Python: Pandas的DataFrame如何按指定list排序
本文首发于微信公众号“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad)
前言
写这篇文章的起由是有一天微信上一位朋友问到一个问题,问题大体意思概述如下:
现在有一个pandas的Series和一个python的list,想让Series按指定的list进行排序,如何实现?
这个问题的需求用流程图描述如下:
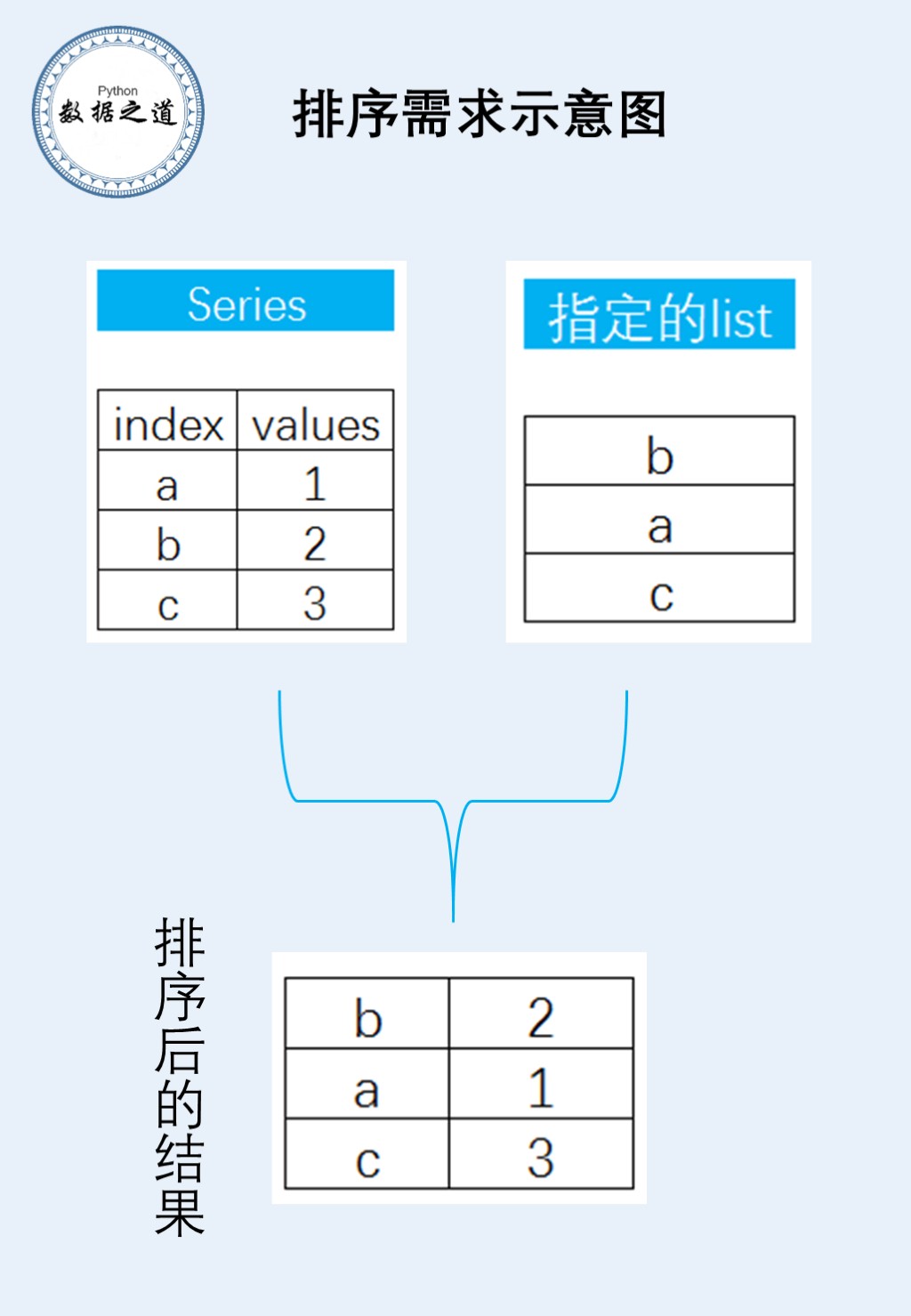
我思考了一下,这个问题解决的核心是引入pandas的数据类型“category”,从而进行排序。
在具体的分析过程中,先将pandas的Series转换成为DataFrame,然后设置数据类型,再进行排序。思路用流程图表示如下:

分析过程
- 引入pandas库
import pandas as pd
- 构造Series数据
s = pd.Series({'a':1,'b':2,'c':3})
s
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
s.index
Index(['a', 'b', 'c'], dtype='object')
- 指定的list,后续按指定list的元素顺序进行排序
list_custom = ['b', 'a', 'c']
list_custom
['b', 'a', 'c']
- 将Series转换成DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(s) df = df.reset_index() df.columns = ['words', 'number'] df
| words | number | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | 1 |
| 1 | b | 2 |
| 2 | c | 3 |
设置成“category”数据类型
# 设置成“category”数据类型
df['words'] = df['words'].astype('category')
# inplace = True,使 recorder_categories生效
df['words'].cat.reorder_categories(list_custom, inplace=True)
# inplace = True,使 df生效
df.sort_values('words', inplace=True)
df
| words | number | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | b | 2 |
| 0 | a | 1 |
| 2 | c | 3 |
指定list元素多的情况:
若指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素多,怎么办?
- reorder_catgories()方法不能继续使用,因为该方法使用时要求新的categories和dataframe中的categories的元素个数和内容必须一致,只是顺序不同。
- 这种情况下,可以使用 set_categories()方法来实现。新的list可以比dataframe中元素多。
list_custom_new = ['d', 'c', 'b','a','e']
dict_new = {'e':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
df_new = pd.DataFrame(list(dict_new.items()), columns=['words', 'value'])
print(list_custom_new)
df_new.sort_values('words', inplace=True)
df_new
['d', 'c', 'b', 'a', 'e']
| words | value | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | b | 2 |
| 1 | c | 3 |
| 2 | e | 1 |
df_new['words'] = df_new['words'].astype('category')
