【Yarn源码分析】FairScheduler资源调度
一、Yarn 资源调度方式
资源调度方式确定了当任务提交到集群,如何为其分配资源执行任务。在 FairScheduler 中提供了两种资源调度方式:心跳调度和连续调度。
- 心跳调度方式:NodeManager 向 ResourceManager 汇报了自身资源情况(比如,当前可用资源,正在使用的资源,已经释放的资源),这个 RPC 会触发 ResourceManager 调用 nodeUpdate() 方法,这个方法为这个节点进行一次资源调度,即,从维护的 Queue 中取出合适的应用的资源请求(合适 ,指的是这个资源请求既不违背队列的最大资源使用限制,也不违背这个 NodeManager 的剩余资源量限制)放到这个NodeManager上运行。这种调度方式一个主要缺点就是调度缓慢,当一个NodeManager即使已经有了剩余资源,调度也只能在心跳发送以后才会进行,不够及时。
- 连续调度方式:由一个独立的线程 ContinuousSchedulingThread 负责进行持续的资源调度,与 NodeManager 的心跳是异步进行的。即不需要等到 NodeManager 发来心跳才开始资源调度。
无论是 NodeManager 心跳时触发调度,还是通过 ContinuousSchedulingThread 进行实时、持续触发,他们对某个节点进行一次调度的算法和原理是公用的,都是通过 synchronized void attemptScheduling(FSSchedulerNode node) 来在某个节点上进行一次调度,方法的的参数代表了准备进行资源分配的节点。两种触发机制不同的地方只有两个:
- 调度时机:心跳调度仅仅发生在收到了某个 NodeManager 的心跳信息的情况下,持续调度则不依赖与NodeManager的心跳通信,是连续发生的,当心跳到来,会将调度结果直接返回给 NodeManager;
- 调度范围:心跳调度机制下,当收到某个节点的心跳,就对这个节点且仅仅对这个节点进行一次调度,即谁的心跳到来就触发对谁的调度,而持续调度的每一轮,是会遍历当前集群的所有节点,每个节点依次进行一次调度,保证一轮下来每一个节点都被公平的调度一次;
在集群环境中,连续调度默认不开启,只有设置 yarn.scheduler.fair.continuous-scheduling-enabled 参数为 true,才会启动该线程。连续调度现在已经不推荐了,因为它会因为锁的问题,而导致资源调度变得缓慢。可以使用 yarn.scheduler.assignmultiple 参数启动批量分配功能,作为连续调度的替代。
二、Yarn 调度流程
本文的调度流程主要介绍心跳调度的方式,下图是 Yarn 心跳调度的主要流程。
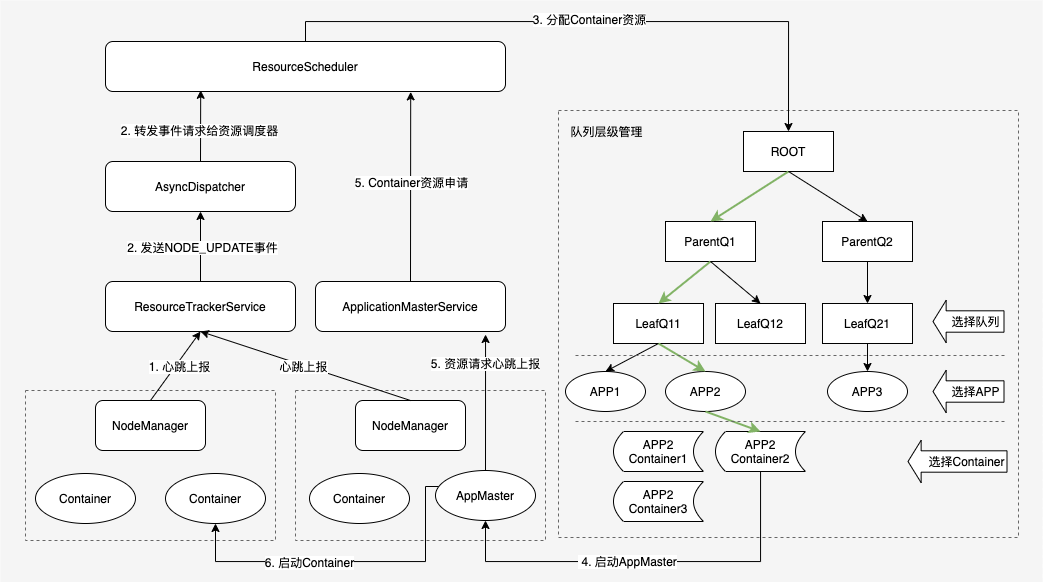
Yarn 调度流程图
2.1 名词解释
- ResrouceSacheduler 是YARN 的调度器,负责 Container 的分配。下面主要是以 FairScheduler 调度器为例。
- AsyncDispatcher 是单线程的事件分发器,负责向调度器发送调度事件。
- ResourceTrackerService 是资源跟踪器,主要负责接收处理 NodeManager 的心跳信息。
- ApplicationMasterService 是作业的 RPC 服务,主要负责接收处理作业的心跳信息。
- AppMaster 是作业的程序控制器,负责跟 YARN 交互获取/释放资源。
2.2 调度流程
YARN 的资源调度是异步进行的,NM 心跳发生时,调度器 ResourceScheduler 根据作业需求将 Container 资源分配给作业后,不会立即通知 AM,而是等待 AM 注册后通过心跳方式来主动获取。YARN 的整个调度流程可以概括为以下几个步骤:
- NM 节点通过心跳方式向 RM 汇报节点资源信息(包括当前可用资源、正在使用的资源、已经释放的资源)。
- ResourceTrackerService 服务收到 NM 的心跳事件,将 NODE_UPDATE 事件交给 中央调度器 AsyncDispatcher 处理;
- AsyncDispatcher 根据事件类型将请求转发给 ResourceScheduler 处理,ResourceScheduler 则按照一定的调度策略(队列层级调度)将 NM 的资源分配到 Container,并将 Container 保存在数据结构中;
- ResourceScheduler 针对作业分配的第一个 Container 用于启动作业的 AM 进程;
- AM 启动后,通过 ApplicationMasterService 定期向 RM 发生资源请求心跳,领取之前记录在 RM 中分配给自己的 Container 资源;
- AM 向 NM 发送启动 Container 的命令,将收到的 Container 在 NM 上启动执行。
其中,Yarn 分配策略确定了在 NM 发生心跳时,如何在所有队列中选择合适的 APP 资源请求以为其分配资源。从上图队列层级结构可以看出一次 Container 的分配流程:每次分配从 root 节点开始,先从队列中选择合适的叶子队列,然后从队列的 APP 中选择合适的 APP,最后选择出该 APP 中合适的 Container 为其分配资源执行任务,选择过程如下:
- 选择队列 (排序)。从根队列开始,使用深度优先遍历算法,从根队列开始,依次遍历子队列找出资源占用率最小的子队列。若子队列为叶子队列,则选择该队列;若子队列为非叶子队列,则以该子队列为根队列重复前面的过程直到找到一个资源使用率最小的叶子队列为止。
- 选择应用 (排序)。在Step1中选好了叶子队列后,取该队列中排序最靠前的应用程序(排序逻辑可以根据应用程序的资源请求量、提交时间、作业名)。
- 选择 Container (排序)。在 Step2中选好应用程序之后,选择该应用程序中优先级最高的 Container。对于优先级相同的 Containers,优选选择满足本地性的 Container,会依次选择 node local、rack local、no local。
三、FairScheduler 资源分配源码分析
3.1 NM 心跳上报
NM 中负责心跳的类是 NodeStatusUpdater 类型的成员变量 nodeStatusUpdater,在 NM 调用 serviceInit() 方法时被创建:
//代码:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/nodemanager/NodeManager.java protected void serviceInit(Configuration conf) throws Exception { ... // 省略 nodeStatusUpdater = createNodeStatusUpdater(context, dispatcher, nodeHealthChecker); ... // 省略 } protected NodeStatusUpdater createNodeStatusUpdater(Context context, Dispatcher dispatcher, NodeHealthCheckerService healthChecker) { return new NodeStatusUpdaterImpl(context, dispatcher, healthChecker, metrics); }
nodeStatusUpdater 在创建时初始化实例 NodeStatusUpdaterImpl,它是真正负责与 RM 通讯的类,其中 serviceStart() 方法中会进行 NM 注册和心跳。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/nodemanager/NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.java @Override protected void serviceStart() throws Exception { // NodeManager is the last service to start, so NodeId is available. this.nodeId = this.context.getNodeId(); this.httpPort = this.context.getHttpPort(); this.nodeManagerVersionId = YarnVersionInfo.getVersion(); try { // Registration has to be in start so that ContainerManager can get the // perNM tokens needed to authenticate ContainerTokens. this.resourceTracker = getRMClient(); registerWithRM(); // NM向RM注册 super.serviceStart(); startStatusUpdater(); // 独立线程进行NM心跳上报 } catch (Exception e) { String errorMessage = "Unexpected error starting NodeStatusUpdater"; LOG.error(errorMessage, e); throw new YarnRuntimeException(e); } }
