20191330雷清逸 stat命令的实现-mystat
学习使用stat(1),并用C语言实现
1.提交学习stat(1)的截图
2.man -k ,grep -r的使用
3.伪代码
4.产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
5.测试代码,mystat 与stat(1)对比,提交截图
1.提交学习stat(1)的截图
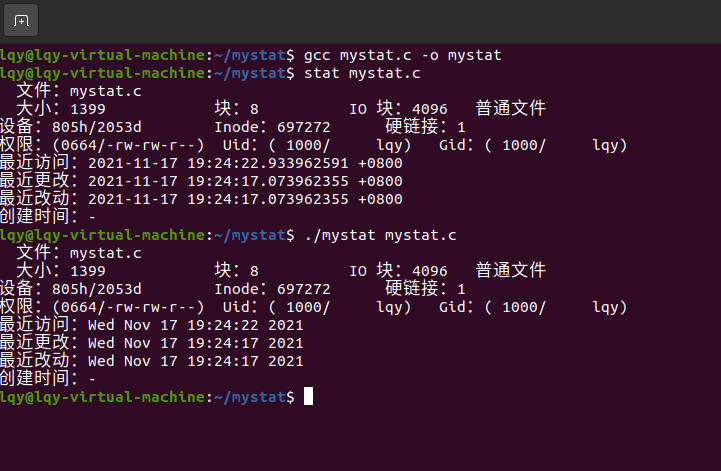
在linux系统下,使用stat(显示inode信息)命令可以查看一个文件的某些信息,我们先来尝试一下,尝试结果如下图所示:

- 显示文件名 :File
- 显示文件大小 :Size
- 文件使用的数据块总数 :Blocks
- IO块大小 : IO Block
- 文件类型(常规文件) :regular file
- 设备编号 :Device
- Inode:Inode号
- 链接数 :Links
- 文件的权限 :Access
- 文件所有权的Gid和Uid :Gid、Uid
Linux下的三个时间:
1.最近访问(Access Time):简写为atime,表示文件的访问时间。当文件内容被访问时,更新这个时间
2.最近更改(Modify Time):简写为mtime,表示文件内容的修改时间,当文件的数据内容被修改时,更新这个时间。
3.最近改动(Change Time):简写为ctime,表示文件的状态时间,当文件的状态被修改时,更新这个时间,例如文件的链接数,大小,权限,Blocks数。
由于我在创建该文件的同时修改了文件内容,所以图中三个时间显示一样。
stat命令相关格式如下:
- stat [文件或目录]
- -f 显示文件系统的信息
- -t 以简洁的方式输出
- stat * 查看该目录下的所有文件及子目录的详细信息
学习相关命令的截图如下:

2.man -k ,grep -r的使用
man 1 stat //学习stat命令用法。
学习截图如下:
man 2 stat //学习stat命令内部结构,分析mystat命令如何编写。
学习截图如下:
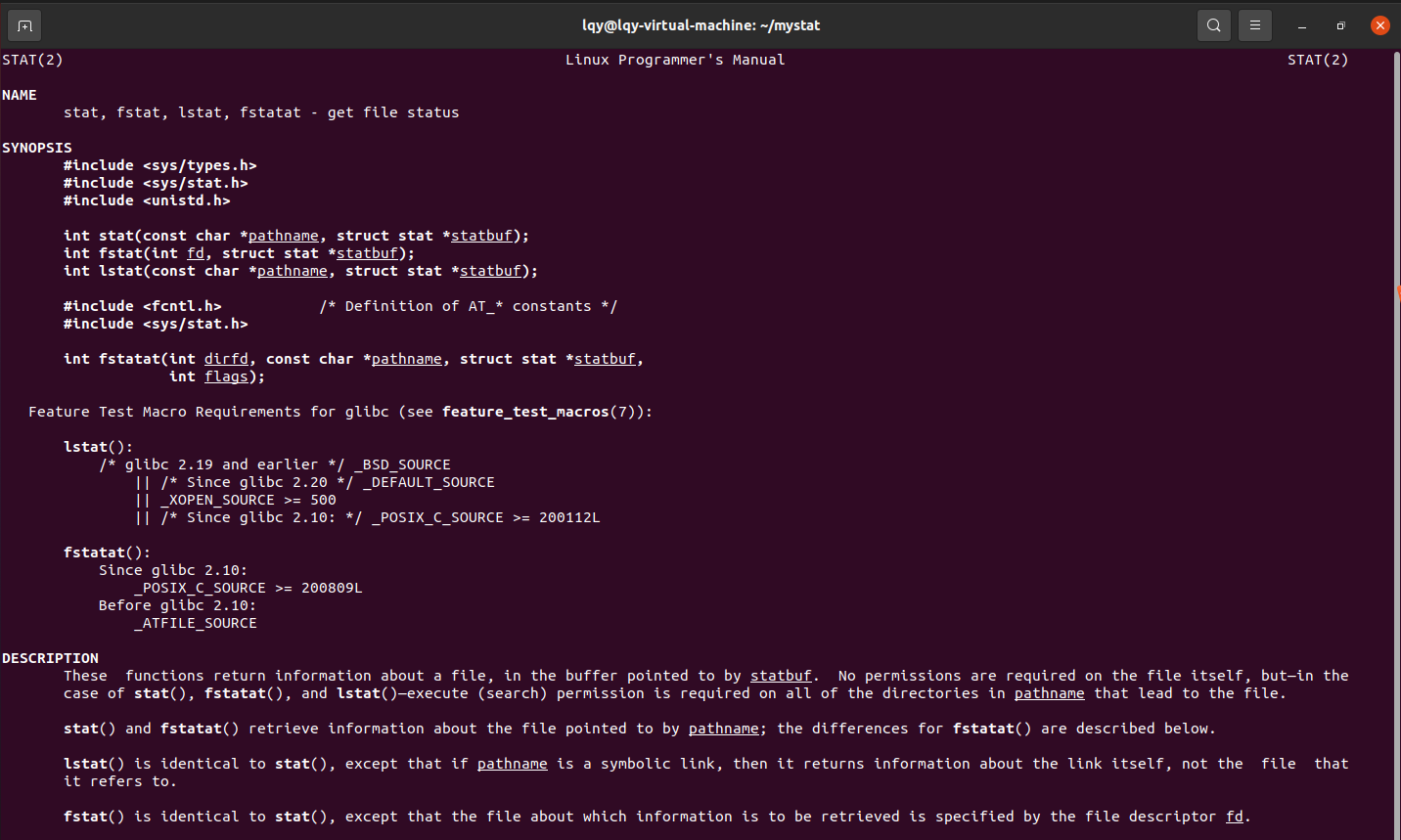
stat命令所包含的结构体如下:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
3.伪代码
读取键入内容
if(键入内容不是文件或文件夹)
{
报错
}
else
{
继续运行
}
根据键入内容获取文件或文件夹信息
打印File
打印Size
打印Blocks
打印IO Block
打印文件类型
打印Device
打印Inode号
