Motion Planning for Mobile Robots 学习笔记3
What this note covers
第3章:基于采样的路径规划
- 第1节:概率路线图算法&快速探索随机树算法
- 第2节:基于采样的最优路径规划算法&基于采样的路径规划算法进阶
- 第3节:作业
Preliminaries
预备知识
Sampling Based-Planners
- Do not attempt to explicitly construct the C-Space and its boundaries
- Simply need to know if a single robot configuration is in collision
- Exploits simple tests for collision with full knowledge of the space
- Collision detection is a separate module-can be tailored to the application
- As collision detection improves, so do these algorithms
- Different approaches for single-query and multi-query requests
Notion of Completeness in Planning
- Complete Planner: always answers a path planning query correctly in bounded time
完备的规划器:在一定的时间内,该规划器总能找到一条路径 - Probabilistic Complete Planner: if a solution exists, planner will eventually find it, using random sampling (e.g. Monte Carlo sampling)
概率完备的规划器:如果存在一条路径,则一定可通过采样的方法得到该路径 - Resolution Complete Planner: same as above but based on a deterministic sampling (e.g sampling on a fixed grid).
Resolution Complete Planner: 与上面类似,但是基于更确定性的采样(如在网格上的采样)
Content
- Probabilistic Road Map
环境路图的构建与如何利用环境路图寻找路径 - Rapidly-exploring Random Tree
快速扩展随机树,RRT - Optimal sampling-based path planning methods
一些改进方法 - Advanced path planning methods
高等方法 - Implementation
应用
Probabilistic Road Map
What is PRM?
期望通过采样的方式,对地图进行简化。用少量的点代表我们的图。
在简化的图结构上寻找路径,而不是在整个地图寻找。
- A graph structure
一种图结构 - Divide planning into two phases:
分为两个阶段- Learning phase:
学习阶段:如何简化?首先要学习图的结构- Sample N point in C-Space
随机采样一部分点,最基本的方法可使用均匀采样。 - Delete points that are not collision-free
在障碍物中的点删除 - Connect to nearest points and get collision-free segments.
首先注意:起点和终点必须被连接。
准则1.(距离准则)根据距离远近,将相距较近的点连接起来。 - Delete segments that are not collision free.
准则2.(障碍物准则)删除不满足碰撞检测的边。
- Sample N point in C-Space
- Query phase:
查询阶段:寻找路径(在空间简化图上,应用图搜索算法)- Search on the road map to find a path from the start to the goal (using Dijkstra's algorithm or the A* algorithm).
- Road map is now similar with the grid map (or a simplified grid map)
- Learning phase:
- Checking sampled configurations and connections between samples for collision can be done efficiently.
- A relatively small number of milestones and local paths are sufficient to capture the connectivity of the free space
Pros and Cons
- Pros
- Probabilistically complete
概率完备的 - 不用在整个环境进行搜索,相对高效
- Probabilistically complete
- Cons
- Required to solve 2 point boundary value problem
需要解决边界值问题 - Build graph over state space but no particular focus on generating a path
第一阶段并不关心如何生成路径,造成了一次“多余的”查询阶段 - Not efficient
不够有效率
- Required to solve 2 point boundary value problem
Towards Improving Efficiency: Lazy collision-checking
-
Lazy collision-checking
经常性地需要检测点/边是否在障碍物内/collision-free,非常影响效率
提出懒惰障碍物检测方法- Collision-checking process is time-consuming, especially in complex or high-dimensional environments.
碰撞检查过程非常耗时,特别是在复杂或高维环境中 - Sample points and generate segments without considering the collision (Lazy)
不考虑是否可性的选取采样点和生成边(惰性)
也即不考虑障碍物准则,只考虑距离准则。
- Find a path on the road map generated without collision-checking
在未进行碰撞检查的情况下在路线图上查找路径 - Delete the corresponding edges and nodes if the path is not collision free.
如果路径不是无碰撞的,删除相应的边和节点。 - Restart path finding
- Collision-checking process is time-consuming, especially in complex or high-dimensional environments.
虽然修改图结构会消耗一些时间,但是避免了大量的碰撞检测,节省了时间。
注意:Lazy collision-checking不仅适合于PRM,还适合于其他方法,如RRT等。
Rapidly-exploring Random Tree
快速扩展随机树(快速搜索随机树)
也是一种基于采样的路径规划算法,但与PRM相比,其更有针对性。在复杂环境/高维环境中,更有效率。
如何在空间中构造一棵树,这棵树如何帮助我们找到路径?
