json-path(json查找与操作)
jsonEditor
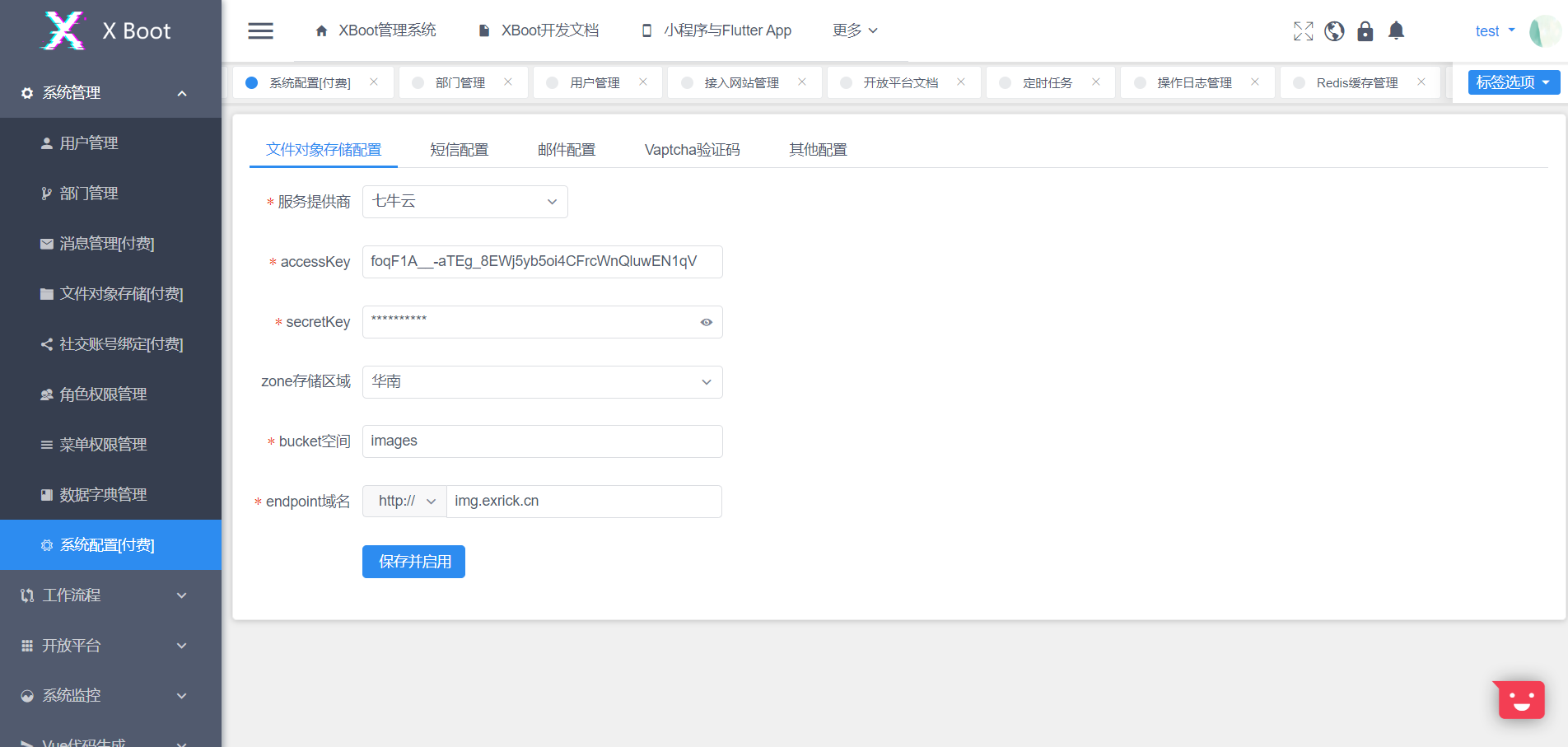
1、jsoneditor
https://github.com/josdejong/jsoneditor
https://jsoneditoronline.org/
效果如下:
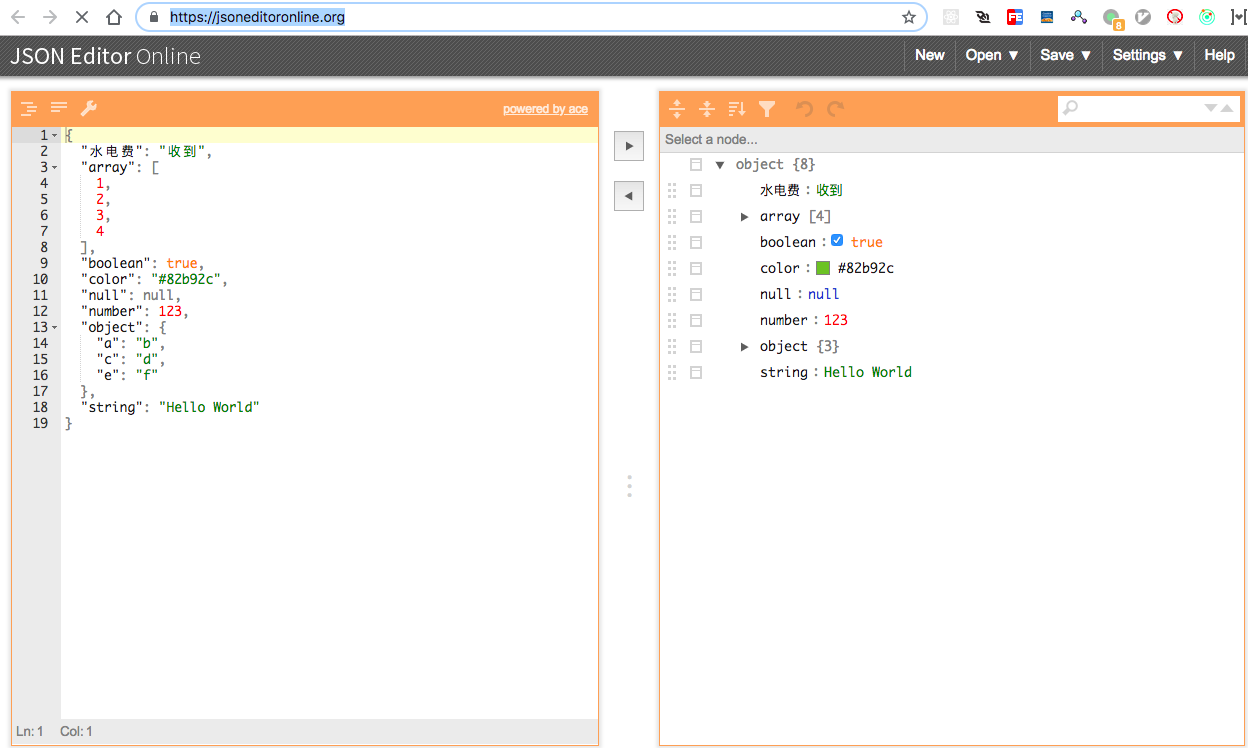
2、json-editor
老版位置:https://github.com/jdorn/json-editor
新版位置:https://github.com/json-editor/json-editor
效果展示:https://json-editor.github.io/json-editor/
根据右边的json数据生成左边的界面
json-path
pom依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId> <artifactId>json-path</artifactId> <version>2.0.0</version> </dependency>
1. 介绍
类似于XPath在xml文档中的定位,JsonPath表达式通常是用来路径检索或设置Json的。其表达式可以接受“dot–notation”和“bracket–notation”格式,例如$.store.book[0].title、$[‘store’][‘book’][0][‘title’]
2. 操作符
|
符号 |
描述 |
|
$ |
查询的根节点对象,用于表示一个json数据,可以是数组或对象 |
|
@ |
过滤器断言(filter predicate)处理的当前节点对象,类似于java中的this字段 |
|
* |
通配符,可以表示一个名字或数字 |
|
.. |
可以理解为递归搜索,Deep scan. Available anywhere a name is required. |
|
.<name> |
表示一个子节点 |
|
[‘<name>’ (, ‘<name>’)] |
表示一个或多个子节点 |
|
[<number> (, <number>)] |
表示一个或多个数组下标 |
|
[start:end] |
数组片段,区间为[start,end),不包含end |
|
[?(<expression>)] |
过滤器表达式,表达式结果必须是boolean |
3. 函数
可以在JsonPath表达式执行后进行调用,其输入值为表达式的结果。
|
名称 |
描述 |
输出 |
|
min() |
获取数值类型数组的最小值 |
Double |
|
max() |
获取数值类型数组的最大值 |
Double |
|
avg() |
获取数值类型数组的平均值 |
Double |
|
stddev() |
获取数值类型数组的标准差 |
Double |
|
length() |
获取数值类型数组的长度 |
Integer |
4. 过滤器
过滤器是用于过滤数组的逻辑表达式,一个通常的表达式形如:[?(@.age > 18)],可以通过逻辑表达式&&或||组合多个过滤器表达式,例如[?(@.price < 10 && @.category == ‘fiction’)],字符串必须用单引号或双引号包围,例如[?(@.color == ‘blue’)] or [?(@.color == “blue”)]。
|
操作符 |
描述 |
|
== |
等于符号,但数字1不等于字符1(note that 1 is not equal to ‘1’) |
