Set集合
Set集合

package SetDemo;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Set01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("java");
set.add("hello"); //不会有重复的元素
//遍历,没有索引所以不能用普通for循环,只能增强for或迭代器,不保证元素的顺序.
Iterator<String> s = set.iterator(); //迭代器 , Iterator
while(s.hasNext()){
String next = s.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
System.out.println("--------");
for (String i :set){ //增强for , enhanced 'for'
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}

package SetDemo;
public class Hash01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建两个内容相同的对象
Students s1 = new Students("Peppa",6);
Students s2 = new Students("Peppa",6);
//同一个对象调用两次hashCode方法,hash值相同
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//990368553
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//990368553
//内容相同的不同对象,hash值不同.
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//990368553
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//1096979270
//字符串不同,hash值一般也不同
System.out.println("hello".hashCode());//99162322
System.out.println("world".hashCode());//113318802
System.out.println("java".hashCode());//3254818
System.out.println("hello".hashCode());//99162322
//也有例外,比如"重地","通话"不同字符串,hash值相同
System.out.println("重地".hashCode());//1179395
System.out.println("通话".hashCode());//1179395
}
}

package SetDemo;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSet_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet <String> hs = new HashSet<>();
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("hello");
//也是不保证元素的顺序,不会有重复的元素
for (String s:hs){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
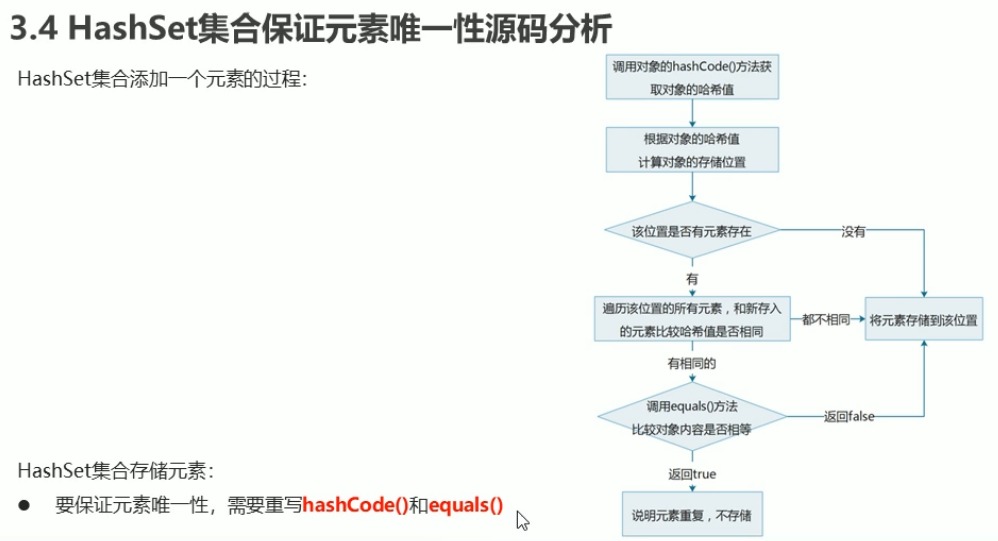
hashCode方法比较哈希值,equals方法比较内容.

