20182320《Program Design and Data Structures》Learning Summary Week9
20182320《Program Design and Data Structures》Learning Summary Week9
1.Summary of Textbook's Content
1.1 Chapter 15:Tree
1.1.1 Concept of Tree:
'Tree' is a data sturcture,which is non-linear. It consists of nodes and edges.

1.1.2 Some important concepts:
The only top node is called root.For example,in the picture above,A is the root of the tree.
The nodes connected with nothing is called leaf.For example,in the picture above,nodes with '#' are all leaves of the tree.
When a node's top is connected to another node,we define that the latter one is the parent of the former one.For example,in the picture above,A is the parent of B and C.
When a node's bottom is connected to other node(s),we define that the latter one(s) is(are) child(children) of the former one.For example,in the picture above,B and C are children of B and C.
When some nodes are in the same layer,like D and E in the picture,we call that they are siblings of each other.
When a tree is a part of another tree,we called the former one the subtree of the latter one.
A node's path length means the number of edges traveled by the path from root to the node.
The height/depth of a tree means the length of the longest path in a tree from its root to leaves.
A tree's order means the number of the children of a node that has the most children.
When the most children of a tree's nodes is n,we called the tree n-ary tree.
1.1.3 Traversal
(1)preorder traversal
Access the root first and then access other nodes from left to right.
(2)inorder traversal
Access the left subtree first,then access the root,the last is the right subtree.
(3)postorder traversal
Similar with the traversals above,but access the root last.
1.2 Chapter 16:Binary Search Tree
1.2.1 Concept of Binary Search Tree:
Binary Search Tree is originated from Tree,but has a rule about the arrangements of the contents.
The rule is: When we set a root here, the node that has a smaller element than the root's,should be set as the leftnode of the root.And on the contrary, a node with a bigger element should be set as the rightnode of the root.It goes all the way down according to this rule.
2.Problems and Solutions in Textbook's Learning
Problem 1:
When it comes to the implements of LinkedBinaryTree,the codes in the textbook involves some knowledge of Iterator,which made me confused.
Solution 1:
CSDN:

From here I learned that Iterator is a great way of implementing Tree Traversal.
3.Problems and Solutions in Code Debugging
Problem 1:
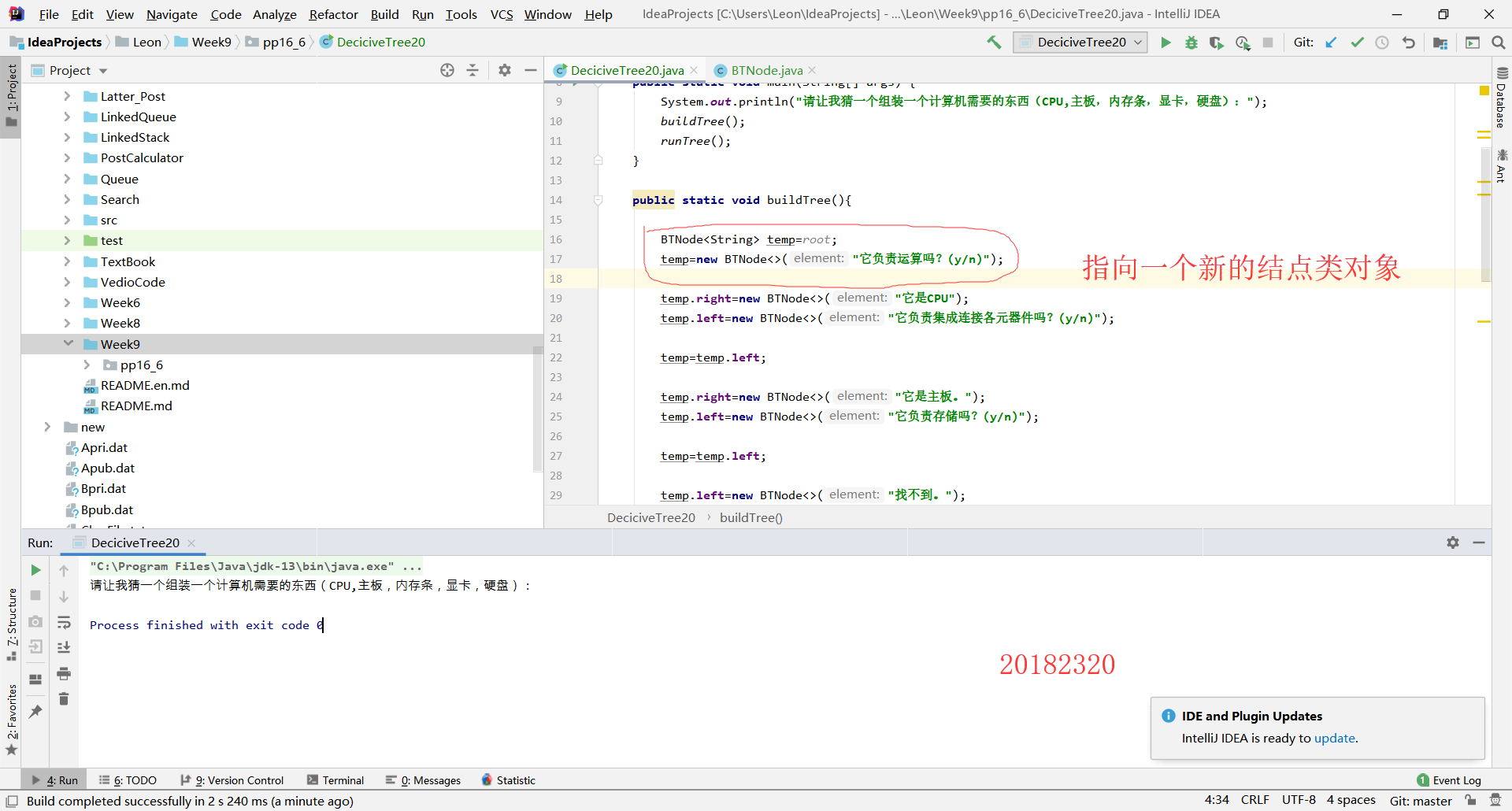
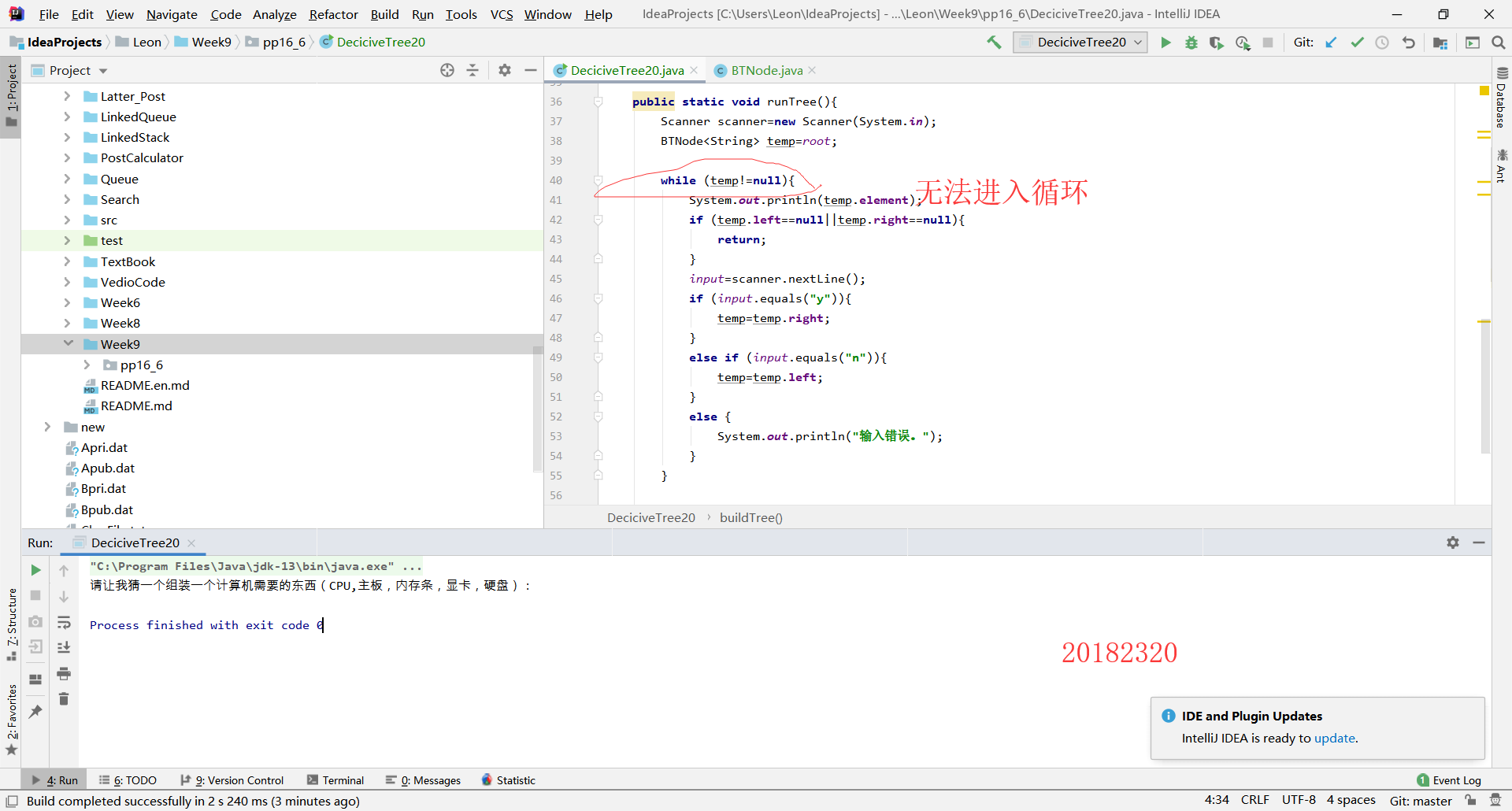
When programming PP16.6,the programme just stopped after outputting a single line.

