Seata源码分析——AT模式底层实现
以AT为例,我们使用Seata时只需要在全局事务的方法上加上@GlobalTransactional,就开启了全局事务的支持。那么Seata的底层到底是怎么实现的呢?
如果对Seata源码无从下手,那么不妨从Spring切入:
GlobalTransactionScanner
在Seata中有一个重要的bean组件:GlobalTranscationScanner,它是用来扫描被标注了@GlobalTransactional,@GlobalLock注解的方法或类的。

GlobalTranscationScanner,全局事务扫描器,它继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean接口。这四个都是spring的类,所以想要知道这个GlobalTransactionScanner做了什么工作,我们首先得介绍一下spring知识:
-
AbstractAutoProxyCreator: 是spring的AOP的一个核心类。
-
InitializingBean:此接口为Bean提供了初始化方法的方式,只包含
afterPropertiesSet方法 -
DisposableBean:这个接口和InitializingBean是一组的.它只包含
destroy方法,作用是为Bean生命周期结束前做一些收尾工作。 -
ApplicationContextAware:实现了这个接口的类可以方便地获得
ApplicationContext中的Bean。 可以简单理解为它就是一个spring容器
可以看出来,GlobalTransactionScanner继承了AOP,可以对Bean进行增强,同时还相当于一个spring容器。接下我们来看它做了实现这些接口都做了什么事。
继承AbstractAutoProxyCreator
实现AOP后,我们重点来看下被重写的wrapIfNecessary, 它是AOP中核心的方法
1.wrapIfNecessary()
/**
* The following will be scanned, and added corresponding interceptor:
*/
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// do checkers
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy:检查是否为TCC(这里我们研究AT,就不看TCC了)
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
} else {
// 不是TCC模式:
Class<?> serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class<?>[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
//判断是否有相关事务的注解,如GlobalTransactional,如果没有就不会代理,直接返回bean
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
//发现存在AT事务相关注解的bean,则添加拦截器———GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
// ...
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
}
}
说明: 此方法会对被全局事务注解的方法所在的类生成代理对象,并织入对应的拦截器。
看源码方法上的注释,也验证了我们的分析
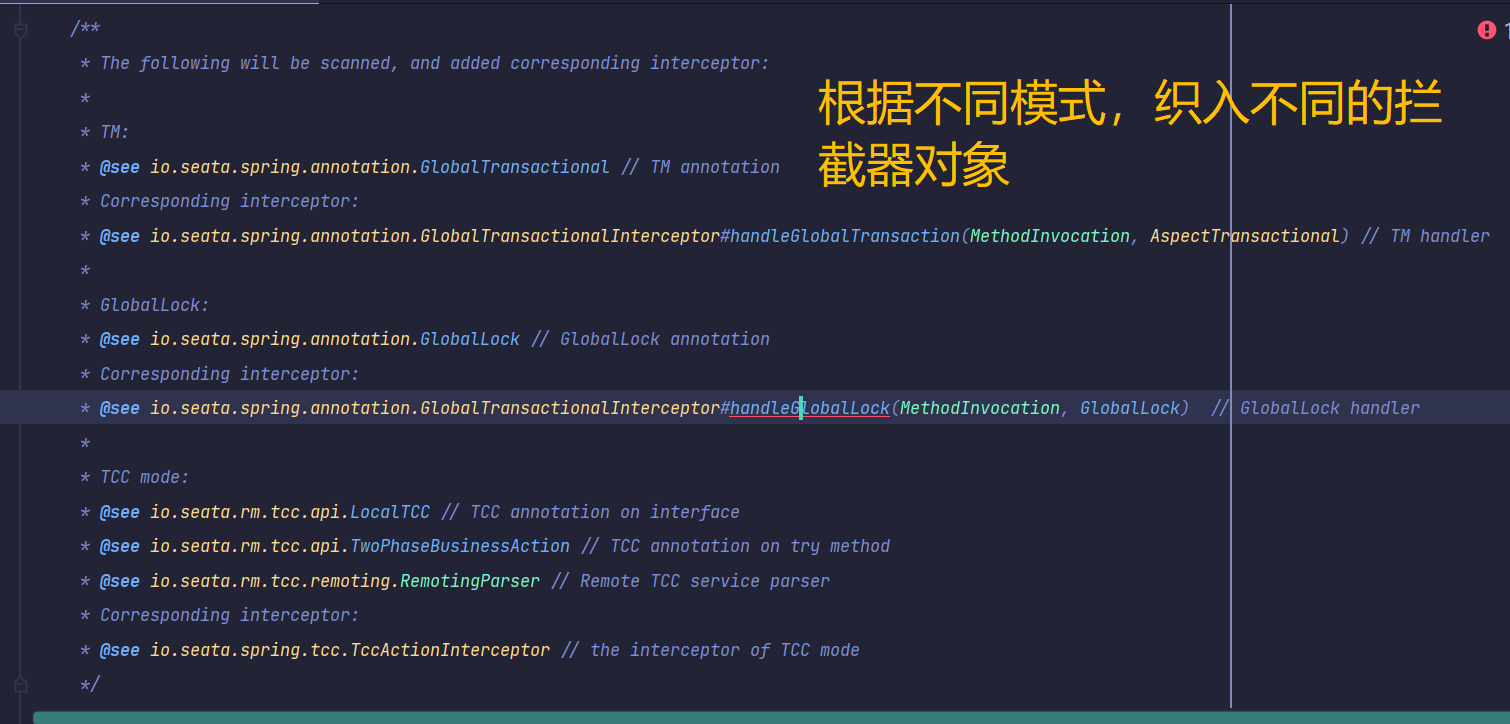
注:这样做的好处,是利用了springAOP的支持对事务的开启做了封装,我们写业务代码的时候只需要标个注解就行了,不需要学习seata的相关方法什么的。(这里推荐阅读末尾的参考文章,seata贡献者做了更详细的分析)
2.invoke()
globalTransactionalInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor这个接口,此接口只有一个方法#invoke():
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
// 1.获取注解标注的执行方法
Class<?> targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// 2.获取全局事务GlobalTransactional的元数据
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
// 3.获取全局锁GlobalLock的元数据.全局锁会将本地事务的执行纳入到seata的管理,一起竞争全局锁,
// 保证全局事务在执行时,不会收到本地其他事务的影响。(隔离性)
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
//4.执行全局事务