打印Links
打印Access
打印Uid,Gid
打印Access Time,Modify Time,Change Time
4.产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
码云链接如下:
https://gitee.com/lei_qing_yi/daxuexuexidaima/blob/master/mystat
代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat st;
stat(argv[1],&st);
if(argc != 2 )
{
printf("Please enter Filename after mystat!\n");
return 0;
}
printf(" 文件:%s\n",argv[1]);
printf(" 大小:%ld 块:%ld IO 块:%ld ",(long)st.st_size,(long)st.st_blocks,(long)st.st_blksize);
switch (st.st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFBLK:
printf("块设备\n");
break;
case S_IFDIR:
printf("目录\n");
break;
case S_IFIFO:
printf("管道\n");
break;
case S_IFLNK:
printf("链接\n");
break;
case S_IFREG:
printf("普通文件\n");
break;
default:
printf("文件类型不确定\n");
break;
}
printf("设备:%lxh/%lud Inode:%ld 硬链接:%ld\n",st.st_dev,st.st_dev,(long)st.st_ino,(long)st.st_nlink);
printf("权限:(0664/-rw-rw-r--)");
printf(" Uid:( %ld/ lqy) Gid:( %ld/ lqy)\n", (long)st.st_uid, (long)st.st_gid);
printf("最近访问:%s", ctime(&st.st_atime));
printf("最近更改:%s", ctime(&st.st_mtime));
printf("最近改动:%s", ctime(&st.st_ctime));
printf("创建时间:-\n") ;
return 0;
}
5.测试代码,mystat 与stat(1)对比,提交截图
mystat命令与stat(1)命令对比如图: