Pytorch中的Embedding
有两个Embedding函数,通常是用前面这一个
ref https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Embedding.html
torch.nn.Embedding( num_embeddings, embedding_dim, padding_idx=None, max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False, sparse=False, _weight=None, device=None, dtype=None)
- num_embeddings: size of the directionary of embedding,也就是词汇表的大小=不同单词的个数
- embedding_dim: the size of each embedding vector,也就是embedding向量的维度
一个简单的lookup table(查找表),用例存储固定了dictionary 和 size 的embeddings
它将所有的embedding(词向量)都存起来了,可以通过词的索引检索它们
输入是一个索引列表,输出是词向量列表
>>> # an Embedding module containing 10 tensors of size 3 >>> # 有10种不同的单词,每个单词表示为一个3维的向量 >>> embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3) >>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each >>> input = torch.LongTensor([[1,2,4,5],[4,3,2,9]]) >>> embedding(input) tensor([[[-0.0251, -1.6902, 0.7172], [-0.6431, 0.0748, 0.6969], [ 1.4970, 1.3448, -0.9685], [-0.3677, -2.7265, -0.1685]], [[ 1.4970, 1.3448, -0.9685], [ 0.4362, -0.4004, 0.9400], [-0.6431, 0.0748, 0.6969], [ 0.9124, -2.3616, 1.1151]]])
embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3),这里embedding是一个表,input是在表中的索引
另一个函数是
ref https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.embedding.html
torch.nn.functional.embedding(input, weight, padding_idx=None, max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False, sparse=False)
- input: Tensor containing indices into the embedding matrix,即在词向量矩阵中的索引列表
- weight: embedding matrix,即词向量矩阵,行数为最大可能的索引数+1,列数为词向量的维度
>>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each >>> input = torch.tensor([[1,2,4,5],[4,3,2,9]]) >>> # an embedding matrix containing 10 tensors of size 3 >>> embedding_matrix = torch.rand(10, 3) >>> F.embedding(input, embedding_matrix) tensor([[[ 0.8490, 0.9625, 0.6753], [ 0.9666, 0.7761, 0.6108], [ 0.6246, 0.9751, 0.3618], [ 0.4161, 0.2419, 0.7383]], [[ 0.6246, 0.9751, 0.3618], [ 0.0237, 0.7794, 0.0528], [ 0.9666, 0.7761, 0.6108], [ 0.3385, 0.8612, 0.1867]]])
这个embedding_matrix不用训练的吗?直接用随机数??
而事实上,在nn.Embedding的内部实现中,也是调用的F.embedding

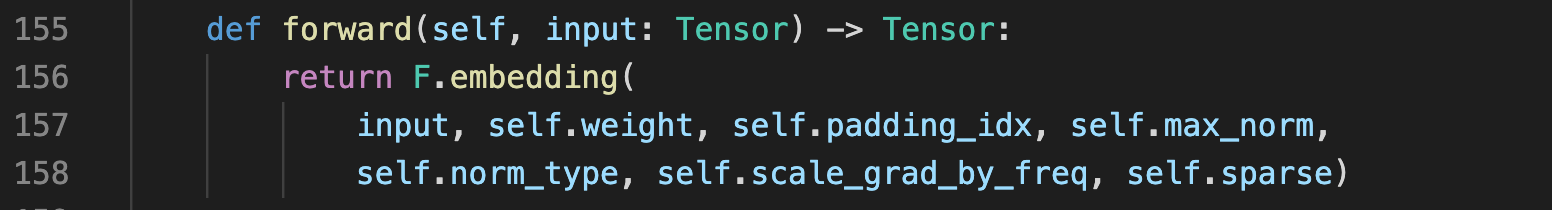
可见embedding matrix也是随机数,因为torch.Tensor(a, b)是正态分布的随机数


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号