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, transactional);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
//4.执行全局锁
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
3.handleGlobalTransaction()
我们重点关注执行全局事务的方法handleGlobalTransaction().它的作用是获取事务信息并且执行全局事务:
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final AspectTransactional aspectTransactional) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
// 调用execute方法,执行全局事务
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
// 获取事务名称
public String name() {
String name = aspectTransactional.getName();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
//获取事务信息,并封装成TransactionInfo对象
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout
int timeout = aspectTransactional.getTimeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());
transactionInfo.setPropagation(aspectTransactional.getPropagation());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInterval(aspectTransactional.getLockRetryInterval());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(aspectTransactional.getLockRetryTimes());
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : aspectTransactional.getRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : aspectTransactional.getRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : aspectTransactional.getNoRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : aspectTransactional.getNoRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
//...
}
} finally {
//...
}
}
说明:
- 这个方法的主要工作是获取事务的名称和信息,并开启全局事务.
- 全局事务的开启调用了transactionalTemplate中的execute()方法.下面继续进入execute方法:
4.execute()
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo 获取事务信息
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 获取当前事务,主要获取XId
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation. 配置不同事务的传播行为,执行不同逻辑.
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
//Spring事务的7种传播行为
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 如果当前事务为空,则新创建一个.
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 开启全局事务.
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
// 发生异常,全局回滚.各个数据根据undo_log进行补偿.
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 如果没有异常发生,则提交全局事务
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
}
}
说明:
-
看到这里可能有些似曾相似,这个流程下来不就是AT模式的2个阶段嘛.我们探究到了AT模式的具体实现!
