nginx
nginx简介
nginx(发音同engine x)是一款轻量级的Web服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,并在一个BSD-like协议下发行。
nginx由俄罗斯的程序设计师Igor Sysoev所开发,最初供俄国大型的入口网站及搜寻引擎Rambler使用。
第一个公开版本0.1.0发布于2004年10月4日。其将源代码以类BSD许可证的形式发布,因它的稳定性、丰富的功能集、示例配置文件和低系统资源的消耗而闻名。2011年6月1日,nginx 1.0.4发布。
nginx的特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上nginx的并发能力确实在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好,中国大陆使用nginx网站用户有:百度、京东、新浪、网易、腾讯、淘宝等。
nginx的特性与优点
nginx的特性
nginx是一个很牛的高性能Web和反向代理服务器,它具有很多非常优越的特性:
- 在高连接并发的情况下,nginx是Apache服务器不错的替代品,能够支持高达50000个并发连接数的响应
- 使用epoll and kqueue作为开发模型
- nginx作为负载均衡服务器:nginx既可在内部直接支持和PHP程序对外进行服务,也可支持作为HTTP代理服务器对外进行服务
- nginx采用C进行编写,不论系统资源开销还是CPU使用效率都比Perlbal( Perl 编写的单线程的事件驱动服务器,可充当 Web 服务器 和 HTTP 负载均衡)要好很多。
nginx的优点
- 高并发连接:官方测试能够支撑5万并发连接,在实际生产环境中跑到2-3万并发连接数
- 内存消耗少:在3万并发连接下,开启的10个nginx进程才消耗150M内存(15M*10=150M)
- 配置文件非常简单:风格跟程序一样通俗易懂
- 成本低廉:nginx为开源软件,可以免费使用。而购买F5 BIG-IP、NetScaler等硬件负载均衡交换机则需要十多万至几十万人民币
- 支持Rewrite重写规则:能够根据域名、URL的不同,将HTTP请求分到不同的后端服务器群组
- 内置的健康检查功能:如果Nginx Proxy后端的某台Web服务器宕机了,不会影响前端访问
- 节省带宽:支持GZIP压缩,可以添加浏览器本地缓存的Header头
- 稳定性高:用于反向代理,宕机的概率微乎其微
- 模块化设计:模块可以动态编译
- 外围支持好:文档全,二次开发和模块较多
- 支持热部署:可以不停机重载配置文件
- 支持事件驱动、AIO(AsyncIO,异步IO)、mmap(Memory Map,内存映射)等性能优化
nginx的功能及应用类别
基本功能
- 静态资源的web服务器,能缓存打开的文件描述符
- http、smtp、pop3协议的反向代理服务器
- 缓存加速、负载均衡
- 支持FastCGI(fpm,LNMP),uWSGI(Python)等
- 模块化(非DSO机制),过滤器zip、SSI及图像的大小调整
- 支持SSL
扩展功能
- 基于名称和IP的虚拟主机
- 支持keepalive
- 支持平滑升级
- 定制访问日志、支持使用日志缓冲区提高日志存储性能
- 支持URL重写
- 支持路径别名
- 支持基于IP及用户的访问控制
- 支持速率限制,支持并发数限制
应用类别
- 使用nginx结合FastCGI运行PHP、JSP、Perl等程序
- 使用nginx作反向代理、负载均衡、规则过滤
- 使用nginx运行静态HTML网页、图片
- nginx与其他新技术的结合应用
nginx的模块与工作原理
nginx由内核和模块组成。其中,内核的设计非常微小和简洁,完成的工作也非常简单,仅仅通过查找配置文件将客户端请求映射到一个location block(location是nginx配置中的一个指令,用于URL匹配),而在这个location中所配置的每个指令将会启动不同的模块去完成相应的工作。
模块分类
从结构上分为三个模块:
-
核心模块
- HTTP模块
- EVENT模块
- MAIL模块
-
基础模块
- HTTP Access模块
- HTTP FastCGI模块
- HTTP Proxy模块
- HTTP Rewrite模块
-
第三方模块
- HTTP Upstream模块
- Request Hash模块
- Notice模块
- HTTP Access Key模块
从功能上分为三类:
-
Handlers(处理器模块)
此类模块直接处理请求,并进行输出内容和修改headers信息等操作。handlers处理器模块一般只能有一个
-
Filters(过滤器模块)
此类模块主要对其他处理器模块输出的内容进行修改操作,最后由nginx输出 -
Proxies(代理器模块)
就是nginx的HTTP Upstream之类的模块,这些模块主要与后端一些服务比如fastcgi等操作交互,实现服务代理和负载均衡等功能
补充
nginx模块分为:核心模块、事件模块、标准Http模块、可选Http模块、邮件模块、第三方模块和补丁等
nginx基本模块:所谓基本模块,指的是nginx默认的功能模块,它们提供的指令,允许你使用定义nginx基本功能的变量,在编译时不能被禁用,包括:
- 核心模块:基本功能和指令,如进程管理和安全。常见的核心模块指令,大部分是放置在配置文件的顶部
- 事件模块:在Nginx内配置网络使用的能力。常见的events(事件)模块指令,大部分是放置在配置文件的顶部
- 配置模块:提供包含机制
具体的指令,请参考 nginx 的官方文档
nginx的工作原理
概述
nginx的模块直接被编译进nginx,因此属于静态编译方式。
启动nginx后,nginx的模块被自动加载,与Apache不一样,首先将模块编译为一个so文件,然后在配置文件中指定是否进行加载。
在解析配置文件时,nginx的每个模块都有可能去处理某个请求,但是同一个处理请求只能由一个模块来完成。
架构图
nginx的进程架构:
启动nginx时,会启动一个Master进程,这个进程不处理任何客户端的请求,主要用来产生worker线程,一个worker线程用来处理n个request。
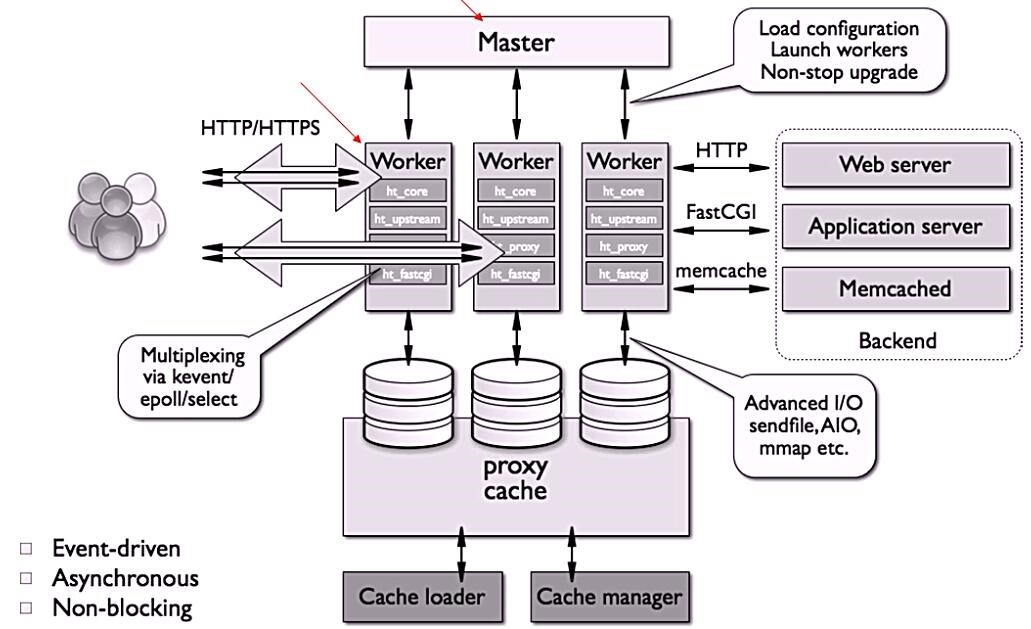
nginx 模块一次常规的HTTP请求和响应的过程如下:
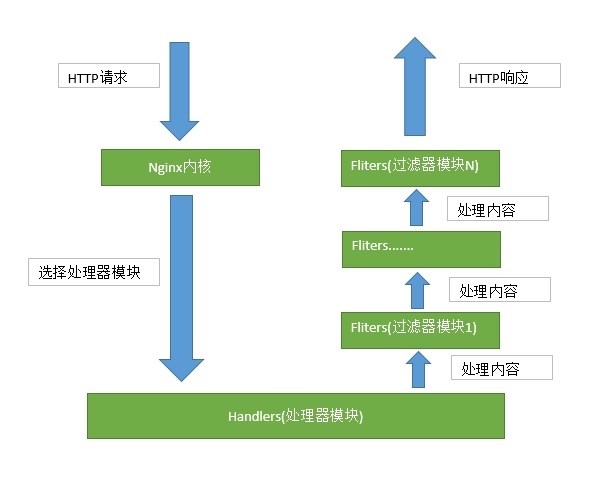
WEB服务请求步骤如下:
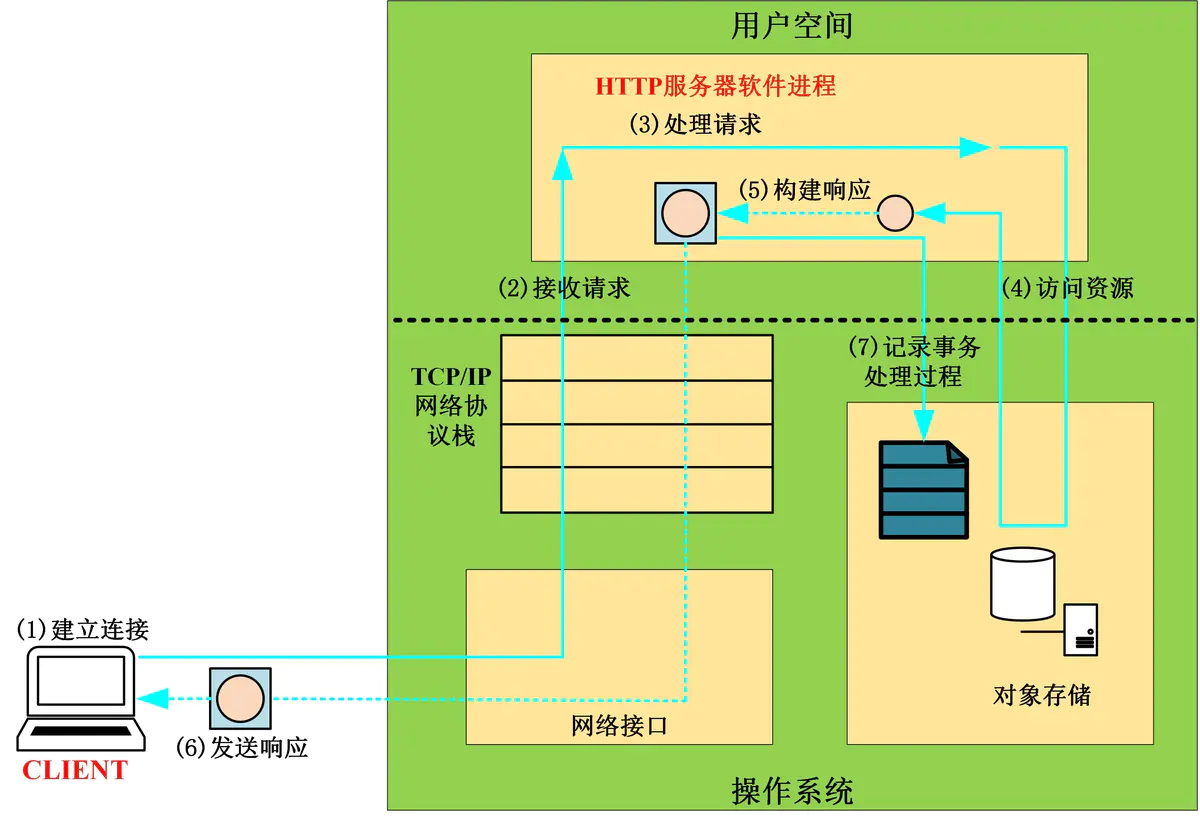
基本步骤概述:
- 建立连接:接收或拒绝连接请求
- 接受请求:接收客户端请求报文中对某资源的一次请求的过程
- 处理请求:服务器对请求报文进行解析,并获取请求的资源及请求方法等相关信息,根据方法,资源,首部和可选的主体部分对请求进行处理
- 访问资源:服务器获取请求报文中请求的资源web服务器,即存放了web资源的服务器,负责向请求者提供对方请求的静态资源,或动态运行后生成的资源资源放置于本地文件系统特定的路径:DocRoot
- 构建响应报文:一旦Web服务器识别除了资源,就执行请求方法中描述的动作,并返回响应报文。响应报文中 包含有响应状态码、响应首部,如果生成了响应主体的话,还包括响应主体
- 发送响应报文:响应报文也包括三个部分,第一部分是状态行,第二部分是Headers,第三部分是Body
- 记录日志:最后,当事务结束时,Web服务器会在日志文件中添加一个条目,来描述已执行的事务
nginx的安装与配置
nginx源码方式安装
//关闭防火墙与selinux
systemctl disable --now firewalld
setenforce 0
sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//创建nginx用户
[root@nginx ~]# useradd -r -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@nginx ~]# id nginx
uid=994(nginx) gid=991(nginx) groups=991(nginx)
//安装工具包和依赖包
[root@nginx ~]# yum -y install vim pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel gd-devel gcc gcc-c++ make
[root@nginx ~]# yum -y groups mark install 'Development tools'
//创建日志存放目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir -p /var/log/nginx
[root@nginx ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/log/nginx
//下载nginx源码包
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/src/
[root@nginx src]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz
[root@nginx src]# ll
total 1040
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 12 2018 debug
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 12 2018 kernels
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1061070 Apr 20 22:46 nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz
//解压源码包
[root@nginx src]# tar xf nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz
[root@nginx src]# ls
debug kernels nginx-1.20.0 nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz
//编译安装
[root@nginx src]# cd nginx-1.20.0
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# ./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-debug \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_image_filter_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log
//启用多核心加速安装
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# make -j $(grep 'processor' /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l) && make install
nginx安装后的配置
配置如下:
//添加环境变量
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# echo 'export PATH=/usr/local/nginx/sbin:$PATH' > /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# source /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# which nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
//服务控制方式,使用nginx命令,查看帮助
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# nginx -help
nginx version: nginx/1.20.0
Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-p prefix]
[-e filename] [-c filename] [-g directives]
Options:
-?,-h : this help #帮助信息
-v : show version and exit #显示版本
-V : show version and configure options then exit #显示版本和配置选项
-t : test configuration and exit #测试配置并退出
-T : test configuration, dump it and exit #测试配置
-q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing #配置测试期间只输出错误信息
-s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload #传递控制信号给主进程
-p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/) #设置路径
-e filename : set error log file (default: /var/log/nginx/error.log) #设置错误日志路径
-c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) #设置配置文件路径
-g directives : set global directives out of configuration file #从配置文件中设置全局指令
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# nginx
[root@nginx nginx-1.20.0]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
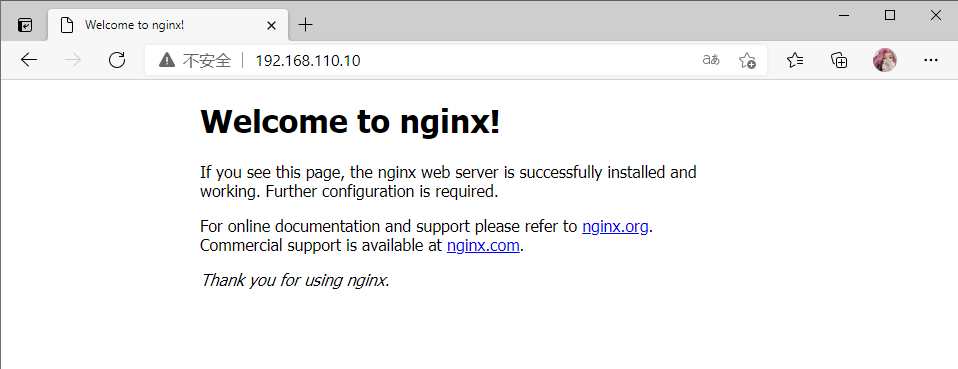
网页访问测试如下:
访问本机IP 192.168.110.10
nginx的配置文件详解
nginx官方文档:nginx文档
主配置文件:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- 默认启动nginx时,使用的配置文件是:安装路径/conf/nginx.conf文件