NM 向 RM 注册逻辑直接跳过,重点看一下心跳逻辑,首先启动心跳线程:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/nodemanager/NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.java protected void startStatusUpdater() { statusUpdaterRunnable = new Runnable() { ... }; statusUpdater = new Thread(statusUpdaterRunnable, "Node Status Updater"); statusUpdater.start(); }
接着来看看 statusUpdaterRunnable 线程如何进行心跳上报:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/nodemanager/NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.java statusUpdaterRunnable = new Runnable() { @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void run() { int lastHeartBeatID = 0; while (!isStopped) { // 在被终止前死循环的跑 // Send heartbeat try { NodeHeartbeatResponse response = null; NodeStatus nodeStatus = getNodeStatus(lastHeartBeatID); // 构建 request 请求信息 NodeHeartbeatRequest request = NodeHeartbeatRequest.newInstance(nodeStatus, NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.this.context .getContainerTokenSecretManager().getCurrentKey(), NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.this.context.getNMTokenSecretManager() .getCurrentKey()); // 重点:这里向 RM 发送心跳 RPC 请求,并得到返回结果 response response = resourceTracker.nodeHeartbeat(request); //get next heartbeat interval from response nextHeartBeatInterval = response.getNextHeartBeatInterval(); updateMasterKeys(response); if (response.getNodeAction() == NodeAction.SHUTDOWN) { // 处理 RM 返回的结果,包括停止运行和重新注册 } ... // 省略 } } } };
至此,NM 已经通过 NodeStatusUpdaterImpl 类向 RM 发送了心跳请求,那 RM 又如何处理该心跳请求呢?我们接着分析。
3.2 RM 接收心跳
NM 与 RM 通讯的接口是通过 ResourceTrackerService 服务来实现。直接来看看 NM 调用 nodeHeartbeat() 方法发送过来的请求。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/ResourceTrackerService.java @Override public NodeHeartbeatResponse nodeHeartbeat(NodeHeartbeatRequest request) throws YarnException, IOException { NodeStatus remoteNodeStatus = request.getNodeStatus(); /** * 处理心跳的流程: * 1. 判断是否是合法的 node(即是否被拉黑过) * 2. 判断是否是一个注册过的 node * 3. 判断这个心跳是否是重复的心跳 * 4. 发送 NM 的状态给 RMNodeStatusEvent 事件处理器 */ ... // 1-3 步跳过 // 4. Send status to RMNode, saving the latest response. RMNodeStatusEvent nodeStatusEvent = new RMNodeStatusEvent(nodeId, remoteNodeStatus.getNodeHealthStatus(), remoteNodeStatus.getContainersStatuses(), remoteNodeStatus.getKeepAliveApplications(), nodeHeartBeatResponse); if (request.getLogAggregationReportsForApps() != null && !request.getLogAggregationReportsForApps().isEmpty()) { nodeStatusEvent.setLogAggregationReportsForApps(request .getLogAggregationReportsForApps()); } this.rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle(nodeStatusEvent); return nodeHeartBeatResponse; }
心跳处理过程的关键是第 4 步,它会通过中央调度器 AsyncDispatcher 向 RM 发送 RMNodeStatusEvent 事件,那这个事件是由谁来处理的呢?在 Yarn 这种事件处理逻辑很常见,关键点是要看事件对应的处理器是如何注册的。上面的 RMNodeStatusEvent 事件处理器继承自 RMNodeEvent,在 RM 的注册处理器代码如下。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/ResourceManager.java // Register event handler for RmNodes rmDispatcher.register( RMNodeEventType.class, new NodeEventDispatcher(rmContext));
其中 RMNodeStatusEvent 事件是交由 NodeEventDispatcher 调度器处理,处理的 handle() 方法如下:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/ResourceManager.java public void handle(RMNodeEvent event) { NodeId nodeId = event.getNodeId(); RMNode node = this.rmContext.getRMNodes().get(nodeId); if (node != null) { try { ((EventHandler<RMNodeEvent>) node).handle(event); } catch (Throwable t) { LOG.error("Error in handling event type " + event.getType() + " for node " + nodeId, t); } } }