|
!= |
不等于符号 |
|
< |
小于符号 |
|
<= |
小于等于符号 |
|
> |
大于符号 |
|
>= |
大于等于符号 |
|
=~ |
判断是否符合正则表达式,例如[?(@.name =~ /foo.*?/i)] |
|
in |
所属符号,例如[?(@.size in [‘S’, ‘M’])] |
|
nin |
排除符号 |
|
size |
size of left (array or string) should match right |
|
empty |
判空符号 |
5. 示例
{ "store": { "book": [ { "category": "reference", "author": "Nigel Rees", "title": "Sayings of the Century", "price": 8.95 }, { "category": "fiction", "author": "Evelyn Waugh", "title": "Sword of Honour", "price": 12.99 }, { "category": "fiction", "author": "Herman Melville", "title": "Moby Dick", "isbn": "0-553-21311-3", "price": 8.99 }, { "category": "fiction", "author": "J. R. R. Tolkien", "title": "The Lord of the Rings", "isbn": "0-395-19395-8", "price": 22.99 } ], "bicycle": { "color": "red", "price": 19.95 } }, "expensive": 10 }
|
JsonPath表达式 |
结果 |
|
$.store.book[*].author 或 $..author |
[ “Nigel Rees”, “Evelyn Waugh”, “Herman Melville”, “J. R. R. Tolkien” ] |
|
$.store.* 显示所有叶子节点值 |
[ [{” category”: “reference”, ”author”: “Nigel Rees”, ”title”: “Sayings of the Century”, ”price”: 8.95 }, {” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “Evelyn Waugh”, ”title”: “Sword of Honour”, ”price”: 12.99 }, {” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “Herman Melville”, ”title”: “Moby Dick”, ”isbn”: “0 - 553 - 21311 - 3”, ”price”: 8.99 }, {” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “J.R.R.Tolkien”, ”title”: “The Lord of the Rings”, ”isbn”: “0 - 395 - 19395 - 8”, ”price”: 22.99 } ], {” color”: “red”, ”price”: 19.95 } ] |
|
$.store..price |
