[Python自学] Nginx+uWSGI启动django项目
一、uWSGI命令运行Django项目
1.Django配置
要让所有IP都能访问,需要配置ALLOWED_HOST:
# settings ALLOWED_HOSTS = ["*"]
2.使用uWSGI启动django应用(踩坑)
在/root/admin_demo目录(django项目为admin_demo,放在/root下)下执行命令:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# uwsgi --http :8001 --static-map /static=/root/admin_demo/static --module admin_demo.wsgi
--http表示使用http协议。
:8001表示监听端口。
--module表示django项目中的wsgi.py模块。
--static-map表示静态资源请求,映射到实际的目录。否则无法返回静态资源。(坑)
3.uWSGI热加载
在uwsgi命令中使用--py-autoreload=1参数来开启热加载:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# uwsgi --http :8001 --static-map /static=/root/admin_demo/static --module admin_demo.wsgi --py-autoreload=1
当开启了热加载后,我们如果实时修改了后端python代码,uwsgi会自动帮我们加载,服务不会停。
二、uWSGI配置文件运行项目
1.创建一个uwsgi.ini配置文件
touch /etc/uwsgi.ini
写入如下配置信息:
[uwsgi] # Django-related settings # the base directory (full path) chdir = /root/admin_demo # 指定django项目的绝对路径 # Django's wsgi file module = admin_demo.wsgi # wsgi.py文件,这里写相对路径,chdir为相对路径 # the virtualenv (full path) home = /root/.virtualenvs/venv_fb # python虚拟环境home目录(绝对路径),使用cdvirtualenv来查看 # process-related settings # master master = true # maximum number of worker processes processes = 4 # 指定uwsgi启动的进程数,视机器配置来定 # the socket (use the full path to be safe # socket = 0.0.0.0:8000 # uwsgi启动一个socket连接,当使用nginx+uwsgi的时候,使用socket参数
http = 0.0.0.0:8000 # uwsgi启动一个socket连接,当不使用nginx,直接使用uwsgi时,使用该参数
# ... with appropriate permissions - may be needed # chmod-socket = 664 # clear environment on exit vacuum = true
2.使用uwsgi.ini配置文件启动
将uwsgi.ini配置文件拷贝到django项目目录下:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb etc]# cp /etc/uwsgi.ini /root/admin_demo/
启动项目:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini [uWSGI] getting INI configuration from uwsgi.ini *** Starting uWSGI 2.0.18 (64bit) on [Thu Jan 30 21:45:19 2020] *** compiled with version: 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) on 30 January 2020 10:24:09 os: Linux-3.10.0-1062.9.1.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Dec 6 15:49:49 UTC 2019 nodename: centos-venv-fb machine: x86_64 clock source: unix pcre jit disabled detected number of CPU cores: 4 current working directory: /root/admin_demo detected binary path: /root/.virtualenvs/venv_fb/bin/uwsgi uWSGI running as root, you can use --uid/--gid/--chroot options *** WARNING: you are running uWSGI as root !!! (use the --uid flag) *** chdir() to /root/admin_demo your processes number limit is 14988 your memory page size is 4096 bytes detected max file descriptor number: 1024 lock engine: pthread robust mutexes thunder lock: disabled (you can enable it with --thunder-lock) uWSGI http bound on 0.0.0.0:8000 fd 4 uwsgi socket 0 bound to TCP address 127.0.0.1:44810 (port auto-assigned) fd 3 uWSGI running as root, you can use --uid/--gid/--chroot options *** WARNING: you are running uWSGI as root !!! (use the --uid flag) *** Python version: 3.7.0 (default, Jun 28 2018, 13:15:42) [GCC 7.2.0] Set PythonHome to /root/.virtualenvs/venv_fb *** Python threads support is disabled. You can enable it with --enable-threads *** Python main interpreter initialized at 0x209b820 uWSGI running as root, you can use --uid/--gid/--chroot options *** WARNING: you are running uWSGI as root !!! (use the --uid flag) *** your server socket listen backlog is limited to 100 connections your mercy for graceful operations on workers is 60 seconds mapped 364520 bytes (355 KB) for 4 cores *** Operational MODE: preforking *** /root/admin_demo/static/ WSGI app 0 (mountpoint='') ready in 1 seconds on interpreter 0x209b820 pid: 3382 (default app) uWSGI running as root, you can use --uid/--gid/--chroot options *** WARNING: you are running uWSGI as root !!! (use the --uid flag) *** *** uWSGI is running in multiple interpreter mode *** spawned uWSGI master process (pid: 3382) spawned uWSGI worker 1 (pid: 3383, cores: 1) spawned uWSGI worker 2 (pid: 3384, cores: 1) spawned uWSGI worker 3 (pid: 3385, cores: 1) spawned uWSGI worker 4 (pid: 3386, cores: 1) spawned uWSGI http 1 (pid: 3387)