这里会调用 RMNode 的handle() 方法,RMNode 是一个接口类,实现类为 RMNodeImpl,对应 handle() 方法如下:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/rmnode/RMNodeImpl.java public void handle(RMNodeEvent event) { LOG.debug("Processing " + event.getNodeId() + " of type " + event.getType()); try { writeLock.lock(); NodeState oldState = getState(); try { stateMachine.doTransition(event.getType(), event); } catch (InvalidStateTransitonException e) { LOG.error("Can't handle this event at current state", e); LOG.error("Invalid event " + event.getType() + " on Node " + this.nodeId); } if (oldState != getState()) { LOG.info(nodeId + " Node Transitioned from " + oldState + " to " + getState()); } } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } }
这里就涉及到 RMNodeImpl 的状态机,由于 RMNodeStatusEvent 事件类型是 RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE,状态机中对这个事件的处理有三种情况:
- 从 RUNNING 到 RUNNING、UNHEALTHY,调用 StatusUpdateWhenHealthyTransition;
- 从 DECOMMISSIONING 到 DECOMMISSIONING、DECOMMISSIONED,调用 StatusUpdateWhenHealthyTransition;
- 从 UNHEALTHY 到 UNHEALTHY、RUNNING,调用 StatusUpdateWhenUnHealthyTransition;
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/rmnode/RMNodeImpl.java //Transitions from RUNNING state .addTransition(NodeState.RUNNING, EnumSet.of(NodeState.RUNNING, NodeState.UNHEALTHY), RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE, new StatusUpdateWhenHealthyTransition()) //Transitions from DECOMMISSIONING state .addTransition(NodeState.DECOMMISSIONING, EnumSet.of(NodeState.DECOMMISSIONING, NodeState.DECOMMISSIONED), RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE, new StatusUpdateWhenHealthyTransition()) //Transitions from UNHEALTHY state .addTransition(NodeState.UNHEALTHY, EnumSet.of(NodeState.UNHEALTHY, NodeState.RUNNING), RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE, new StatusUpdateWhenUnHealthyTransition())
这里选择最常见的状态转换,从 RUNNING 到 RUNNING,查看被调用的 StatusUpdateWhenHealthyTransition 状态机的 transition() 方法:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/rmnode/RMNodeImpl.java public NodeState transition(RMNodeImpl rmNode, RMNodeEvent event) { RMNodeStatusEvent statusEvent = (RMNodeStatusEvent) event; // Switch the last heartbeatresponse. rmNode.latestNodeHeartBeatResponse = statusEvent.getLatestResponse(); NodeHealthStatus remoteNodeHealthStatus = statusEvent.getNodeHealthStatus(); rmNode.setHealthReport(remoteNodeHealthStatus.getHealthReport()); rmNode.setLastHealthReportTime( remoteNodeHealthStatus.getLastHealthReportTime()); NodeState initialState = rmNode.getState(); boolean isNodeDecommissioning = initialState.equals(NodeState.DECOMMISSIONING); ... // 跳过 unhealthy 和 decommsission 的判断逻辑 rmNode.handleContainerStatus(statusEvent.getContainers()); List<LogAggregationReport> logAggregationReportsForApps = statusEvent.getLogAggregationReportsForApps(); if (logAggregationReportsForApps != null && !logAggregationReportsForApps.isEmpty()) { rmNode.handleLogAggregationStatus(logAggregationReportsForApps); } if(rmNode.nextHeartBeat) { rmNode.nextHeartBeat = false; // 重点:向 RM 发送一个 NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent 事件 rmNode.context.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle( new NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent(rmNode)); } // Update DTRenewer in secure mode to keep these apps alive. Today this is // needed for log-aggregation to finish long after the apps are gone. if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) { rmNode.context.getDelegationTokenRenewer().updateKeepAliveApplications( statusEvent.getKeepAliveAppIds()); } return initialState; } }
这里关键的逻辑是向 RM 发送了一个 NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent 事件,那这个事件又是谁处理的呢?NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent 继承自 SchedulerEvent,SchedulerEvent在RM中注册的处理器如下:
