springboot项目搭建及常用技术整合
一.在你建立的工程下创建 Module 选择Spring initializr创建。
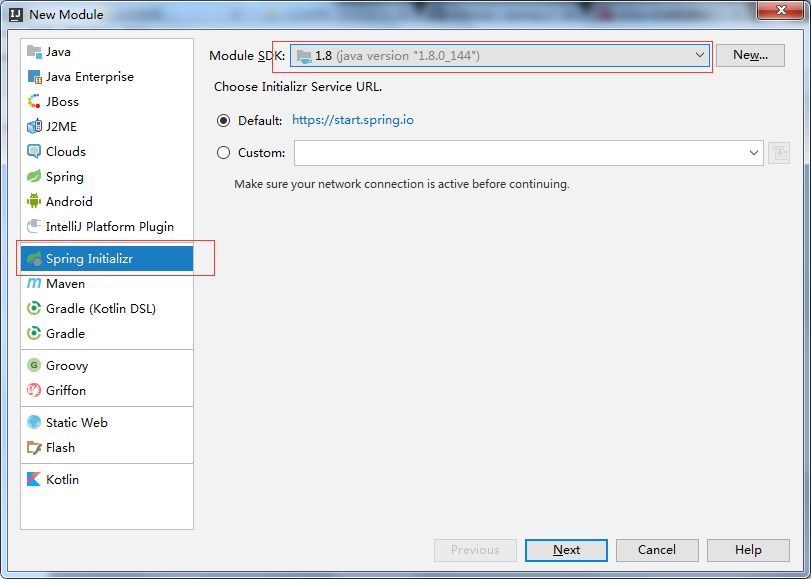
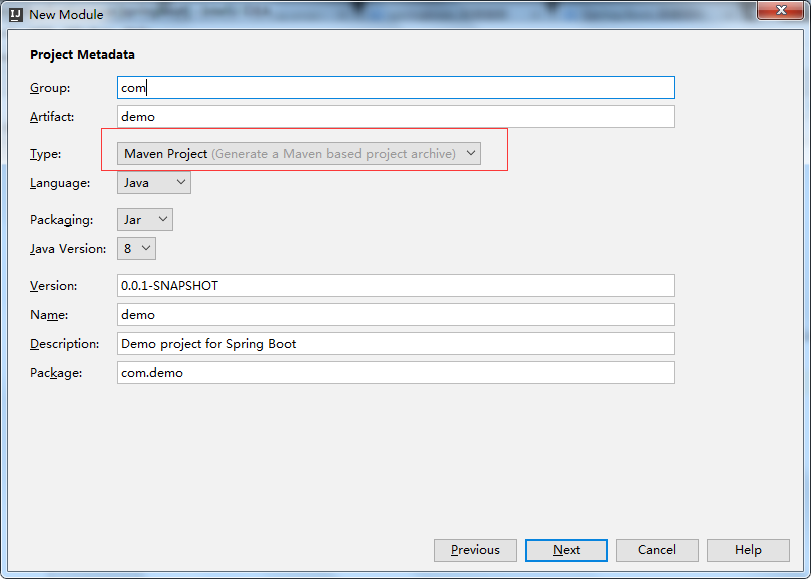
二.在Type处选择: Maven Project(项目的构建工具)
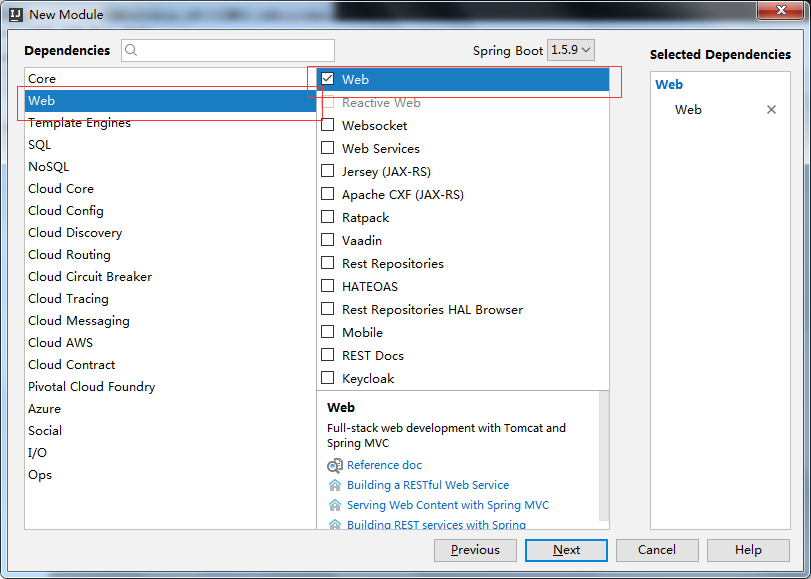
三.创建依赖时勾上web,mybatis,mysql(这个看你个人需要吧,可以自主选择)

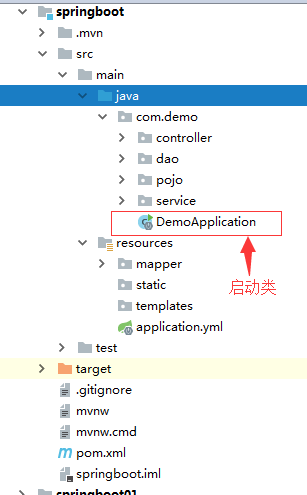
建立好的项目结构如下:
DemoApplication代码:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo.web", "com.example.demo.config"})
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:config/jdbc.properties"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = false)//未找到文件时报错
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式一
// SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
//方式二
SpringApplication SpringApplication = new SpringApplication(DemoApplication.class);
SpringApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);//关闭banner图
SpringApplication.run(args);
}
}
注意要加exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,否则没有配置数据源时会报错:
Failed to configure a DataSource: 'url' attribute is not specified and no embedded datasource could be configured.
Reason: Failed to determine a suitable driver class
启动方式:
1、启动类中右键执行main方法;
2、Terminal命令行中直接执行命令:mvn spring-boot:run (点击X号close session即关闭项目)
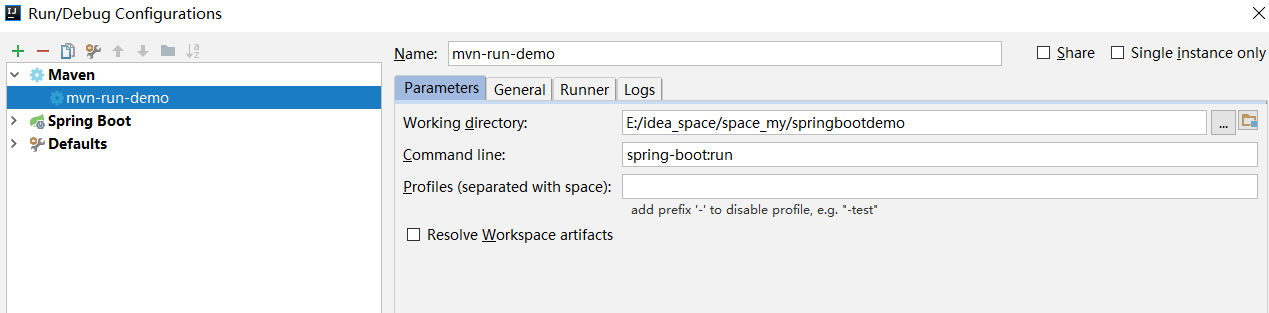
3、edit Configurations中添加maven命令,注意Command line中只有spring-boot:run,没有mvn
4、执行mvn install生成jar包,执行命令如:java -jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar 启动
启动banner图设置:
打开地址生成banner文案:http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&h=3&v=3&f=4Max&t=springboot
复制生成的文本保存到banner.txt放到maven项目resouces目录下,启动即可看到效果。若要更改命名或者存放位置可通过配置更改:
banner.location= classpath:banner.txt
若要关闭可通过:
代码方式:SpringApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
配置方式:spring.main.banner-mode= off(默认console)
自定义消息转化器
方式一:
在@Configuration的类中添加消息转化器的@bean加入到Spring容器,就会被Spring Boot自动加入到容器中。
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean//bean不存在情况下创建 public StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter(){ StringHttpMessageConverter converter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); return converter; }
效果相当于在xml文件中配置bean标签,此配置在spring容器中的名字即方法名,故一般方法名即是bean名
方式二:
自定义springmvc配置
有些时候我们需要自已配置SpringMVC而不是采用默认,比如说增加一个拦截器,这个时候就得通过实现WebMvcConfigurer然后重写父类中的configureMessageConverters方法进行扩展。
@Configuration public class NewMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{ @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { HandlerInterceptor handlerInterceptor = new HandlerInterceptor() { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("新 de 自定义拦截器............"); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { } }; registry.addInterceptor(handlerInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**"); } // 自定义消息转化器的第二种方法 @Override public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { StringHttpMessageConverter converter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); converters.add(converter); } }
@PropertySource({"classpath:static/testpro.properties"})引入properties文件
可通过注解:@Value("${test.my.name}")在bean属性中直接获取properties属性值