[ 8.95, 12.99, 8.99, 22.99, 19.95 ] |
|
$..book[0,1] 或 $..book[:2] |
[{” category”: “reference”, ”author”: “Nigel Rees”, ”title”: “Sayings of the Century”, ”price”: 8.95 }, {” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “Evelyn Waugh”, ”title”: “Sword of Honour”, ”price”: 12.99 } ] |
|
$..book[-2:] |
获取最后两本书 |
|
$..book[2:] |
[{” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “Herman Melville”, ”title”: “Moby Dick”, ”isbn”: “0 - 553 - 21311 - 3”, ”price”: 8.99 }, {” category”: “fiction”, ”author”: “J.R.R.Tolkien”, ”title”: “The Lord of the Rings”, ”isbn”: “0 - 395 - 19395 - 8”, ”price”: 22.99 } ] |
|
$..book[?(@.isbn)] |
所有具有isbn属性的书 |
|
$.store.book[?(@.price < 10)] |
所有价格小于10的书 |
|
$..book[?(@.price <= $[‘expensive’])] |
所有价格低于expensive字段的书 |
|
$..book[?(@.author =~ /.*REES/i)] |
所有符合正则表达式的书 [{” category”: “reference”, ”author”: “Nigel Rees”, ”title”: “Sayings of the Century”, ”price”: 8.95 }] |
|
$..* |
返回所有 |
|
$..book.length() |
[ 4 ] |
测试请点击http://jsonpath.herokuapp.com/?path=$.store.book[*].author
6. 常见用法
通常是直接使用静态方法API进行调用,例如:
String json = "...";
List<String> authors = JsonPath.read(json, "$.store.book[*].author");
但以上方式仅仅适用于解析一次json的情况,如果需要对同一个json解析多次,不建议使用,因为每次read都会重新解析一次json,针对此种情况,建议使用ReadContext、WriteContext,例如:
String json = "..."; ReadContext ctx = JsonPath.parse(json); List<String> authorsOfBooksWithISBN = ctx.read("$.store.book[?(@.isbn)].author"); List<Map<String, Object>> expensiveBooks = JsonPath .using(configuration) .parse(json) .read("$.store.book[?(@.price > 10)]", List.class);
7. 返回值是什么?
