Seata源码分析——SessionManager
我们知道Seata服务端TC在全局事务中需要协调TM,RM分工干活,一个全局事务
GlobalSession是由多个分支事务BranchSession组成的,那么TC端必须要对这些全局事务和分支事务进行管理,比如事务的创建、更新、删除...我们今天就来聊一聊Seata中的用来管理事务的 SessionManager。
*这里为什么叫SessionManager:有博客说Seata的中的事务也叫会话,会话管理器也叫事务管理器。我们就这样叫吧
事务管理器
SessionManager
SessionManager顾名思义它是用来管理事务的,是一个接口,我们来看它的继承关系:
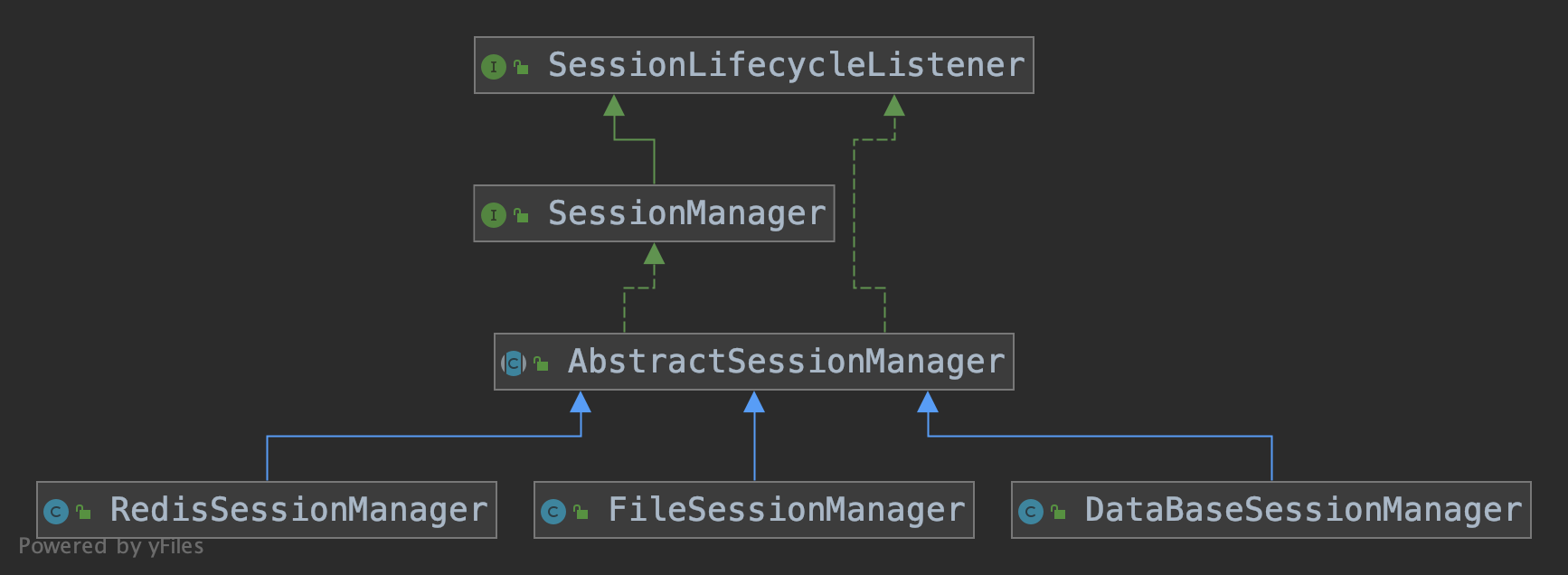 *这种结构还挺常见的,Seata的Netty模块也是这样,一个顶级接口,一个抽象类,然后下面就是具体模式的实现类。
*这种结构还挺常见的,Seata的Netty模块也是这样,一个顶级接口,一个抽象类,然后下面就是具体模式的实现类。
SessionLifecycleListener
看字眼Lifecycle,说明在Seata中,事务是有生命周期的:从开始到结束,中间会有很多状态的变化SessionLifecycleListener,就是事务生命周期的监听器,使用了观察者模式,这个接口定义了一系列要监听的事件:
public interface SessionLifecycleListener {
/**
* 监听全局事务的开启,当处理全局事务开启请求时,会调用该方法
*/
void onBegin(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务对象GlobalSession的状态变化,只要是GlobalSession的状态发生变化,就会调用该方法
*/
void onStatusChange(GlobalSession globalSession, GlobalStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听分支事务状态的变化,在处理分支状态报告请求时,会调用该方法
*/
void onBranchStatusChange(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession, BranchStatus status)
throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听新的分支事务注册
*/
void onAddBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听分支事务从全局事务对象中移除,
* 当处理全局事务回滚请求全局事务提交请求时,都会有移除分支事务的动作,因此都会触发该方法
*/
void onRemoveBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务关闭,也就是监听GlobalSession的close方法。
* 在处理全局事务提交请求和全局事务回滚请求时,都会调用GlobalSession的close方法。
*/
void onClose(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务终止,也就是监听GlobalSession的end方法。
* 当要求全局事务提交或者回滚时,无论最后成功与否,seata都会调用GlobalSession的end方法,因此都会触发onEnd
*/
void onEnd(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
}
SessionManager则定义了GlobalSession状态发生变化时应该执行的动作方法
public interface SessionManager extends SessionLifecycleListener, Disposable {
/**
* 将全局事务对象添加到会话管理器中,当全局事务异步提交或者异步回滚时,都会调用该方法
*/
