生成 有向无环图
1. 引言
做 图的相关算法 的 代码测试的时候, 光看 映射表很不直观, 有时候 生成的图 有问题 也没法 很快 很直观的发现, 有了 PlantUML 就可以直接渲染出来,很直观.
2. 相关代码
2.1. 数据结构
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author CC11001100
*/
public class Vector<T> {
private T name;
private List<Vector<T>> from;
private List<Vector<T>> to;
public Vector(T name) {
this.name = name;
this.from = new ArrayList<>();
this.to = new ArrayList<>();
}
public T getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(T name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void toNode(Vector<T> t){
this.to.add(t);
}
public void fromNode(Vector<T> t){
this.from.add(t);
}
public boolean isEmptyTo(){
return this.to.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isEmptyFrom(){
return this.from.isEmpty();
}
public List<Vector<T>> getFrom() {
return from;
}
//
public List<Vector<T>> getTo() {
return to;
}
}
2.2. 生成 DAG 映射关系图
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 生成随机DAG
*
* @author CC11001100
*/
public class DAGGenerator {
private static HashMap<String, Boolean> m_map = new HashMap<String, Boolean>();
private static final int NodeRange = 5;
private static String buildKey(int startIndex, int targetIndex){
return String.format("%d_%d", startIndex, targetIndex);
}
private static <T> boolean DFS(Stack<Vector<T>> stack, Vector<T> tNode){
Vector<T> NodeA = stack.lastElement();
int size = NodeA.getTo().size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i ++){
Vector<T> NodeB = NodeA.getTo().get(i);
if (NodeB == tNode){
return true;
}
stack.push(NodeB);
boolean ret = DFS(stack, tNode);
if (ret){
return true;
}
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
/*
通过 DFS 避免出现 环状
遍历 start 找到 start 到 target 的通路
*/
private static <T> boolean checkCircleDFS(int startIndex, int targetIndex, List<Vector<T>> vectorList){
String key = buildKey(startIndex, targetIndex);
if (m_map.containsKey(key)){
System.out.println("m_map contains " + key);
return true;
}else {
Vector<T> NodeA = vectorList.get(startIndex);
Stack<Vector<T>> stack = new Stack<Vector<T>>();
stack.push(NodeA);
Vector<T> targetNode = vectorList.get(targetIndex);
boolean ret = DFS(stack, targetNode);
if (ret){
System.out.println("DFS find " + key);
m_map.put(key, true);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static <T> int getANode(List<Vector<T>> vectorList, int index){
int random_index = 0;
int dowhileTag = -1;
Random random = new Random();
Vector<T> NodeA = vectorList.get(index);
int find_count = 20;
int vec_count = vectorList.size();
do {
random_index = random.nextInt(vec_count - 1);
dowhileTag = 0;
if (random_index == index) {
dowhileTag = 1;
}
if ((dowhileTag == 0) && NodeA.getTo().contains(vectorList.get(random_index))) {
dowhileTag = 2;
}
if ((dowhileTag == 0) && checkCircleDFS(random_index, index, vectorList)) {
find_count = find_count - 1;
dowhileTag = 3;
}
System.out.println(" index = " + index + " random_index = " + random_index + " dowhileTag = " + dowhileTag + " NodeA.getTo() = " + NodeA.getTo().size() );
}while ((dowhileTag > 0) && (find_count > 0)); // 检查 是否存在 反向的路径
if (find_count <= 0){
random_index = -1;
}
return random_index;
}
/**
* DFS 来 给 vectorList 建立 边的关系 确保没有环状
*
* @param vectorList
* @return
*/
public static <T> void randomDFS(List<Vector<T>> vectorList) {
Random random = new Random();
m_map.clear();
int vec_count = vectorList.size();
for (int i = 0, end = vec_count; i < end; i++) {
int range = random.nextInt(1, NodeRange);
Vector<T> NodeA = vectorList.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < range; j++) {
int random_index = getANode(vectorList, i);
if (random_index > 0) {
Vector<T> NodeB = vectorList.get(random_index);
NodeA.toNode(NodeB);
NodeB.fromNode(NodeA);
}
}
}
// 检查是否有除了第一个顶点之外入度为0的顶点,如果有的话就从前面的顶点中随机选一个连过来,这个是为了避免有独立的顶点存在
for (int i = 1, end = vec_count; i < end; i++) {