Solution 1:
The problem was found as below:
Code Management
Summary of Mistakes in Exams(Last Week)
Mistake 1:
Typically, in heap implementations, we keep track of the position of the last node or, more precisely, the last leaf in the tree.
A.root
B.internal node
C.leaf
D.tree
Correct Answer:C
Mistake by:A
Conclusion 1:
Just because of carelessness.
Mutual Evaluation
Commented Blogs
- Mutual Blog Evaluation(This Week)
- 20182307
- Paring Study Details
- Tree
- BinarySearchTree
- Mutual Blog Evaluation(Last Week)
Others
Since Tree is a non-linear data structure,it took me a lot of time to comprehend it.Tree has some advantages in searching and sorting,but its travesal,especially when implemented by Inheritance,still requires further study to make sense of.
Progress Bar
| CodeLines(New/Accumulation) | Blogs' number(New/Accumulation) | Learning hours(New/Accumulation) | Important progress | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goal | 10000 lines | 30 blogs | 400 hours | |
| Week1 | 208/208 | 2/2 | 9/9 | |
| Week2 | 258/466 | 2/4 | 15/24 | |
| Week3 | 693/1159 | 2/6 | 22/46 | |
| Week4 | 1383/2542 | 2/8 | 30/76 | |
| Week5 | 1300/3842 | 2/10 | 22/98 | |
| Week6 | 1998/5840 | 2/12 | 24/122 | |
| Week7 | 2901/8741 | 2/14 | 30/152 | |
| Week8 | 3556/12297 | 2/16 | 30/182 |