解决uwsgi找不到静态文件的问题,在uwsgi.ini配置文件中加上:
static-map = /static=/root/admin_demo/static
让uwsgi在后台运行,在uwsgi.ini配置文件中加上:
daemonize = yes
再来运行:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini [uWSGI] getting INI configuration from uwsgi.ini [uwsgi-static] added mapping for /static => /root/admin_demo/static
查看进程信息:
(venv_fb) [root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# ps -ef | grep uwsgi root 3405 1 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3406 3405 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3407 3405 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3408 3405 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3409 3405 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3410 3405 0 21:50 ? 00:00:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini root 3412 2561 0 21:51 pts/3 00:00:00 grep --color=auto uwsgi
三、Nginx+uWSGI
在前面的一二节中,我们已经可以使用uWSGI来启动Django项目。
下面我们配置Nginx作为反向代理服务器。
1.准备工作
1)安装nginx服务器
2)确认uWSGI服务监听端口
192.168.1.191:8000
3)去除uWSGI的一些配置
由于静态资源请求,我们可以直接让Nginx来处理,所以可以将uWSGI中的静态资源目录映射去除。
# 去除
static-map = /static=/root/admin_demo/static
如果使用supervisor来管理uwsgi进程,则将daemonize配置项也去除:
# 去除
daemonize = yes
4)修改uwsgi的重要配置
[uwsgi] # Django-related settings # the base directory (full path) chdir = /root/admin_demo # Django's wsgi file module = admin_demo.wsgi # the virtualenv (full path) home = /root/.virtualenvs/venv_fb # process-related settings # master master = true # maximum number of worker processes processes = 4 # the socket (use the full path to be safe socket = 0.0.0.0:8000 #http = 0.0.0.0:8000 # ... with appropriate permissions - may be needed # chmod-socket = 664 # clear environment on exit vacuum = true #static-map = /static=/root/admin_demo/static #daemonize=yes
非常重要:当我们要使用nginx+uwsgi时,需要使用socket配置项。而单独使用uwsgi时,则使用http配置项。
2.配置Nginx(踩坑)
1)配置nginx
Nginx安装在uwsgi同服务器。IP地址都为192.168.1.191。
Nginx安装目录为/opt/nginx。
vi /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
修改其中部分配置:
http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; #access_log "pipe:rollback logs/access_log interval=1d baknum=7 maxsize=2G" main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; # nginx监听端口,即对外暴露端口 server_name 192.168.1.191; # 本机IP #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; #access_log "pipe:rollback logs/host.access_log interval=1d baknum=7 maxsize=2G" main; location / { # 当我们访问192.168.1.191:80时,请求会转给uwsgi监听的8000端口 include /opt/nginx/conf/uwsgi_params; # 包含uwsgi_params中的配置(固定写) uwsgi_pass 192.168.1.191:8000; # uwsgi服务器绑定地址和端口 } location /static/ { alias /root/admin_demo/static/; # 注意,这里使用nginx直接提供静态资源响应(uwsgi只做动态资源响应) } } # server end } http end
3)解决静态资源访问403错误
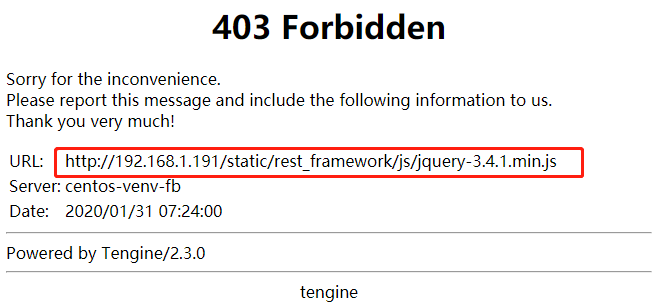
我们访问页面时,动态资源能够正常拿到,但静态资源,例如css、js、图片等资源都无法请求。
这是因为在Nginx的配置文件中,虽然我们配置了/static的访问路径:
location /static/ { alias /root/admin_demo/static/; }
但是Nginx启动时使用的用户叫nobody,可以查看进程看到:
[root@centos-venv-fb admin_demo]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 8255 1 0 08:08 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /opt/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf nobody 8256 8255 0 08:08 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 8258 7718 0 08:08 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
而nobody对静态资源文件没有访问权限。所以,我们在nginx的配置文件中将user修改为root即可:
#user nobody;
user root;
关于默认的nobody用户,可以参考:http://alisa365.com/linux/104.html 中的说明。
重新载入或重新启动Nginx后,可以正常访问静态资源:
systemctl restart nginx
systemctl reload nginx
☿

