进程间通信(1)-管道
匿名管道(Anonymous Pipe)和有名管道(Named Pipe,也称为FIFO)是两种不同的进程间通信方式,它们有以下主要区别:
- 命名和使用方式:
- 匿名管道没有名字,只能在具有亲缘关系的进程之间使用,通常是在调用pipe()函数后直接使用,无需其他步骤。
- 有名管道有一个文件名,它在文件系统中有一个路径,不限于亲缘关系的进程之间使用,可以通过文件系统路径来访问。它们由mkfifo()函数创建,并可以通过文件系统进行访问。
- 持久性:
- 匿名管道在创建它们的进程终止时自动销毁,因此只存在于创建它们的进程生命周期内。
- 有名管道在文件系统中存在,即使创建它们的进程终止,它们也可以被其他进程访问,直到显式地被删除或文件系统卸载。
- 通信方式:
- 匿名管道只能支持单向通信,通常是用于父子进程之间的通信。
- 有名管道支持双向通信,可以被不相关的进程之间使用。
- 进程间关系:
- 匿名管道通常用于具有父子关系的进程间通信,因为它们是通过fork()创建的子进程继承的。
- 有名管道可以用于任意两个进程间的通信,只要它们能够访问相同的有名管道文件。
匿名管道demo如下:
pipefd[0]只读不写,pipefd[1]只写不读
#include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #define BUFFER_SIZE 25 int main() { char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; int pipefd[2]; // 用于存放管道的文件描述符,pipefd[0]表示读取端,pipefd[1]表示写入端 pid_t pid; // 创建管道 if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) { perror("pipe"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // 创建子进程 pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { perror("fork"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (pid > 0) { // 父进程 close(pipefd[0]); // 关闭读取端,父进程只负责写入数据 printf("Parent process is writing to the pipe...\n"); write(pipefd[1], "Hello from parent process!", 26); close(pipefd[1]); // 写入完成后关闭写入端 } else { // 子进程 close(pipefd[1]); // 关闭写入端,子进程只负责读取数据 printf("Child process is reading from the pipe...\n"); read(pipefd[0], buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); printf("Child process received: %s\n", buffer); close(pipefd[0]); // 读取完成后关闭读取端 } return 0; }
执行结果如下:
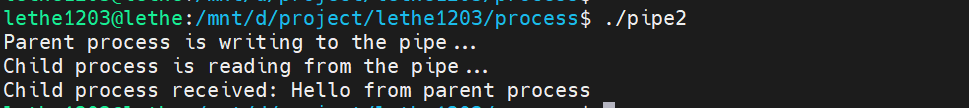
有名管道demo如下:
进程1:写入数据到有名管道
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #define BUFFER_SIZE 25 #define FIFO_FILE "/tmp/myfifo" int main() { char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; int fd; // 创建有名管道 mkfifo(FIFO_FILE, 0666); // 打开有名管道以写入数据 fd = open(FIFO_FILE, O_WRONLY); if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // 写入数据到管道 printf("Process 1 is writing to the named pipe...\n"); write(fd, "Hello from Process 1!", 21); printf("Process 1 wrote: Hello from Process 1!\n"); // 关闭管道 close(fd); return 0; }
进程2:从有名管道读取数据
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #define BUFFER_SIZE 25 #define FIFO_FILE "/tmp/myfifo" int main() { char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; int fd; // 创建有名管道 mkfifo(FIFO_FILE, 0666); // 打开有名管道以读取数据 fd = open(FIFO_FILE, O_RDONLY); if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // 从管道中读取数据 printf("Process 2 is reading from the named pipe...\n"); read(fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); printf("Process 2 received: %s\n", buffer); // 关闭管道 close(fd); return 0; }
执行结果如下:



