巧用location.hash保存页面状态
在我们的项目中,有大量ajax查询表单+结果列表的页面,由于查询结果是ajax返回的,当用户点击列表的某一项进入详情页之后,再点击浏览器回退按钮返回ajax查询页面,这时大家都知道查询页面的表单和结果都回到了默认状态。
如果每次返回页面都要重新输入查询条件,或有甚者还得转到列表的第几页,那这种体验用户真的要抓狂了。
在我们的项目中,写了一个很简单的JavaScript基类来处理location.hash从而保存页面状态,今天在此就分享给大家。
(本文的内容可能对于JavaScript初学者来讲有点难度,因为涉及到JS面向对象的知识,如定义类、继承、虚方法、反射等)
先看看我们的需求
我们的项目是一个基于微信的H5任务管理系统,要完成的页面原型如下图所示:
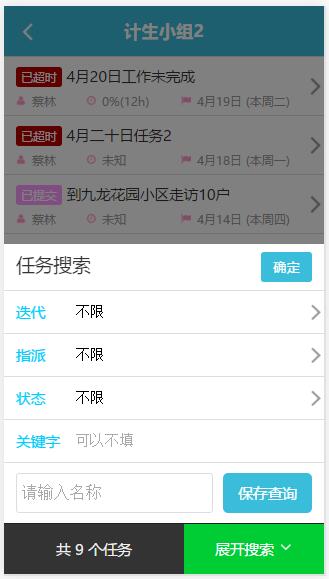
需求应该都很清晰,就是点击查询表单,用ajax返回查询结果,然后点击列表中的某一个任务进入任务详情页。由于管理员(项目经理)通常会一次处理多个任务,所以就会不断在任务详情页跟查询列表页切换,这时如果按返回键不能保存查询页面状态的话,那每次返回查询页面都要重新输入查询条件,这样的体验肯定是不能忍受的。
所以,我们需要想办法将页面状态保存下来,以便用户按回退键的时候,查询条件和结果都还在。
解决思路
保存页面状态的思路有很多啦,但是我们觉得用location.hash应该是最好的方法。
思路如下:
- 用户输入查询条件并点击确定后,我们将查询条件序列化成一个字符串,并通过“#”将查询条件加到url后面得到一个新的url,然后调用location.replace(新的url)修改浏览器地址栏中的地址。
- 当用户按回退键回退到查询页面时,也可以说是页面加载时,将location.hash反序列化成查询条件,然后将查询条件更新到查询表单并执行查询即可。
思路很简单,关键的地方就是location.replace方法,这个方法不仅仅是修改浏览器中地址栏的url,更重要的是会在window.history中替换当前页面的记录。如果不用location.replace方法,那么每次回退都会回退到上一个查询条件。当然,这样的需求可能对某些项目还有用。
最终解决方案
如果本文只是分享上面的解决思路,那价值就不大了。本文的价值应该是我们写的那个虽然简单但是却很强大的JavaScript类。
如果你看明白了上面的解决思路,那就看看这个简单的JavaScript类吧:
1 (function() { 2 if (window.HashQuery) { 3 return; 4 } 5 window.HashQuery = function() { 6 7 }; 8 9 HashQuery.prototype = { 10 parseFromLocation: function() { 11 if (location.hash === '' || location.hash.length === 1) { 12 return; 13 } 14 var properties = location.hash.substr(1).split('|'); 15 var index = 0; 16 for (var p in this) { 17 if (!this.hasOwnProperty(p) || typeof this[p] != 'string') { 18 continue; 19 } 20 21 if (index < properties.length) { 22 this[p] = properties[index]; 23 if (this[p] === '-') { 24 this[p] = ''; 25 } 26 } 27 index++; 28 } 29 }, 30 updateLocation: function() { 31 var properties = []; 32 for (var p in this) { 33 if (!this.hasOwnProperty(p) || typeof this[p] != 'string') { 34 continue; 35 } 36 var value = this[p]; 37 properties.push(value === '' ? '-' : value); 38 } 39 var url = location.origin + location.pathname + location.search + "#" + properties.join('|'); 40 location.replace(url); 41 } 42 }; 43 })();
这个类只有2个方法,HashQuery.parseFromLocation() 方法从location.hash反序列化为HashQuery子类的实例,HashQuery.updateLocation() 方法将当前HashQuery子类的实例序列化并更新到window.location。
可以看到HashQuery这个类没有任何属性,那是因为我们只定义了一个基类,类的属性都在子类中进行定义。这也是符合实际的,因为查询条件都只有在具体的页面才知道有哪些属性。