Overview
- Build up a tree through generating "next states" in the tree by executing random controls
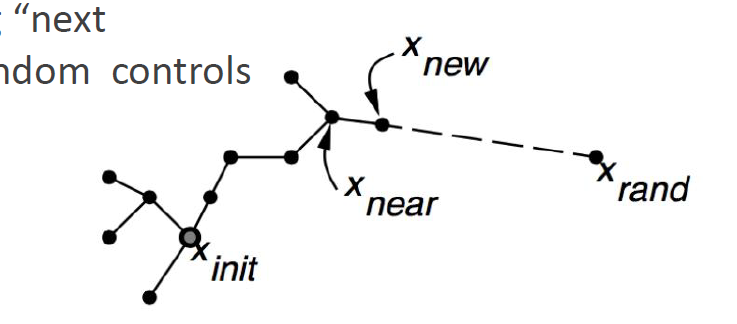
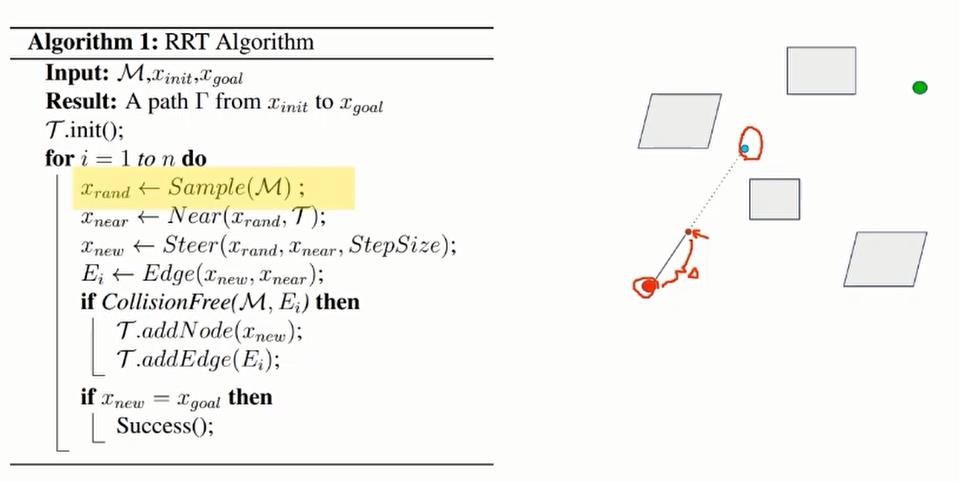
随机采样得到蓝色点,连接起点与蓝色点的线段,在这个线段上前进一段距离,得到小的红色点。
如果小红色点与连接起点和小红色点的线段都可通过碰撞检测,则将其加入树中。
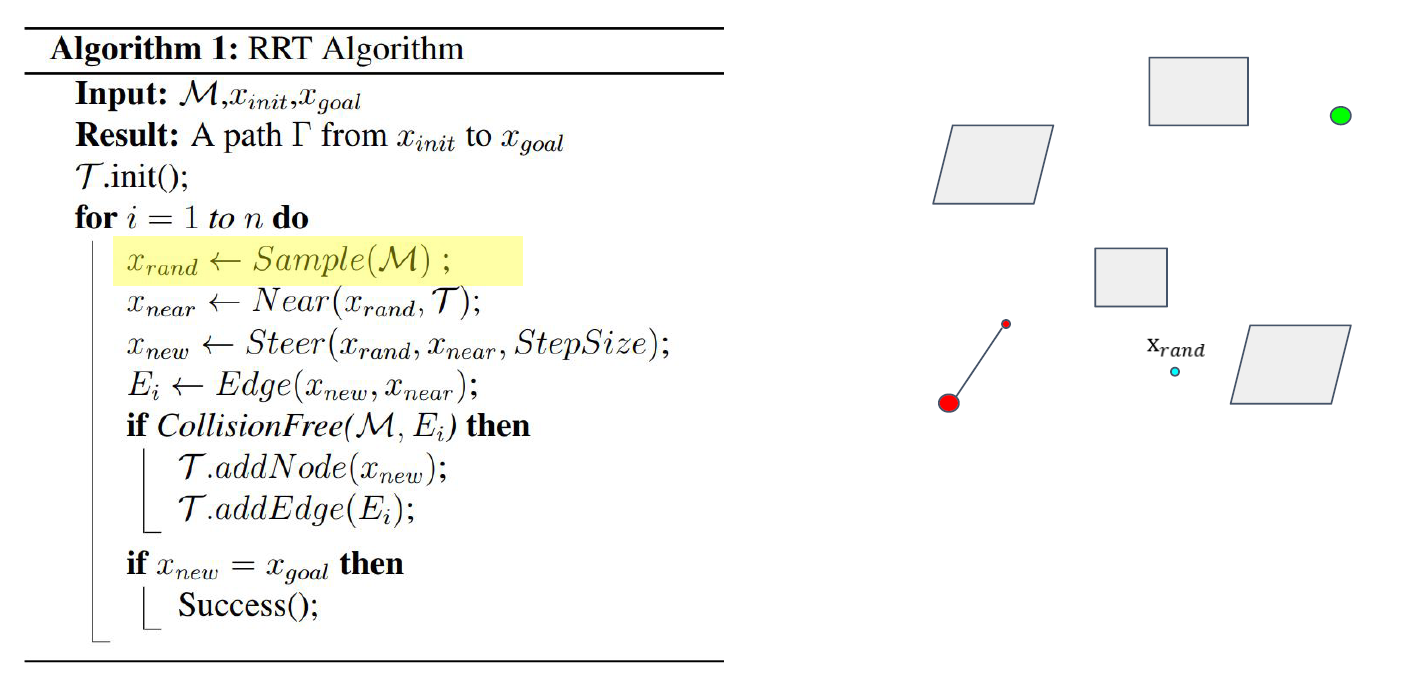
再次随机采样,得到蓝色点。
注意:这里的采样方法与PRM中类似,可以在整个空间均匀撒点,也可以用一定的采样规律撒点(偏置采样)。
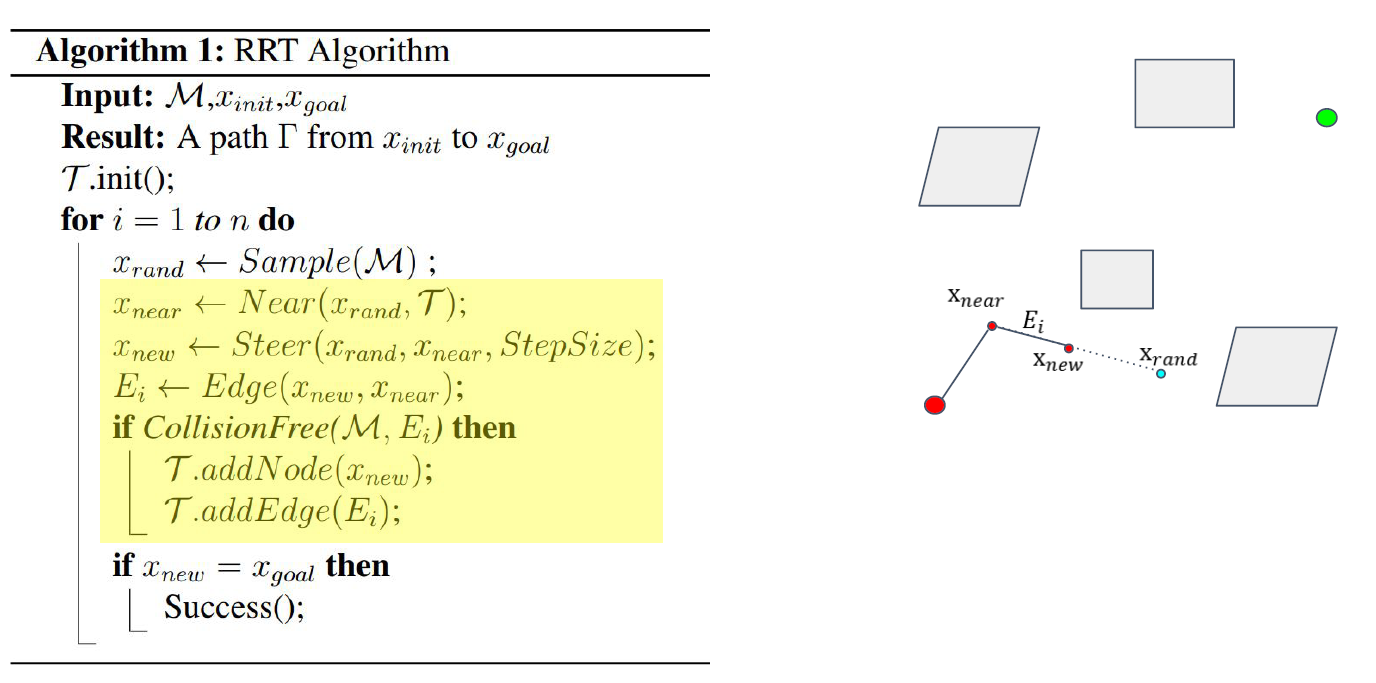
在树上找到一个离蓝色点最近的一个点(从大红点和小红点中选择)<Near函数>
在二者两线上移动一定的距离,<Steer函数>
得到一个边,<Edge函数>
如果其满足碰撞检测,将其加入树中,实现一次树的扩展。<addNode函数、addEdge函数>
如果终点或者终点周围的点被加入树,则算法结束。
一次回溯其父节点,形成路径。
对于狭窄环境(Narrow Passage Environment),RRT的效率不高。