Vector<T> NodeA = vectorList.get(i);
if (NodeA.isEmptyTo() && NodeA.isEmptyFrom()) {
int random_index = getANode(vectorList, i);
if (random_index > 0) {
Vector<T> NodeB = vectorList.get(random_index);
NodeA.toNode(NodeB);
NodeB.fromNode(NodeA);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 传入一个拓扑排序好的顶点列表,然后从这个拓扑排序中随机生成一个DAG
*
* @param vectorList
* @return
*/
public static <T> void randomTuopu(List<Vector<T>> vectorList) {
Random random = new Random();
int vec_count = vectorList.size();
for (int i = 0, end = vec_count - 1; i < end; i++) {
int range = random.nextInt(1, NodeRange);
range = Math.min(range, vec_count - i - 1);
System.out.print(" i = "+ i + " range = " + range);
Vector<T> NodeA = vectorList.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < range; j++) {
int random_index = random.nextInt(i + 1, vec_count);
Vector<T> NodeB = vectorList.get(random_index);
while(NodeA.getTo().contains(NodeB)){
random_index = random.nextInt(i + 1, vec_count);
NodeB = vectorList.get(random_index);
System.out.print(" i = "+ i + " j = " + j + " random_index = " + random_index + " range = " + range);
}
NodeA.toNode(NodeB);
NodeB.fromNode(NodeA);
}
}
// 检查是否有除了第一个顶点之外入度为0的顶点,如果有的话就从前面的顶点中随机选一个连过来,这个是为了避免有独立的顶点存在
for (int i = 1, end = vectorList.size(); i < end; i++) {
Vector<T> to = vectorList.get(i);
if (to.getFrom().isEmpty()) {
Vector<T> from = vectorList.get(random.nextInt(i));
from.getTo().add(to);
to.getFrom().add(from);
}
}
}
}
2.3. 调用代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author CC11001100
*/
public class TestDAGGenerator {
/**
* FORMAT:
*
* <pre>
* digraph abc{
* a;
* b;
* c;
* d;
*
* a -> b;
* b -> d;
* c -> d;
* }
* </pre>
*
* @param graphName
* @param vectorList
*/
public static <T> String convertToDot(String graphName, List<Vector<T>> vectorList) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("@startuml\n\n")