通常read后的返回值会进行自动转型到指定的类型,对应明确定义definite的表达式,应指定其对应的类型,对于indefinite含糊表达式,例如包括..、?(<expression>)、[<number>, <number> (, <number>)],通常应该使用数组。如果需要转换成具体的类型,则需要通过configuration配置mappingprovider,如下:
String json = "{\"date_as_long\" : 1411455611975}";
//使用JsonSmartMappingProvider
Date date = JsonPath.parse(json).read("$['date_as_long']", Date.class);
//使用GsonMappingProvider
Book book = JsonPath.parse(json).read("$.store.book[0]", Book.class);
8. MappingProvider SPI反序列化器
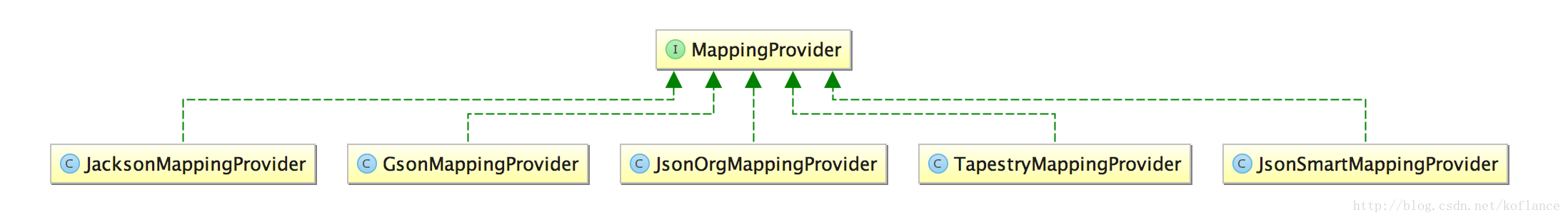
其中JsonSmartMappingProvider提供了如下基本数据类型的转换,此provider是默认设置的,在Configuration.defaultConfiguration()中返回的DefaultsImpl类,使用的就是JsonSmartMappingProvider。
DEFAULT.registerReader(Long.class, new LongReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(long.class, new LongReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(Integer.class, new IntegerReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(int.class, new IntegerReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(Double.class, new DoubleReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(double.class, new DoubleReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(Float.class, new FloatReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(float.class, new FloatReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(BigDecimal.class, new BigDecimalReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(String.class, new StringReader()); DEFAULT.registerReader(Date.class, new DateReader());
切换Provider,如下:
Configuration.setDefaults(new Configuration.Defaults() { private final JsonProvider jsonProvider = new JacksonJsonProvider(); private final MappingProvider mappingProvider = new JacksonMappingProvider(); @Override public JsonProvider jsonProvider() { return jsonProvider; }
@Override public MappingProvider mappingProvider() { return mappingProvider; } @Override public Set<Option> options() { return EnumSet.noneOf(Option.class); } });
9. Predicates过滤器断言
有三种方式创建过滤器断言。
9.1 Inline Predicates
即使用过滤器断言表达式?(<@expression>),例如:
List<Map<String, Object>> books = JsonPath.parse(json)
.read("$.store.book[?(@.price < 10)]");
9.2 Filter Predicates
使用Filter API。例如:
import static com.jayway.jsonpath.JsonPath.parse; import static com.jayway.jsonpath.Criteria.where; import static com.jayway.jsonpath.Filter.filter; ... Filter cheapFictionFilter = filter( where("category").is("fiction").and("price").lte(10D) ); List<Map<String, Object>> books = parse(json).read("$.store.book[?]", cheapFictionFilter); Filter fooOrBar = filter( where("foo").exists(true)).or(where("bar").exists(true) ); Filter fooAndBar = filter( where("foo").exists(true)).and(where("bar").exists(true) );
注意:
JsonPath表达式中必须要有断言占位符?,当有多个占位符时,会依据顺序进行替换。
多个filter之间还可以使用or或and。
9.3 Roll Your Own
自己实现Predicate接口。
Predicate booksWithISBN = new Predicate() { @Override public boolean apply(PredicateContext ctx) { return ctx.item(Map.class).containsKey("isbn"); } }; List<Map<String, Object>> books = reader.read("$.store.book[?].isbn", List.class, booksWithISBN);