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/ResourceManager.java // 注册 SchedulerEventDispatcher schedulerDispatcher = createSchedulerEventDispatcher(); addIfService(schedulerDispatcher); rmDispatcher.register(SchedulerEventType.class, schedulerDispatcher); // 注册方法 protected EventHandler<SchedulerEvent> createSchedulerEventDispatcher() { return new SchedulerEventDispatcher(this.scheduler); }
其中 scheduler 对象是根据配置 yarn.resourcemanager.yarn.resourcemanager 指定的类生成的对象,这里使用 org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.fair.FairScheduler。那就进入到 FairScheduler 的 handle() 方法,这里只看 NODE_UPDATE 事件的处理逻辑,其他的先省略。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FairScheduler.java @Override public void handle(SchedulerEvent event) { long start = getClock().getTime(); switch (event.getType()) { case NODE_ADDED: // 省略 case NODE_REMOVED: // 省略 case NODE_UPDATE: if (!(event instanceof NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent)) { throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected event type: " + event); } NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent nodeUpdatedEvent = (NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent)event; nodeUpdate(nodeUpdatedEvent.getRMNode()); fsOpDurations.addHandleNodeUpdateEventDuration(getClock().getTime() - start); break; case APP_ADDED: // 省略 case APP_REMOVED: // 省略 case NODE_RESOURCE_UPDATE: // 省略 case APP_ATTEMPT_ADDED: // 省略 case APP_ATTEMPT_REMOVED: // 省略 case CONTAINER_EXPIRED: // 省略 case CONTAINER_RESCHEDULED: // 省略 default: LOG.error("Unknown event arrived at FairScheduler: " + event.toString()); } }
由于 NM 的心跳事件是 RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE,可以得知这里处理的事件类型为 SchedulerEventType.NODE_UPDATE,进入NODE_UPDATE处理逻辑。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FairScheduler.java private void nodeUpdate(RMNode nm) { try { writeLock.lock(); long start = getClock().getTime(); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("nodeUpdate: " + nm + " cluster capacity: " + getClusterResource()); } eventLog.log("HEARTBEAT", nm.getHostName()); FSSchedulerNode node = getFSSchedulerNode(nm.getNodeID()); // Containe 状态更新:处理新运行或者运行完成的 Container // 判断 NM 是否是 DECOMMISSIONING 状态 // 核心调度入口,无论是否开启连续调度入口都是 attemptScheduling(node) 方法 if (continuousSchedulingEnabled) { if (!completedContainers.isEmpty()) { attemptScheduling(node); } } else { attemptScheduling(node); } long duration = getClock().getTime() - start; fsOpDurations.addNodeUpdateDuration(duration); } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } }
看看核心调度入口,这里获取了一个 FSSchedulerNode 实例,并尝试进行调度。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FairScheduler.java synchronized void attemptScheduling(FSSchedulerNode node) { // 检查是否是有效的 node // Assign new containers... // 1. 检查是否有资源预留的应用 // 2. 没有预留则进行调度分配新的 Container boolean validReservation = false; FSAppAttempt reservedAppSchedulable = node.getReservedAppSchedulable(); if (reservedAppSchedulable != null) { validReservation = reservedAppSchedulable.assignReservedContainer(node); } if (!validReservation) { // No reservation, schedule at queue which is farthest below fair share int assignedContainers = 0; Resource assignedResource = Resources.clone(Resources.none()); Resource maxResourcesToAssign = Resources.multiply(node.getAvailableResource(), 0.5f); while (node.getReservedContainer() == null) { boolean assignedContainer = false; // 重点:核心分配逻辑开始,从 ROOT 队列开始调度 Resource assignment = queueMgr.getRootQueue().assignContainer(node); if (!assignment.equals(Resources.none())) { assignedContainers++; assignedContainer = true; Resources.addTo(assignedResource, assignment); } if (!assignedContainer) { break; } if (!shouldContinueAssigning(assignedContainers, maxResourcesToAssign, assignedResource)) { break; } } } updateRootQueueMetrics(); }