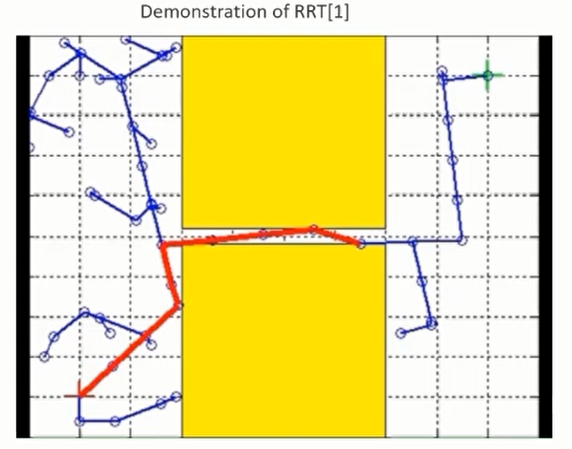
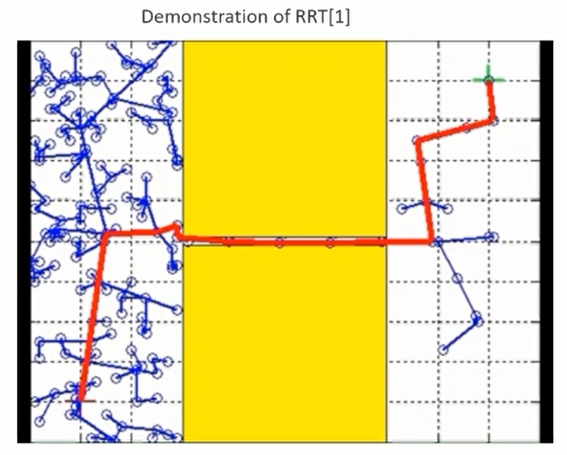
Pros and Cons
- Pros:
- Aims to find a path from the start to the goal
更针对目标去寻找路径 - More target-oriented than PRM
- Aims to find a path from the start to the goal
- Cons:
- Not optimal solution
并不是最优解 - Not efficient(leave room for improvement)
并不是很高效(仍有改进的空间)
针对伪代码中的函数进行改进 - Sample in the whole space
仍是在整个空间中进行采样
- Not optimal solution
Towards Improving Efficiency
Kd-tree
Kd-tree:程序上的改进
改进Near函数,用于快速寻找树上最近的点。
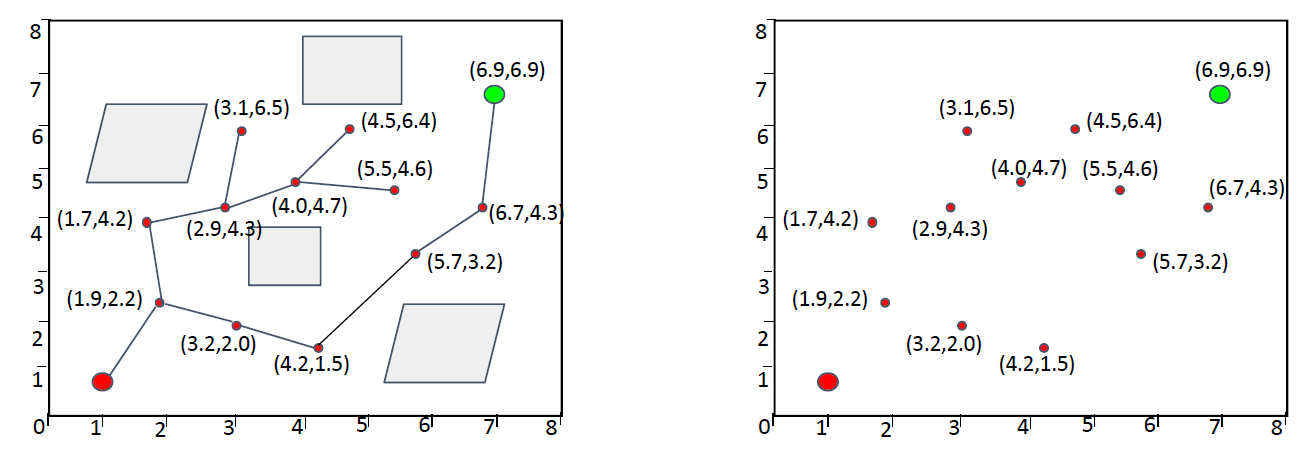
如图所示,左侧产生了一个RRT的树。
当有新的点被采样出时,如何选取最近点呢?
