[RH124] 9-服务管理
1.什么是服务
daemon:一个后台进程。
服务 :可以理解为就是daemon。或者理解为对一个后台程序的包装。
一个服务启动起来了:就是一个后台程序跑起来了。
2.查看系统的服务
systemctl list-unit-files :查看系统所有的服务。
systemctl list-unit-files --type service :查看所有后缀为service的服务。
实验:
使用rpm或yum安装一个服务,例如vsftp。
rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/vsftpd-3.0.2-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
安装完毕后,系统中就有一个vsftp的服务,我们可以使用以下命令查看:
systemctl list-unit-files | grep vsftp
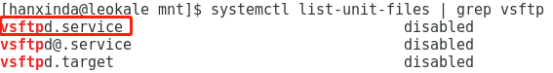
3.管理服务
# 查看一个服务是否启动,如果未启动,显示unknown。已启动,显示actived。 systemctl is-active vsftpd.service #启动服务: systemctl start vsftpd.service #关闭服务: systemctl stop vsftpd.service #重启服务: systemctl restart vsftpd.service #查看服务是否已设置开机启动: systemctl is-enabled vsftpd.service #设置开机启动: systemctl enable vsftpd.service #取消开机启动: systemctl disable vsftpd.service #禁用服务:当前已启动服务暂时不受影响。重启时受影响。 systemctl mask vsftpd.service #取消禁用: systemctl unmask vsftpd.service
#查看服务状态:
systemctl status vsftpd.service
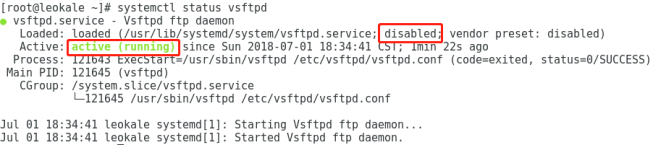
其中,第一个disabled表示未设置开机启动,绿色的active表示目前正在运行。
4.服务定义
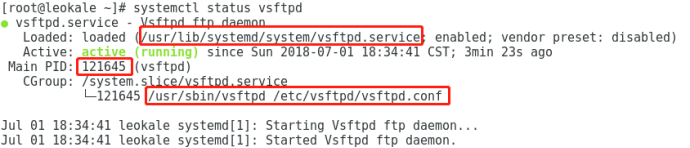
如图中红框所示:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service :在这里定义vsftpd服务。所有的服务都在 /usr/lib/systemd/system/ 中定义的。
121645:这个服务对应后台进程的PID。
/usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf :表示如何运行的vsftpd。命令+参数。
实验:
自己定义一个服务。例如我们自己写了一个程序叫myproc。
myproc 1000 :手动运行myproc,参数为1000。
1) cd /usr/lib/systemd/system ,我们复制一份vsftpd.service文件:
cp vsftpd.serivce myproc.serivce
2)编辑myproc.service文件:
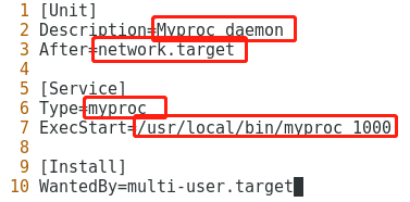
Discription:描述信息,随便写。
After:表示在网络服务启动后运行。
Type:随便写?
ExecStart:运行该程序的命令,包含程序的路径和参数。
3)保存文件。
4)执行 systemctl list-unit-files | grep myproc 查看服务是否存在了。

5)使用命令启动服务
systemctl start myproc.service
systemctl enable myproc.service
===


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号