分配 Container 是从 ROOT 队列开始,这里调用 queueMgr.getRootQueue() 方法找到 ROOT 队列,然后调用 assignContainer(node) 方法。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSParentQueue.java @Override public Resource assignContainer(FSSchedulerNode node) { Resource assigned = Resources.none(); // 如果超过了队列的 maxShare 则直接返回 if (!assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { return assigned; } TreeSet<FSQueue> sortedChildQueues = new TreeSet<>(policy.getComparator()); /* * 这里对所有叶子队列进行排序,有两个情况需要考虑下: * 1. 新增加一个 queue,不影响结果的正确性,下次会处理新 queue * 2. 删除一个 queue,最好处理一下以不对该 queue 进行分配,不过目前没有处理,也没有影响 */ readLock.lock(); try { sortedChildQueues.addAll(childQueues); for (FSQueue child : sortedChildQueues) { assigned = child.assignContainer(node); if (!Resources.equals(assigned, Resources.none())) { break; } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } return assigned; }
这里是 FSParentQueue 父队列的 assignContainer() 逻辑,对所有孩子节点进行遍历,递归调用该该方法,调用过程有两种情况:
- 如果孩子节点是 FSParentQueue 父队列,则递归进入 FSParentQueue 类相同的逻辑中。
- 如果孩子节点是 FSLeafQueue 叶子队列,则进入到下一步的调用逻辑。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSLeafQueue.java @Override public Resource assignContainer(FSSchedulerNode node) { Resource assigned = none(); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Node " + node.getNodeName() + " offered to queue: " + getName() + " fairShare: " + getFairShare()); } // 检查是否超过队列的 maxShare 限制 if (!assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { return assigned; } // 遍历叶子节点所有有资源需求的 APP,并对其尝试分配 Container for (FSAppAttempt sched : fetchAppsWithDemand(true)) { if (SchedulerAppUtils.isBlacklisted(sched, node, LOG)) { continue; } assigned = sched.assignContainer(node); if (!assigned.equals(none())) { if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Assigned container in queue:" + getName() + " " + "container:" + assigned); } break; } } return assigned; }
这里获取叶子节点的 APP 调用了 fetchAppsWithDemand() 方法,该方法主要是对该队列所有 APP 进行遍历,找到真正有资源需求的 APP,过滤掉没有资源的 APP。
//位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSLeafQueue.java private TreeSet<FSAppAttempt> fetchAppsWithDemand(boolean assignment) { TreeSet<FSAppAttempt> pendingForResourceApps = new TreeSet<>(policy.getComparator()); readLock.lock(); try { for (FSAppAttempt app : runnableApps) { // 判断 APP 是否有资源需求,即有资源还没有得到满足 if (!Resources.isNone(app.getPendingDemand()) && (assignment || app.shouldCheckForStarvation())) { pendingForResourceApps.add(app); } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } return pendingForResourceApps; }
获取到叶子节点有资源需求的 APP 后,调用 FSAppAttempt 类的实例 assignContainer(node) 方法,进行接下来的分配逻辑。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSAppAttempt.java @Override public Resource assignContainer(FSSchedulerNode node) { // 这里主要检查队列已使用资源是否达到了用于运行 AM 的资源限制 if (isOverAMShareLimit()) { List<ResourceRequest> ask = appSchedulingInfo.getAllResourceRequests(); Resource amResourceRequest = Resources.none(); if (!ask.isEmpty()) { amResourceRequest = ask.get(0).getCapability(); } if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("AM resource request: " + amResourceRequest + " exceeds maximum AM resource allowed, " + getQueue().dumpState()); } return Resources.none(); } return assignContainer(node, false); }
这里主要检查队列已使用资源是否达到了用于运行 AM 的资源限制,如果没有的话,则继续调度。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSAppAttempt.java private Resource assignContainer(FSSchedulerNode node, boolean reserved) { if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) { LOG.trace("Node offered to app: " + getName() + " reserved: " + reserved); } // 对 APP 的所有 ResourceRequest 按照 priority 排序 Collection<Priority> prioritiesToTry = (reserved) ? Arrays.asList(node.getReservedContainer().getReservedPriority()) : getPriorities(); // For each priority, see if we can schedule a node local, rack local // or off-switch request. Rack of off-switch requests may be delayed // (not scheduled) in order to promote better