-
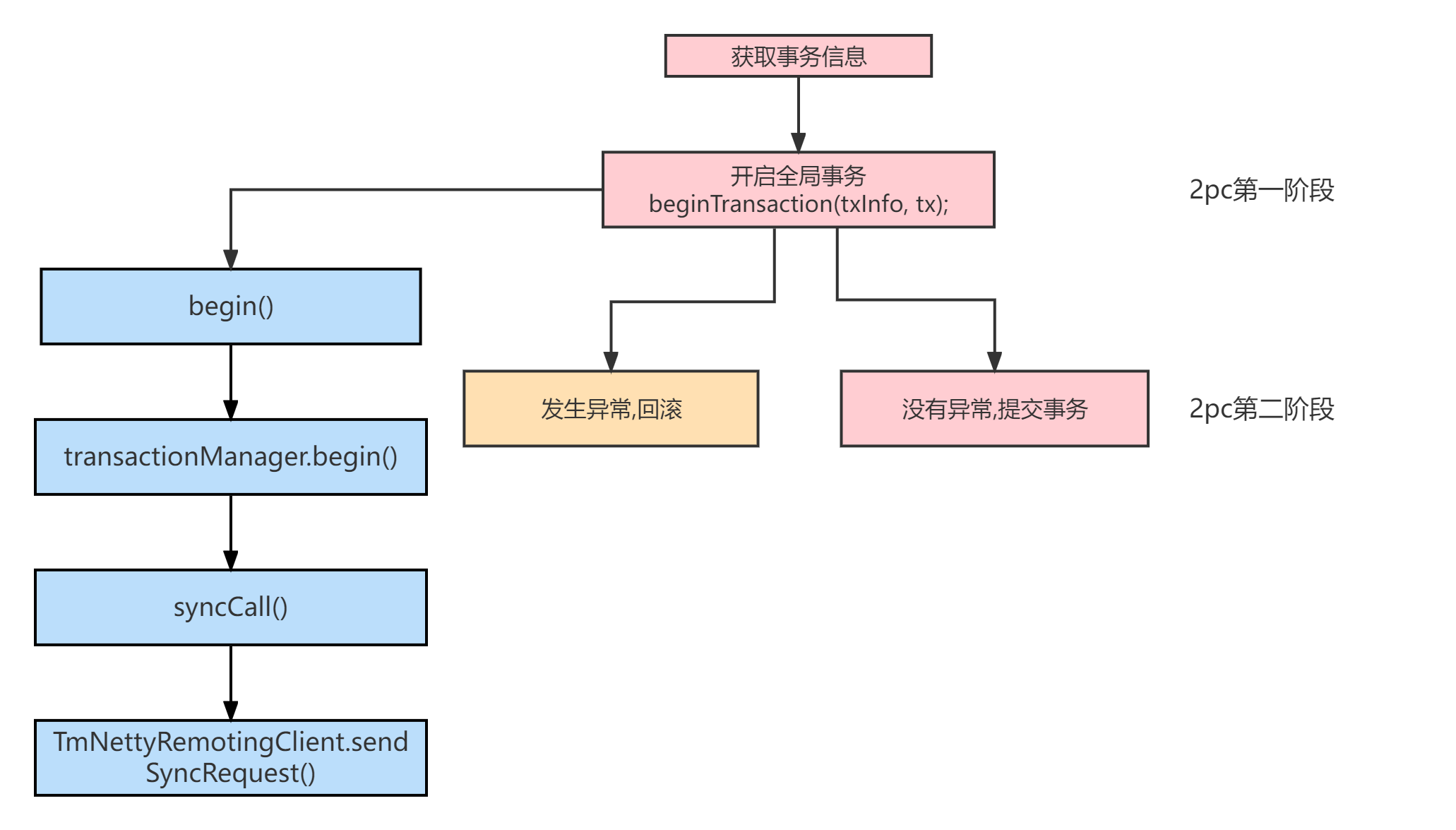
在此方法中,我们终于看到了开启全局事务的关键方法: beginTransaction(). 不过,我们知道TM要开启全局事务,首先得向TC发起请求. 说明我们还得进入beginTransaction()方法中一探究竟,这里面还调用了不少方法,大家看的时候可以只看注释的一行往下推进:
4.1 beginTransaction()
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
triggerBeforeBegin();
//对TC发起请求
tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName());
triggerAfterBegin();
} //...
