log4j2异步日志解读(一)AsyncAppender

log4j、logback、log4j2 历史和关系,我们就在这里不展开讲了。直接上干货,log4j2突出于其他日志的优势,异步日志实现。
看一个东西,首先看官网文档 ,因为前面文章已经讲解了disruptor源码,本文主要展开说说异步日志AsyncAppender和AsyncLogger(基于disruptor实现)。
一、AsyncAppender

我们先来看看AsyncApperder核心,就是logger将数据通过append方法放入到阻塞队列中,随后后台线程从队列中取出数据然后进行后续的操作。
那这样看来,就很简单了,一个append()方法,一个后台线程执行就是我们要看的核心代码了。围绕我们要看的类AsyncAppender,来看看类关系图。
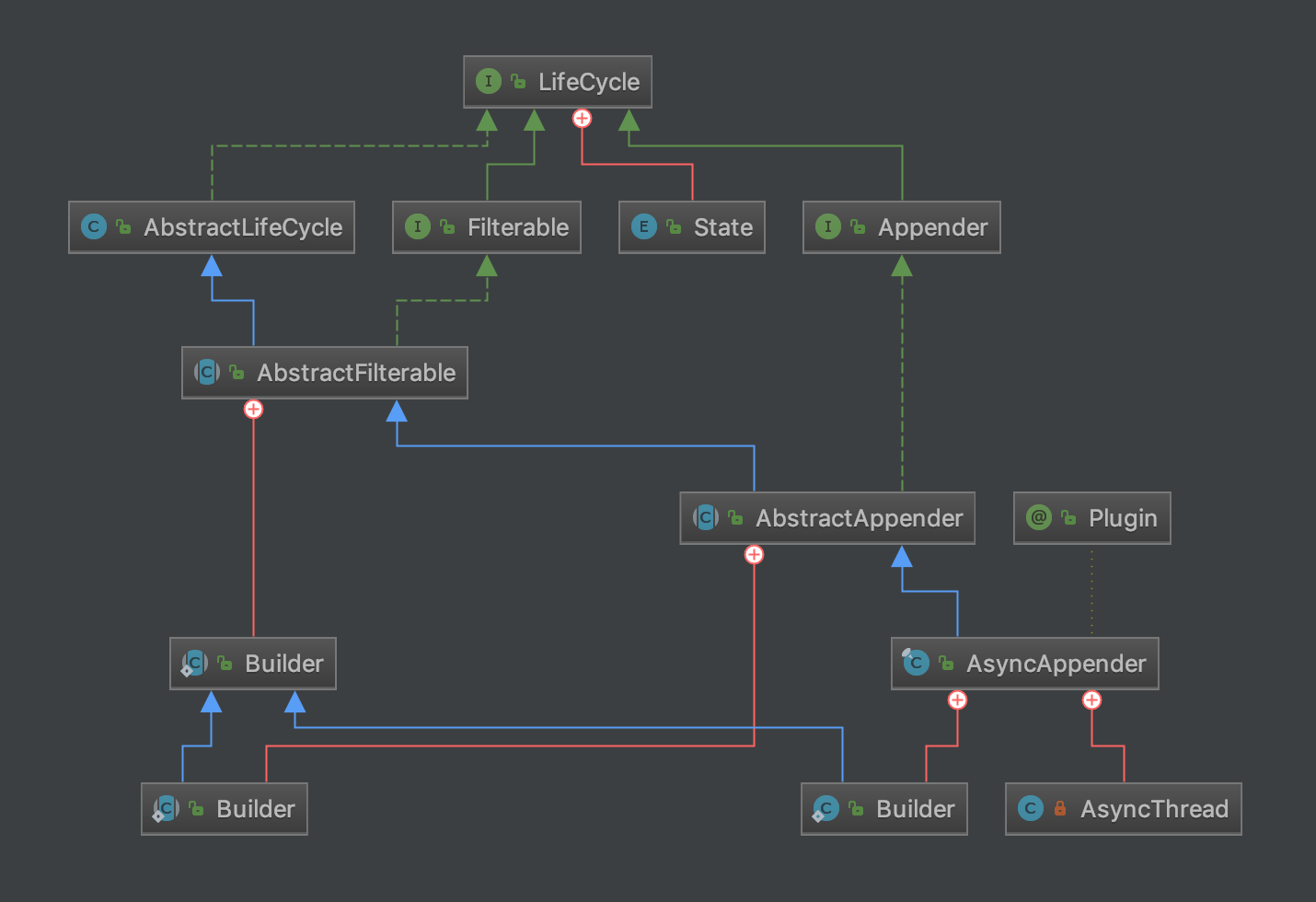
一、放入队列
主要实现就是logger将数据通过append方法放入到阻塞队列中。
//AsyncAppender.java /** * Actual writing occurs here. * * @param logEvent The LogEvent. */ @Override public void append(final LogEvent logEvent) { if (!isStarted()) { throw new IllegalStateException("AsyncAppender " + getName() + " is not active"); } //创建Log4jLogEvent的对象memento final Log4jLogEvent memento = Log4jLogEvent.createMemento(logEvent, includeLocation); InternalAsyncUtil.makeMessageImmutable(logEvent.getMessage()); //transfer(memento)将event放入队列 //默认ArrayBlockingQueueFactory 大小1024 if (!transfer(memento)) { if (blocking) { if (AbstractLogger.getRecursionDepth() > 1) { // LOG4J2-1518, LOG4J2-2031 // If queue is full AND we are in a recursive call, call appender directly to prevent deadlock AsyncQueueFullMessageUtil.logWarningToStatusLogger(); logMessageInCurrentThread(logEvent); } else { // delegate to the event router (which may discard, enqueue and block, or log in current thread) final EventRoute route = asyncQueueFullPolicy.getRoute(thread.getId(), memento.getLevel()); route.logMessage(this, memento); } } else { error("Appender " + getName() + " is unable to write primary appenders. queue is full"); logToErrorAppenderIfNecessary(false, memento); } } } private boolean transfer(final LogEvent memento) { return queue instanceof TransferQueue ? ((TransferQueue<LogEvent>) queue).tryTransfer(memento) : queue.offer(memento); }