void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 根据XID查找GlobalSession
*/
GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid) ;
/**
* 不同的存储模式下,本方法和上面的方法实现不同,如果存储模式是file,则两个方法完全一致,
* 如果存储模式是db,则上面的方法相当于调用findGlobalSession(xid, true)
* 如果第二个参数为true,表示返回的GlobalSession对象中带有分支事务集合
*/
GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions);
/**
* 更新事务对象的状态
*/
void updateGlobalSessionStatus(GlobalSession session, GlobalStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 从管理器中移除GlobalSession
* 当异步提交重试超时时,会调用该方法
*/
void removeGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 向GlobalSession中添加分支事务对象,当分支事务注册时,会调用该方法
*/
void addBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 更新分支事务状态
*/
void updateBranchSessionStatus(BranchSession session, BranchStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 从全局事务中移除分支事务,当全局事务提交或者回滚时,会调用该方法
*/
void removeBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 返回所有的全局会话对象
*/
Collection<GlobalSession> allSessions();
/**
* 根据条件查找符合要求的GlobalSession
*/
List<GlobalSession> findGlobalSessions(SessionCondition condition);
/**
* 对全局事务对象加锁,当修改全局事务对象的状态时,都会加锁
*/
<T> T lockAndExecute(GlobalSession globalSession, GlobalSession.LockCallable<T> lockCallable)
throws TransactionException;
}
AbstractSessionManager
AbstractSessionManager是下一层的封装,它有三个实现类,分别对应三种存储模式:文件,数据库和Redis
它实现了SessionManager中定义的方法,还增加了一个重要的方法:writeSession,对Session管理的方法大多都直接或间接地调用了writeSession;我们简单来看一个:
@Override
public void removeGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("MANAGER[{}] SESSION[{}] {}", name, session, LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE);
}
writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE, session);
}
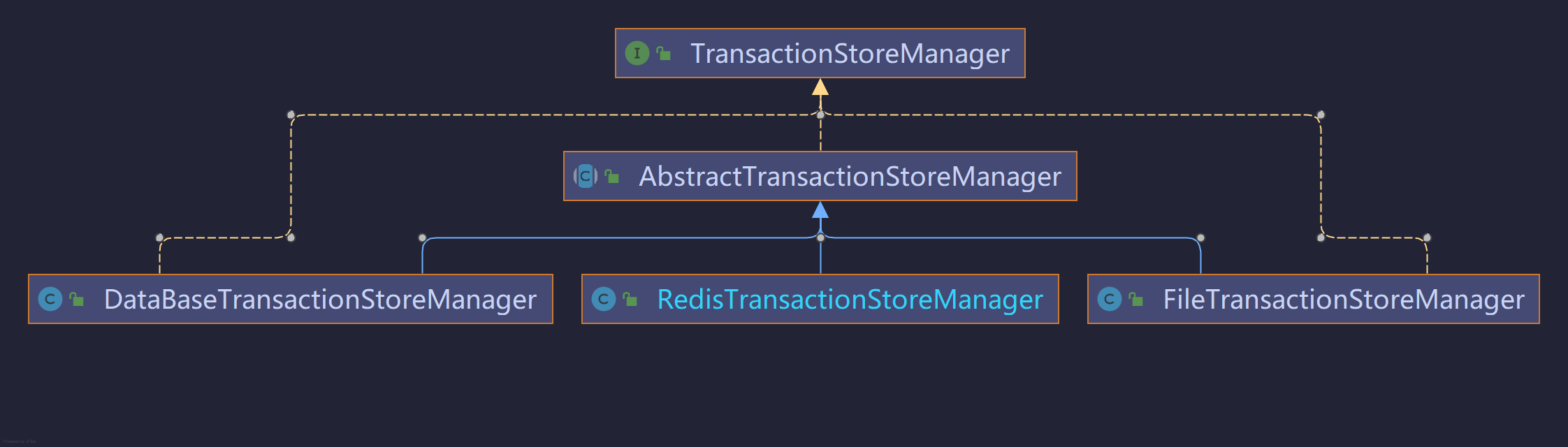
AbstractSessionManager中还持有一个变量:事务存储管理器,也有三种实现,分别是文件,数据库和Redis。下面就继续分析它。
/**
* The Transaction store manager.
