod_file_cache.so
#LoadModule filter_module modules/mod_filter.so
#LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.so
#LoadModule heartbeat_module modules/mod_heartbeat.so
#LoadModule heartmonitor_module modules/mod_heartmonitor.so
#LoadModule ident_module modules/mod_ident.so
#LoadModule imagemap_module modules/mod_imagemap.so
LoadModule include_module modules/mod_include.so
#LoadModule info_module modules/mod_info.so
LoadModule isapi_module modules/mod_isapi.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bybusyness_module modules/mod_lbmethod_bybusyness.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_byrequests_module modules/mod_lbmethod_byrequests.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bytraffic_module modules/mod_lbmethod_bytraffic.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_heartbeat_module modules/mod_lbmethod_heartbeat.so
#LoadModule ldap_module modules/mod_ldap.so
#LoadModule logio_module modules/mod_logio.so
LoadModule log_config_module modules/mod_log_config.so
#LoadModule log_debug_module modules/mod_log_debug.so
#LoadModule log_forensic_module modules/mod_log_forensic.so
#LoadModule lua_module modules/mod_lua.so
#LoadModule macro_module modules/mod_macro.so
LoadModule mime_module modules/mod_mime.so
#LoadModule mime_magic_module modules/mod_mime_magic.so
LoadModule negotiation_module modules/mod_negotiation.so
#LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
#LoadModule proxy_ajp_module modules/mod_proxy_ajp.so
#LoadModule proxy_balancer_module modules/mod_proxy_balancer.so
#LoadModule proxy_connect_module modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
#LoadModule proxy_express_module modules/mod_proxy_express.so
#LoadModule proxy_fcgi_module modules/mod_proxy_fcgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_ftp_module modules/mod_proxy_ftp.so
#LoadModule proxy_html_module modules/mod_proxy_html.so
#LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
#LoadModule proxy_scgi_module modules/mod_proxy_scgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_wstunnel_module modules/mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