10. 返回检索到的Path路径列表
有时候需要返回当前JsonPath表达式所检索到的全部路径,可以如下使用:
Configuration conf = Configuration.builder() .options(Option.AS_PATH_LIST).build(); List<String> pathList = using(conf).parse(json).read("$..author"); assertThat(pathList).containsExactly( "$['store']['book'][0]['author']", "$['store']['book'][1]['author']", "$['store']['book'][2]['author']", "$['store']['book'][3]['author']");
11. 配置Options
11.1 DEFAULT_PATH_LEAF_TO_NULL
当检索不到时返回null对象,否则如果不配置这个,会直接抛出异常PathNotFoundException,例如:
[ { "name" : "john", "gender" : "male" }, { "name" : "ben" } ] Configuration conf = Configuration.defaultConfiguration(); //Works fine String gender0 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[0]['gender']"); //PathNotFoundException thrown String gender1 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[1]['gender']"); Configuration conf2 = conf.addOptions(Option.DEFAULT_PATH_LEAF_TO_NULL); //Works fine String gender0 = JsonPath.using(conf2).parse(json).read("$[0]['gender']"); //Works fine (null is returned) String gender1 = JsonPath.using(conf2).parse(json).read("$[1]['gender']");
11.2 ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST
总是返回list,即便是一个确定的非list类型,也会被包装成list。
11.3 SUPPRESS_EXCEPTIONS
不抛出异常,需要判断如下:
ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST开启,则返回空list
ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST关闭,则返回null
11.4 AS_PATH_LIST
返回path
11.5 REQUIRE_PROPERTIES
如果设置,则不允许使用通配符,比如$[*].b,会抛出PathNotFoundException异常。
12. Cache SPI
每次read时都会获取cache,以提高速度,但默认情况下是不启用的。
@Override public <T> T read(String path, Predicate... filters) { notEmpty(path, "path can not be null or empty"); Cache cache = CacheProvider.getCache(); path = path.trim(); LinkedList filterStack = new LinkedList<Predicate>(asList(filters)); String cacheKey = Utils.concat(path, filterStack.toString()); JsonPath jsonPath = cache.get(cacheKey); if(jsonPath != null){ return read(jsonPath); } else { jsonPath = compile(path, filters); cache.put(cacheKey, jsonPath); return read(jsonPath); } }
JsonPath 2.1.0提供新的spi,必须在使用前或抛出JsonPathException前配置。目前提供了两种实现:
com.jayway.jsonpath.spi.cache.NOOPCache (no cache)
com.jayway.jsonpath.spi.cache.LRUCache (default, thread safe)
如果想要自己实现,例如:
CacheProvider.setCache(new Cache() { //Not thread safe simple cache private Map<String, JsonPath> map = new HashMap<String, JsonPath>(); @Override public JsonPath get(String key) { return map.get(key); } @Override public void put(String key, JsonPath jsonPath) { map.put(key, jsonPath); } });
小惊喜
1、积少成多,下载高佣联盟,领取各大平台隐藏优惠券,每次购物省个几十块钱不香吗。
使用方法:复制商品链接打开高佣联盟自动弹出优惠券,点击跳转到对应平台app内领券购买,或者直接高佣联盟内搜索有优惠券商品点击跳转到淘宝等平台领券购买。
通过下方二维码注册的用户可添加微信liershuang123(微信号)领取价值千元海量学习视频。
为表诚意奉献部分资料:
软件电子书:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_cUtPtZZbtYTF7C_jwtxwQ 提取码:8ayn
架构师二期:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1yMhDFVeGpTO8KTuRRL4ZsA 提取码:ui5v
架构师阶段课程:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/16xf1qVhoxQJVT_jL73gc3A 提取码:2k6j

2、本人重金购买付费前后端分离脚手架源码一套,现10元出售,加微信liershuang123获取源码