- 可以在启动nginx时通过-c选项来指定要读取的配置文件
nginx 常见的配置文件及其作用
| 配置文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| nginx.conf | nginx的基本配置文件 |
| mime.types | MIME类型关联的扩展文件 |
| fastcgi.conf | 与fastcgi相关的配置 |
| proxy.conf | 与proxy相关的配置 |
| sites.conf | 配置nginx提供的网站,包括虚拟主机 |
nginx.conf配置详解
nginx.conf的内容分为以下几段:
- main配置段:全局配置段。其中main配置段中可能包含event配置段
- event {}:定义event模型工作特性
- http {}:定义http协议相关的配置
配置指令:
#要以分号结尾,语法格式如下:
derective value1 [value2 ...];
支持使用变量:
- 内置变量:模块会提供内建变量定义
- 自定义变量:
set var_name value
用于调试、定位问题的配置参数
daemon {on|off}; //是否以守护进程方式运行nginx,调试时应设置为off
master_process {on|off}; //是否以master/worker模型来运行nginx,调试时可以设置为off
error_log 位置 级别; //配置错误日志
error_log 级别分为:
- debug
- info,
- notice,
- warn
- error
- crit( 默认为crit)
crit 记录的日志最少,而debug记录的日志最多
正常运行必备的配置参数
user USERNAME [GROUPNAME]; //指定运行worker进程的用户和组
pid /path/to/pid_file; //指定nginx守护进程的pid文件
worker_rlimit_nofile number; //设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024
worker_rlimit_core size; //指明所有worker进程所能够使用的总体的最大核心文件大小,保持默认即可
优化性能的配置参数
worker_processes n; //启动n个worker进程,这里的n为了避免上下文切换,通常设置为cpu总核心数-1或等于总核心数
worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...; //将进程绑定到某cpu中,避免频繁刷新缓存
//cpumask:使用8位二进制表示cpu核心,如:
0000 0001 //第一颗cpu核心
0000 0010 //第二颗cpu核心
0000 0100 //第三颗cpu核心
0000 1000 //第四颗cpu核心
0001 0000 //第五颗cpu核心
0010 0000 //第六颗cpu核心
0100 0000 //第七颗cpu核心
1000 0000 //第八颗cpu核心
timer_resolution interval; //计时器解析度。降低此值,可减少gettimeofday()系统调用的次数
worker_priority number; //指明worker进程的nice值
事件相关的配置:event{}段中的配置参数
accept_mutex {off|on}; //master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁;on表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求
lock_file file; //accept_mutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径
use [epoll | rtsig | select | poll]; //指明使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自行选择
worker_connections #; //每个进程能够接受的最大连接数
网络连接相关的配置参数
keepalive_timeout number; //长连接的超时时长,默认为65s
keepalive_requests number; //在一个长连接上所能够允许请求的最大资源数
keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none]; //为指定类型的UserAgent禁用长连接
tcp_nodelay on|off; //是否对长连接使用TCP_NODELAY选项,为了提升用户体验,通常设为on
client_header_timeout number; //读取http请求报文首部的超时时长
client_body_timeout number; //读取http请求报文body部分的超时时长
send_timeout number; //发送响应报文的超时时长
fastcgi的相关配置参数
LNMP部署时候需要:php要启用fpm模型
配置示例如下:
location ~ \.php$ { root html; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; //定义反向代理 fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params;}
常需要进行调整的参数
-
worker_processes 工作进程数
- 1.默认:worker_processes: 1
- 2.调大:worker_processes: CPU核心数,(双核4线程,可以设置为4)
-
worker_connections 单个工作进程可以允许同时建立外部连接的数量
数字越大,能同时处理的连接越多
- 1.默认:worker_connections: 1024
- 2.调大:worker_connections: 100000,(调大到10万连接)
-
worker_cpu_affinity 性能优化CPU,绑定物理cup
-
worker_priority work进程nice值
nginx作为web服务器时使用的配置:http{}段的配置参数
http{...}:配置http相关,由ngx_http_core_module模块引入。nginx的HTTP配置主要包括四个区块,结构如下:
http { //协议级别
include mime.types; //包含mime.types(定义的对应关系来告诉浏览器如何处理服务器传给浏览器的这个文件,是打开还是下载)
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
upstream { //负载均衡配置
...
}
server { //服务器级别,每个server类似于httpd中的一个 <VirtualHost> 表示虚拟主机
listen 80; //监听的端口号
server_name localhost; //虚拟主机名称,域名
location / { //请求级别,类似于httpd中的<Location>,用于定义URL与本地文件系统的映射关系
root html; //相对路径
index index.html index.htm; //优先访问前面的网页
}
}
}
http{}段配置指令:
server {}:定义一个虚拟主机,示例如下:
server {
listen 80; //监听端口
server_name www.xxxx.com; //域名
root "/vhosts/web"; //网页存放路径
}
listen:指定监听的地址和端口
listen address[:port]; //指定IP地址+端口
listen port; //默认方式:指定端口
server_name NAME [...]; 后面可跟多个主机,名称可使用正则表达式或通配符
当有多个server时,匹配顺序如下:
- 先做精确匹配检查
- 左侧通配符匹配检查,如
*.idfsoft.com - 右侧通配符匹配检查,如
mail.* - 正则表达式匹配检查,如
~ ^.*\.idfsoft\.com$ - default_server
root path; 设置资源路径映射,用于指明请求的URL所对应的资源所在的文件系统上的起始路径
alias path; 用于location配置段,定义路径别名
index file; 默认主页面
index index.php index.html;
error_page code [...] [=code] URI | @name 根据http响应状态码来指明特用的错误页面,例如 error_page 404 /404_customed.html
[=code]:以指定的响应码进行响应,而不是默认的原来的响应,默认表示以新资源的响应码为其响应码,例如 error_page 404 =200 /404_customed.html
注意:访问404的时候跳转到200表示成功,使访问更加友好。
log_format 定义日志格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main; //这里的main可以自定义名称,但是上下配置要一致,access.log是日志名称
//注意:此处可用变量为nginx各模块内建变量
日志内容
[root@localhost logs]# tail -f access.log
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:20:49:40 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
location区段,通过指定模式来与客户端请求的URI相匹配
需要配合echo模块使用,详情请见:nginx平滑升级
//功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location配置块中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能//语法:location [ 修饰符 ] pattern {......}
常用修饰符说明:
| 修饰符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 |
| ~ | 正则表达式模式匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则表达式模式匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模块开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了,不支持正则表达式 |
| @ | 定义命名location区段,这些区段客户端不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如try_files或error_page等 |
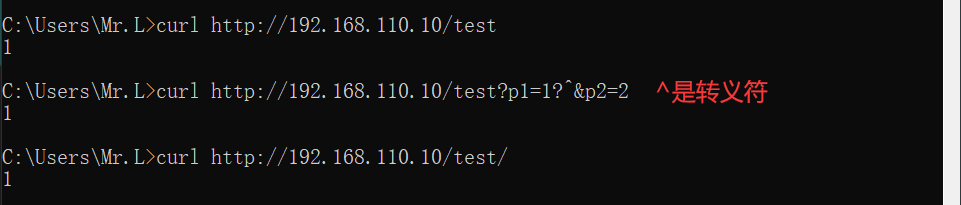
没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始,如:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /test {
echo "1";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
=:表示必须与指定的模式精确匹配,如:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html;
}
location /test {
echo "1";
}
location = /test {
echo "2";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
如下内容则无法匹配:

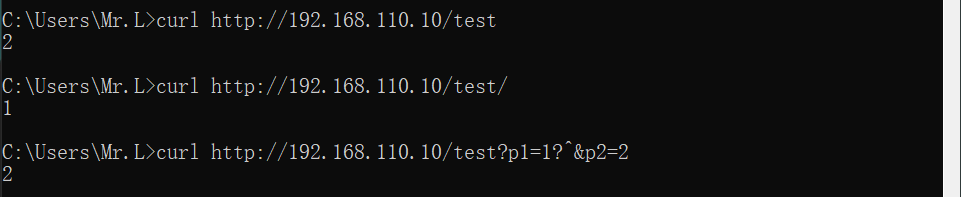
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写,如:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html;
}
location /test {
echo "1";
}
location ~ ^/test$ {
echo "2";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
如下内容则无法匹配:
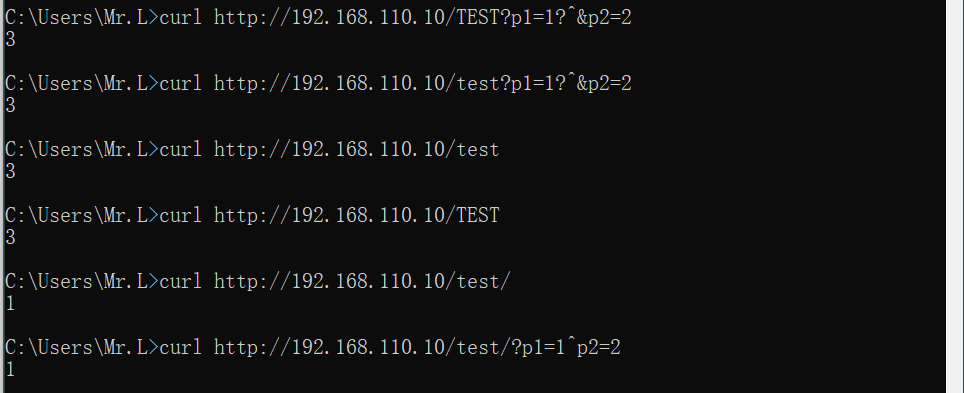
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html;
}
location /test {
echo "1";
}
location ~* /test$ {
echo "3";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
如下内容则无法匹配:
~:类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,则停止搜索其他模式
查找顺序和优先级:由高到底依次为
- 带有
=的精确匹配优先 - 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 带有
^~修饰符的,开头匹配 - 带有
~或~*修饰符的,如果正则表达式与URI匹配 - 没有修饰符的精确匹配
优先级次序如下:
( location = 路径 ) --> ( location ^~ 路径 ) --> ( location ~ 正则 ) --> ( location ~* 正则 ) --> ( location 路径 )
访问控制
allow:设定允许哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
deny:设定禁止哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
注意:不写deny默认就是allow
示例:
用于location段: 针对网站服务的某个资源
创建一个测试网页,访问测试
//在html下创建一个test目录,存放一个测试网页
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@nginx html]# echo "Hellow My Friend!" > test/index.html
[root@nginx html]# cat test/index.html
Hellow My Friend!