#LoadModule ratelimit_module modules/mod_ratelimit.so
#LoadModule reflector_module modules/mod_reflector.so
#LoadModule remoteip_module modules/mod_remoteip.so
#LoadModule request_module modules/mod_request.so
#LoadModule reqtimeout_module modules/mod_reqtimeout.so
#LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
#LoadModule sed_module modules/mod_sed.so
#LoadModule session_module modules/mod_session.so
#LoadModule session_cookie_module modules/mod_session_cookie.so
#LoadModule session_crypto_module modules/mod_session_crypto.so
#LoadModule session_dbd_module modules/mod_session_dbd.so
LoadModule setenvif_module modules/mod_setenvif.so
#LoadModule slotmem_plain_module modules/mod_slotmem_plain.so
#LoadModule slotmem_shm_module modules/mod_slotmem_shm.so
#LoadModule socache_dbm_module modules/mod_socache_dbm.so
#LoadModule socache_memcache_module modules/mod_socache_memcache.so
#LoadModule socache_shmcb_module modules/mod_socache_shmcb.so
#LoadModule speling_module modules/mod_speling.so
#LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
#LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so
#LoadModule substitute_module modules/mod_substitute.so
#LoadModule unique_id_module modules/mod_unique_id.so
#LoadModule userdir_module modules/mod_userdir.so
#LoadModule usertrack_module modules/mod_usertrack.so
#LoadModule version_module modules/mod_version.so
#LoadModule vhost_alias_module modules/mod_vhost_alias.so
#LoadModule watchdog_module modules/mod_watchdog.so
#LoadModule xml2enc_module modules/mod_xml2enc.so
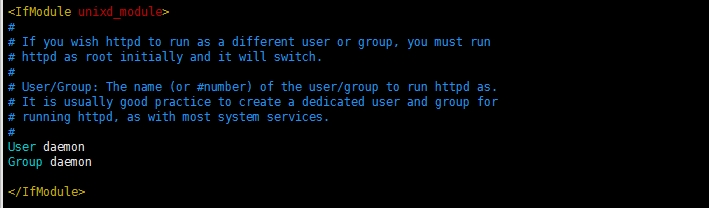
<IfModule unixd_module>【这里指的是unix系统吗?】
#
# If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run
# httpd as root initially and it will switch.
#如果你希望httpd以不同的用户或组来运行,你必须最初以root运行httpd,它将切换过去【?】
#
# User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as.
# It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for
# running httpd, as with most system services.
#User/Group:运行httpd的用户名/组 的名字。对于大多数系统服务来讲,为运行httpd创建一个专用用户和组是一个好的实践方法。
#
User daemon
Group daemon
</IfModule>
# 'Main' server configuration
#“主”服务器配置
# The directives in this section set up the values used by the 'main'
# server, which responds to any requests that aren't handled by a
# <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for
# any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file.
#本节的指令集用来设置“main"服务器所使用的值,服务器响应任何没有被<VirtualHost>定义所处理的请求。
#这些值也为任何稍后你可能在下面定义的<VirtualHost>容器【containers】提供默认值。
#
# All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers,
# in which case these default settings will be overridden for the
# virtual host being defined.
#
#所有这些指令可能显示在<VirtualHost>容器里面,在这种情况下【case】这些默认设置将被覆盖【?】
#
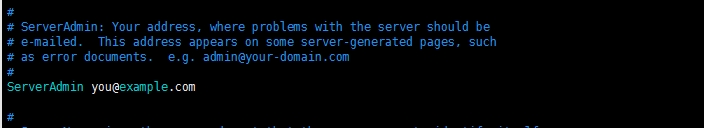
# ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be
# e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such
# as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com
#ServerAdmin:你的邮箱地址,当发生问题时服务器将向此邮箱发送邮件。这个邮箱显示在一些服务器生成的页面,例如错误文档。如:admin@your-domain.com
ServerAdmin admin@example.com
###################################################################
#
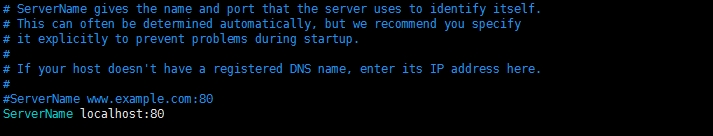
# ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself.
# This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify
# it explicitly to prevent problems during startup.
#ServerName提供用于识别它自己的名字和端口。名字和端口通常由服务器自动定义,但是我们建议你明确地指定它以避免启动过程中产生问题。
#
# If your host doesn't have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here.
#如果你的主机没有注册DNS名称,在这里输入DNS的IP地址。
#
#ServerName www.example.com:80
#
# Deny access to the entirety of your server's filesystem. You must
# explicitly permit access to web content directories in other
# <Directory> blocks below.
#拒绝所有对你服务器文件系统的访问。你必须在下面其它的<Directory>区明确许可访问web内容目录
#
<Directory />
AllowOverride none
Require all denied
</Directory>
###################################################################
#
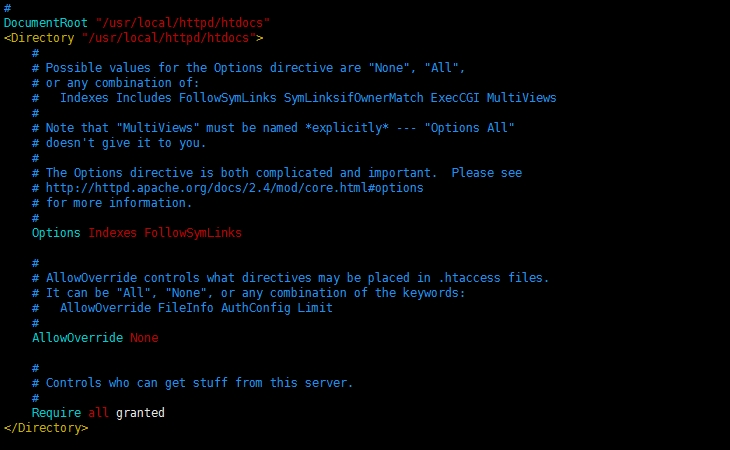
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#DocumentRoot:你要使用【serve】的文档的目录。默认为所有请求都从这个目录获取,但是可以使用符号连接【symbolic link】和别名指定其它位置。
#【下面这个指令指定文档目录,也就是网站的根目录】
DocumentRoot "c:/Apache24/htdocs"
<Directory "c:/Apache24/htdocs">
#
# Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All",
# or any combination of:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#可能的设置指令值是“None”,“All”,或者以下任意组合:
#Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#
# Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All"