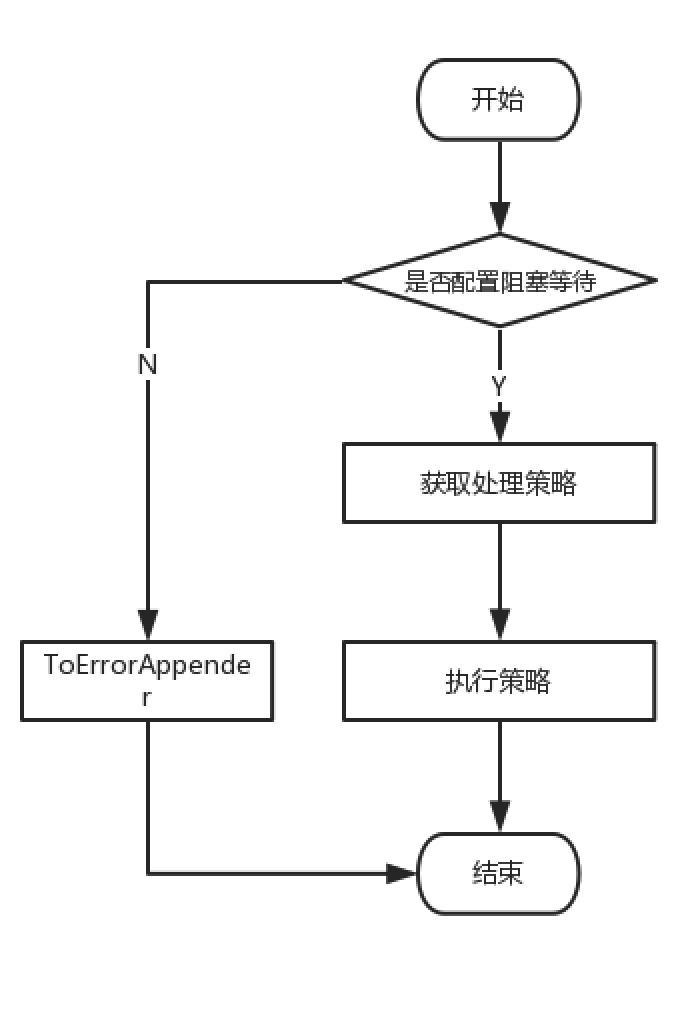
如流程图所示,首先会判断用户是否设置了blocking选项,默认是true,如果设置为false,则Appender直接会ToErrorAppender,如果用户没有配置或者配置为true,则会按照一定的策略来处理这些消息。策略可以分为2种,他们分别为:
1、DefaultAsyncQueueFullPolicy---等待队列,转为同步操作策略
public class DefaultAsyncQueueFullPolicy implements AsyncQueueFullPolicy { @Override public EventRoute getRoute(final long backgroundThreadId, final Level level) { // LOG4J2-471: prevent deadlock when RingBuffer is full and object // being logged calls Logger.log() from its toString() method if (Thread.currentThread().getId() == backgroundThreadId) { return EventRoute.SYNCHRONOUS; } return EventRoute.ENQUEUE; }
2、DiscardingAsyncQueueFullPolicy---按照日志等级抛弃日志策略
//DiscardingAsyncQueueFullPolicy.java @Override public EventRoute getRoute(final long backgroundThreadId, final Level level) { if (level.isLessSpecificThan(thresholdLevel)) { if (discardCount.getAndIncrement() == 0) { LOGGER.warn("Async queue is full, discarding event with level {}. " + "This message will only appear once; future events from {} " + "are silently discarded until queue capacity becomes available.", level, thresholdLevel); } return EventRoute.DISCARD; } return super.getRoute(backgroundThreadId, level); }
二、后台线程执行后续操作。
主要就是后台线程从队列中取出数据然后进行后续的操作。
//AsyncAppender.java private class AsyncThread extends Log4jThread { private volatile boolean shutdown = false; private final List<AppenderControl> appenders; private final BlockingQueue<LogEvent> queue; public AsyncThread(final List<AppenderControl> appenders, final BlockingQueue<LogEvent> queue) { super("AsyncAppender-" + THREAD_SEQUENCE.getAndIncrement()); this.appenders = appenders; this.queue = queue; setDaemon(true); } @Override public void run() { while (!shutdown) { LogEvent event; try { event = queue.take(); if (event == SHUTDOWN_LOG_EVENT) { shutdown = true; continue; } } catch (final InterruptedException ex) { break; // LOG4J2-830 } event.setEndOfBatch(queue.isEmpty()); final boolean success = callAppenders(event); if (!success && errorAppender != null) { try { errorAppender.callAppender(event); } catch (final Exception ex) { // Silently accept the error. } } } // Process any remaining items in the queue. LOGGER.trace("AsyncAppender.AsyncThread shutting down. Processing remaining {} queue events.", queue.size()); int count = 0; int ignored = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { try { final LogEvent event = queue.take(); if (event instanceof Log4jLogEvent) { final Log4jLogEvent logEvent = (Log4jLogEvent) event; logEvent.setEndOfBatch(queue.isEmpty()); callAppenders(logEvent); count++; } else { ignored++; LOGGER.trace("Ignoring event of class {}", event.getClass().getName()); } } catch (final InterruptedException ex) { // May have been interrupted to shut down. // Here we ignore interrupts and try to process all remaining events. } } LOGGER.trace("AsyncAppender.AsyncThread stopped. Queue has {} events remaining. " + "Processed {} and ignored {} events since shutdown started.", queue.size(), count, ignored); } ... }
该线程会一直尝试从阻塞队列中获取LogEvent,如果获取成功,调用AppenderRef所引用Appender的append方法。我们也可以看到,AsyncAppender实际上主要是类似于中转,日志异步化,当消息放入阻塞队列,返回成功,这样能够大幅提高日志记录的吞吐。用户可以在权衡性能与日志收集质量上进行权衡配置策略(设置blocking选项),当然也可以设置不同类型的阻塞队列已到达更好的日志记录吞吐。
AsyncAppender配置参数
https://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/manual/appenders.html#AsyncAppender


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号