//修改nginx默认首页,方便接下来的演示
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@nginx html]# ls
50x.html index.html test
#备份默认网页
[root@nginx html]# cp index.html index.html.bak
[root@nginx html]# ls
50x.html index.html index.html.bak test
#修改默认首页内容
[root@nginx html]# echo 'Welcom to nginx!' > index.html
//访问测试
#启动nginx
[root@nginx html]# nginx
#测试
[root@nginx html]# curl 192.168.110.10
Welcom to nginx!
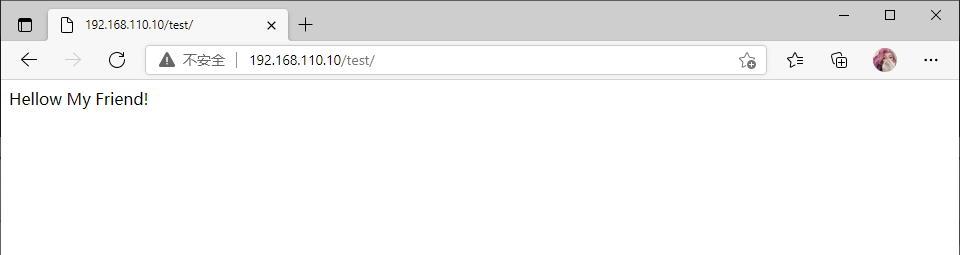
[root@nginx html]# curl 192.168.110.10/test/
Hellow My Friend!
禁止192.168.110.10访问test目录下的网页
//编辑配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑location字段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /test { //这里的test只限制test目录下的网页内容
deny 192.168.110.10; //只限制这一个IP地址禁止访问test目录下的网页,其它主机正常访问
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//访问测试,本机192.168.110.10访问不到test目录下的网页,可以访问nginx默认首页
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10
Welcom to nginx!
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10/test/
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.20.0</center>
</body>
</html>
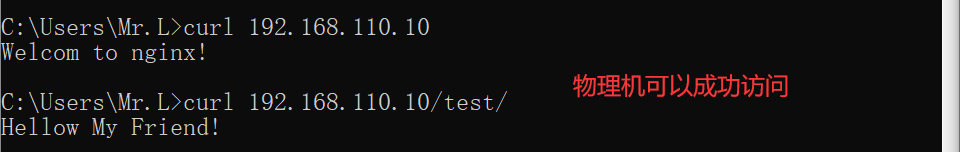
只允许192.168.110.10访问test目录下的网页
//编辑配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑location字段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /test {
allow 192.168.110.10; //只放行这一个IP地址访问
deny all; //拒绝其他所有访问
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//访问测试,只要192.168.110.10可以访问test目录下的内容,其它被拒绝
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10/test/
Hellow My Friend!
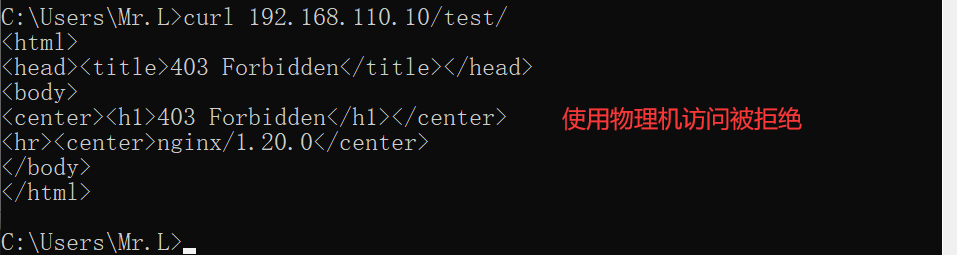
用于server段:针对整个网站
只允许192.168.110.10访问网站
//编辑配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑server字段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