@ImportResource({"classpath:config.xml","classpathsome.xml"})引入xml文件
整合mybatis
Mybatis和Spring Boot的整合有两种方式:
第一种:使用mybatis官方提供的Spring Boot整合包实现,地址:https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter
第二种:使用mybatis-spring整合的方式,也就是我们传统的方式
这里我们推荐使用第二种,因为这样我们可以很方便的控制Mybatis的各种配置。
1、springbootapplication类中配置数据源类
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
private String jdbcDriverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String jdbcUsername;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String jdbcPassword;
@Bean(destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(jdbcDriverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(jdbcUrl);
dataSource.setUsername(jdbcUsername);
dataSource.setPassword(jdbcPassword);
return dataSource;
}
2、创建mybatis配置类
@Configuration public class MyBatisConfig { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean //当容器里没有指定的Bean的情况下创建该对象 public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory() { SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); // 设置数据源 sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource); // 设置mybatis的主配置文件 ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); Resource mybatisConfigXml = resolver.getResource("classpath:config/mybatis-config.xml"); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(mybatisConfigXml); // 设置别名包 sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.example.demo.model"); //mapper文件路径匹配 Resource[] mapperResourceList = null; try { mapperResourceList = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapper/**/*.xml"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(mapperResourceList); return sqlSessionFactoryBean; } }
3、创建mapper接口扫描类
@Configuration @AutoConfigureAfter(MyBatisConfig.class) //保证在MyBatisConfig实例化之后再实例化该类 public class MapperScannerConfig { @Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() { MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.example.demo.dao"); return mapperScannerConfigurer; } }
4、设置事务管理
当引入jdbc依赖之后,Spring Boot会自动默认分别注入DataSourceTransactionManager或JpaTransactionManager,所以我们不需要任何额外配置就可以用@Transactional注解进行事务的使用。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency>
注意引入配置文件:
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:config/jdbc.properties"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = false)//最好设置未找到文件时报错
mybatis-config.xml文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 全局参数 --> <settings> <!-- 使全局的映射器启用或禁用缓存。 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 全局启用或禁用延迟加载。当禁用时,所有关联对象都会即时加载。 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 设置关联对象加载的形态,此处为按需加载字段(加载字段由SQL指 定),不会加载关联表的所有字段,以提高性能 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> <!-- 是否允许单条sql 返回多个数据集 (取决于驱动的兼容性) default:true --> <setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 是否可以使用列的别名 (取决于驱动的兼容性) default:true --> <setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/> <!-- 允许JDBC 生成主键。需要驱动器支持。如果设为了true,这个设置将强制使用被生成的主键,有一些驱动器不兼容不过仍然可以执行。 default:false --> <setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/> <!