*/
protected TransactionStoreManager transactionStoreManager;
事务存储管理器
事务管理器的作用是对Seata的事务进行管理,管理完了还得存储起来 。AbstractSessionManager这个类中还持有了TransactionStoreManager,它是用来实现存储事务状态的。
下面我们以RedisTransactionStoreManager为例进行分析:
RedisTransactionStoreManager
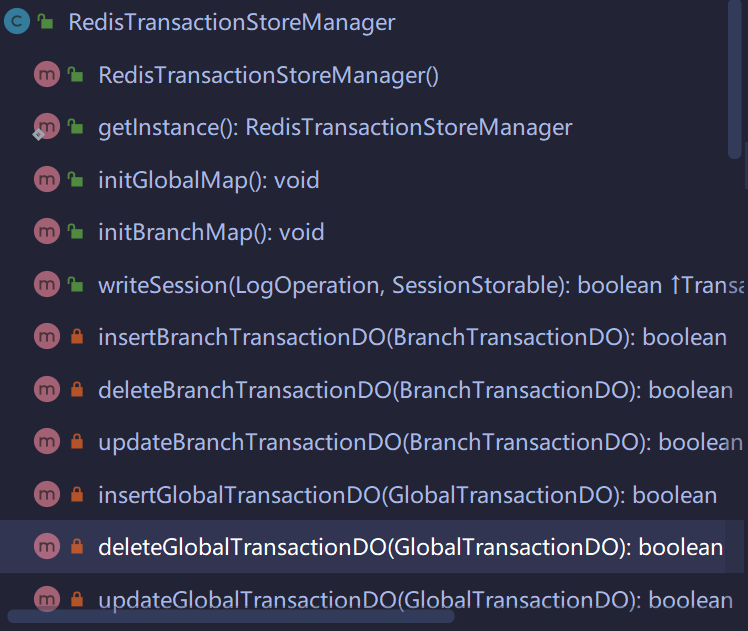
可以看到有不少insert,delete的操作,说明这里就真正将事务信息存到Redis的逻辑了,我们挑一个来看一下:
/**
* Insert the global transaction.
* @param globalTransactionDO
* @return
*/
// GlobalTransactionDO:要插入数据库的类,和global_table的字段是一一对应的
private boolean insertGlobalTransactionDO(GlobalTransactionDO globalTransactionDO) {
// 获取全局事务的键
String globalKey = buildGlobalKeyByTransactionId(globalTransactionDO.getTransactionId());
//使用了Jedis和Pipeline
try (Jedis jedis = JedisPooledFactory.getJedisInstance(); Pipeline pipelined = jedis.pipelined()) {
Date now = new Date();
//构建要插入的DO
globalTransactionDO.setGmtCreate(now);
globalTransactionDO.setGmtModified(now);
//通过pipeline执行
pipelined.hmset(globalKey, BeanUtils.objectToMap(globalTransactionDO));
pipelined.rpush(buildGlobalStatus(globalTransactionDO.getStatus()), globalTransactionDO.getXid());
pipelined.sync();
return true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RedisException(ex);
}
}
TO BE CONTINUE...