- 暴力穷举
计算所有点与该点的距离 - Kd-tree
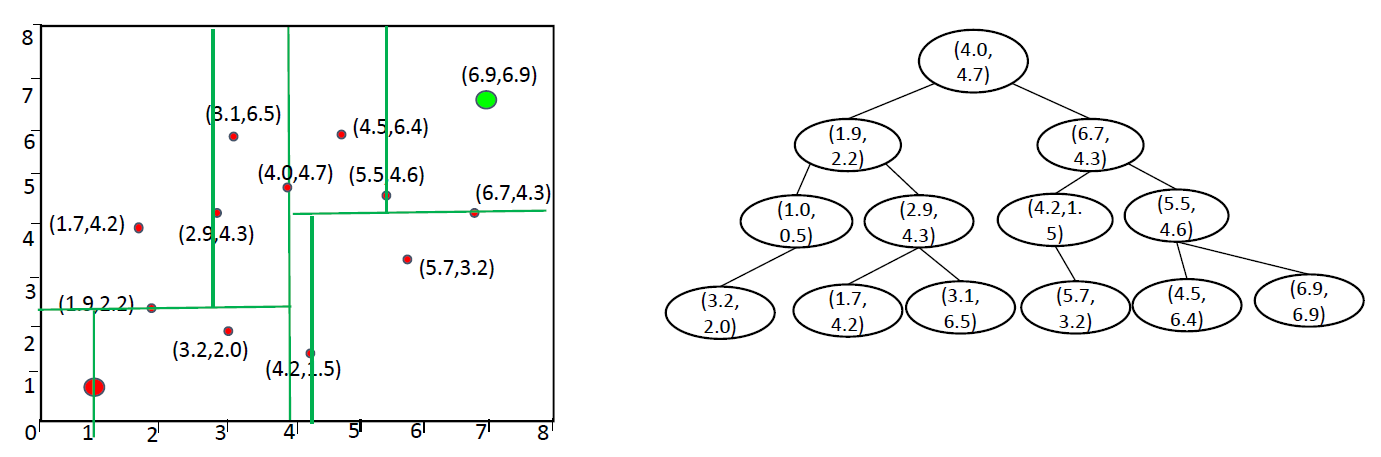
左图是Kd-tree对空间的划分。
划分方法:
- 横向寻找所有节点坐标的中位数,将其划分为左右两支
- 纵向寻找所有节点坐标的中位数,将其继续划分
依次方法,持续划分
Other variants: Spatial grid, hill climbing,etc
Kd-tree的介绍:https://blog.csdn.net/junshen1314/article/details/51121582
Bidirectional RRT/ RRT Connect
- Grow a tree from both the start point and the goal point
起点终点同时扩展两棵树,实现一次撒点,两树构建 - Path finding when two trees are connected
当两棵树相连时,路径即产生
对于Narrow Passage的特殊情况:终点在Narrow Passage中,RRT Connect有很好的效果:
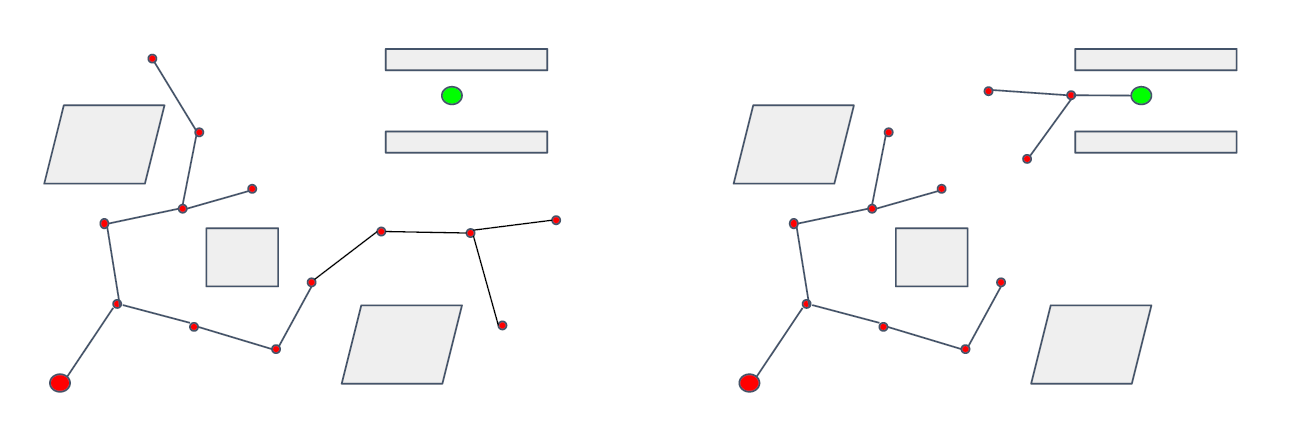
但是,对于Narrow Passage问题本身来讲,RRT Connect并不是最好的解决方式。
更多人采用改进采样的方法来解决这一问题。
设计采样函数,在Narrow Passage中多采点,从而实现树在Narrow Passage中的快速生长。