另外,请注意这里的序列化和反序列化。这里的序列化仅仅是利用JavaScript反射机制将实例的所有字符串属性(按顺序)的值用“|”分隔;而序列化则是将字符串用“|”分隔后,再利用反射更新到实例的属性(按顺序)。
如何使用HashQuery类
使用的时候就非常简单了。
第一步,定义一个子类,将需要用到的查询条件都加到字符串属性当中,如我们的代码:
1 (function() { 2 window.TaskSearchHashQuery = function () { 3 HashQuery.constructor.call(this); 4 this.iterationId = ''; 5 this.assignedUserId = ''; 6 this.status = ''; 7 this.keyword = ''; 8 }; 9 10 TaskSearchHashQuery.constructor = TaskSearchHashQuery; 11 TaskSearchHashQuery.prototype = new HashQuery(); 12 })();
第二步,在查询页面调用HashQuery.parseFromLocation() 和 HashQuery.updateLocation()方法即可。下面的代码是我们完整的查询页面:
1 (function() { 2 var urls = { 3 list: "/app/task/list" 4 }; 5 var hashQuery = null; 6 var pager = null; 7 8 $(document).ready(function () { 9 hashQuery = new TaskSearchHashQuery(); 10 hashQuery.parseFromLocation();//在这里调用的哦,从location反序列化object 11 updateFormByHashQuery(); 12 13 $("#btnSearch").click(function() { 14 updateHashQueryByForm(); 15 hashQuery.updateLocation();//在这里调用的哦,将查询条件序列化之后更新到location.hash 16 $("#lblCount").html("加载中..."); 17 pager.reload(); 18 page.hideSearch(); 19 }); 20 21 pager = new ListPager("#listTasks", urls.list); 22 pager.getPostData = function(index) { 23 return "pageIndex=" + index + "&pageSize=50" + "&projectId=" + page.projectId 24 + "&iterationId=" + hashQuery.iterationId 25 + "&assignedUserId=" + hashQuery.assignedUserId 26 + "&status=" + hashQuery.status 27 + "&keyword=" + hashQuery.keyword; 28 }; 29 pager.onLoaded = function() { 30 $("#lblCount").html("共 " + $("#hfPagerTotalCount").val() + " 个任务"); 31 $("#hfPagerTotalCount").remove(); 32 }; 33 pager.init(); 34 }); 35 36 function updateHashQueryByForm() { 37 hashQuery.iterationId = $("#ddlIterations").val(); 38 hashQuery.assignedUserId = $("#ddlUsers").val(); 39 hashQuery.status = $("#ddlStatuses").val(); 40 hashQuery.keyword = $("#txtKeyword").val(); 41 }; 42 43 function updateFormByHashQuery() { 44 $("#ddlIterations").val(hashQuery.iterationId); 45 $("#ddlUsers").val(hashQuery.assignedUserId); 46 $("#ddlStatuses").val(hashQuery.status); 47 $("#txtKeyword").val(hashQuery.keyword); 48 }; 49 50 })();
总结
这就是我们项目中使用location.hash来保存页面状态的全部知识了。不知道大家的WEB项目中是如何处理这样的需求的呢?
最后,大家可以看看我们的开源项目:https://github.com/leotsai/mvcsolution,一个讲ASP.NET MVC应用架构的项目,里面也有不少JavaScript的架构和高级用法。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)