allow 192.168.110.10;
deny all;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//访问测试,只允许192.168.110.10访问网页
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10
Welcom to nginx!
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10/test/
Hellow My Friend!
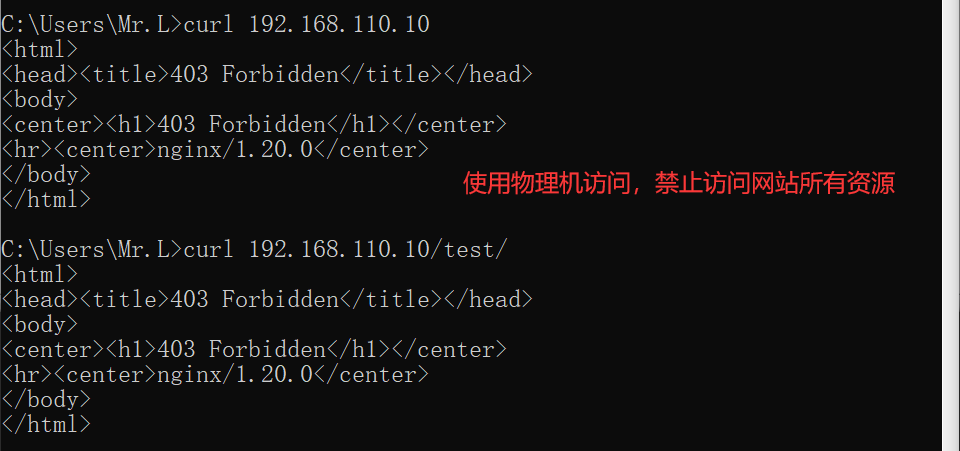
基于用户认证
auth_basic "欢迎信息";
auth_basic_user_file "/path/to/user_auth_file"
user_auth_file内容格式为:
username:password
这里的密码为加密后的密码串,建议用htpasswd来创建此文件:
htpasswd -c -m /path/to/.user_auth_file USERNAME
示例:
用于location段: 访问网站某个资源时候需要用户认证
test目录下的网页内容需要用户(eric)认证
//安装htpasswd命令
[root@nginx ~]# yum -y install httpd-tools
//创建一个加密文件,用户名是eric密码是123456
#注意这里的用户,是虚拟用户,本机不能有此用户
[root@nginx nginx]# htpasswd -c -m .user_auth_file eric
New password:(输入123456)
Re-type new password:(输入123456)
Adding password for user eric
#加密文件名称为.user_auth_file
[root@nginx nginx]# ls -a
. client_body_temp fastcgi_temp logs sbin .user_auth_file
.. conf html proxy_temp scgi_temp uwsgi_temp
#查看加密文件
[root@nginx nginx]# cat .user_auth_file
eric:$apr1$YC85KT2I$cDWQztvrJrN4tw1yrJF1H/
//编辑配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑location字段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /test {
root html;
index index.html
auth_basic "你好啊,我的朋友!";
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/.user_auth_file";
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//可以访问默认网页
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10
Welcom to nginx!
访问192.168.110.10/test/ 输入用户名:eric 密码:123456
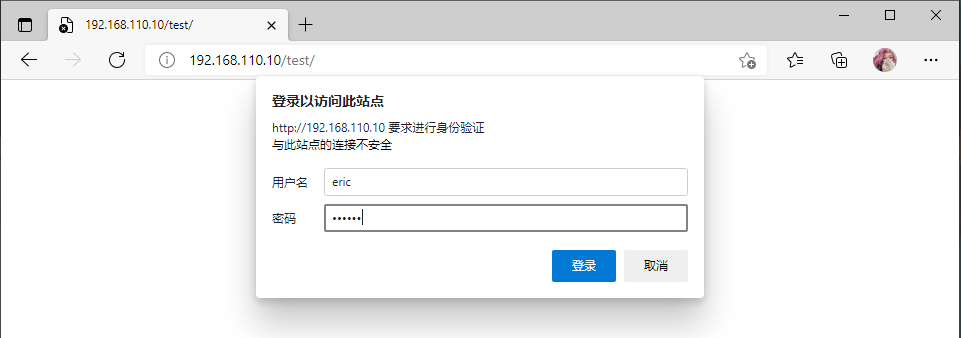
访问成功
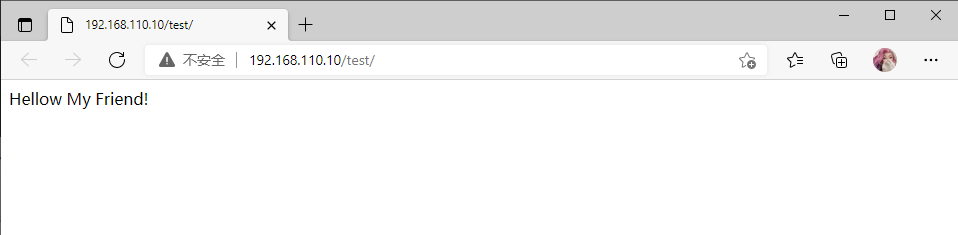
访问默认首页不需要用户认证
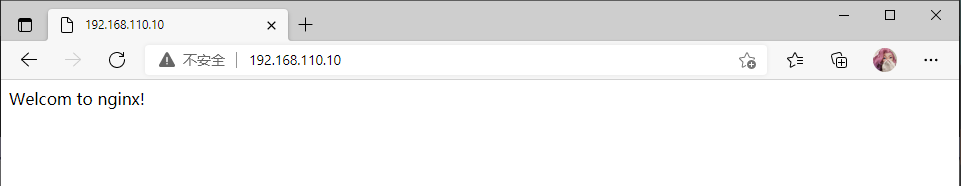
用于server段: 访问网站时需要用户认证