locality. synchronized (this) { // 按照 priority 从高到低遍历所有 ResourceRequest for (Priority priority : prioritiesToTry) { // 判断该 Container 是否有预留 // hasContainerForNode() 会分 node、rack、any 三种情况考虑该节点是否有合适的 Container if (!reserved && !hasContainerForNode(priority, node)) { continue; } // 调度机会计数加 1 addSchedulingOpportunity(priority); // 下面的逻辑主要根据 NODE_LOCAL、RACK_LOCAL、OFF_SWITCH 三种情况判断该 ResourceRequest 满足哪一种调度方式 ResourceRequest rackLocalRequest = getResourceRequest(priority, node.getRackName()); ResourceRequest localRequest = getResourceRequest(priority, node.getNodeName()); if (localRequest != null && !localRequest.getRelaxLocality()) { LOG.warn("Relax locality off is not supported on local request: " + localRequest); } // 省略三种情况的具体选择逻辑 } } return Resources.none(); }
上面这段代码,主要是按照 priority 从高到低的顺序遍历所有的 ResourceRequest,针对每个 ResourceRequest,在待分配的 node 节点上,根据 NODE_LOCAL、RACK_LOCAL、OFF_SWITCH 三种情况判断该 ResourceRequest 满足哪一种调度方式,这里以 NODE_LOCAL 参数为例进入到下一步的调度逻辑。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSAppAttempt.java private Resource assignContainer( FSSchedulerNode node, ResourceRequest request, NodeType type, boolean reserved) { // 当前 ResoureRequest 需要多少资源 Resource capability = request.getCapability(); // 当前 node 还剩多少资源可分配 Resource available = node.getAvailableResource(); Container reservedContainer = null; // 判断是否有预留,有预留在直接从该 node 获取对应资源。这里不考虑预留的情况 if (reserved) { reservedContainer = node.getReservedContainer().getContainer(); } // 判断该 ResourRequest 的资源需求是否能够在该 node 上得到满足 if (Resources.fitsIn(capability, available)) { // 重点:node 资源足够的话,这里会分配出一个 Container RMContainer allocatedContainer = allocate(type, node, request.getPriority(), request, reservedContainer); if (allocatedContainer == null) { // Did the application need this resource? if (reserved) { unreserve(request.getPriority(), node); } return Resources.none(); } // If we had previously made a reservation, delete it if (reserved) { unreserve(request.getPriority(), node); } // 通知 node 记录该分配出来的 Container node.allocateContainer(allocatedContainer); // If not running unmanaged, the first container we allocate is always // the AM. Set the amResource for this app and update the leaf queue's AM // usage if (!isAmRunning() && !getUnmanagedAM()) { setAMResource(capability); getQueue().addAMResourceUsage(capability); setAmRunning(true); } return capability; } ... // 省略 }
重点看看分配逻辑 allocate() 方法。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FSAppAttempt.java synchronized public RMContainer allocate(NodeType type, FSSchedulerNode node, Priority priority, ResourceRequest request, Container reservedContainer) { // 更新 locality 级别,忽略 NodeType allowed = allowedLocalityLevel.get(priority); if (allowed != null) { if (allowed.equals(NodeType.OFF_SWITCH) && (type.equals(NodeType.NODE_LOCAL) || type.equals(NodeType.RACK_LOCAL))) { this.resetAllowedLocalityLevel(priority, type); } else if (allowed.equals(NodeType.RACK_LOCAL) && type.equals(NodeType.NODE_LOCAL)) { this.resetAllowedLocalityLevel(priority, type); } } // Required sanity check - AM can call 'allocate' to update resource // request without locking the scheduler, hence we need to check if (getTotalRequiredResources(priority) <= 0) { return null; } Container container = reservedContainer; if (container == null) { // 重点:这里会具体创建一个 Container 实例 container = createContainer(node, request.getCapability(), request.getPriority()); } // 用 RMContainer 记录新创建出来的 Container 实例 RMContainer rmContainer = new RMContainerImpl(container, getApplicationAttemptId(), node.getNodeID(), appSchedulingInfo.getUser(), rmContext); // 重点:记录 rmContainer,等待下次 AM 心跳发生时,会从这里把分配出来的 Container 带走 newlyAllocatedContainers.add(rmContainer); liveContainers.put(container.getId(), rmContainer); // Update consumption and track allocations List<ResourceRequest> resourceRequestList = appSchedulingInfo.allocate( type, node, priority, request, container); Resources.addTo(currentConsumption, container.getResource()); getQueue().incUsedResource(container.getResource()); // Update resource requests related to "request" and store in RMContainer ((RMContainerImpl) rmContainer).setResourceRequests(resourceRequestList); // 这里发送 Container 的 START 事件,更新 Container 状态 rmContainer.handle( new RMContainerEvent(container.getId(), RMContainerEventType.START)); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("allocate: applicationAttemptId=" + container.getId().getApplicationAttemptId() + " container=" + container.getId() + " host=" + container.getNodeId().getHost() + " type=" + type); } RMAuditLogger.logSuccess(getUser(), AuditConstants.ALLOC_CONTAINER, "SchedulerApp", getApplicationId(), container.getId()); return rmContainer; }
至此,一个全新的 Container 已经分配出来了,并保存在 RM 的内存数据结构中,那分配出来的 Container 是如何被用到的呢?我们接着后续的逻辑。
3.3 AM 认领资源
上面知道,分配的 Container 已经保存在 RM 的内存数据结构中了,接下来就是 AM 的心跳上报定时领取给自己分配的资源。
3.3.1 AM 启动并发起资源请求
作业在启动时,会首先启动 ApplicationMaster 进程,启动入口如下:
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/applications/distributedshell/ApplicationMaster.java public static void main(String[] args) { boolean result = false; try { ApplicationMaster appMaster = new ApplicationMaster(); LOG.info("Initializing ApplicationMaster"); boolean doRun = appMaster.init(args); if (!doRun) { System.exit(0); } // ApplicationMaster 启动 run() 方法 appMaster.run(); result = appMaster.finish(); } catch (Throwable t) { LOG.fatal("Error running ApplicationMaster", t); LogManager.shutdown(); ExitUtil.terminate(1, t); } if (result) { LOG.info("Application Master completed successfully. exiting"); System.exit(0); } else { LOG.info("Application Master failed. exiting"); System.exit(2); } }
run() 方法做了什么事呢?主要是进行 ApplicationMaster 的注册和心跳。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/applications/distributedshell/ApplicationMaster.java public void run() throws YarnException, IOException { LOG.info("Starting ApplicationMaster"); ... // 省略 // 初始化 AMRMClient 实例,用于向 RM 发送 RPC 请求,这里采用异步方式,每个 AMRMClient 都是单独的线程 AMRMClientAsync.CallbackHandler allocListener = new RMCallbackHandler(); amRMClient = AMRMClientAsync.createAMRMClientAsync(1000, allocListener); amRMClient.init(conf); amRMClient.start(); containerListener = createNMCallbackHandler(); nmClientAsync = new NMClientAsyncImpl(containerListener); nmClientAsync.init(conf); nmClientAsync.start(); appMasterHostname = NetUtils.getHostname(); // 重要:AM 通过 RPC 请求向 RM 注册,心跳线程在注册逻辑里启动 RegisterApplicationMasterResponse response = amRMClient .registerApplicationMaster(appMasterHostname, appMasterRpcPort, appMasterTrackingUrl); ... // 省略 }
AM 向 RM 发送 RPC 请求是通过 ApplicationMasterService 服务实现的,这里的 AM 注册和心跳都需要通过该服务与 RM 进行通讯。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/client/api/async/impl/AMRMClientAsyncImpl.java public RegisterApplicationMasterResponse registerApplicationMaster( String appHostName, int appHostPort, String appTrackingUrl) throws YarnException, IOException { RegisterApplicationMasterResponse response = client .registerApplicationMaster(appHostName, appHostPort, appTrackingUrl); // 启动 AM 心跳线程 heartbeatThread.start(); return response; }
这里忽略 registerApplicationMaster() 注册的逻辑,主要是心跳线程做了些什么,即 heartbeatThread 线程的工作。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/client/api/async/impl/AMRMClientAsyncImpl.java public void run() { while (true) { AllocateResponse response = null; // synchronization ensures we don't send heartbeats after unregistering synchronized (unregisterHeartbeatLock) { if (!keepRunning) { return; } try { // 重要:AM 通过 AMRMClient 客户端向 RM 发送请求,进行资源的 allocate() 操作 response = client.allocate(progress); } catch (ApplicationAttemptNotFoundException e) { handler.onShutdownRequest(); LOG.info("Shutdown requested. Stopping callback."); return; } catch (Throwable ex) { LOG.error("Exception on heartbeat", ex); savedException = ex; // interrupt handler thread in case it waiting on the queue handlerThread.interrupt(); return; } if (response != null) { while (true) { try { responseQueue.put(response); break; } catch (InterruptedException ex) { LOG.debug("Interrupted while waiting to put on response queue", ex); } } } } try { Thread.sleep(heartbeatIntervalMs.get()); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { LOG.debug("Heartbeater interrupted", ex); } } }