-- 指定 MyBatis 如何自动映射 数据基表的列 NONE:不隐射 PARTIAL:部分 FULL:全部 --> <setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/> <!-- 这是默认的执行类型 (SIMPLE: 简单; REUSE: 执行器可能重复使用prepared statements语句;BATCH: 执行器可以重复执行语句和批量更新) --> <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/> <!-- 使用驼峰命名法转换字段,自动映射数据库下划线 到驼峰字段。 --> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> <!-- 允许使用rowbounds嵌套语句 --> <setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/> <!-- 设置本地缓存范围 session:就会有数据的共享 statement:语句范围 (这样就不会有数据的共享 ) defalut:session --> <setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/> <!-- 设置但JDBC类型为空时,某些驱动程序 要指定值,default:OTHER,插入空值时不需要指定类型 --> <!-- <setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/> --> <!-- 指定对象的方法启用懒加载 --> <setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/> </settings> <plugins> <!-- 分页插件 --> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"> <!-- 数据库类型,可选值为oracle,mysql,mariadb,sqlite,hsqldb,postgresql --> <!-- <property name="dialect" value="mysql"/> --> </plugin> </plugins> <!-- <typeAliases> <package name="com.xiaomu.context.config.model"/> </typeAliases> --> </configuration>
整合redis
1、引入springbootredis
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> <!-- 1.5的版本默认采用的连接池技术是jedis 2.0以上版本默认连接池是lettuce, 在这里采用jedis,所以需要排除lettuce的jar --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <groupId>io.lettuce</groupId> <artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.29</version> </dependency> <!-- 添加jedis客户端 --> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </dependency> <!--spring2.0集成redis所需common-pool2--> <!-- 必须加上,jedis依赖此 --> <!-- spring boot 2.0 的操作手册有标注 大家可以去看看 地址是:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.3.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId> <version>2.4.2</version> </dependency>
2、application.properties配置文件中配置redis
# 连接工厂使用的数据库索引(默认为0) spring.redis.database= 0 # Redis服务器主机。 spring.redis.host= 127.0.0.1 # redis服务器端口 spring.redis.port= 6380 # 登录redis服务器的密码。 spring.redis.password= # 给定时间池可以分配的最大连接数。 使用负值为无限制。 spring.redis.pool.max-active= 100 # 池中“空闲”连接的最大数量。 使用负值来表示无限数量的空闲连接。 spring.redis.pool.max-idle= 10 # 连接分配在池耗尽之前在抛出异常之前应阻止的最大时间量(以毫秒为单位)。 使用负值无限期地阻止。 spring.redis.pool.max-wait= -1 # 定义池中维护的最小空闲连接数。 此设置只有在正值时才有效果。 spring.redis.pool.min-idle= 0 # 连接超时(毫秒)。 spring.redis.timeout= 1000
3、配置redisconfig,配置的redisTemplate用于存取对象,普通字符串存取直接使用StringRedisTemplate即可
@Configuration public class RedisConfig{ @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory ) { //设置序列化 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class); ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om); // 配置redisTemplate RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<String, Object>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory); RedisSerializer stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer); // key序列化 redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer); // Hash key序列化 redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); // value序列化 redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); // Hash value序列化 redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } }
4、写redis工具方法

@Component public class RedisClient { @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate; @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; /** * 删除缓存 * @param key 可以传一个值 或多个 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void del(String... key) { if (key != null && key.length > 0) { if (key.length == 1) { redisTemplate.delete(key[0]); } else { redisTemplate.delete(CollectionUtils.arrayToList(key)); } } } /** * 普通缓存获取 * @param key 键 * @return 值 */ public String get(String key) { return key == null ? null : stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); } public Object getObj(String key) { return key == null ? null : redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); } /** * 普通缓存放入 * @param key 键 * @param value 值 * @return true成功 false失败 */ public boolean set(String key, String value) { try { stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); return true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return false; } } public boolean set(String key, Object value) { try { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); return true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return false; } } }
配置freemarker
1、引入freemarker依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId> </dependency>
2、配置freemarker
spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/page/ spring.freemarker.charset=utf-8 spring.freemarker.cache=false spring.freemarker.suffix=.ftl
3、写controller和页面(model类或者map放值都可以加入到页面)
@RequestMapping(value="testpage",method= RequestMethod.GET) public String testPage(Map<String,Object> map, Model model){ model.addAttribute("test1","test值放入"); map.put("test","test值放入2"); return "page"; }
配置拦截器
1、写拦截器实现
@Component public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器先行方法。。。123 "); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器后置方法。。。abc"); } }
2、继承WebMvcConfigurationSupport添加拦截器并设置拦截路径
@Configuration public class SpringMVCConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 添加拦截器并设置拦截路径 registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/test*/**"); } }
打包部署
1、更改包属性为war工程:<packaging>war</packaging>
2、添加tomcat依赖并设置为provider
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
3、springboot入口类继承SpringBootServletInitializer并重写configure方法
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo"})
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:config/jdbc.properties"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = false)
public class DemoApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer{
//。。。
//重写方法用于部署到tomcat中运行
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
// return super.configure(builder);
return builder.sources(DemoApplication.class);
}
}
4、执行maven命令package打包成war包部署即可。
说明:打包后的war包解压后WEB-INFO目录下没有web.xml文件,web入口由继承的SpringBootServletInitializer类在org目录下生成了很多关于项目入口的类
springboot整合缓存cache
第一步: 导入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency>
注:配置文件中spring.cache.type=redis指定缓存类型
第二步: @EnableCaching开启缓存
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo"})
