OpenCV笔记(5)(定位票据并规范化、调库扫描文本)
一、定位和变换票据
定位照片中的不规范票据或矩形文本,并将其变换为正规矩形,以供OCR识别。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'Leo.Z' import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def show_img(img, win_name): cv.imshow(win_name, img) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows() def image_process(img_path): # 读入图像 img = cv.imread(img_path) show_img(img, 'img') # 转换为灰度图 gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # 高斯模糊,消除一些噪声 gray = cv.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0) show_img(gray, 'gray') # 寻找边缘 edged = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 120) show_img(edged, 'edged') # 形态学变换,由于光照影响,有很多小的边缘需要进行腐蚀和膨胀处理 kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8) morphed = cv.dilate(edged, kernel, iterations=3) morphed = cv.erode(morphed, kernel, iterations=3) show_img(morphed, 'morphed') # 找轮廓 morphed_copy = morphed.copy() cnts, _ = cv.findContours(morphed_copy, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 排序,并获取其中最大的轮廓 if len(cnts) is not 0: cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv.contourArea, reverse=True)[:1] else: print("Did not find contours\n") return # 用周长的0.1倍作为阈值,对轮廓做近似处理,使其变成一个矩形 epsilon = 0.1 * cv.arcLength(cnts[0], True) approx = cv.approxPolyDP(cnts[0], epsilon, True) # 在原图的拷贝上画出轮廓 ticket_copy = img.copy() cv.drawContours(ticket_copy, [approx], -1, (255, 0, 0), 2) show_img(ticket_copy, 'ticket_copy') # 获取透视变换的原坐标 if approx.shape[0] is not 4: print("Found a non-rect\n") return src_coor = np.reshape(approx, (4, 2)) src_coor = np.float32(src_coor) # 右上,左上,左下,右下 坐标 (tr, tl, bl, br) = src_coor # 计算宽 w1 = np.sqrt((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2 + (tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2) w2 = np.sqrt((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2 + (br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2) # 求出比较大的w max_w = max(int(w1), int(w2)) # 计算高 h1 = np.sqrt((bl[0] - tl[0]) ** 2 + (bl[1] - tl[1]) ** 2) h2 = np.sqrt((br[0] - tr[0]) ** 2 + (br[1] - tr[1]) ** 2) # 求出比较大的h max_h = max(int(h1), int(h2)) # 透视变换的目标坐标 dst_coor = np.array([[max_w - 1, 0], [0, 0], [0, max_h - 1], [max_w - 1, max_h - 1]], dtype=np.float32) # 求转换矩阵 trans_mat = cv.getPerspectiveTransform(src_coor, dst_coor) # 进行转换,将图中对应坐标的图片截取出来,并转换到dst_coor大小 warped = cv.warpPerspective(img, trans_mat, (max_w, max_h)) return warped if __name__ == '__main__': wrap = image_process('zhengshu.png') show_img(wrap, 'result')
效果如下:
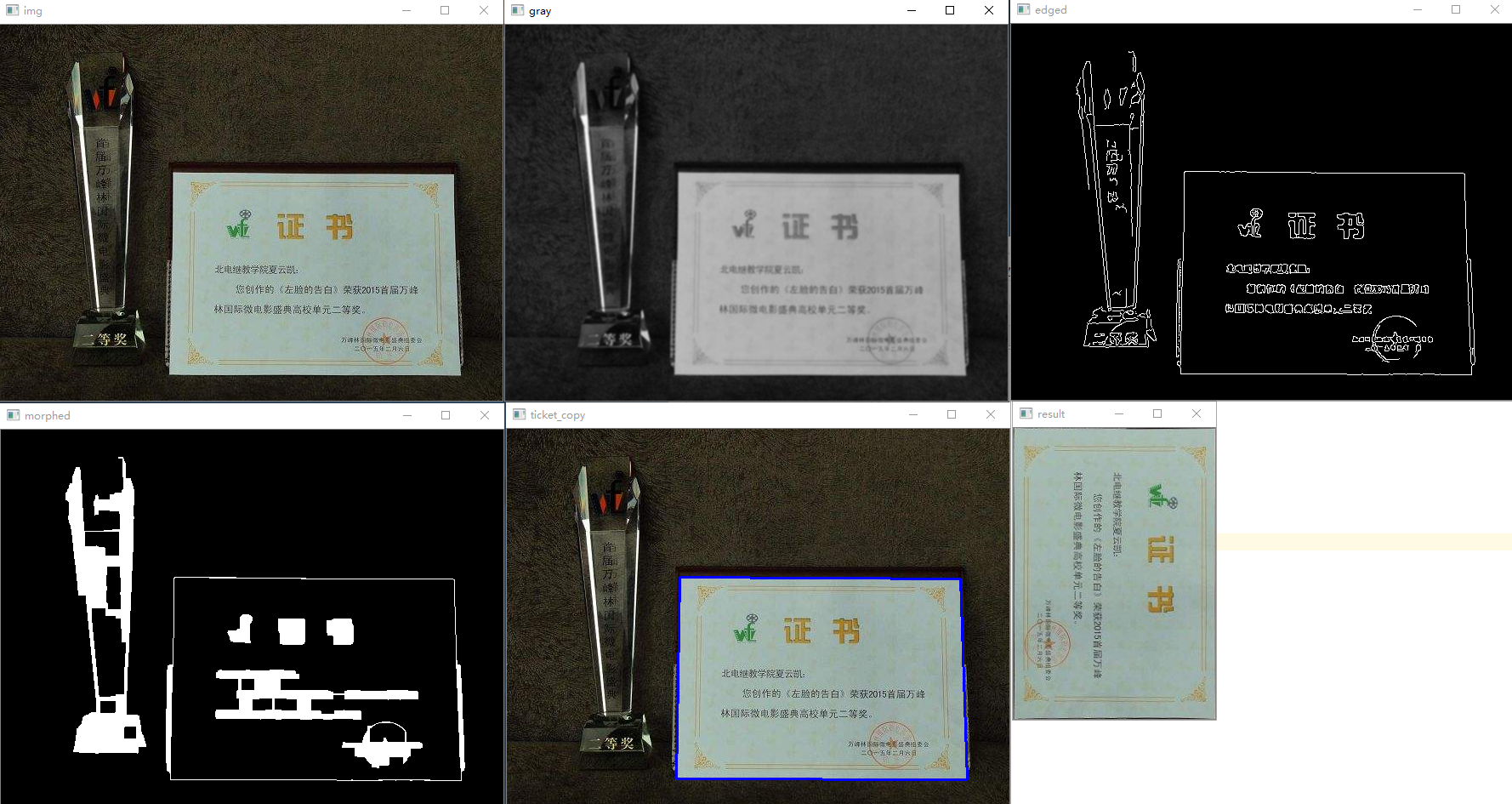

注意:本例是一个相对简单的示例,对于背景复杂,或票据与背景灰度相近时,可能效果不好。本例只作为前面学习内容的一个综合案例。如果要用到实际环境中需要结合更多技术,使其具有更好的鲁棒性。
二、使用OCR库实现文本扫描
我们使用一个名叫Tesseract的OCR库来实现图片上的文本扫描。
1.下载一个版本的Tesseract :https://digi.bib.uni-mannheim.de/tesseract/
2.安装并将安装目录加到环境变量path中,假设为
D:/Dev_apps/Tesseract-OCR/tesseract.exe
3.在pycharm中安装pytesseract,并修改D:\......\Lib\site-packages\pytesseract\pytesseract.py中的
tesseract_cmd = 'D:/Dev_apps/Tesseract-OCR/tesseract.exe'
在python中使用该库:(可以将已经预处理完毕的图像,例如小票发票等使用该OCR库进行处理)
import pytesseract img = cv.imread('piao6.png') # 使用tesseract来处理图片,并获取文本 text = pytesseract.image_to_string(img) print(text)
保持学习,否则迟早要被淘汰*(^ 。 ^ )***