至此,AM 已经向 RM 发送资源请求,接下来看看 RM 是如何处理这个 RPC 请求的。
3.3.2 RM 处理 AM 请求
RM 中负责处理 AM 心跳请求是通过 ApplicationMasterService 服务,其内部的 allocate() 负责处理 AM 的 RPC 资源分配请求,具体逻辑如下:
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/ApplicationMasterService.java @Override public AllocateResponse allocate(AllocateRequest request) throws YarnException, IOException { AMRMTokenIdentifier amrmTokenIdentifier = authorizeRequest(); ApplicationAttemptId appAttemptId = amrmTokenIdentifier.getApplicationAttemptId(); ApplicationId applicationId = appAttemptId.getApplicationId(); this.amLivelinessMonitor.receivedPing(appAttemptId); // 针对每个 appAttempt,会有一个独立的锁对象 AllocateResponseLock lock = responseMap.get(appAttemptId); if (lock == null) { String message = "Application attempt " + appAttemptId + " doesn't exist in ApplicationMasterService cache."; LOG.error(message); throw new ApplicationAttemptNotFoundException(message); } synchronized (lock) { AllocateResponse lastResponse = lock.getAllocateResponse(); // 省略一些神圣的检查工作 // 重点:AM 资源请求的心跳函数,发送新请求和接收之前的分配都需要进行 Allocation allocation = this.rScheduler.allocate(appAttemptId, ask, release, blacklistAdditions, blacklistRemovals); // 省略一些状态更新操作 lock.setAllocateResponse(allocateResponse); return allocateResponse; } }
继续跟进 this.rScheduler.allocate() 方法,这里的 scheduler 配置的是 FairScheduler,来看看它的 allocate 方法。
// 位置:org/apache/hadoop/yarn/server/resourcemanager/scheduler/fair/FairScheduler.java @Override public Allocation allocate(ApplicationAttemptId appAttemptId, List<ResourceRequest> ask, List<ContainerId> release, List<String> blacklistAdditions, List<String> blacklistRemovals) { // 跳过一些检查工作 // 记录 Container 分配的开始开始时间 application.recordContainerRequestTime(getClock().getTime()); // 释放 AM 认为要释放的 Container releaseContainers(release, application); synchronized (application) { if (!ask.isEmpty()) { if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("allocate: pre-update" + " applicationAttemptId=" + appAttemptId + " application=" + application.getApplicationId()); } application.showRequests(); // 更新应用的资源请求 application.updateResourceRequests(ask); application.showRequests(); } Set<ContainerId> preemptionContainerIds = application.getPreemptionContainerIds(); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug( "allocate: post-update" + " applicationAttemptId=" + appAttemptId + " #ask=" + ask.size() + " reservation= " + application .getCurrentReservation()); LOG.debug("Preempting " + preemptionContainerIds.size() + " container(s)"); } if (application.isWaitingForAMContainer(application.getApplicationId())) { // Allocate is for AM and update AM blacklist for this application.updateAMBlacklist( blacklistAdditions, blacklistRemovals); } else { application.updateBlacklist(blacklistAdditions, blacklistRemovals); } // 重要:这里就是 AM 获取最近分配的 Container。这里获取的其实就是前面保存在 RM 内存数据结构的 Container。 ContainersAndNMTokensAllocation allocation = application.pullNewlyAllocatedContainersAndNMTokens(); // Record container allocation time if (!(allocation.getContainerList().isEmpty())) { application.recordContainerAllocationTime(getClock().getTime()); } return new Allocation(allocation.getContainerList(), application.getHeadroom(), preemptionContainerIds, null, null, allocation.getNMTokenList()); } }
至此,AM 已经顺利拿到 RM 分配的 Container,整理 FairScheduler 资源分配流程基本就是这样。
【参考资料】


