pytorch 基础内容
一些基础的操作:
import torch as th a=th.rand(3,4) #随机数,维度为3,4的tensor b=th.rand(4)
print(a)
print(b) a+b
tensor([[0.3777, 0.4128, 0.6244, 0.7772],
[0.0859, 0.9350, 0.1705, 0.9116],
[0.4136, 0.1211, 0.5960, 0.8962]])
tensor([0.5063, 0.4809, 0.4810, 0.4716])
tensor([[0.8840, 0.8937, 1.1054, 1.2487],
[0.5922, 1.4159, 0.6515, 1.3831],
[0.9200, 0.6020, 1.0770, 1.3678]])
a=th.ones(3,4)*5 #全为1的tensor b=th.ones(4) a/b
tensor([[5., 5., 5., 5.],
[5., 5., 5., 5.],
[5., 5., 5., 5.]])
a=th.full([2,2],3) #完全填充tensor
a.pow(2) #几次方
tensor([[9., 9.],
[9., 9.]])
a.sqrt() #开根号
tensor([[1.7321, 1.7321],
[1.7321, 1.7321]])
a=th.exp(th.ones(2,2)) #e的指数
tensor([[2.7183, 2.7183],
[2.7183, 2.7183]])
th.log(a) #e的对数
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
grad=th.rand(2,3)*15
grad.max() #取最大值
grad.median() #取中位数
tensor(12.9437)
tensor(5.4597)
grad.clamp(0,10) #截取
tensor([[ 5.4597, 10.0000, 2.1924],
[ 3.2563, 10.0000, 10.0000]])
import torch import numpy as np a= torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.]) #通过list初始化一个tensor #print(a) a.shape b = torch.Tensor(2, 3) #注意是大写Tensor,输入的是维度信息 #print(b) c = np.array([1., 2., 3.]) c = torch.from_numpy(c) #将numpy类型的数据转换为tensor类型 #print(c) c.type() #tensor的类型 b.dim() #tensor有几个维度 b.numel() #tensor的元素个数 d=torch.randn(3,2,1) f = torch.rand_like(d) #和输入的tensor的维度一致的随机tensor f = torch.randn(3, 3) #0均值,方差为1的随机正态分布 f = torch.normal(mean=torch.full([10], 0), std=torch.arange(1, 0, -0.1))# 返回一个张量,包含从给定参数means,std的离散正态分布中抽取随机数。 均值means是一个张量,包含每个输出元素相关的正态分布的均值。 std是一个张量,包含每个输出元素相关的正态分布的标准差。 f = torch.full([2, 3], 7) #用后面的值填充一个tensor f = torch.arange(1,10) #得到int的tensor,并且不包含最后一个元素,左闭右开 #f = torch.range(1, 10, 2) #默认的浮点数, 同时左闭右闭 f = torch.randperm(2) #生产n个从1~n随机顺序的整数值
# pytorch 索引和切片 import torch as th a=th.randn(4, 3, 28, 28) a[0].shape #将a理解为4张图片,每张图片3个通道,每个通道的维度为28*28,a[0]就是取第一个图片 a[0,0].shape #取0图的0通道 a[0,0,2,4] #取0图0通道的2,4位置像素大小 a.shape a[:2].shape #表示第0,1张图片。 :为开区间的取值范围 a[:2,-1:,:,:].shape #-1表示last N. python中可以正着编号,也可以从后向前编号(负数) a[:,:,::2,::2].shape #::2, 表示间隔为2取值,select by steps a.index_select(2,th.arange(8)).shape #select by specific index 按照索引进行取值,第一个参数为选择维度,后面为选择的索引 x=th.randn(3,4) mask=x.ge(0.5) #进行mask标记 th.masked_select(x,mask) #选取mask的元素
# pytorch Tensor维度变换 import torch as th\ #1 view /reshape a=th.rand(4,1,28,28) a.view(4, 28*28).shape #必须保持合理的逻辑 #2 squeeze (去除掉维度为1的dim) / unsqueeze (在指定位置添加维度) b=th.randn(1,2,3,5) b.unsqueeze(0).shape #torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 5]) b.unsqueeze(-1).shape #torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 5, 1]) b.squeeze().shape #torch.Size([2, 3, 5]) ,当然也可以指定削减那个维度 #3 expand / repeat # Expand: broadcasting 扩展维度,在需要时才扩展数据, 推荐使用 # Repeat: memory copied b=th.rand(1, 32, 1, 1) b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14).shape #注意,expand, 扩展前后的维度数要一致,并且是1->N 才可以。 2->N 会报错 b=th.rand(1, 32, 1, 1) b.expand(-1, 32, 14, 12).shape # -1表示该维度不进行扩展 torch.Size([1, 32, 14, 12]) b=th.rand(1, 32, 1, 1) b.repeat(4, 32, 1, 1).shape #第一个维度拷贝4次, 第二个维度拷贝32次 torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1]) #4 .t() 矩阵转置操作, 只能使用于2D tensor b=th.rand(2,3) b.t().shape #torch.Size([3, 2]) # transpose(需要转置的维度) b=th.rand(1,2,3,4) #b.transpose(1,3).shape #torch.Size([1, 4, 3, 2]) #转置之后的维度恢复要十分注意 a = b.transpose(1,3).contiguous().view(1, 4*3*2).view(1, 4, 3, 2).transpose(1, 3) # view只能用在contiguous的variable上。如果在view之前用了transpose, permute等,需要用contiguous()来返回一个contiguous copy。 th.all(th.eq(a, b)) # permute 对原来的维度进行重新排序交换,会打乱内存,需要用contiguous() b.permute(0,2,3,1).shape #将原来的第2维度,放到1,...
# pytorch 拼接与分割 import torch as th a1=th.rand(4,3,32,32) a2=th.rand(5,3,32,32) th.cat([a1,a2],dim=0).shape #在指定维度dim拼接tensor, 除了要拼接的dim之外其他维度要一致 # torch.Size([9, 3, 32, 32]) a1=th.rand(32,8) a2=th.rand(32,8) th.stack([a1,a2],dim=0).shape #在要concat的维度前插入一个维度,表示拼接前后的信息 # torch.Size([2, 32, 8]) #按照长度拆分 a3=th.rand(3,32) a4=a3.split(1, dim=0) #拆分0度,每一块的len为1 aa,bb=a3.split([2,1],dim=0) #拆分某一维度,拆成指定的维度[2,1] aa.shape, bb.shape #(torch.Size([2, 32]), torch.Size([1, 32])) #按照数量拆分 a,b,c=a3.chunk(3,dim=0) a.shape,b.shape,c.shape # (torch.Size([1, 32]), torch.Size([1, 32]), torch.Size([1, 32]))
# pytorch 数学运算 import torch as th # 对于 + - * / 建议使用重载的运算符号 # 关于矩阵的乘法运算, 要注意: * : element wise 对应元素相乘 ;@ 或 .matmul : 矩阵相乘 # Torch.matmul @(符号重载) a=th.rand(2,2) b=th.rand(2,4) torch.matmul(a, b) a@b #建议 x=torch.randn(1,10) w=torch.randn(1,10,requires_grad=True) #习惯是(out, in) o=torch.sigmoid(x@w.t()) o.shape # 对于多于2D 仅对最后两维进行操作 a=th.rand(4,3,28,64) b=th.rand(4,3,64,32) th.matmul(a,b).shape #torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 32])