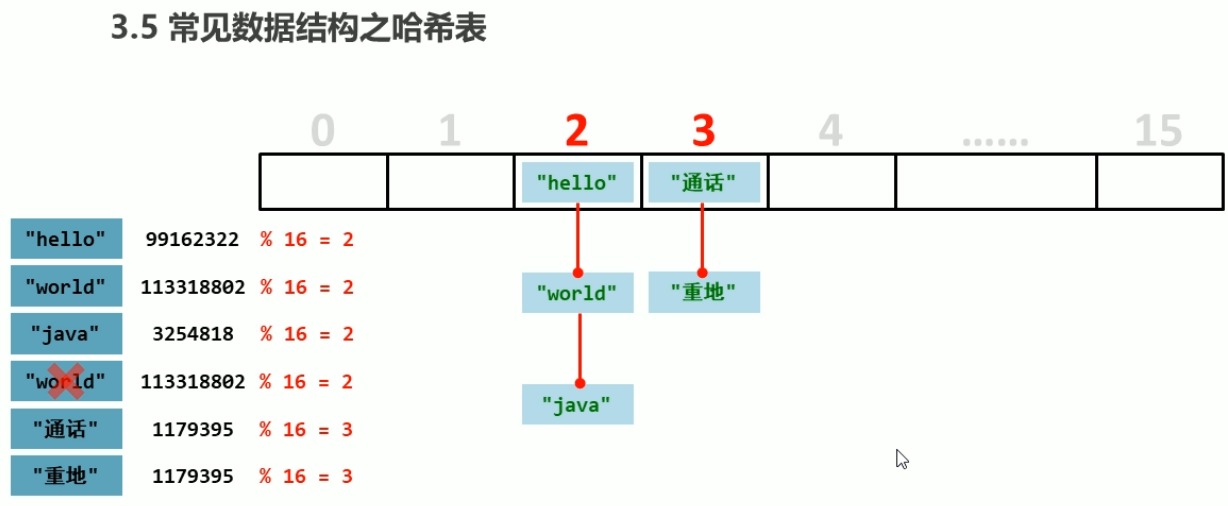
对象的哈希值被16取余就是在数组中存储的位置, 先判断该位置有没有数据,再用hashCode方法判断哈希值是否相同
,如果相同,再用equals方法判断内容是否相同,如果相同就不予存储.
案例: HashSet集合存储学生对象并遍历
需求: 创建一个存储学生对象的集合, 存储多个学生对象, 遍历集合.要求:对象的属性相同时,我们认为是同一个对象,不予添加.
package SetDemo;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class studentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
HashSet<Students> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
//创建对象
Students s1 = new Students("Peppa",6);
Students s2 = new Students("George",4);
//添加对象
hashSet.add(s1);
hashSet.add(s2);
//创建内容重复的对象并添加入集合
Students s3 = new Students("Peppa",6);
hashSet.add(s3);
//遍历集合
for (Students i:hashSet){
System.out.println(i.getName()+","+i.getAge());
}
/*控制台输出了:重复的元素,想要实现需求就要再Students类中重写
hashCode和equals方法.(自动生成就可以)
George,4 Peppa,6 Peppa,6
方法重写后控制台输出: George,4 Peppa,6
*/
}
}
//------------------------------
//在Students中重写hashCode和equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Students students = (Students) o;
if (age != students.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(students.name) : students.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}

LinkedHashSet集合的特点有序,唯一.
package SetDemo;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class LinkedHashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
LinkedHashSet<String> lhs = new LinkedHashSet<>();
//添加元素
lhs.add("hello");
lhs.add("world");
lhs.add("java");
// lhs.add("java"); 哈希表保证元素唯一
//遍历集合 链表保证元素有序
for (String i:lhs){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}

package SetDemo;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
TreeSet<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
//添加对象
treeSet.add(333); //自动装箱
treeSet.add(66);
treeSet.add(99);
treeSet.add(99); //不能包括重复元素.
//遍历
for (Integer i : treeSet){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
/*控制台: 66
99
333
*/
}
自然排序Comparable的使用

package SetDemo;
/*
自然排序Comparable的使用
- 存储学生对象并遍历, 创建TreeSet集合使用无参构造方法.
- 要求: 按照年龄从小到大排序, 年龄相同时, 按照姓名的字母顺序排序.
*/
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
TreeSet<Students> ts = new TreeSet<Students>();
//创建对象
Students s1 = new Students("aa",6);
Students s2 = new Students("bb",3);
Students s3 = new Students("cc",5);
Students s4 = new Students("dd",5);//年龄相同
Students s5 = new Students("dd",5);//名字和年龄都相同,不予存储
//添加对象
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
//遍历集合
for (Students i:ts){
System.out.println(i.getName()+","+i.getAge());
}
}
}
//-----------------------------
//Students类要实现Comparable接口,并重写compareTo()方法
public class Students implements Comparable<Students>{
@Override
public int compareTo(Students o) {
//如果返回0为重复元素不添加,正数为升序,负数为降序.
int i = this.age - o.age; //从小到大排序
// int j = o.Age-this.Age; //从大到小排序
//String类实现了comparable接口,所以说字符串本身就可以自然排序.
int j = i==0?this.name.compareTo(o.name):i;
//如果i==0(年龄相同)再比较名字(也是自然排序),如果名字相同就返回0.
return j;
}
}

//teacher类
public class teacher {
int age ;
String name;
...}
//-------------------------
//测试类
package SetDemo;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*自然排序是在: Students类要实现Comparable接口,并重写compareTo()方法
比较器排序是在: TreeSet构造方法中传递一个Comparator比较器接口, 他们的规则定义是一样的.
*/
public class TreeSetDemoComparator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合, 参数是接口就是接口的实现类对象,可以自己写一个类,这里用匿名内部类.
TreeSet<teacher> tea = new TreeSet<teacher>(new Comparator<teacher>() {
@Override
public int compare(teacher o1, teacher o2) {
//o1==this,, o==s 在测试类里就不能用this了
int i = o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();//比较age
int j = i==0?o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()):i;//比较name
return j;
}
});
//创建对象
teacher t1 = new teacher(20,"bb");
teacher t2 = new teacher(30,"aa");
teacher t3 = new teacher(26,"cc");
teacher t4 = new teacher(30,"dd");//年龄重复元素
teacher t5 = new teacher(30,"dd");//重复元素
//添加对象
tea.add(t1);
tea.add(t2);
tea.add(t3);
tea.add(t4);
tea.add(t5);
//遍历
for (teacher i : tea){
System.out.println(i.getName()+","+i.getAge());
}
}
}
案例: 成绩排序
package SetDemo;
//学生成绩类
public class StudentScore {
private String name;
private int Chinese;
private int Math;
public StudentScore() {
}
public StudentScore(String name, int chinese, int math) {
this.name = name;
Chinese = chinese;
Math = math;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getChinese() {
return Chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese) {
Chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath() {
return Math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
Math = math;
}
public int getSum(){ //求成绩总和的方法
return Chinese+Math;
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
package SetDemo;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*测试类
案例:成绩排序
需求:用TreeSet集合存储多个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩),并遍历该集合
要求:按照总分从高到低出现
思路: 1. 定义学生类
2. 创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序
3. 创建学生对象
4. 把学生对象添加到集合
5. 遍历集合
*/
public class StudentScoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序
TreeSet<StudentScore> ss = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<StudentScore>() {
@Override
public int compare(StudentScore o1, StudentScore o2) {
//主要条件: 按照总分从高到低出现 降序是用o2减o1
// int i = (o2.getChinese()+ o2.getMath())-(o1.getChinese()+o1.getMath());
int i = o2.getSum()- o1.getSum(); //用o2总分减o1总分, 调用求总分方法
//次要条件: 1.当总分相同时,Chinese成绩降序
int j = i==0? o2.getChinese()-o1.getChinese():i;
//次要条件: 2.再用compareTo()方法比较name
int k = i == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : i;
return k;
}
});
//创建学生对象
StudentScore s1 =new StudentScore("ci",80,78);
StudentScore s2 =new StudentScore("aoa",81,82);
StudentScore s3 =new StudentScore("min",97,90);
StudentScore s4 =new StudentScore("biy",80,83);
StudentScore s5 =new StudentScore("kid",79,100);
//把学生对象添加到集合
ss.add(s1);
ss.add(s2);
ss.add(s3);
ss.add(s4);
ss.add(s5);
//遍历集合
for (StudentScore i:ss){
System.out.println(i.getName()+","+i.getChinese()+","+i.getMath()+", Total:"+i.getSum());
}
}
}

package SetDemo;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*
案例:不重复的随机数
需求:编写一个程序,获取10个1—20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复,并在控制台输出
思路:
1.创建Set集合对象
2.创建随机数对象
3.判断集合的长度是不是小于10
是:产生一个随机数,添加到集合
回到3继续
4. 遍历集合
*/
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Set集合对象
Set<Integer> ts = new HashSet<>(); //用HashSet集合是没有排序的
// Set<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>(); TreeSet集合是排序的
//创建随机数对象
Random r = new Random();
while(ts.size()<10) {
ts.add(r.nextInt(0, 20));
}
for (Integer i: ts){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构