.append("digraph ").append(graphName).append(" {\n");
vectorList.forEach(vector -> sb.append(" ").append(vector.getName()).append(";\n"));
sb.append("\n");
vectorList.forEach(from -> from.getTo().forEach(to -> {
sb.append(" ").append(from.getName()).append(" -> ").append(to.getName()).append(";\n");
}));
sb.append("}\n")
.append("\n@enduml\n");
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// final int vectorCount = 30;
final int vectorCount = 15;
List<Vector<Integer>> vectorList = new ArrayList<>(vectorCount);
for (int i = 0; i < vectorCount; i++) {
vectorList.add(new Vector<>(i));
}
// DAGGenerator.randomDFS(vectorList);
DAGGenerator.randomTuopu(vectorList);
String dotGraph = convertToDot("test_DAG_generator", vectorList);
System.out.println(dotGraph);
}
}
3. 输出结果
大概是 这样, 这是 UML 的语法
@startuml
digraph test_DAG_generator {
0;
1;
2;
3;
4;
5;
6;
7;
8;
9;
10;
11;
12;
13;
14;
0 -> 7;
0 -> 12;
1 -> 11;
1 -> 5;
1 -> 6;
1 -> 9;
2 -> 5;
3 -> 4;
3 -> 10;
3 -> 11;
4 -> 11;
4 -> 1;
6 -> 2;
6 -> 9;
6 -> 7;
6 -> 13;
7 -> 8;
7 -> 11;
7 -> 10;
7 -> 9;
8 -> 13;
9 -> 12;
10 -> 13;
10 -> 11;
11 -> 9;
11 -> 2;
11 -> 8;
12 -> 13;
12 -> 2;
12 -> 5;
12 -> 8;
13 -> 2;
13 -> 5;
14 -> 5;
14 -> 8;
14 -> 2;
14 -> 6;
}
@enduml
将输出结果 复制到 PlantUML 接可以看到 这个渲染图了
https://www.planttext.com/
4. 渲染图展现
4.1. 30 个节点的 拓扑排序 生成的 有向无环图
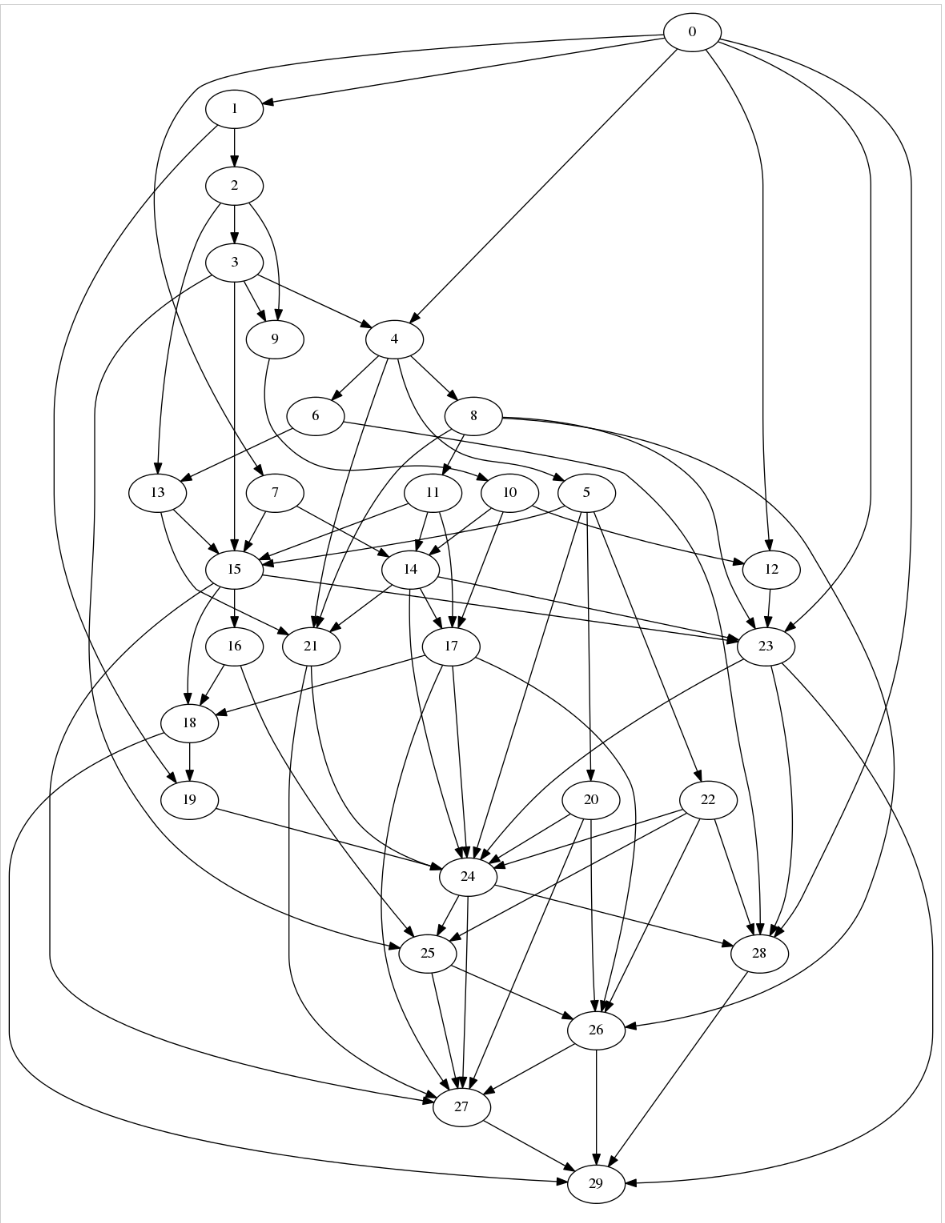
4.2 30 个节点的 DFS 生成的 有向无环图
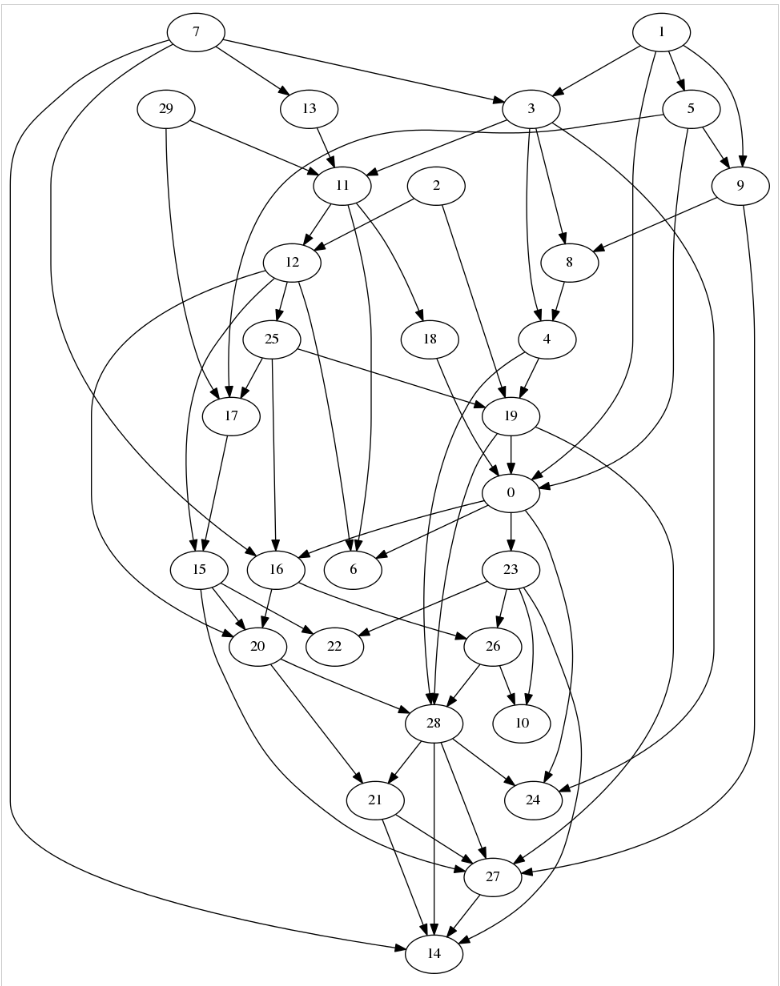
5. 相关概念
拓扑排序的介绍
在图论中,拓扑排序(Topological Sorting)是一个有向无环图(DAG, Directed Acyclic Graph)的所有顶点的线性序列。且该序列必须满足下面两个条件:
每个顶点出现且只出现一次。
若存在一条从顶点 A 到顶点 B 的路径,那么在序列中顶点 A 出现在顶点 B 的前面。
有向无环图(DAG)才有拓扑排序,非DAG图没有拓扑排序一说。
作者:灰睛眼蓝
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/b59db381561a
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
6. 结语
本文代码 基于 CC11001100 的代码, 感谢作者
用他的代码主体, 但是他的代码生成的图 结点稍微多点 就过于复杂, 所以我上手改了改



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号