Optimal sampling-based path planning methods
基于采样的最优路径规划方法
Rapidly-exploring Random Tree* (RRT*)
Recall Cons of RRT
- Cons:
- Not optimal solution
并不是最优解 - Not efficient(leave room for improvement)
并不是很高效(仍有改进的空间) - Sample in the whole space
仍是在整个空间中进行采样 - 所产生的路径并不适合机器人执行
- Not optimal solution
RRT*针对性的解决RRT生成路径不最优的问题
RRT* Overview
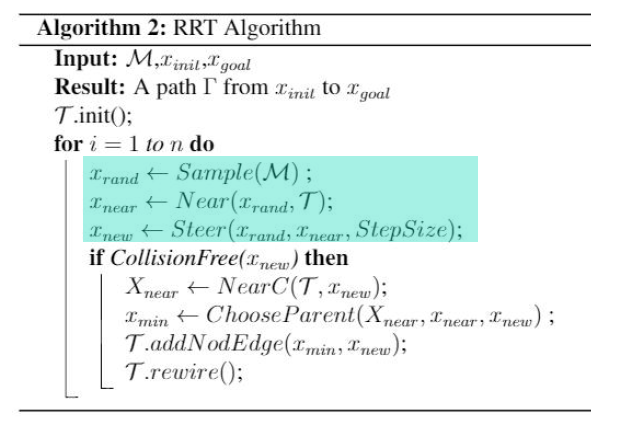
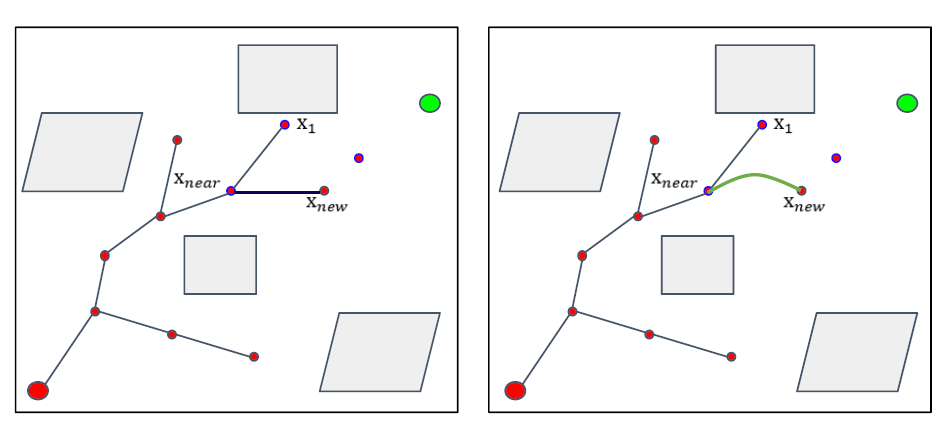
一开始与RRT并无区别。
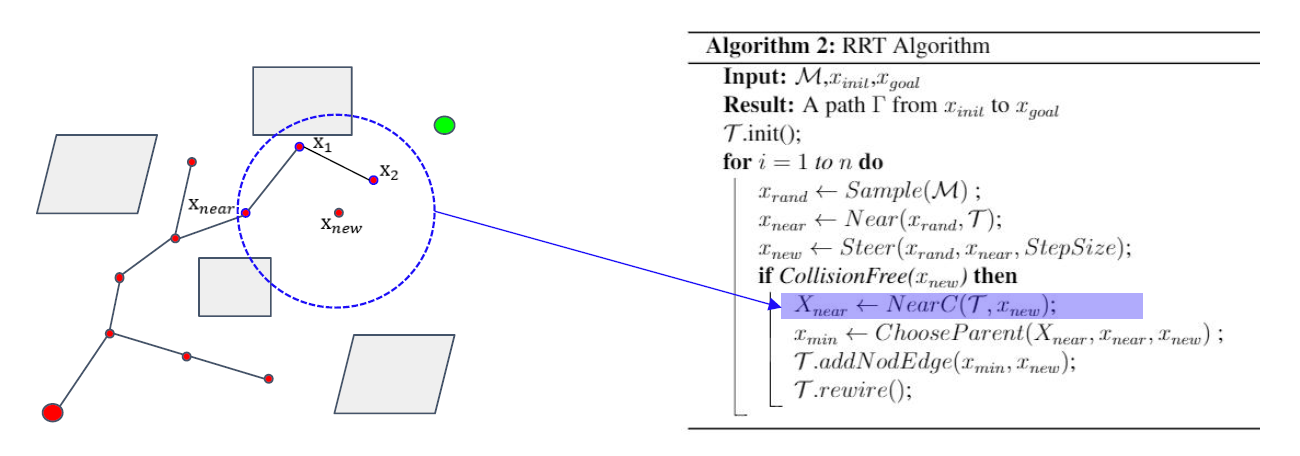
但在找到\(x_{new}\)之后,会对\(x_{new}\)周围进行搜索,寻找其附近的节点。
找到\(x_{near},x_1,x_2\)三个节点。<NearC函数>
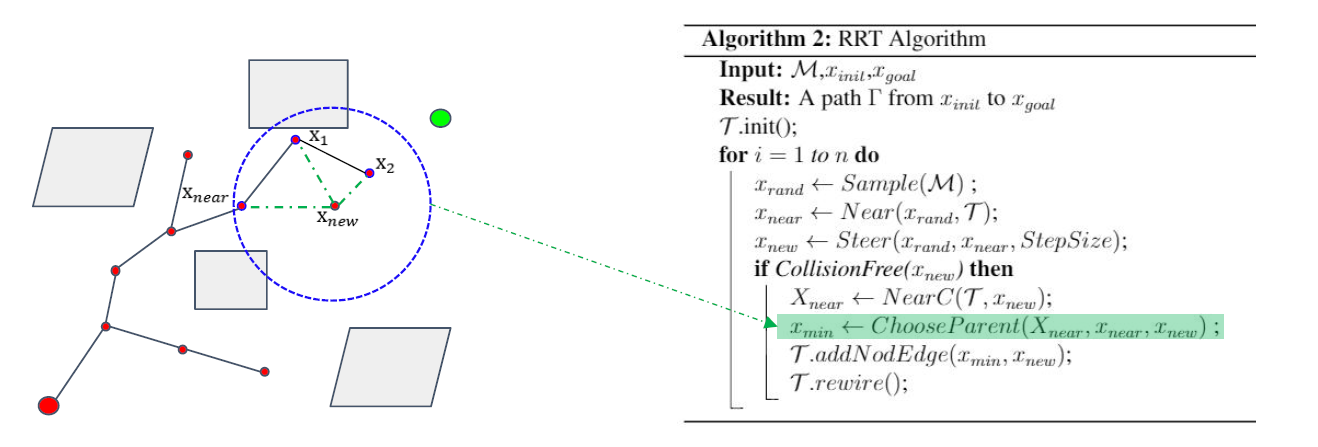
下面选取\(x_{new}\)节点的父节点。<ChooseParent函数>