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:config/jdbc.properties"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = false)
@EnableCaching
public class DemoApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer{
...
}
第三步: 使用缓存注解
//@CachePut: 既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存 //修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存 //运行: // 1.先调用目标方法 // 2.将目标方法的结果缓存起来 @Override @CachePut(value=CACHE_NAME,key = "#sysmenu.autoId") public SysMenu updateMenu(SysMenu sysmenu) { sysMenuDao.update(sysmenu); return sysmenu; } //@CacheEvict:缓存清除 //key:指定要清除的数据 //allEntries = true : 指定清除这个缓存中的所有数据 //beforeInvocation=fales: 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除 //beforeInvocation=true 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除 @Override @CacheEvict(value=CACHE_NAME,key = "#menu_id", beforeInvocation = true) public void delete(String menu_id) { sysMenuDao.delete(menu_id); } @Override public int add(SysMenu sysMenu) { return sysMenuDao.add(sysMenu); } //查询时根据指定的参数查询缓存有无数据,有则直接返回,无则调用方法后将返回值放入缓存 //注意unless条件为真不缓存,记得指定结果为空不缓存,否则查询会缓存空结果导致若有此值新增将查询不到正确数据 @Override @Cacheable(value=CACHE_NAME,key = "#autoId", unless = "#result==null") public SysMenu getByAutoId(String autoId){ return sysMenuDao.getByAutoId(autoId); }
注解及参数说明:
@Cacheable
@Cacheable 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
|
参数 |
解释 |
example |
|
value |
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
|
key |
缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 |
@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
|
condition |
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 |
@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
@CachePut
@CachePut 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
|
参数 |
解释 |
example |
|
value |
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 |
@CachePut(value=”my cache”) |
|
key |
缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 |
@CachePut(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
|
condition |
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 |
@CachePut(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
@CacheEvict
@CachEvict 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
|
参数 |
解释 |
example |
|
value |
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 |
@CacheEvict(value=”my cache”) |
|
key |
缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 |
@CacheEvict(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
|
condition |
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 |
@CacheEvict(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
|
allEntries |
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 |
@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
|
beforeInvocation |
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 |
@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true) |
@CacheConfig
@Cacheable(value="xxx")注解在类上,统一声明方法中的value属性,如果你在你的方法写别的名字,那么依然以方法的名字为准。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012240455/article/details/80844361