# doesn't give it to you.
#注意那个"MultiViews"必须准确命名-----“Options All”将不会起什么作用【doesn't give it to you】【?】
#
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#选项指令复杂且重要。请参阅http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options以得到更多信息 #
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords:
# AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
# AllowOverride控制的指令可能包含在.htaccess文件中。它可以是“all”、“None”、或以下关键字的任意组合:
# AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
#
AllowOverride None
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#下面的指令控制谁能从这台服务器上获取东西
#
Require all granted
</Directory>
###################################################################
#
# DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory
# is requested.
# DirectoryIndex:设置当Apache服务得到一个目录请求的时候访问的文件【即默认首页】
#
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.html
</IfModule>
#
# The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being
# viewed by Web clients.
#下面的行禁止.htaccess和.htpasswd文件被web客户端查看【禁止从浏览器访问.htaccess和.htpasswd文件】
#
<Files ".ht*">
Require all denied
</Files>
#
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost>
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost>
# container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here.
# ErrorLog:错误日志文件的位置。如果你没有在<VirtualHost>容器中指定一个ErrorLog指令,与那个虚拟主机相关的错误消失将记录在这里。如果你确实为一个<VirtualHost>容器定义了错误消息文件,那么主机的错误日志将被记录在那里而不是这里。
#
ErrorLog "logs/error.log"
#
# LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log.
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
#LogLEvel:日志级别,控制记录到错误日志文件中的消息的数量。可能包括的值有:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit
#
LogLevel warn
<IfModule log_config_module>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#下列指令为使用【用户?】自定义指令定义了一些昵称格式(看下面)
#
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
<IfModule logio_module>
# You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O 你需要使mod_logio.c可用以使用 %I和%O
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" %I %O" combinedio
</IfModule>
#
# The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format).
# If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost>
# container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do*
# define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be
# logged therein and *not* in this file.
#
#访问日志文件的位置和格式。如果你没有定义任何<VirtualHost>容器访问日志文件,它们将记录在这里。反之,如果你确定定义了全部<VirtualHost>访问日志文件,事务【transactions】将把日志记录在那里而非这里的文件。
CustomLog "logs/access.log" common
#
# If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information
# (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive.
#如果你指定一个日志文件的访问、代理和参考信息(包含日志格式)你可以使用下面的指令。
#
#CustomLog "logs/access.log" combined
</IfModule>
<IfModule alias_module>
#
# Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to
# exist in your server's namespace, but do not anymore. The client
# will make a new request for the document at its new location.
#Redirect:允许你通知客户端以前存在于服务器名字空间的文档,现在已经不存在了。客户端将发送一个新请求以获得新的文档位置。
# Example:
# Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar
#
# Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to
# access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot.
# Alias:别名,映射网络路径到文件系统路径并被且用于访问不存在于网站根目录的内容。
# Example:
# Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path
#
# If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will
# require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely
# need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to
# the filesystem path.
#如果你包含了 trainng/on/webpath 那么服务器将获取它并呈现在URL中。【?】
#
# ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts.
# ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that
# documents in the target directory are treated as applications and
# run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the
# client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias
# directives as to Alias.
#ScriptAlias:脚本别名,它控制着那些包含服务器脚本的目录。“脚本别名”本质上与“别名”是相同的,除非目标目录中的文档被当作应用程序对待并且当被请求时由服务器运行而不是当作文档被发送到客户端。【当目标目录中的文档是应用程序,客户端有请求时被服务器运行,而不是以文档形式被发送到客户端,只有这个时候脚本别名与别名是不同的】【?】。以斜杠“/”结尾这个规则对于ScriptAlias和Alias指令是相同的。
#
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "c:/Apache24/cgi-bin/"
</IfModule>
<IfModule cgid_module>
#
# ScriptSock: On threaded servers, designate the path to the UNIX socket used to communicate with the CGI daemon of mod_cgid.