分别与寻找到的三个节点连接,选取从起点经该点到\(x_{new}\)点代价(代价函数是可以自定义的)最低的点作为其父节点。
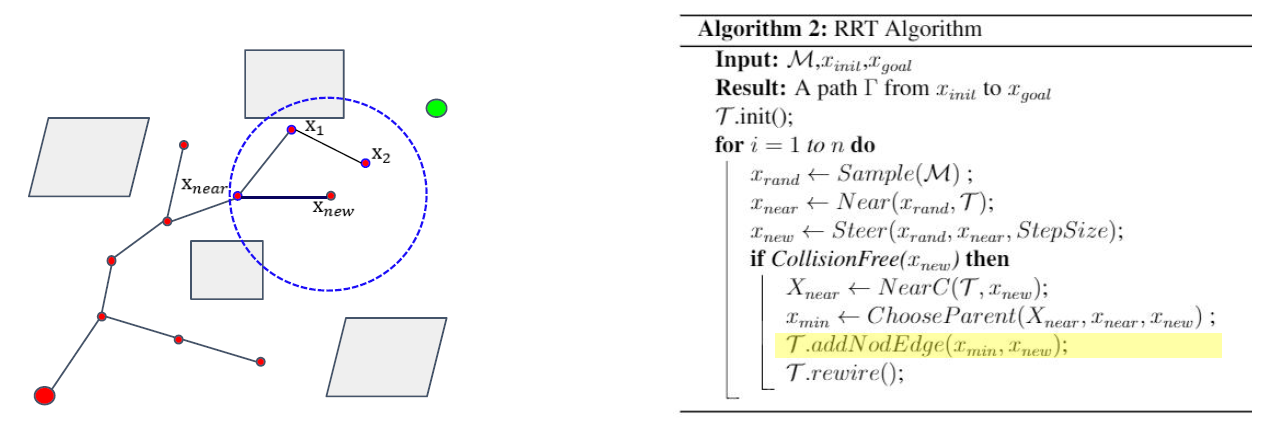
连接边与\(x_{new}\)点。<addNodEdge函数>
以上是RRT*的第一个特点(改进)
第二个特点(改进)在于对树的修改<rewire函数>
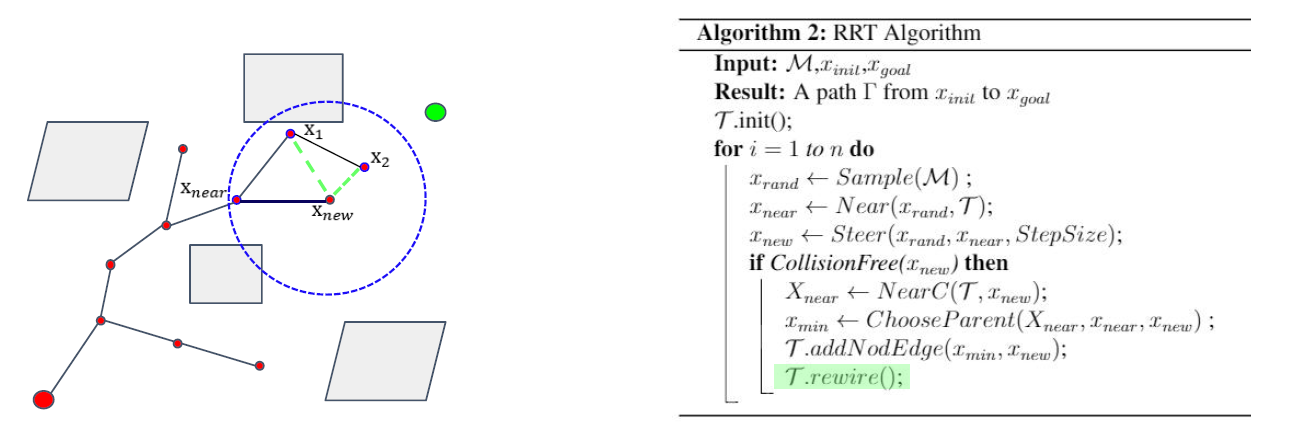
添加\(x_{new}\)之后,对于刚才未选取的备选父节点,考虑能否通过\(x_{new}\)减少从起点到达本节点的代价。
若是,则使其修改自身的父节点为\(x_{new}\)。
Example
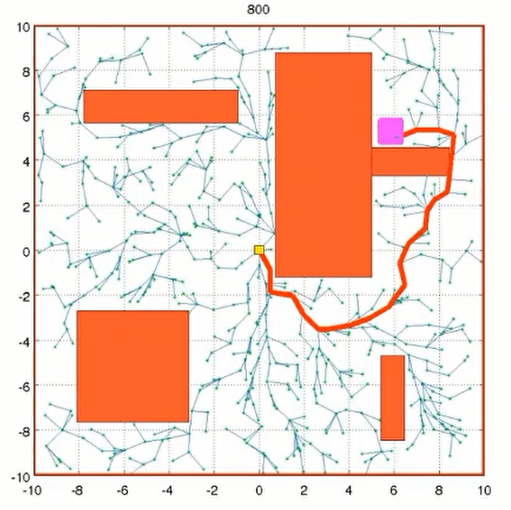
找到路径后,仍继续算法以优化路径:

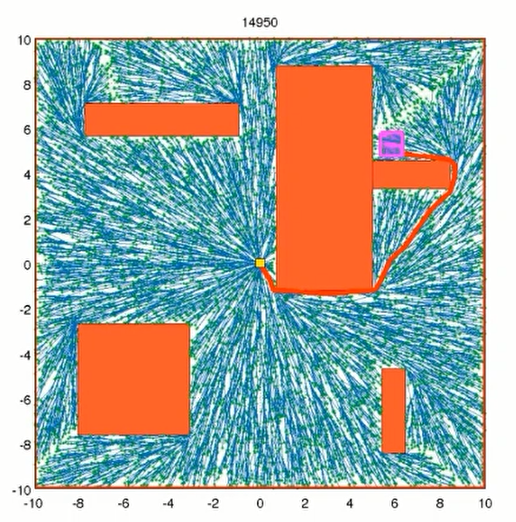
Kinodynamic-RRT*
不管是RRT还是RRT*,通常情况下点与点的连接都是由直线所连的,所寻找的路径也是一堆直线段组成的。
对于机器人来说,不一定可以满足其运动学约束。
Kinodynamic-RRT*用于解决这一问题,主要改进了Steer()函数。
Change Steer() function to fit with motion or other constraints in robot navigation.