注意: 只需要用户认证一次,就可以访问该网站所有资源
访问网站需要用户认证
//编辑配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑server字段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
auth_basic "你好啊,我的朋友!";
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/.user_auth_file";
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
访问默认首页,需要用户(eric)认证
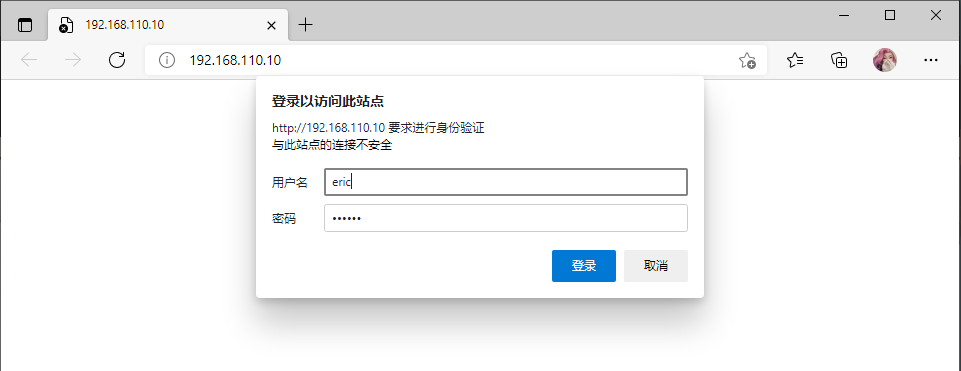
访问成功
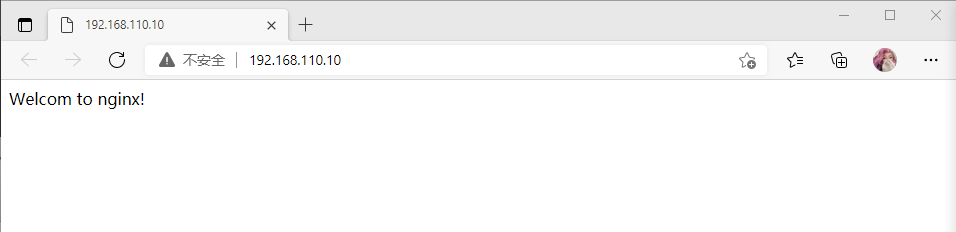
可以直接访问test目录下的网页
https配置
生成私钥,生成证书签署请求并获得证书,然后在nginx.conf中配置如下内容:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.xxxxx.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
示例:
生成一个免费证书
一个免费证书网站:FreeSSL
访问网站注册一个账号登录
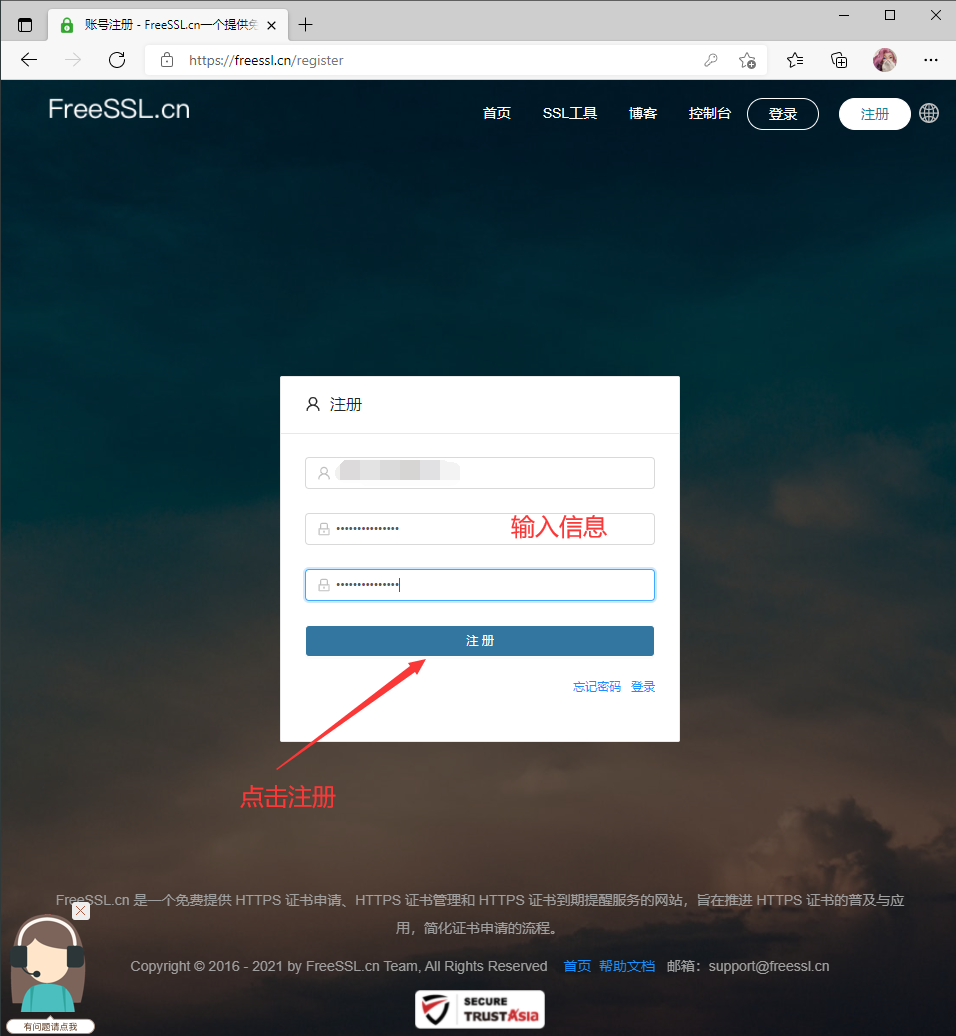
在邮箱点击激活
输入信息,点击登录,完成手机验证即可
页面如下
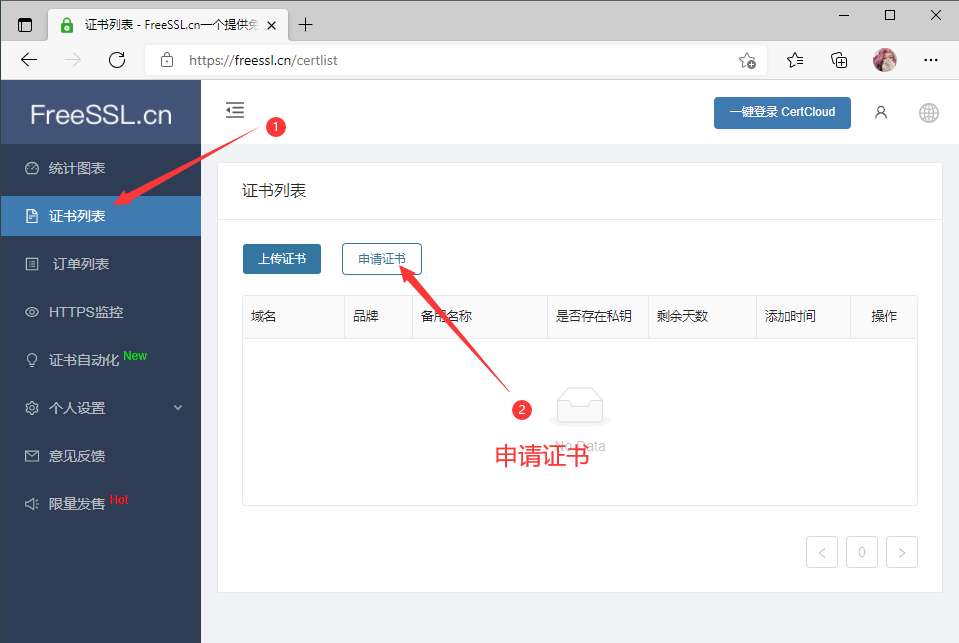
申请证书
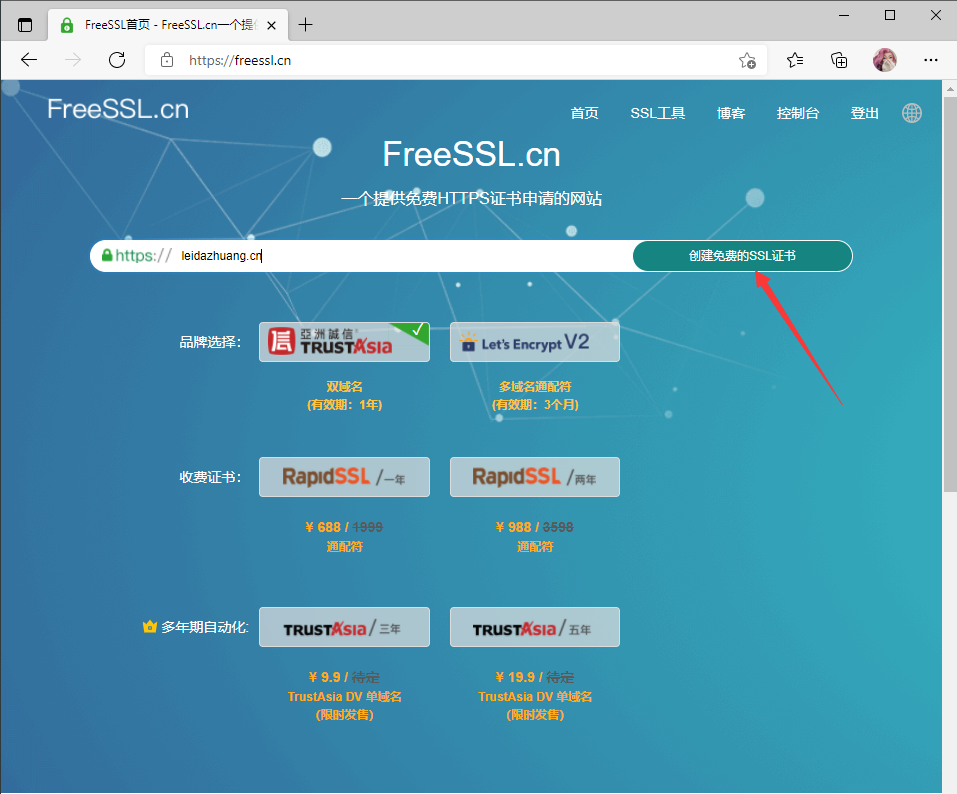
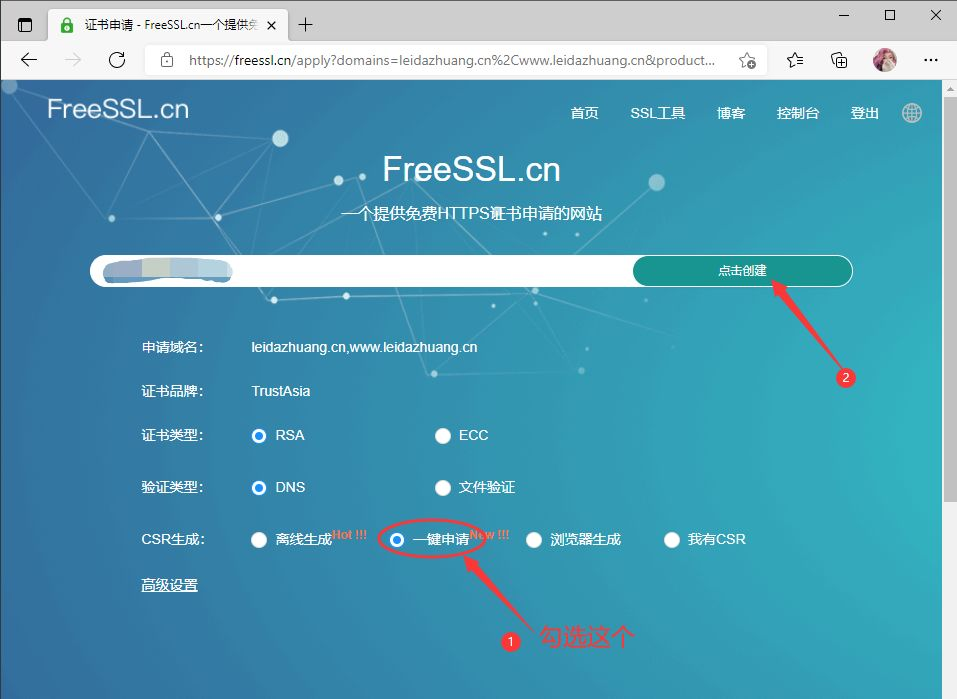
按如图提示步骤完成
下载完KeyManager后,点击KeyManager

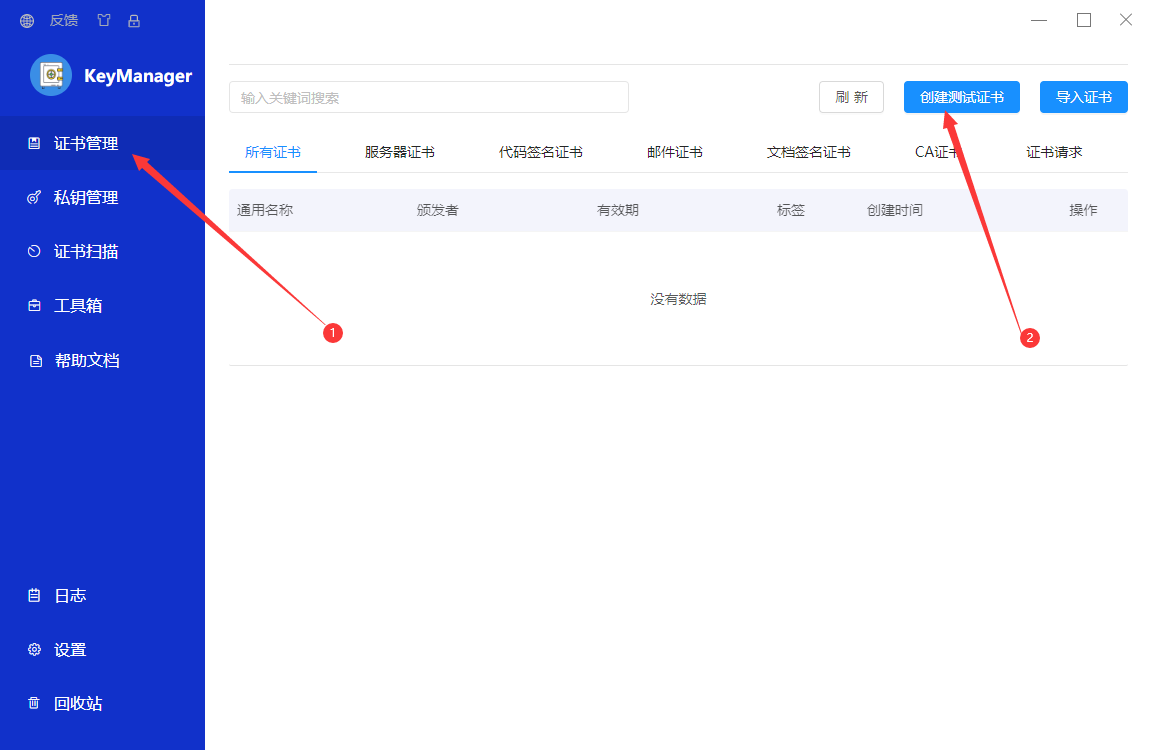
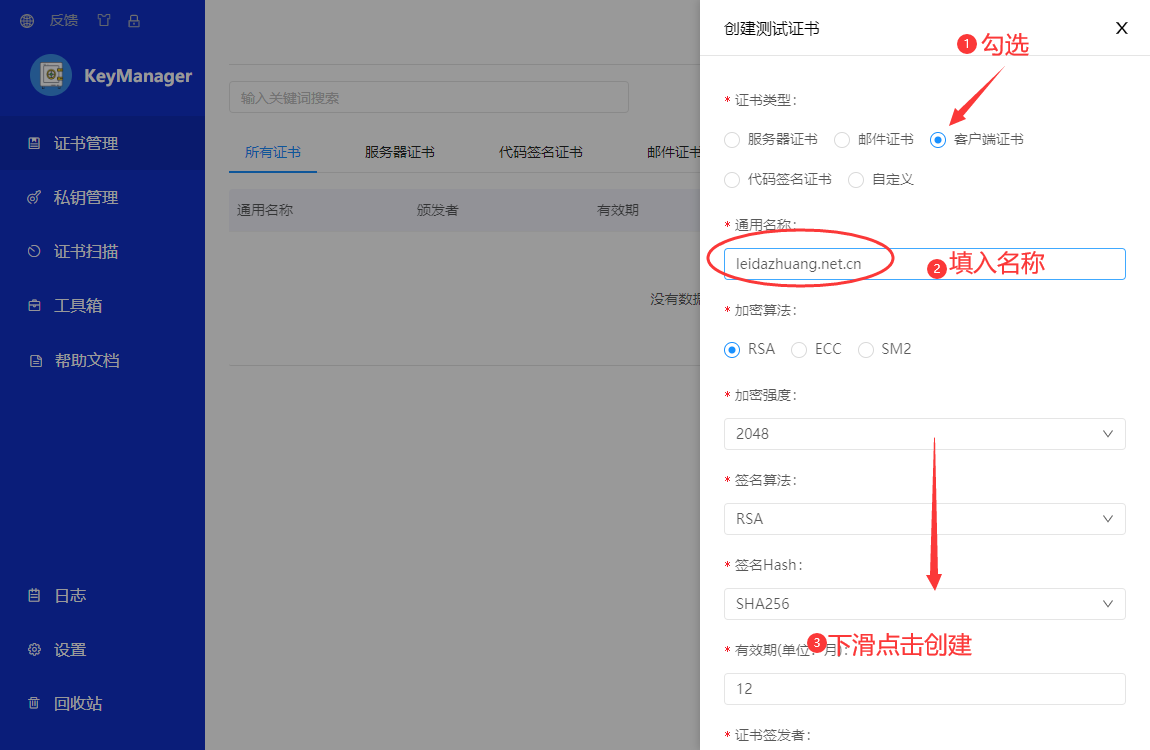
创建证书
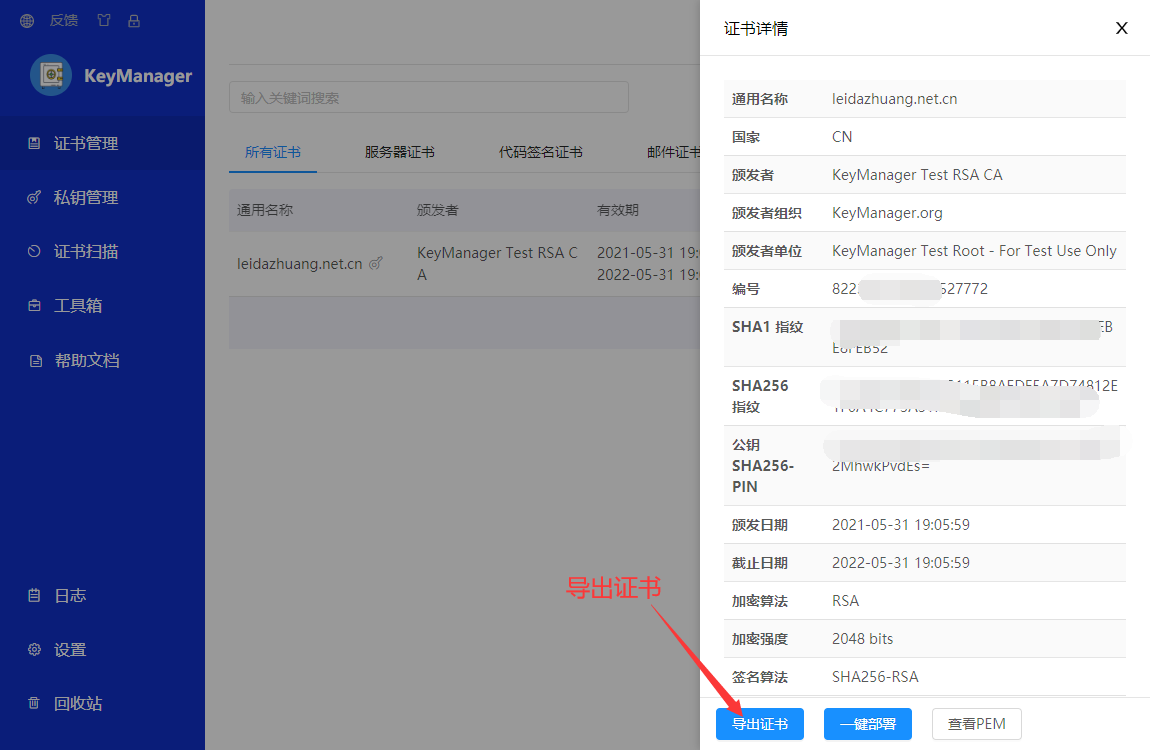
导出证书
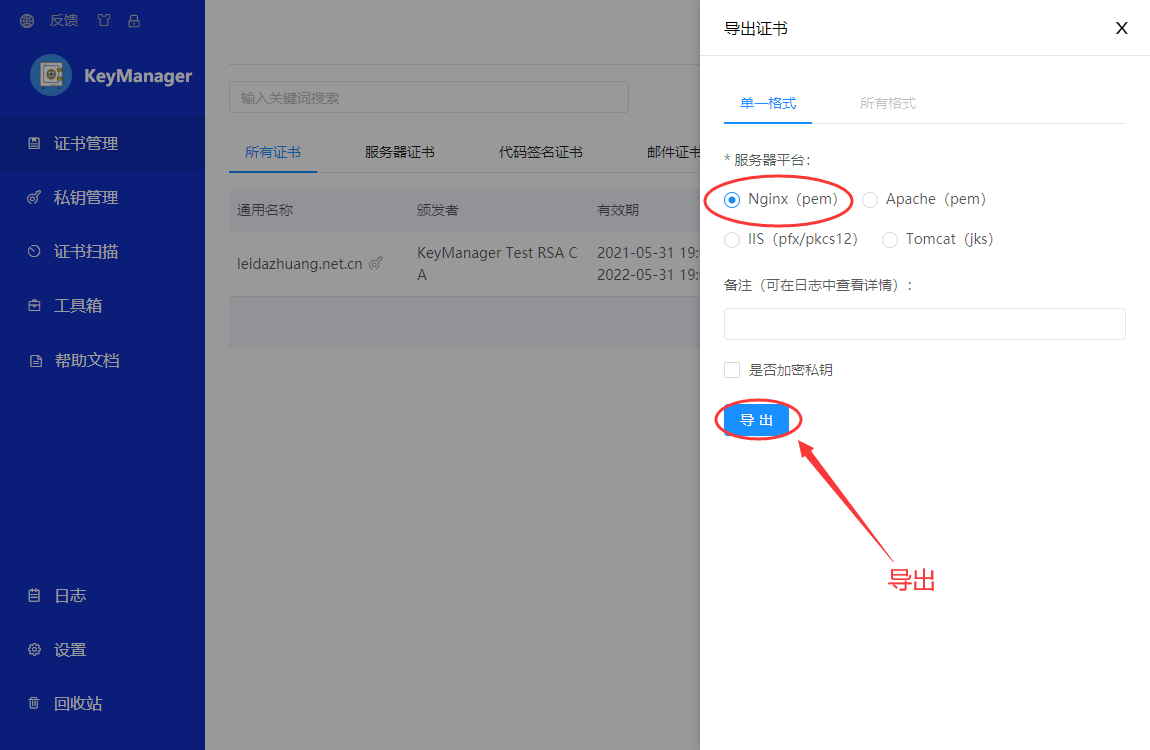
导入证书,开始配置
//导入证书
#当前位置
[root@nginx nginx]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx
#创建ssl目录
[root@nginx nginx]# mkdir ssl
[root@nginx nginx]# cd ssl/
#传到这个ssl目录下
[root@nginx ssl]# ls
leidazhuang-net-cn-nginx-0601030912.zip
#解压证书文件
[root@nginx ssl]# yum -y install unzip
[root@nginx ssl]# unzip leidazhuang-net-cn-nginx-0601030912.zip
Archive: leidazhuang-net-cn-nginx-0601030912.zip
inflating: leidazhuang.net.cn_chain.crt
inflating: leidazhuang.net.cn_key.key
[root@nginx ssl]# ls
leidazhuang.net.cn_chain.crt leidazhuang-net-cn-nginx-0601030912.zip
leidazhuang.net.cn_key.key
//编辑配置文件
#返回上级目录
[root@nginx ssl]# cd ..