# inplace = True,使 set_categories生效
df_new['words'].cat.set_categories(list_custom_new, inplace=True)
df_new.sort_values('words', ascending=True)
| words | value | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | c | 3 |
| 0 | b | 2 |
| 2 | e | 1 |
指定list元素少的情况:
若指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素少,怎么办?
- 这种情况下,set_categories()方法还是可以使用的,只是没有的元素会以NaN表示
注意下面的list中没有元素“b”
list_custom_new = ['d', 'c','a','e']
dict_new = {'e':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
df_new = pd.DataFrame(list(dict_new.items()), columns=['words', 'value'])
print(list_custom_new)
df_new.sort_values('words', inplace=True)
df_new
['d', 'c', 'a', 'e']
| words | value | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | b | 2 |
| 1 | c | 3 |
| 2 | e | 1 |
df_new['words'] = df_new['words'].astype('category')
# inplace = True,使 set_categories生效
df_new['words'].cat.set_categories(list_custom_new, inplace=True)
df_new.sort_values('words', ascending=True)
| words | value | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | NaN | 2 |
| 1 | c | 3 |
| 2 | e | 1 |
总结
根据指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素的多或少,可以分为三种情况:
- 相等的情况下,可以使用 reorder_categories和 set_categories方法;
- list的元素比较多的情况下, 可以使用set_categories方法;
- list的元素比较少的情况下, 也可以使用set_categories方法,但list中没有的元素会在DataFrame中以NaN表示。
源代码
需要的童鞋可在微信公众号“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad)后台回复关键字获取视频,关键字如下:
“2017-025”(不含引号)
作者:Lemon
出处:个人微信公众号:“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad)和博客园:http://www.cnblogs.com/lemonbit/
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文出处,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
出处:个人微信公众号:“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad)和博客园:http://www.cnblogs.com/lemonbit/
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文出处,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号