考虑机器人的运动学约束或其他约束。
Kinodynamic RRT*: Optimal Motion Planning for Systems with Linear Differential Constraints

当采用曲线段连接各点之后,会出现一些新的问题:
比如,在左图中,连接\(x_{near}\)与\(x_{new}\)时,若使用直线段,会因为不满足碰撞检测而被舍弃。
但是,其会使用一条曲线轨迹(2),是满足碰撞检测的。
此方向还是一个比较火的方向,可以多做了解。
Anytime-RRT*
Keep optimizing the leaf RRT tree when the robot executes the current trajectory Anytime Fashion
在获得一条轨迹之后,机器人一边进行轨迹跟踪,一边同时进行RRT*的路径优化,当然起始点是实时更新的。
Anytime-RRT*能更好地适应环境变化,同时其路径也可以做到较为优化。
Advanced Sampling-based Methods
基于采样的路径规划算法进阶
重点在于采样阶段
Informed RRT*
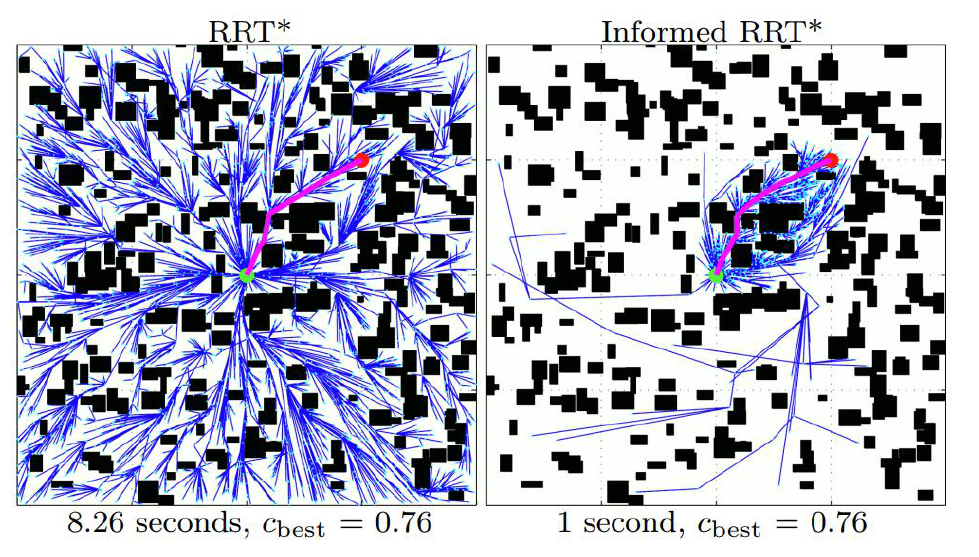
Informed RRT*: Optimal sampling-based path planning focused via direct sampling of an admissible ellipsoidal heuristic
当找到从起点到终点的路径之后,Informed RRT*将采样区域限定在一个椭圆中
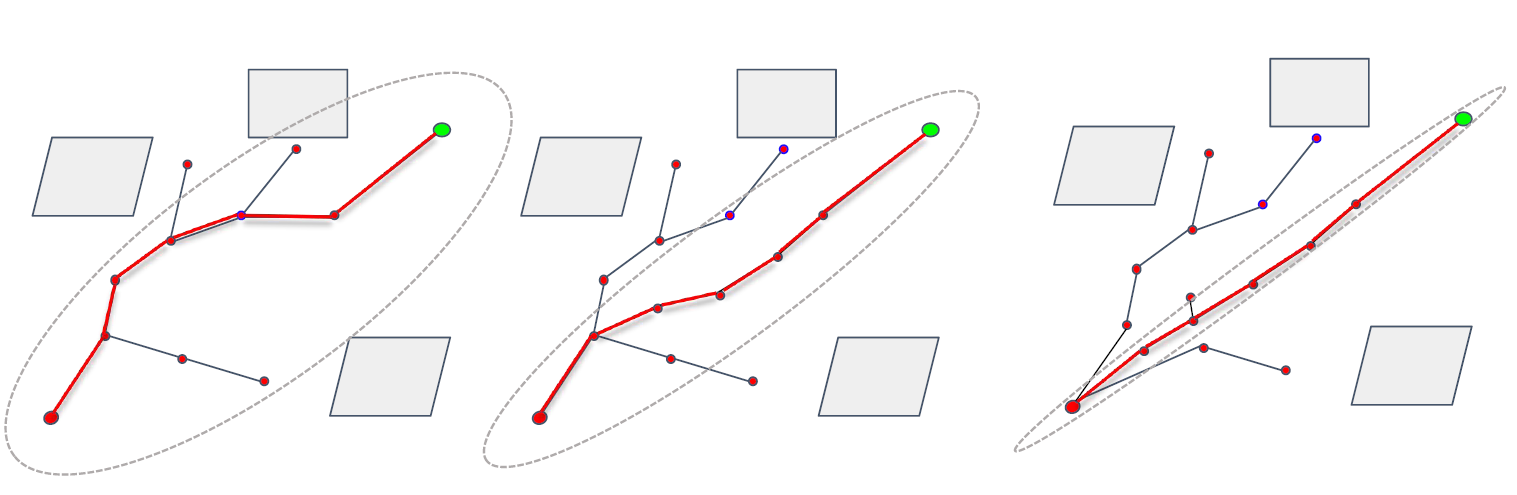
如何构建椭圆呢?
