快速排序的实现
Java
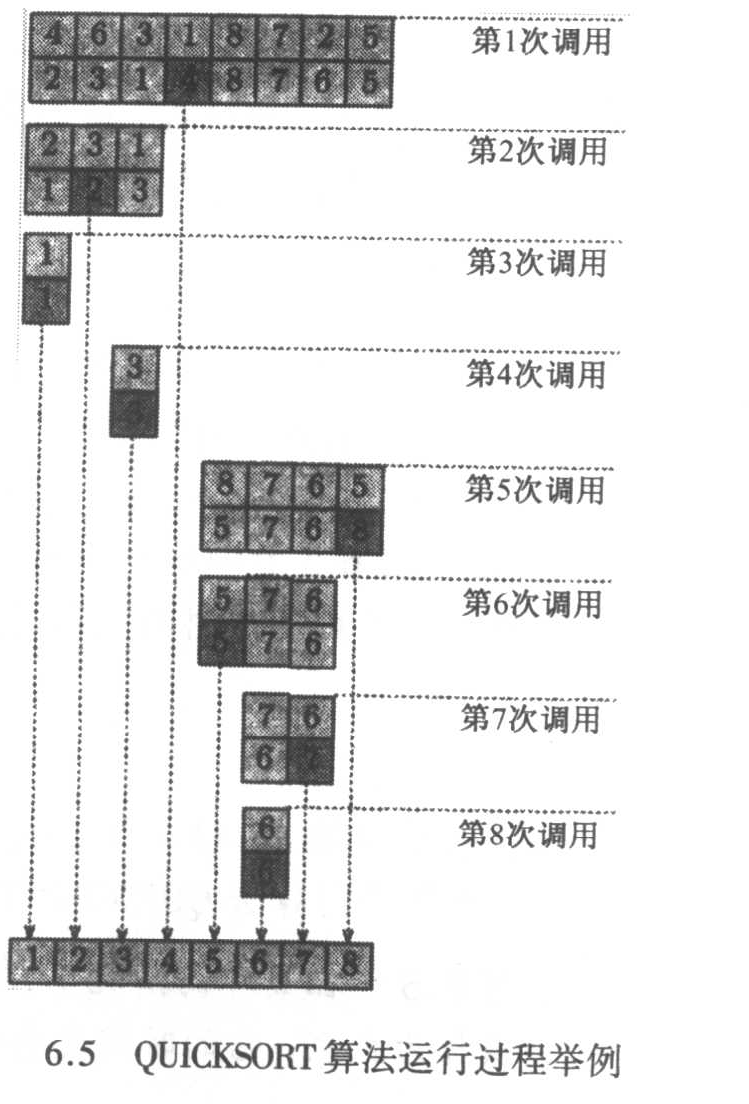
快速排序也是一种交换排序。首先选定一个基准元素(一般取第一个或最后一个元素),根据基准元素,将序列分为2个子序列,左边子序列的全部元素都小于等于基准元素,右边序列的全部元素都大于等于该基准元素。然后对左右这两个序列,递归重复上面的算法,直到序列排序完成。
快速排序的时间复杂度期望是 $O(nlogn)$,最慢可达到 $O(n^2)$。一般在一个乱序的大列表中,快速排序还是最快的排序算法。
以下是java代码简单实现:
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 3 public class QuickSort { 4 5 public void sort(int[] input) { 6 quickSort(input, 0, input.length-1); 7 } 8 9 private void quickSort(int[] input, int low, int high) { 10 if (low < high) { 11 int middle = this.getMiddle_swap(input, low, high); 12 this.quickSort(input, low, middle-1); 13 this.quickSort(input, middle+1, high); 14 } 15 } 16 17 private int getMiddle_swap(int[] input, int low, int high) { 18 int tmp = input[low]; // 取一个基准元素 19 20 while (low < high) { 21 while (low < high && input[high] >= tmp) { 22 high--; 23 } 24 25 input[low] = input[high]; 26 27 while (low < high && input[low] <= tmp) { 28 low++; 29 } 30 31 input[high] = input[low]; 32 } 33 34 input[low] = tmp; 35 return low; 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) { 39 int a[]={5,4,4,5,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,34,15,35,25,53,51}; 40 new QuickSort().sort(a); 41 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 42 } 43 }
C实现




#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; int a[maxn], n; int split(int low, int high) { int i = low; int x = a[low]; // 额外的空间,O(1) for(int j = low+1;j <= high;j++) { if(a[j] <= x) { i++; if(i != j) swap(a[i], a[j]); } } swap(a[low], a[i]); return i; } void quickSort(int low, int high) { if(low < high) { int pos = split(low, high); quickSort(low, pos-1); quickSort(pos+1, high); } } int main() { scanf("%d\n", &n); for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); quickSort(0, n); for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) printf("%d ", a[i]); }
参考链接:
1. https://buzheng.org/quick-sort.html
2. 《算法设计技巧与分析》
个性签名:时间会解决一切


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号