where 相比于for if循环可以利用GPU高度并行化加速:
import torch cond=torch.rand(2,2) print(cond) a=torch.zeros(2,2) b=torch.ones(2,2) torch.where(cond>0.5, a, b)

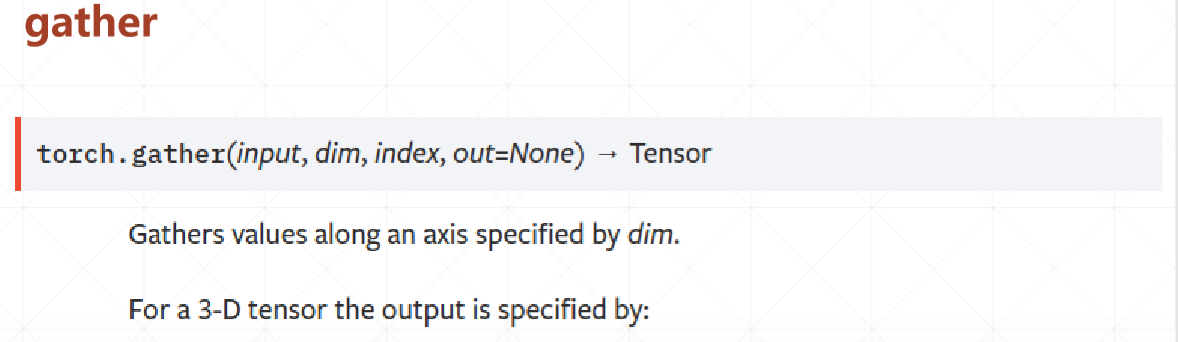
gather对应的查表收集操作,参数:查找表,需要查找的索引维度,索引。(通过索引将对应的索引的查找表的元素填入)







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
2018-08-11 RS485通信电路
2018-08-11 EEPROM存储电路(M24C64芯片)