# ScriptSock:在线程服务器上,指定指向UNIX socket的路径被用于【经常?】与mod_cgid这个CGI守护进程通信。
#
#Scriptsock cgisock
</IfModule>
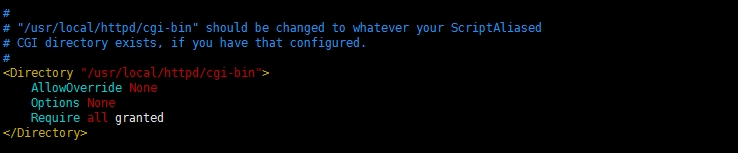
#
# "c:/Apache24/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased
# CGI directory exists, if you have that configured.
#如果你配置了脚本别名指定的CGI目录并且它是存在的,那么"c:/Apache24/cgi-bin"这个目录应该改为那个目录。
#
<Directory "c:/Apache24/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<IfModule mime_module>
#
# TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from filename extension to MIME-type.
# TypesConfig指向一个文件,这个文件包含一个从文件扩展名到mime-type的映射列表【TypesConfig指向一个文件,这个文件包含一个文件扩展名与mime-type的映射列表】
#
TypesConfig conf/mime.types
#
# AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration
# file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types.
# AddType允许你为特殊的文件类型添加或覆盖在TypesConfig中规定的mime配置文件
#
#AddType application/x-gzip .tgz
#
# AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this.
# AddEncoding允许你有特定的浏览器解压缩信息的自适应能力。注意:并非所有浏览器都支持。
#
#AddEncoding x-compress .Z
#AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you
# probably should define those extensions to indicate media types:
#如果上面的AddEncoding指令被注释,那么你可能应该定义那些扩展名以指出媒体类型。
#
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers":
# actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server
# or added with the Action directive (see below)
# AddHandler允许你映射特定文件扩展名到"handlers":动作与文件类型无关。这也可以内建于服务器或者与动作指令【Action directive】一起添加(看下面)
#
# To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories:
# (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.)
#为了在脚本别名指定的目录外使用CGI脚本:(你也需要添加"ExecCGI"到"Options"指令)
#AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
# For type maps (negotiated resources):为了类型映射(协议资源)【?】
#AddHandler type-map var
#
# Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client.
# Filters允许你在内容被发送到客户端之前处理它。
#
# To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI):
# (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.)
#为“服务器端包含”分析.shtml文件:(你也需要添加“includes”到"Options"指令)
#AddType text/html .shtml
#AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml
</IfModule>
#
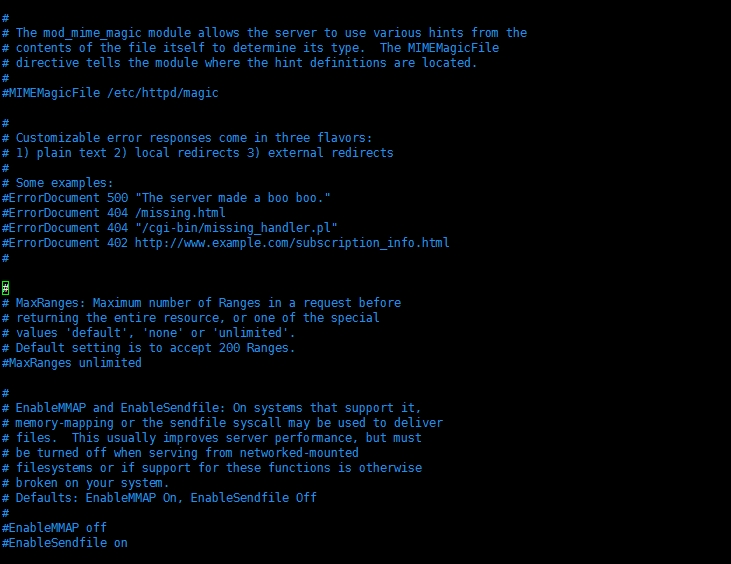
# The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the
# contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile
# directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located.
# mod_mime_magic模块允许服务器使用多种提示,这些提示来自文件自身内容用来定义它【指的是文件?】自己的类型
#MIMEMagicFile conf/magic
#
# Customizable error responses come in three flavors:
# 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects
#可定制的错误响应支持三种方式:1)明文 2)本地重定向 3)外部重定向
# Some examples:
#ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo."
#ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html
#ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl"
#ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html
#
#
# MaxRanges: Maximum number of Ranges in a request before
# returning the entire resource, or one of the special
# values 'default', 'none' or 'unlimited'.
# Default setting is to accept 200 Ranges.
# MaxRanges:定义了在一个请求返回全部资源之前Ranges的最大数字,或者在'default', 'none' or 'unlimited'三个值中指定的一个值。
#MaxRanges unlimited
#
# EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it,
# memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver
# files. This usually improves server performance, but must
# be turned off when serving from networked-mounted filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise broken on your system.
# Defaults: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off
# EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile:在支持它的系统上,内存映射或“发送文件系统调用”可被用于分发文件。这通常能提高服务器性能,但是当服务来自“网络设定的文件系统”【?】时它必须被关闭。或者在你的系统上对于这些功能的支持因为其它原因被破坏。【?】
#EnableMMAP off
#EnableSendfile on
# Supplemental configuration
#补充配置
#
# The configuration files in the conf/extra/ directory can be
# included to add extra features or to modify the default configuration of
# the server, or you may simply copy their contents here and change as
# necessary.
# conf/extra/ directory目录中的配置文件可以被包含以添加扩展功能或修改服务器的默认配置,或者必要时你可以在这里只是复制它们的内容
# Server-pool management (MPM specific)
#服务器池管理
#Include conf/extra/httpd-mpm.conf
# Multi-language error messages 多语言错误消息
#Include conf/extra/httpd-multilang-errordoc.conf
# Fancy directory listings动态目录列表形式配置
#Include conf/extra/httpd-autoindex.conf
# Language settings 语言设置
#Include conf/extra/httpd-languages.conf
# User home directories 用户家庭目录
#Include conf/extra/httpd-userdir.conf
# Real-time info on requests and configuration 请求和配置上的实时信息
#Include conf/extra/httpd-info.conf
# Virtual hosts 虚拟主机
#Include conf/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf
# Local access to the Apache HTTP Server Manual 本地访问Apache Http Server手册。
#Include conf/extra/httpd-manual.conf
# Distributed authoring and versioning (WebDAV) 分布式创作和版本控制
#Include conf/extra/httpd-dav.conf
# Various default settings 多种类默认设置
#Include conf/extra/httpd-default.conf
# Configure mod_proxy_html to understand HTML4/XHTML1 配置mod_proxy_html,使它支持HTML4/XHTML1
<IfModule proxy_html_module>
Include conf/extra/proxy-html.conf
</IfModule>
# Secure (SSL/TLS) connections安全连接
#Include conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
#
# Note: The following must must be present to support
# starting without SSL on platforms with no /dev/random equivalent
# but a statically compiled-in mod_ssl.
#注意:
#
<IfModule ssl_module>
SSLRandomSeed startup builtin
SSLRandomSeed connect builtin
</IfModule>
#
# uncomment out the below to deal with user agents that deliberately
# violate open standards by misusing DNT (DNT *must* be a specific
# end-user choice)
#
#<IfModule setenvif_module>
#BrowserMatch "MSIE 10.0;" bad_DNT
#</IfModule>
#<IfModule headers_module>
#RequestHeader unset DNT env=bad_DNT
#</IfModule>