#配置文件,取消注释,修改证书密钥路径
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
# HTTPS server
#
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name leidazhuang.net.cn;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/ssl/leidazhuang.net.cn_chain.crt; //修改此行
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/ssl/leidazhuang.net.cn_key.key; //修改此行
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
//检查nginx配置文件是否有误,并重读配置文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//443端口已经启用了
[root@nginx nginx]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
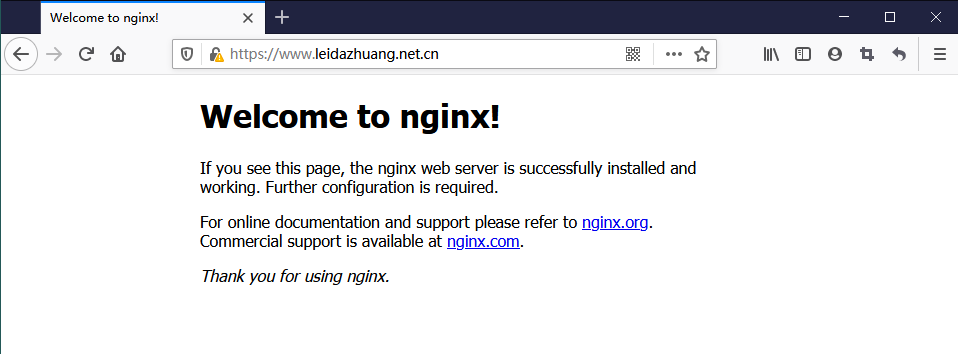
配置域名和IP映射关系
在本机window上,把 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 文件移动到桌面,修改完成后移动回去
//在桌面用记事本打开hosts文件
#添加此行
192.168.110.10 www.leidazhuang.net.cn leidazhuang.net.cn
访问测试
推荐 Firefox 火狐浏览器
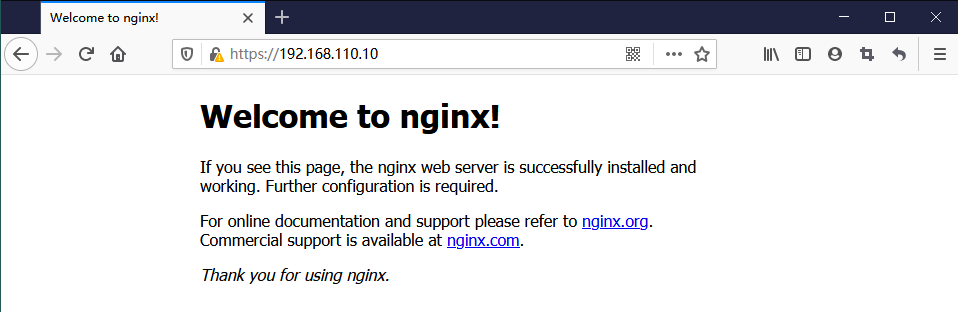
通过IP地址 https://192.168.110.10 访问
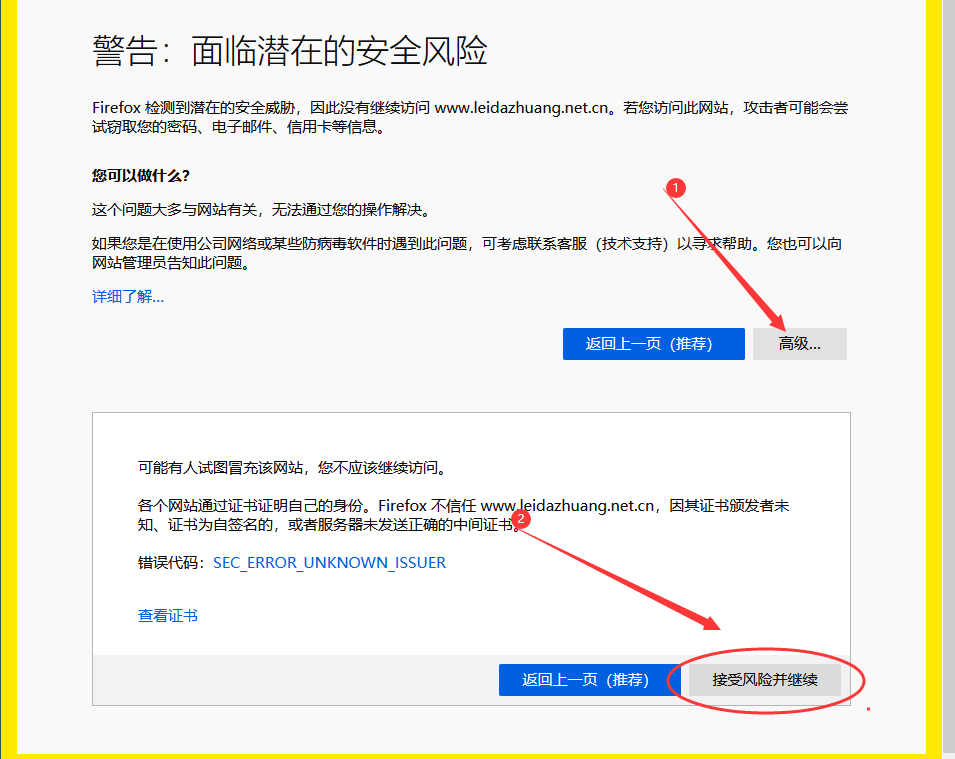
成功访问
通过域名 https://leidazhuang.net.cn 访问
开启状态界面
开启status:
location /status {
stub_status {on | off};
allow ip;
deny all;
}
访问状态页面的方式:http://server_ip/status
状态页面信息详解:
| 状态码 | 表示的意义 |
|---|---|
| Active connections 2 | 当前所有处于打开状态的连接数 |
| accepts | 总共处理了多少个连接 |
| handled | 成功创建多少握手 |
| requests | 总共处理了多少个请求 |
| Reading | nginx读取到客户端的Header信息数,表示正处于接收请求状态的连接数 |
| Writing | nginx返回给客户端的Header信息数,表示请求已经接收完成, 且正处于处理请求或发送响应的过程中的连接数 |
| Waiting | 开启keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active - (reading + writing), 意思就是Nginx已处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接 |
示例:
开启status状态页面
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑location段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
allow 192.168.110.10; //允许192.168.110.10
allow 192.168.110.1; //允许192.168.110.1
deny all;
}
//检查配置文件是否有误,并重读文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
网页访问
案例
案例一:统计nginx访问ip次数
1. 开启日志功能
//编辑配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#打开日志功能
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#取消以下4行的注释
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
//重读配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
2. 通过网页刷新访问,终端命令curl 192.168.110.10访问
- 网页5次
- 终端3次
//查看日志
[root@localhost logs]# tail -f access.log
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:04 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:05 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:05 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:05 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
192.168.110.1 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:06 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 Edg/90.0.818.66" "-"
192.168.110.10 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:14 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "curl/7.61.1" "-"
192.168.110.10 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:15 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "curl/7.61.1" "-"
192.168.110.10 - - [30/May/2021:21:15:15 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "curl/7.61.1" "-"
3. 使用awk取出访问次数
[root@localhost ~]# awk '{ip[$1]++}END{for(c in ip) print c,ip[c]}' /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log
192.168.110.1 5
192.168.110.10 3
4. 以第二列数值进行排序
#倒序
[root@localhost ~]# awk '{ip[$1]++}END{for(c in ip) print c,ip[c]}' /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log|sort -rk 2
192.168.110.1 5
192.168.110.10 3
#顺序
[root@localhost ~]# awk '{ip[$1]++}END{for(c in ip) print c,ip[c]}' /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log|sort -k 2
192.168.110.10 3
192.168.110.1 5
#排名前十访问次数 head
[root@localhost ~]# awk '{ip[$1]++}END{for(c in ip) print c,ip[c]}' /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log|sort -rk 2|head
192.168.110.1 5
192.168.110.10 3
案例二:状态界面监控
环境说明:
| 主机名称 | IP地址 | 需要安装的应用 | 系统版本 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 客户端:nginx | 192.168.110.10 | nginx zabbix_agent | redhat 8 |
| 服务端:zabbix | 192.168.110.30 | lamp架构 zabbix_server zabbix_agent | redhat 8 |
准备工作:
zabbix的服务端和客户端的部署详情请见:zabbix服务端安装 + zabbix客户端部署实例
//关闭防火墙和selinux
systemctl disable --now firewalld
setenforce 0
sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
开启状态界面
[root@nginx nginx]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
#编辑location段
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
allow 192.168.110.10; //允许192.168.110.10
allow 192.168.110.1; //允许192.168.110.1
deny all;
}
//检查配置文件是否有误,并重读文件
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
//访问状态
#成功访问
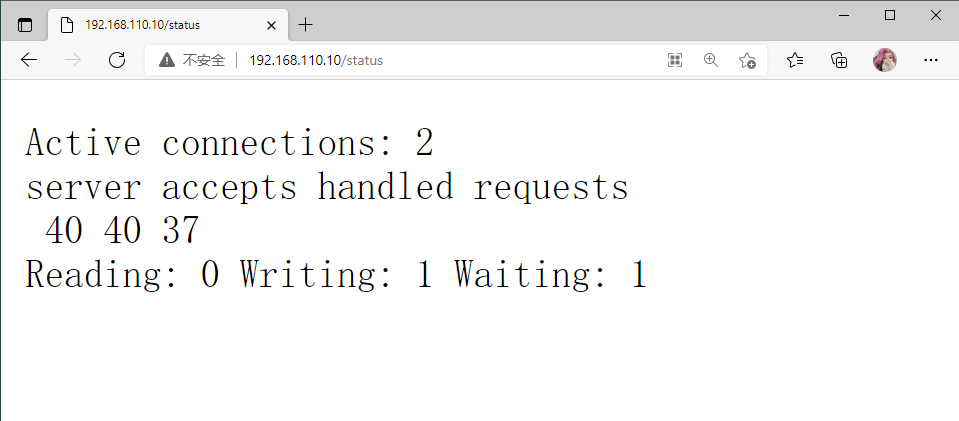
[root@nginx nginx]# curl 192.168.110.10/status/
Active connections: 1
server accepts handled requests
10 10 9
Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
安装zabbix客户端
nginx端主机安装zabbix_agent客户端服务
//安装依赖包
[root@nginx ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ bzip2 pcre* make
//下载zabbix安装包,并解压
[root@nginx ~]# wget https://cdn.zabbix.com/zabbix/sources/stable/5.2/zabbix-5.2.6.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg zabbix-5.2.6.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# tar xf zabbix-5.2.6.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg zabbix-5.2.6 zabbix-5.2.6.tar.gz
//安装zabbix
[root@nginx ~]# cd zabbix-5.2.6
[root@nginx zabbix-5.2.6]# ls
aclocal.m4 ChangeLog config.sub database install-sh man README
AUTHORS compile configure depcomp m4 misc sass
bin conf configure.ac include Makefile.am missing src
build config.guess COPYING INSTALL Makefile.in NEWS ui
[root@nginx zabbix-5.2.6]# ./configure --enable-agent --disable-dependency-tracking
***********************************************************
* Now run 'make install' *
* *
* Thank you for using Zabbix! *
* <http://www.zabbix.com> *
***********************************************************
[root@nginx zabbix-5.2.6]# make install
//修改主动模式和被动模式
[root@agent ~]# cd /usr/local/etc/
[root@agent etc]# ls
zabbix_agentd.conf zabbix_agentd.conf.d
[root@agent etc]# vim zabbix_agentd.conf
# Mandatory: yes, if StartAgents is not explicitly set to 0
# Default:
# Server=
Server=192.168.110.30 //修改为服务端ip地址
# Mandatory: no
# Default:
# ServerActive=
ServerActive=192.168.110.30 //修改为服务端ip地址
# Mandatory: no
# Default:
# Hostname=
Hostname=nginx //设置唯一主机名,后面在网页中配置需要一致
//启动agent
[root@agent etc]# useradd -r -M -s /sbin/nologin zabbix
[root@agent etc]# zabbix_agentd
[root@agent etc]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
//重启nginx
#停止
[root@nginx ~]# nginx-s stop
#启动
[root@nginx ~]# nginx
#查看端口
[root@nginx ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
在被监控端nginx主机上,编写监控脚本
//创建脚本目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /scripts
//修改属主属组为zabbix
[root@nginx ~]# cd /scripts
[root@nginx scripts]# chown zabbix.zabbix /scripts
[root@nginx scripts]# ll / | grep scripts
drwxr-xr-x 2 zabbix zabbix 35 Jun 2 10:47 scripts
//编写脚本
[root@nginx scripts]# vim check_nginx_status.sh
#!/bin/bash
#这里的变量名称可以自己定义,但是以下的配置需要和这个变量匹配
#这里的IP地址是被监控端nginx的IP地址 192.168.110.10
nginx_server=192.168.110.10
requests(){
requests=`curl -s http://${nginx_server}/status | awk 'NR==3{print $3}'`
echo ${requests}
}
Reading(){
Reading=`curl -s http://${nginx_server}/status | awk 'NR==4{print $2}'`
echo ${Reading}
}
Writing(){
Writing=`curl -s http://${nginx_server}/status | awk 'NR==4{print $4}'`
echo ${Writing}
}
Waiting(){
Waiting=`curl -s http://${nginx_server}/status | awk 'NR==4{print $6}'`
echo ${Waiting}
}
main(){
case $1 in
requests)
requests;
;;
Reading)
Reading;
;;
Writing)
Writing;
;;
Waiting)
Waiting;
;;
esac
}
main $1
//给脚本执行权限
[root@nginx scripts]# chmod +x check_nginx_status.sh
[root@nginx scripts]# ll
total 4
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 736 Jun 2 10:46 check_nginx_status.sh
//开启自定义监控并添加指标
#编辑配置文件 /usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf
...此处省略n行...
# TLSCipherAll=
#在配置文件最后,添加以下两行
UnsafeUserParameters=1
UserParameter=check_nginx_status[*],/scripts/check_nginx_status.sh $1
//重启zabbix
[root@nginx ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
[root@nginx ~]# pkill zabbix_agent
[root@nginx ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
[root@nginx ~]# zabbix_agentd
[root@nginx ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
//在zabbix服务端测试
#测试是否可以获取客户端的指标
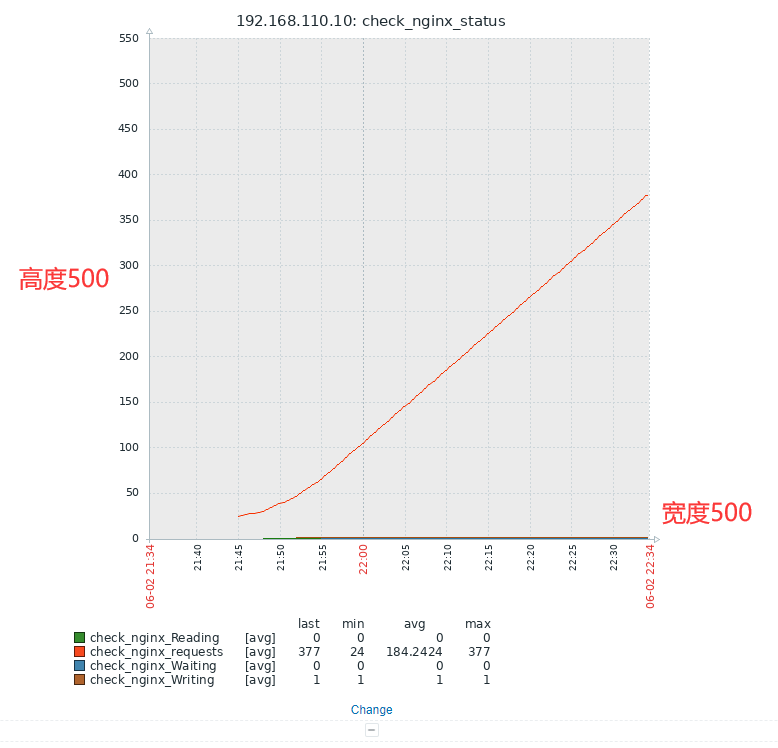
[root@zabbix ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.110.10 -k check_nginx_status['requests']
16
[root@zabbix ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.110.10 -k check_nginx_status['Reading']
0
[root@zabbix ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.110.10 -k check_nginx_status['Writing']
1
[root@zabbix ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.110.10 -k check_nginx_status['Waiting']
0
网页配置
访问 192.168.110.30 开始配置
添加主机组
Configuration —— Host groups —— 右上角 Create host group
添加主机
Configuration —— Hosts —— 右上角 Create host
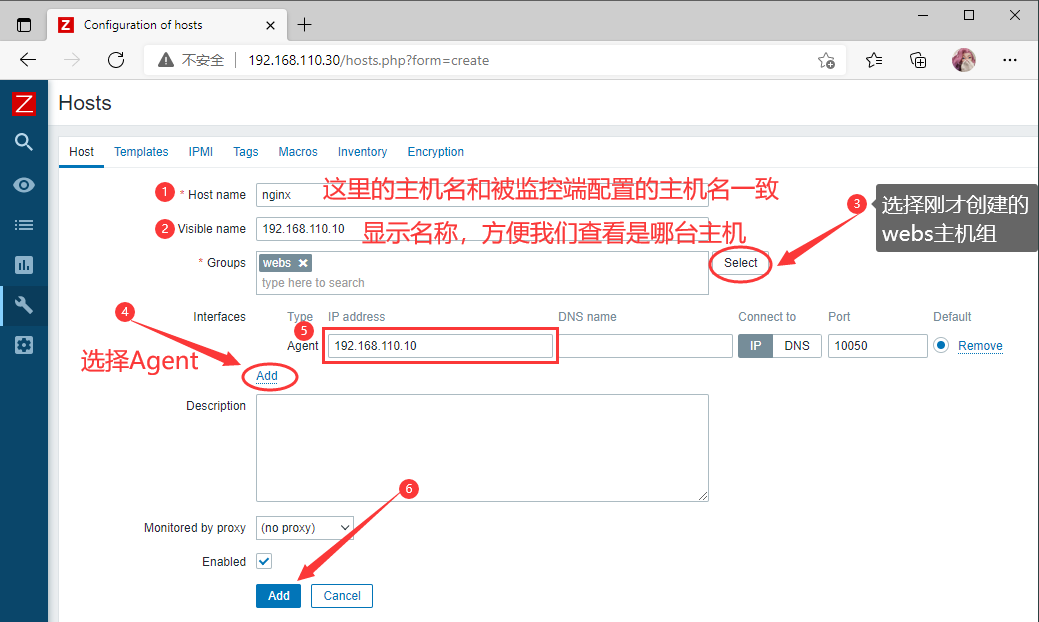
添加监控项
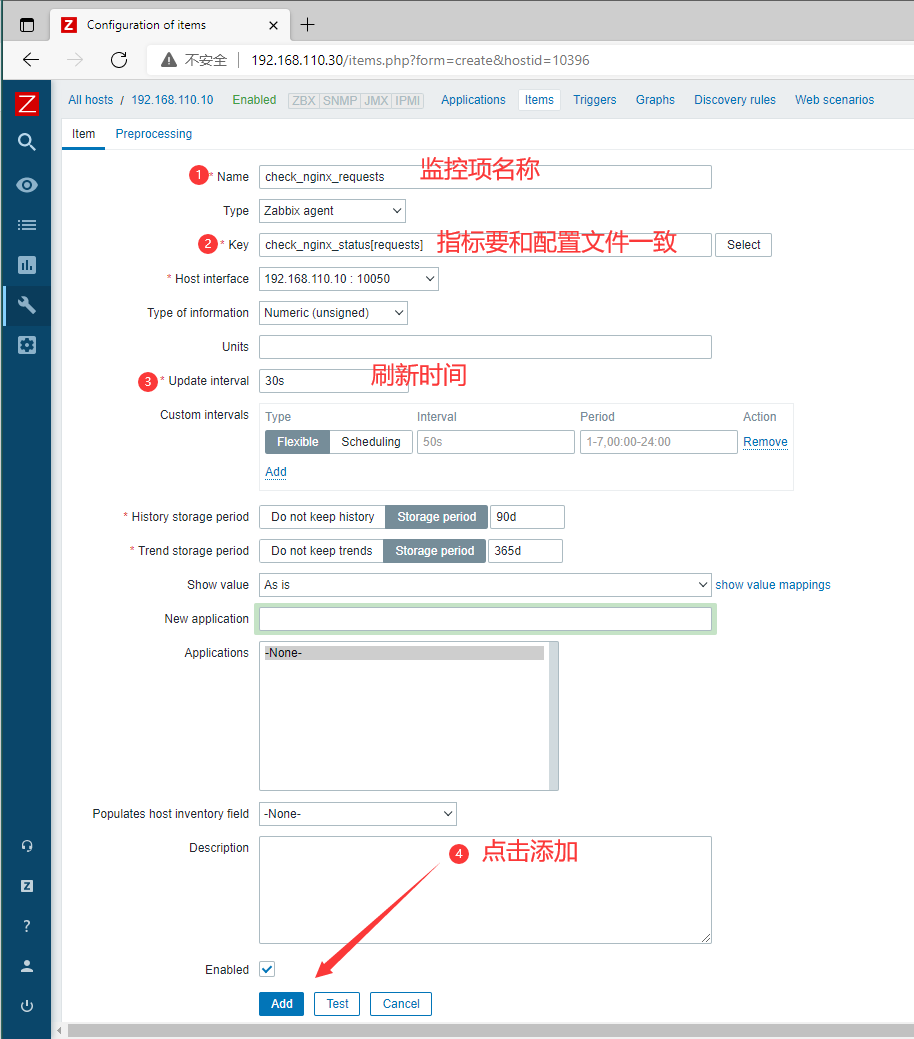
Configuration --- Hosts --- 客户机的Items --- 右上角Create Items
- 添加第一个监控项:
requests
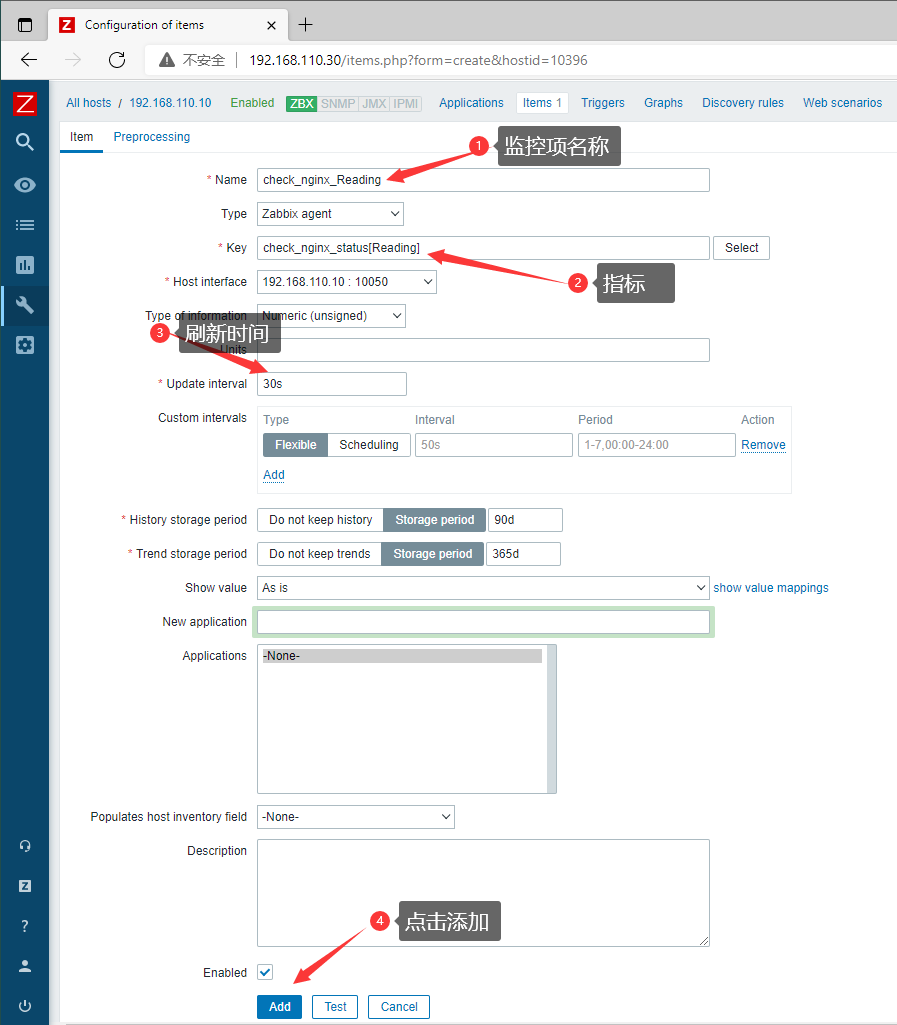
- 添加第二个监控项:
Reading
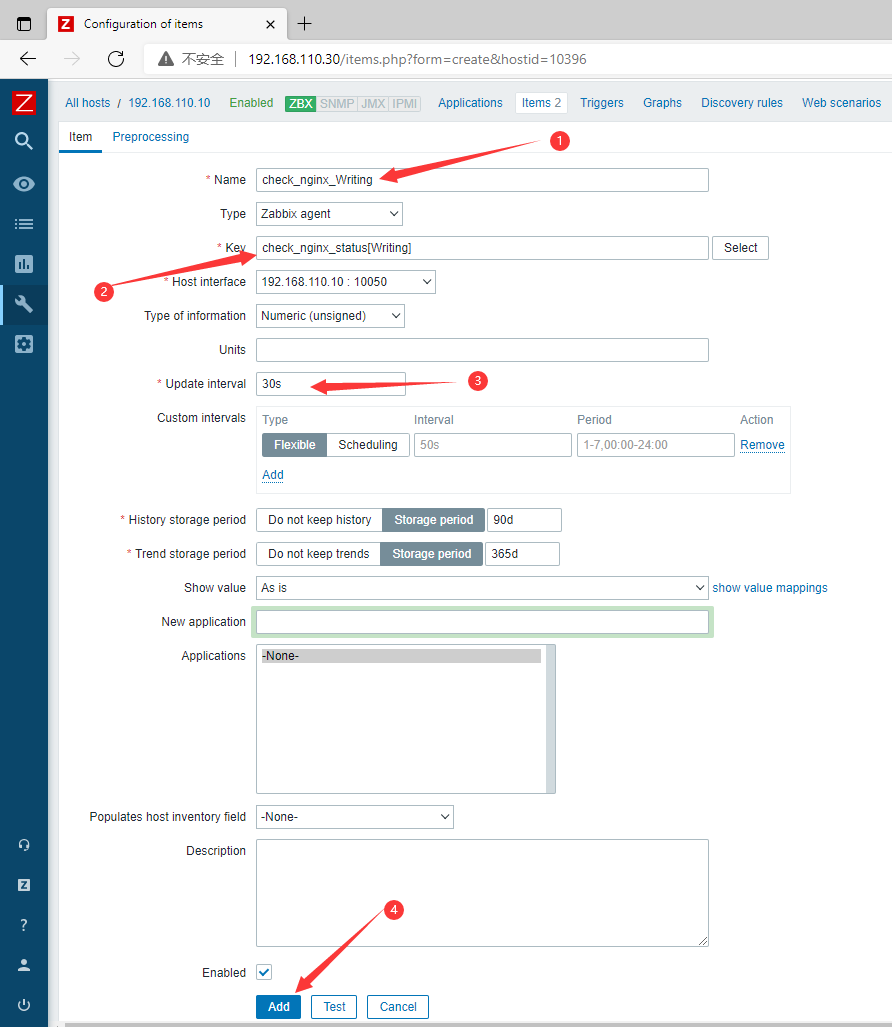
- 添加第三个监控项:
Writing
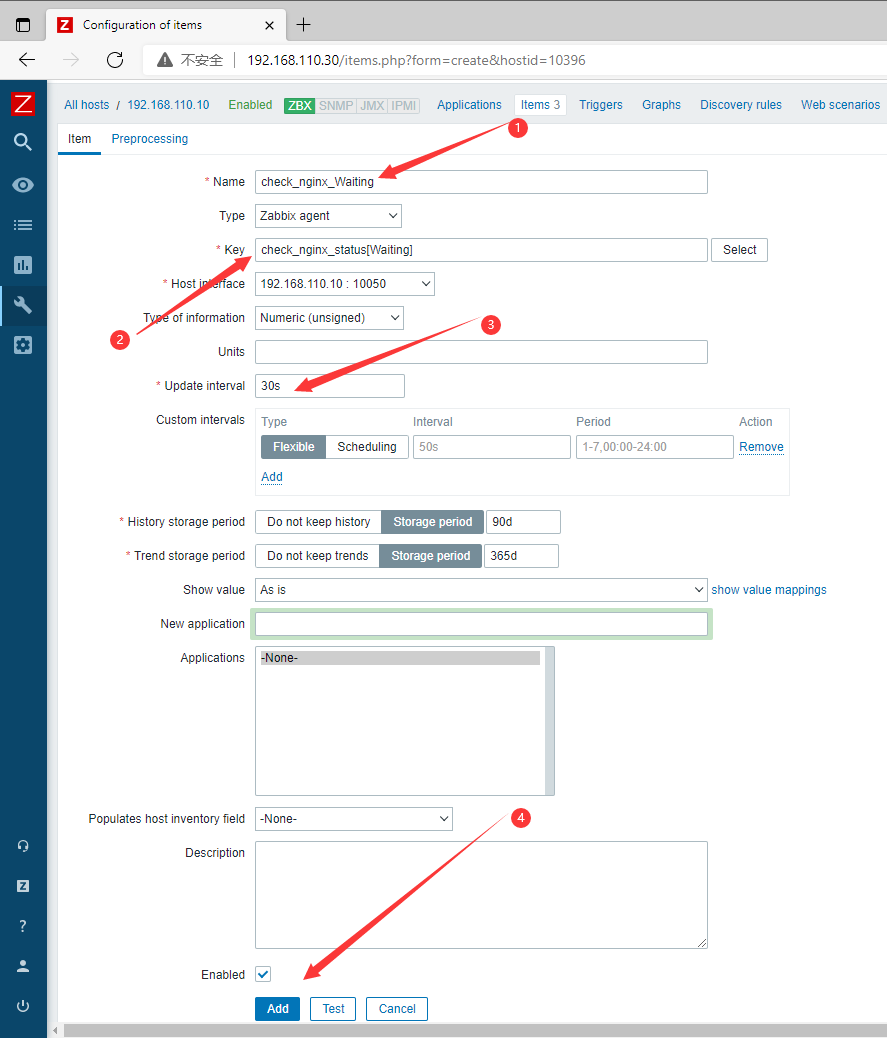
- 添加第四个监控项:
Waiting
- 添加成功
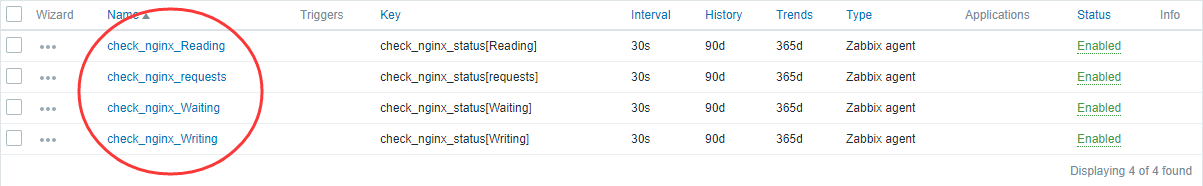
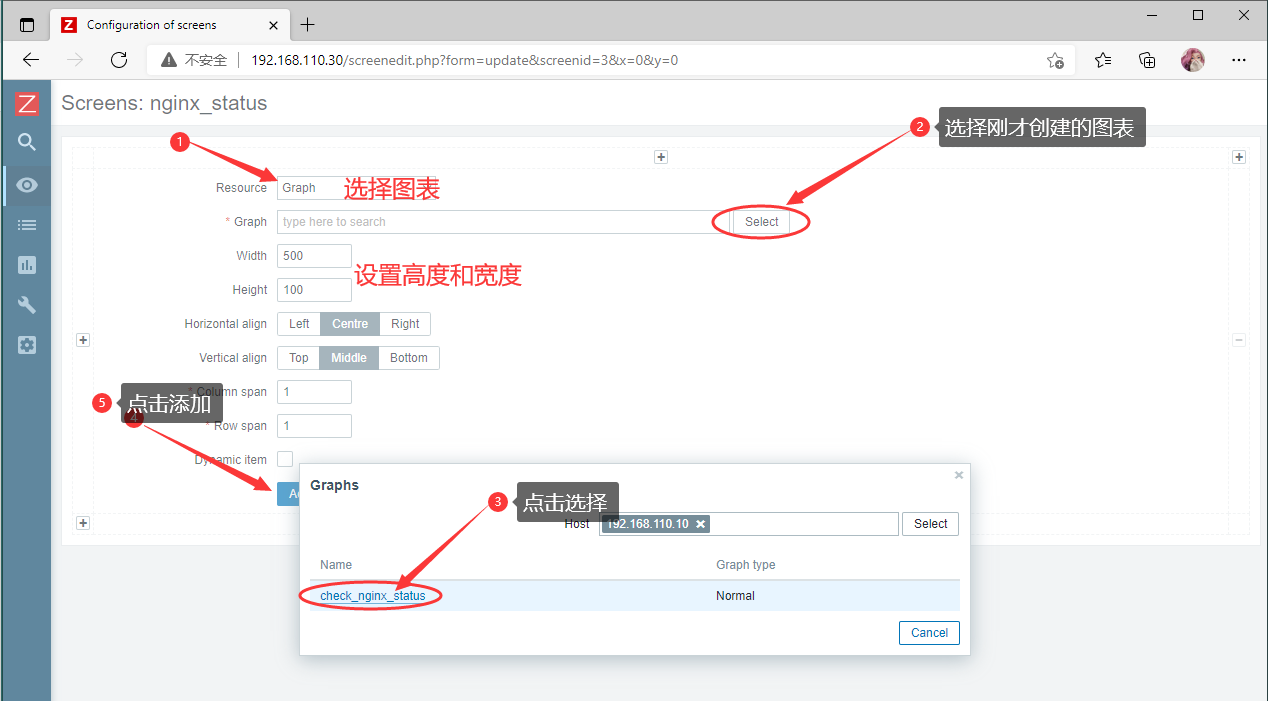
添加自定义图表
Configuration --- Hosts --- 客户机的Graphs --- 右上角Create graph
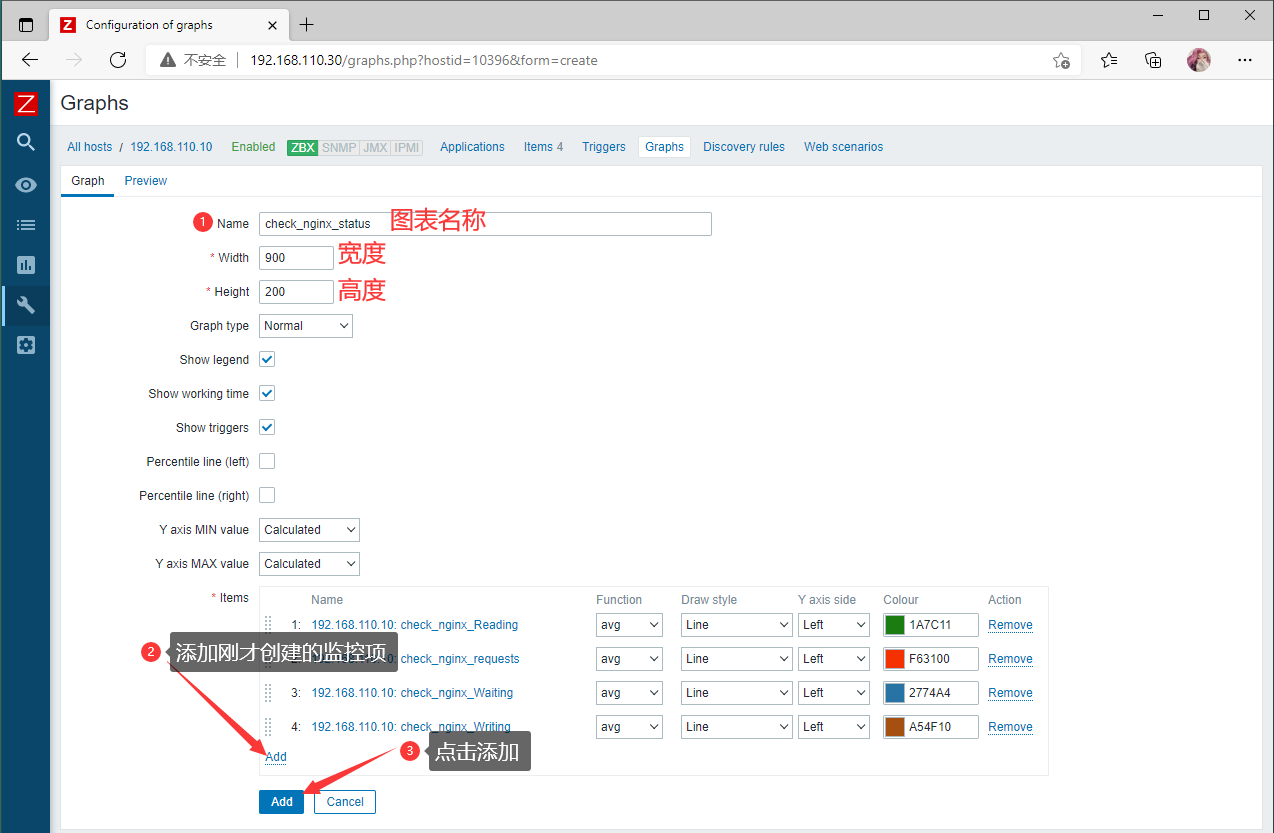
在Screens上添加图表方便监控
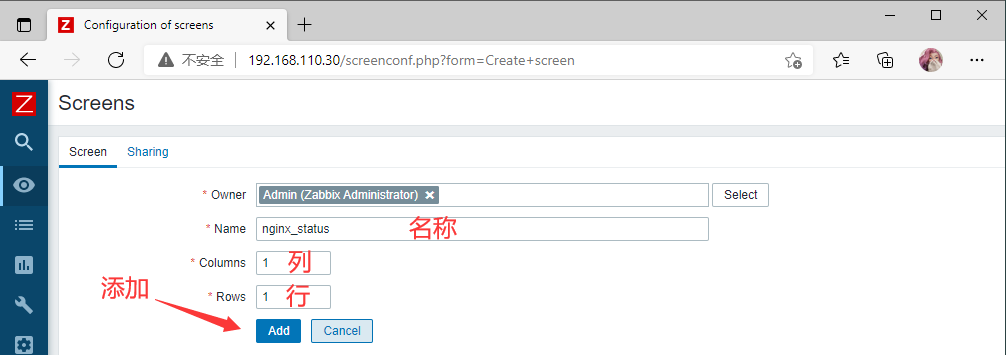
Monitoring --- Screens --- 右上角Create creens
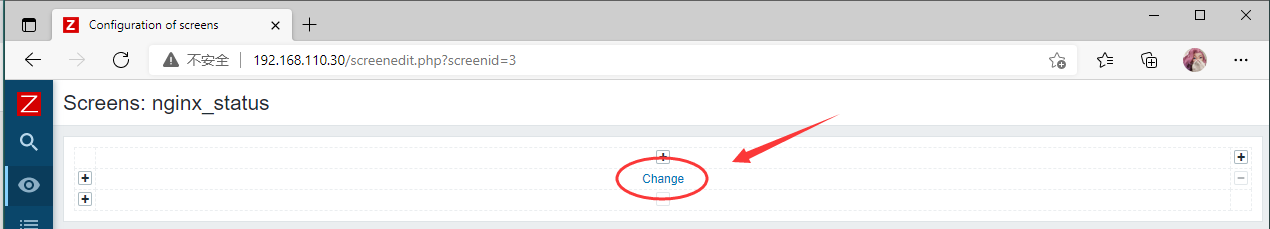
创建成功
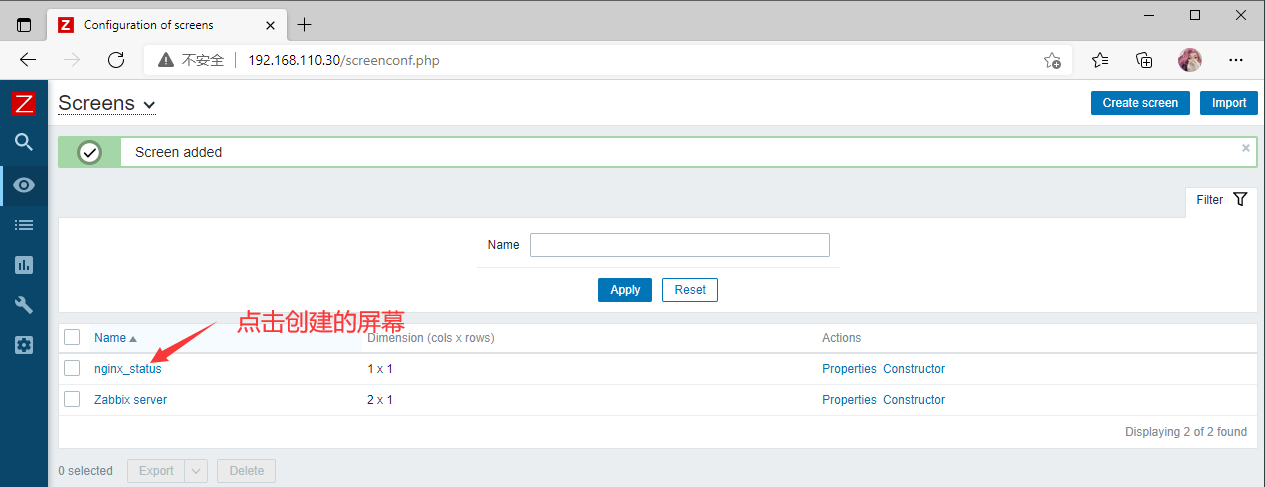
nginx_status --- 右上角Edit screen
成功查看状态页面