}
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
// 判断事务的发起者是不是TM,如果不是抛异常
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();
String currentXid = RootContext.getXID(); //获取Xid
if (currentXid != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," +
" can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid);
}
//调用transactionManager.begin()
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
// 关键:syncCall 同步请求
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
return response.getXid();
}
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 通过Netty发起请求
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}
实现InitializingBean接口
InitializingBean接口只有一个方法afterPropertiesSet(),GlobalTransactionScanner对它进行了重写:
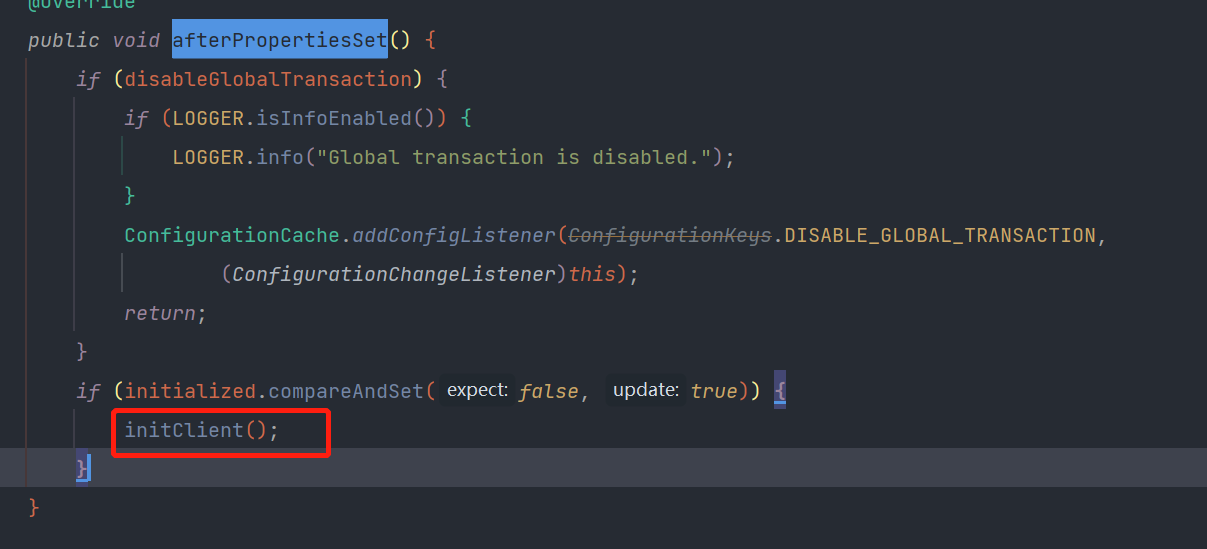
说明: 调用了initCLient方法:初始化了TM和RM
private void initClient() {
// ....
//init TM
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
// 日志
//init RM
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
// 日志
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}
初始化TM:
public static void init(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String accessKey, String secretKey) {
// 获取TMRpc客户端实例
TmNettyRemotingClient tmNettyRemotingClient = TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
//初始化 TM Client
tmNettyRemotingClient.init();
}
调用 TmRpcClient.getInstance() 方法会获取一个 TM 客户端实例.
在获取过程中,会创建 Netty 客户端配置文件对象,以及创建 messageExecutor 线程池,该线程池用于在处理各种与服务端的消息交互,在创建 TmRpcClient 实例时,创建 ClientBootstrap,用于管理 Netty 服务的启停,以及 ClientChannelManager,它是专门用于管理 Netty 客户端对象池.
初始化TM客户端:
To Be Continue...
写在最后
博主也是刚开始学习Seata,编程功力不太深,很多代码的精妙之处也看不出来.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步