以起点和终点作为椭圆的焦点,以路径长度作为点到两个焦点的距离之和。
如果没有障碍物,椭圆会越来越扁,采样速度也会越来越快。
这里只考虑了路径最短,当然,也可以加入诸如动力学限制等。
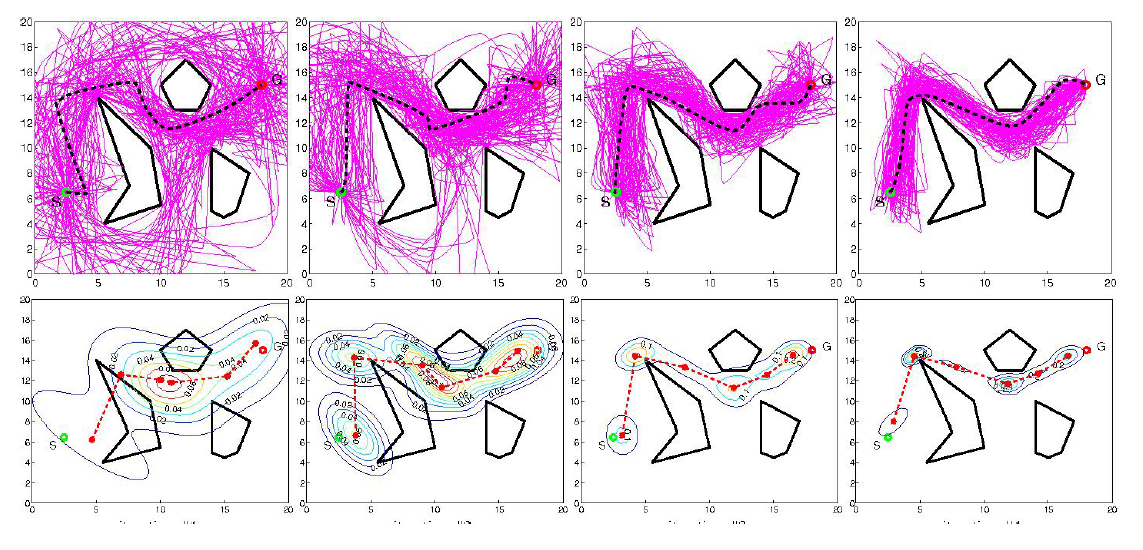
Cross-entropy Motion Planning
也是基于RRT的方法,但是其树不是显式被构建的。

- 生成一条路径
可以用RRT*等各种方法。 - 在轨迹的节点周围采样
如图,6个节点构成了一个多高斯模型,每一个部分都是以节点为均值,以所指定的方差为方差。
在6个圈内进行采样,可以构成无数条路径。 - 重新选取采样空间
如图所示,得到了3条路径。现在就具有14个节点。
对多个轨迹的多个节点求其均值,再次得到6个高斯分布。
进行下一次的优化。
Other variants
- Lower Bound Tree RRT (LBTRRT)[a]
- parse Stable RRT[b]
- Transition-based RRT (T-RRT)[c]
- Vector Field RRTId]
- Parallel RRT (pRRT)[e]
- Etc.[f]
[1] An Overview of the Class of Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees
[2] http://msl.cs.uiuc.edu/rrt/
[a] https://arxiv.org/pdf/1308.0189.pdf
[b] http://pracsyslab.org/sst_software
[c] http://homepages.laas.fr/jcortes/Papers/jaillet_aaaiWS08.pdf
[d] https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6606360
[e] https://robotics.cs.unc.edu/publications/Ichnowski2012_IROS.pdf
[f] https://github.com/zychaoqun
Implementation
在实际中的运用
Open Motion Planning Library and Moveit
Open Motion Planning Library
集成很多路径规划的算法。
配合Moveit with ROS
[1] https://ompl.kavrakilab.org/
[2] https://moveit.ros.org/
Tutorials: [3] https://industrial-training-master.readthedocs.io/en/melodic/source/session4/Motion-Planning-CPP.html
OMPL和Moveit在机械臂中使用较多,在移动机器人中使用较少。
但移动机器人和空中机器人也可以理解成关节较少的移动机械臂。
故此方法也是可以运用的。
Navigation stick - ROS
这是专门用于移动机器人的库
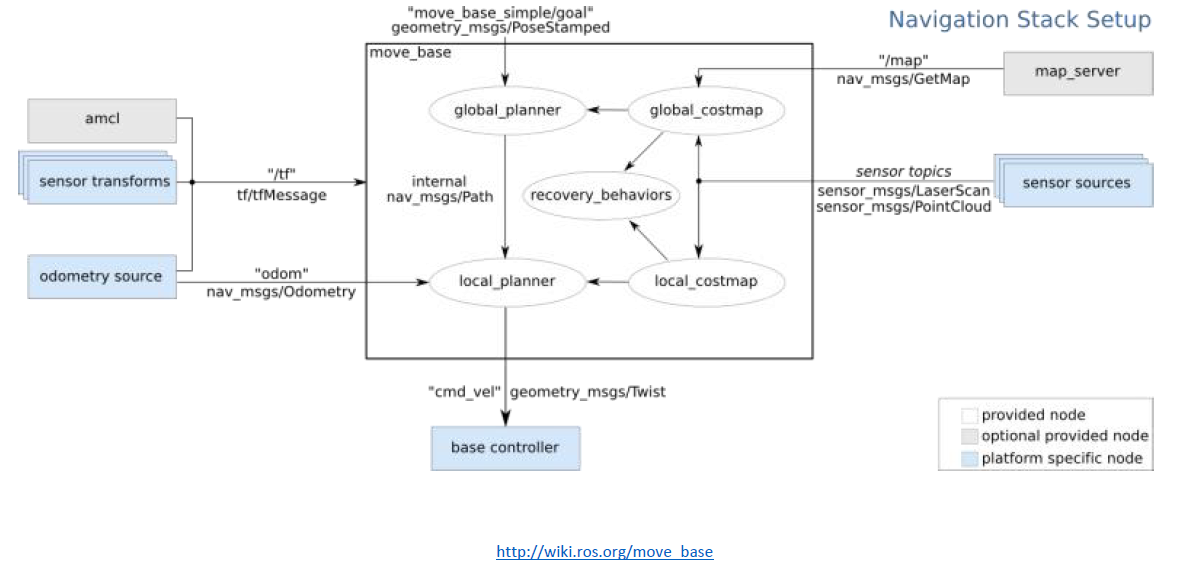
- Global planner
不考虑太多的运动约束- A,D, RRTs,etc
- Local planner
考虑具体的执行,与控制有关- Dwa,eband, Teb,etc
Video demonstration of RRT implemented on ROS : https://youtu.be/FsZ9b6fsQUg
Homework
- Implementation of RRT
- You can either use MATLAB or C++
- Hints: write RRT as a global planner in ROS
- Bonus: Implementation of Informed-RRT*


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号